Abstract
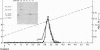
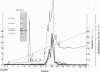
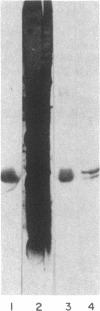
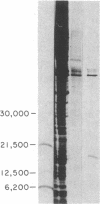
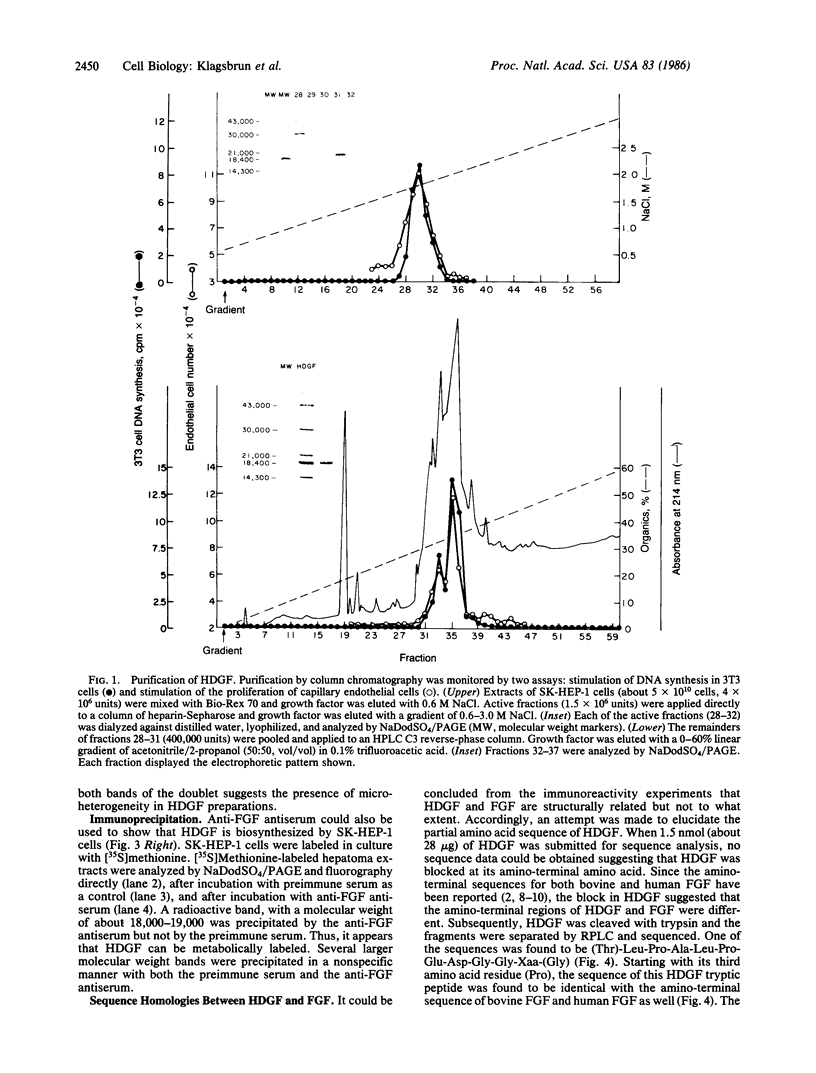
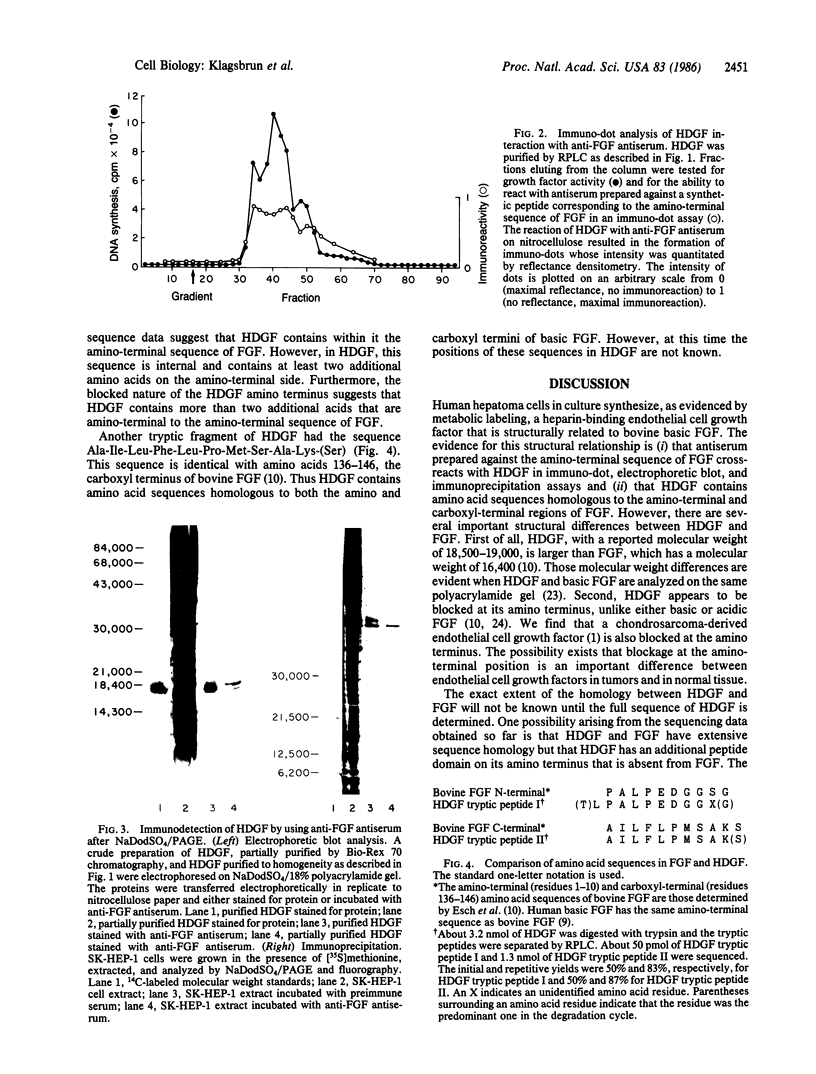
A human hepatoma cell line synthesizes, as evidenced by metabolic labeling, an endothelial cell mitogen that is found to be mostly cell associated. The hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF) has been purified to homogeneity by a combination of Bio-Rex 70, heparin-Sepharose, and reverse-phase chromatography; it is a cationic polypeptide with a molecular weight of about 18,500-19,000. HDGF is structurally related to basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Immunological analysis demonstrates that antiserum prepared against a synthetic peptide corresponding to the amino-terminal sequence of basic FGF cross-reacts with HDGF when analyzed by electrophoretic blotting and by immunoprecipitation. Sequence analysis of tryptic fragments demonstrates that HDGF contains sequences that are homologous to both amino-terminal and carboxyl-terminal sequences of basic FGF.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böhlen P., Baird A., Esch F., Ling N., Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and partial molecular characterization of pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5364–5368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Esch F., Baird A., Jones K. L., Gospodarowicz D. Human brain fibroblast growth factor. Isolation and partial chemical characterization. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80765-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell mitogens derived from retina and hypothalamus: biochemical and biological similarities. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1545–1549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Fogh J. M., Orfeo T. One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):221–226. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Böhlent P. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6963–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Langer R., Levenson R., Smith S., Lillehei C. The stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in chondrocytes and 3T3 cells by a growth factor isolated from cartilage. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 1;105(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Shing Y. Heparin affinity of anionic and cationic capillary endothelial cell growth factors: analysis of hypothalamus-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Fett J. W. Purification of two distinct growth factors from bovine neural tissue by heparin affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6295–6299. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Shing Y., D'Amore P., Jacobs J., Klagsbrun M. Purification and characterization of heparin-binding endothelial cell growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1924–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K. Simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens using the peroxidase-labeled antibody method: a study on pituitary glands of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Sep;16(9):557–560. doi: 10.1177/16.9.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Jibson M., Muller G., Arnon R. Immunity and protection against influenza virus by synthetic peptide corresponding to antigenic sites of hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2461–2465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Haudenschild C., Lund D., Crum R., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenesis is stimulated by a tumor-derived endothelial cell growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):275–287. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Klagsbrun M. Purification of cartilage-derived growth factor by heparin affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2399–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Giménez-Gallego G., DiSalvo J., Bennett C., Rodkey J., Fitzpatrick S. Pure brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor is a potent angiogenic vascular endothelial cell mitogen with sequence homology to interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]