Abstract
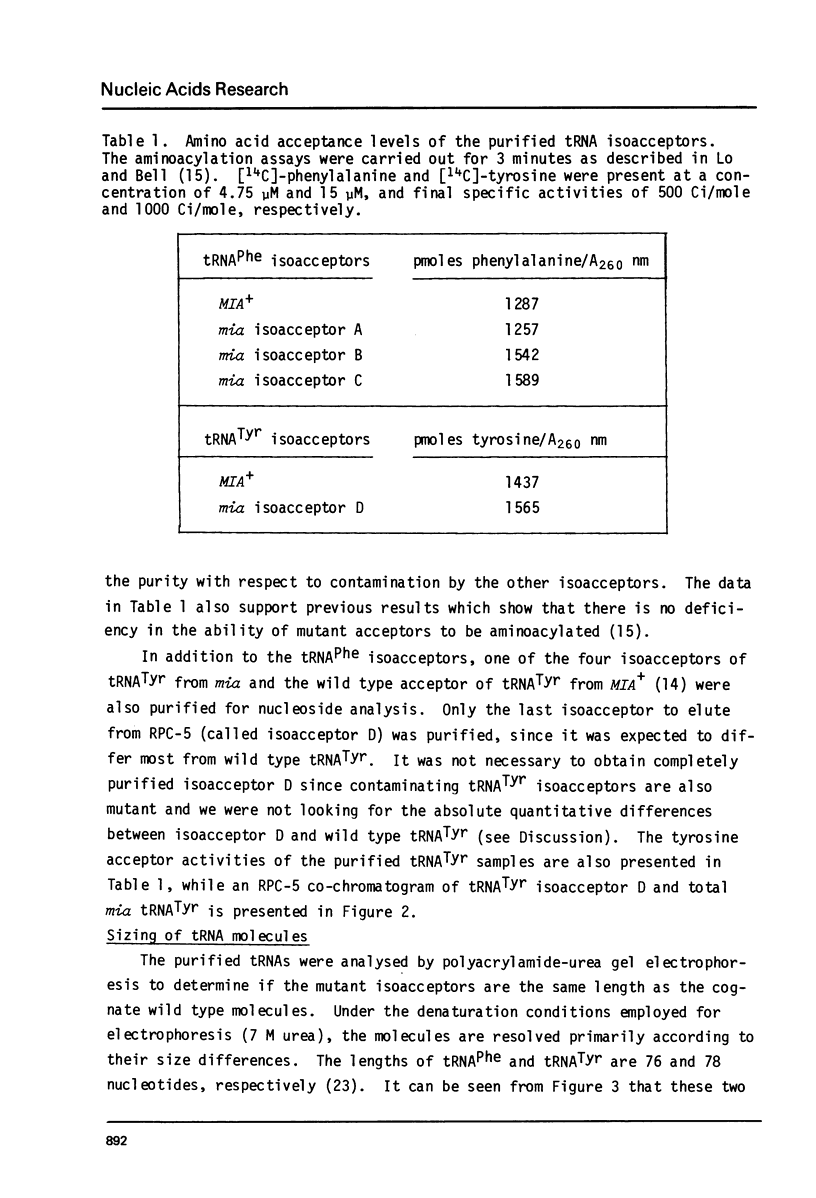
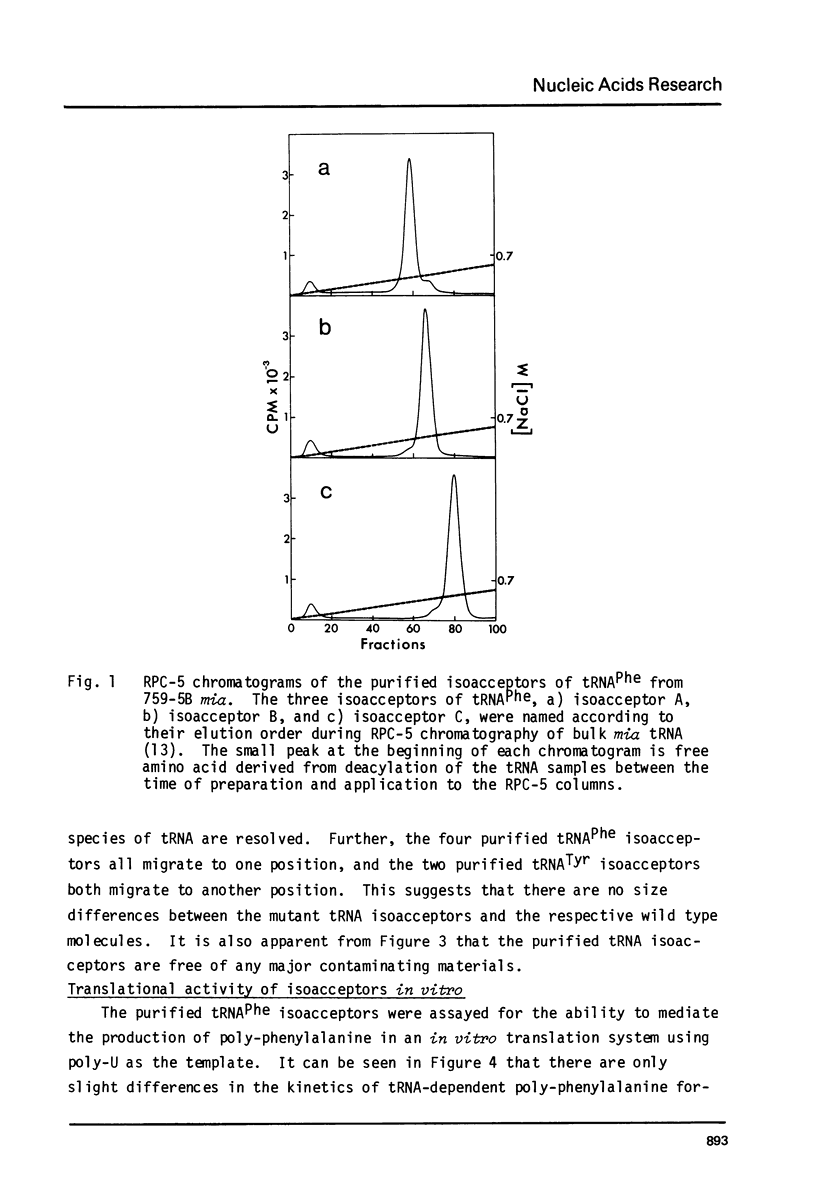
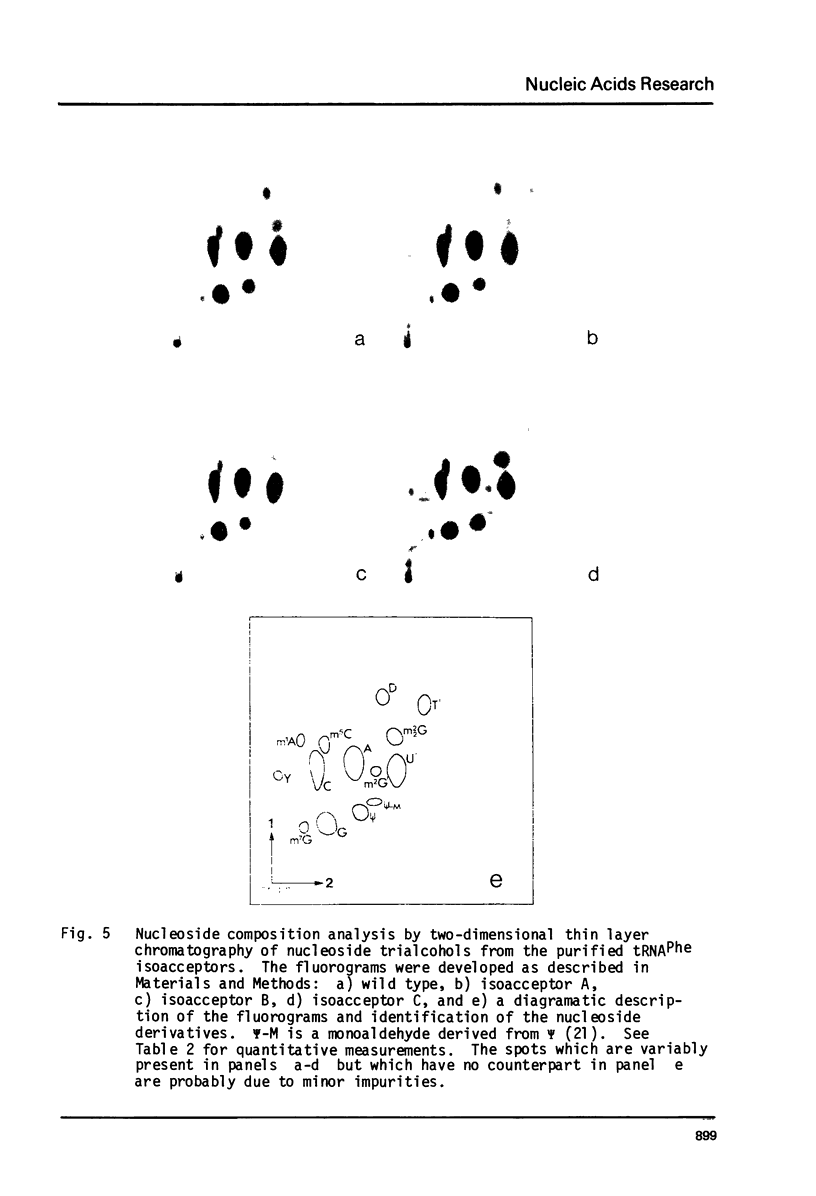
A mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, designated mia, is responsible for the production of isoaccepting tRNA molecules with reduced extents of nucleoside modifications. The mia isoacceptors of tRNAPhe and one of the mutant isoacceptors of tRNATyr were highly purified for nucleoside composition analyses. The data indicate that the mutant isoacceptors are lacking some of the dihydrouridine moieties. This is consistent with our previous hypothesis that the mutant isoacceptors were accumulated due to a defect in a modification process [Lo, R.Y.C. and Bell, J.B. (1981) Current Genetics 3, 73-82). Data from in vitro poly-U translation experiments also support the previous results, suggesting in vivo biological activity of these mutant tRNAs.
Full text
PDF


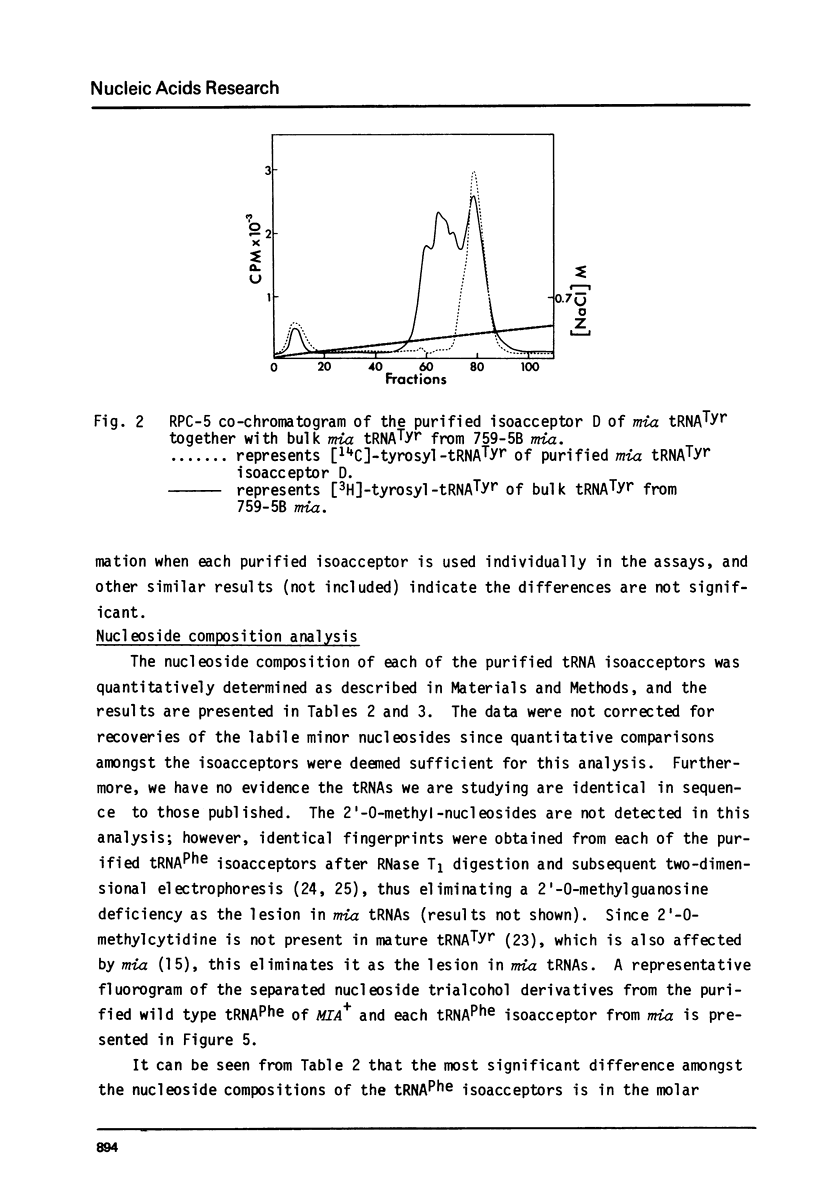

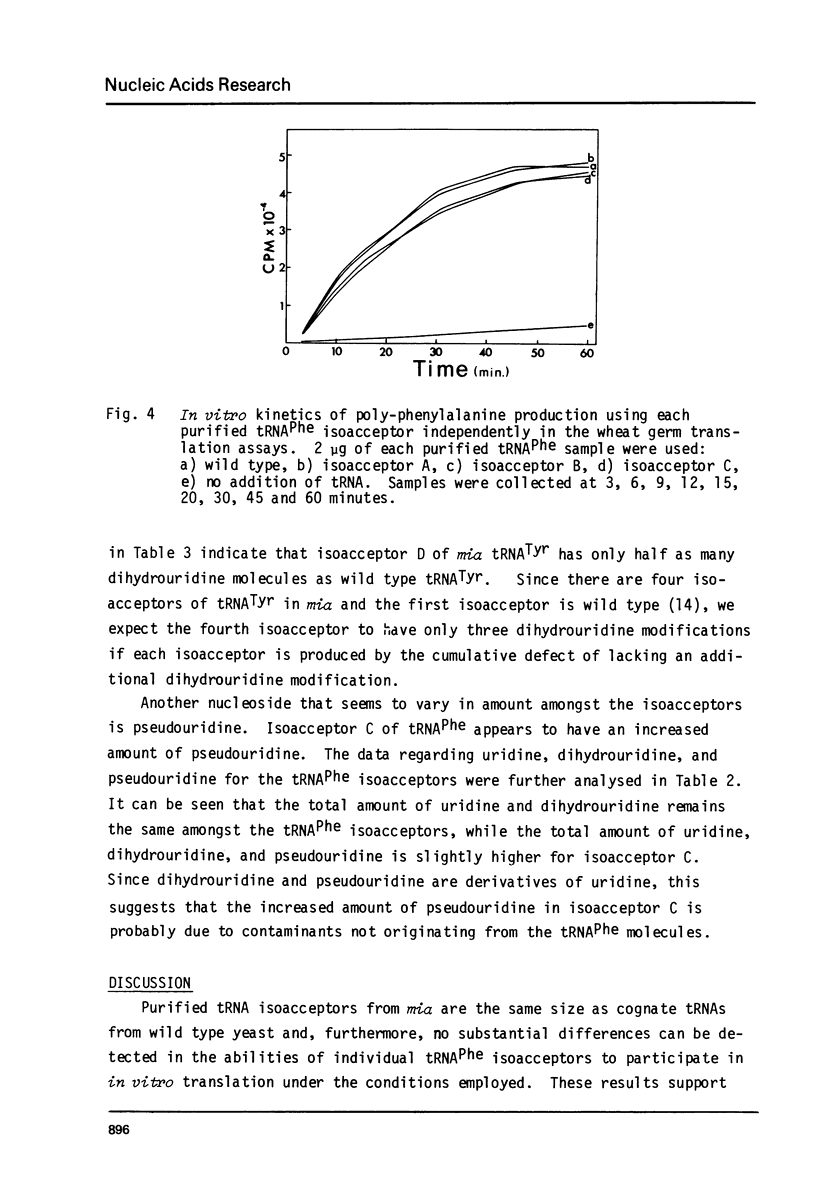
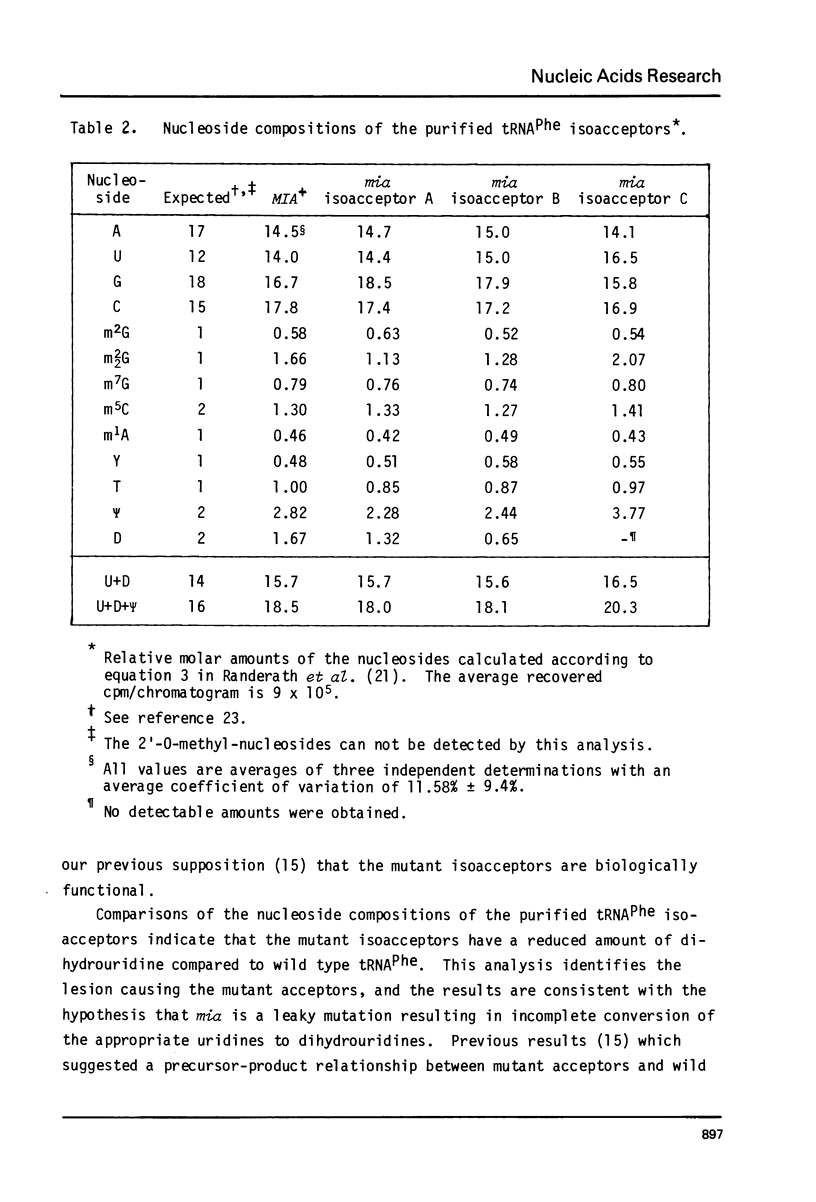
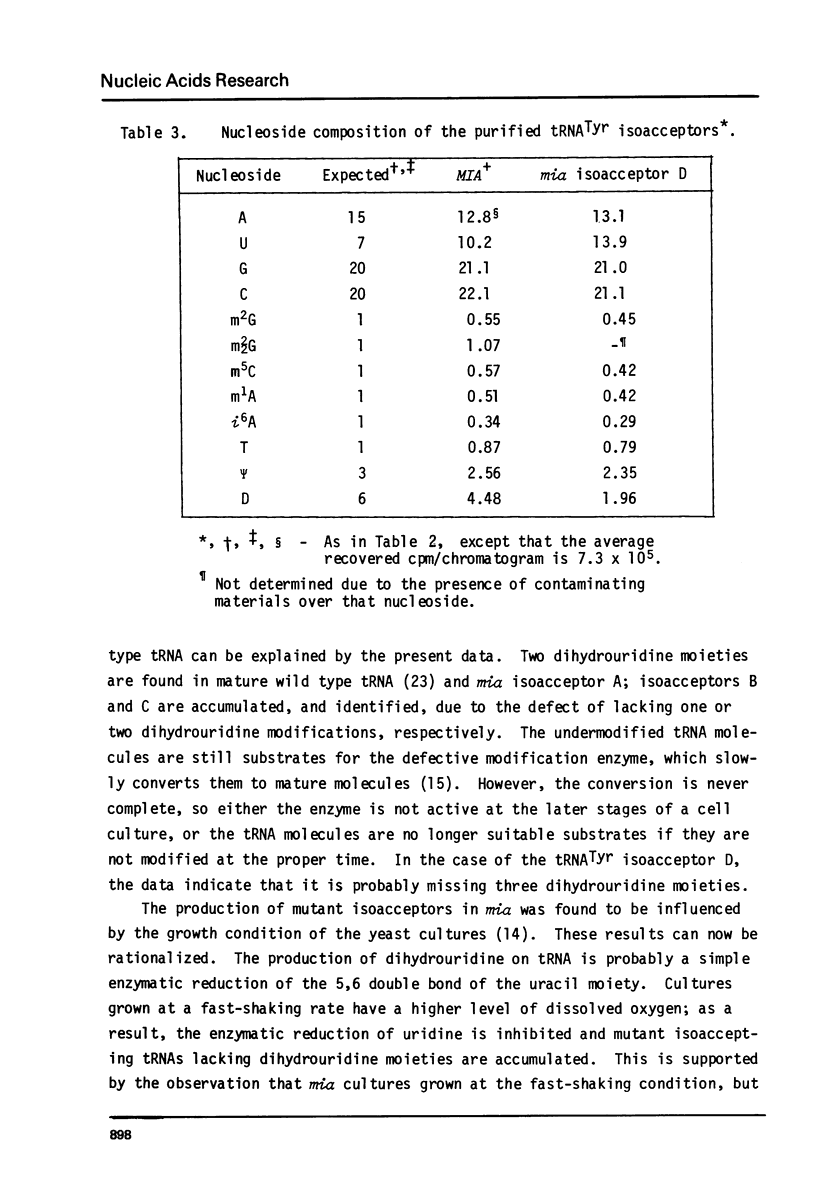



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman S. Transfer RNA processing enzymes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90262-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. B., Gelugne J. P., Jacobson K. B. A nonspecific inhibitory effect of tRNA on the activity of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 2;435(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk G. R., Neidhardt F. C. Physiological and biochemical studies on the function of 5-methyluridine in the transfer ribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):99–111. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.99-111.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r1–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp G., Beckmann J. S., Johnson P. F., Fuhrman S. A., Abelson J. Transcription and processing of intervening sequences in yeast tRNA genes. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):221–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laten H., Gorman J., Bock R. M. Isopentenyladenosine deficient tRNA from an antisuppressor mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4329–4342. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., De Robertis E. M., Cortese R. Order and intracellular location of the events involved in the maturation of a spliced tRNA. Nature. 1980 Mar 13;284(5752):143–148. doi: 10.1038/284143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., De Robertis E. M. RNA processing in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. Sequential addition of base modifications in the spliced transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 15;145(2):405–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S., Harada F., Narushima U., Seno T. Purification of methionine-, valine-, phenylalanine- and tyrosine-specific tRNA from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):133–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Cordell B., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Structure and processing of yeast precursor tRNAs containing intervening sequences. Nature. 1978 Aug 3;274(5670):438–445. doi: 10.1038/274438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden R. C., Beckman J. S., Abelson J., Kang H. S., Söll D., Schmidt O. In vitro transcription and processing of a yeast tRNA gene containing an intervening sequence. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. L., Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. Improved separation of transfer RNA's on polychlorotrifuoroethylene-supported reversed-phase chromatography columns. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 11;228(3):770–774. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90748-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Kjellin-Stråby K. Studies on microbial ribonucleic acid. IV. Two mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacking N-2-dimethylguanine in soluble ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Gupta R. C., Randerath E. 3H and 32P derivative methods for base composition and sequence analysis of RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):638–680. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Brownlee G. G., Barrell B. G. A two-dimensional fractionation procedure for radioactive nucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):373–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C. E., Smith G. R., Cortese R., Ames B. N. [Mutant tRNA His ineffective in repression and lacking two pseudouridine modifications]. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):72–74. doi: 10.1038/newbio238072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolar N., Hellman U., Svensson I. Two transfer RNA (1-methylguanine) methylases from yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jun;2(6):993–1004. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.6.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Székely M., Sanger F. Use of polynucleotide kinase in fingerprinting non-radioactive nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 14;43(3):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Maxwell I. H., Tener G. M. A simple method for isolating highly purified yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2623–2628. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]