Abstract
The sequence of more than 100 nucleotides at the 3'-end of Neurospora crassa 18S-rRNA was determined by chemical sequencing techniques. Extensive homologies with 18S-rRNA from other eukaryotes were found. Inspection of the nucleotide sequence at the 3'-end of N. crassa 5S-rRNA revealed the presence of sequences complementary to a region near the 3'-terminus of 18S-rRNA. Under the appropriate conditions a complex was formed between 18S-rRNA and 5S-rRNA (Tm 53 degrees C). Interaction was detected between 5S-rRNA and a specific 3'-terminal fragment from 18S-rRNA and between 18S-rRNA and a specific 3'-terminal fragment from 5S-rRNA. These findings are consistent with the idea that intermolecular base-pairing between nucleotides at the 3'-ends of 18S-rRNA and 5S-rRNA may be functionally important within the ribosome. Further investigation revealed that this intermolecular base-pairing is not essential for ribosome stability.
Full text
PDF


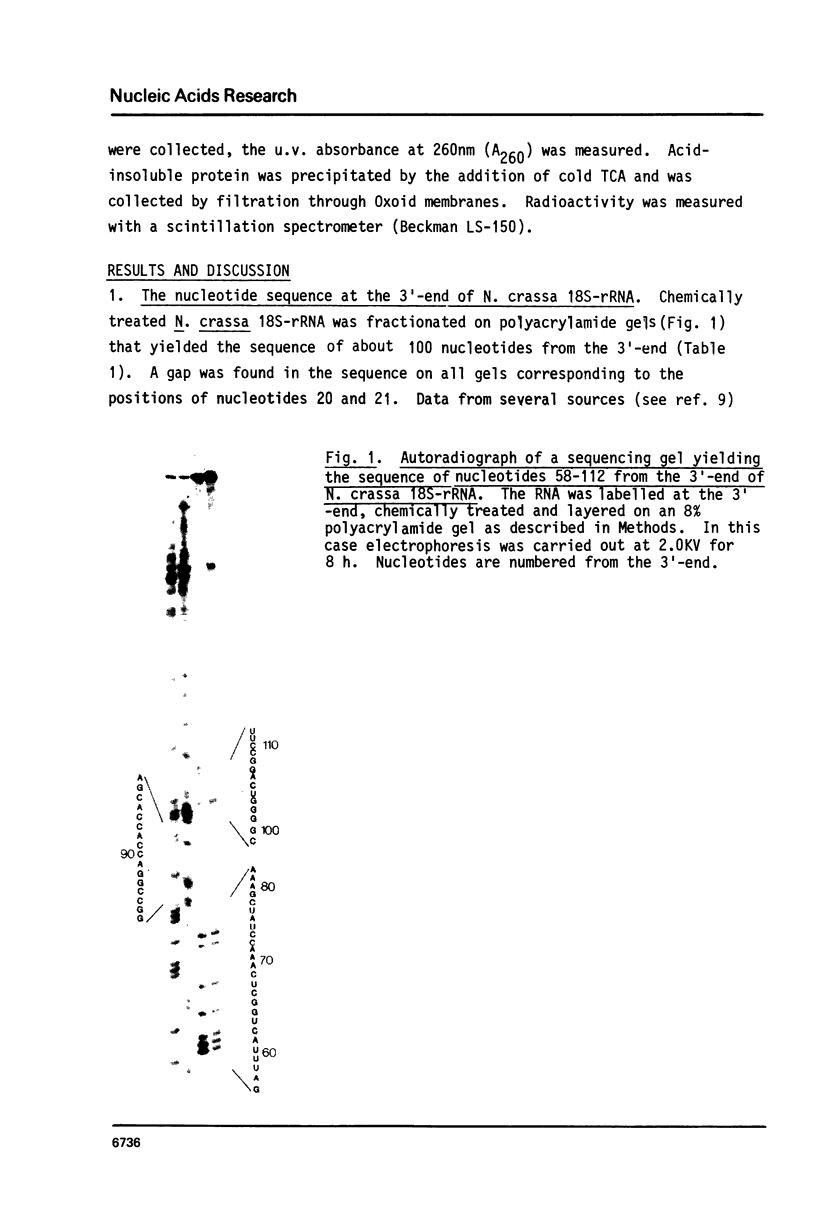




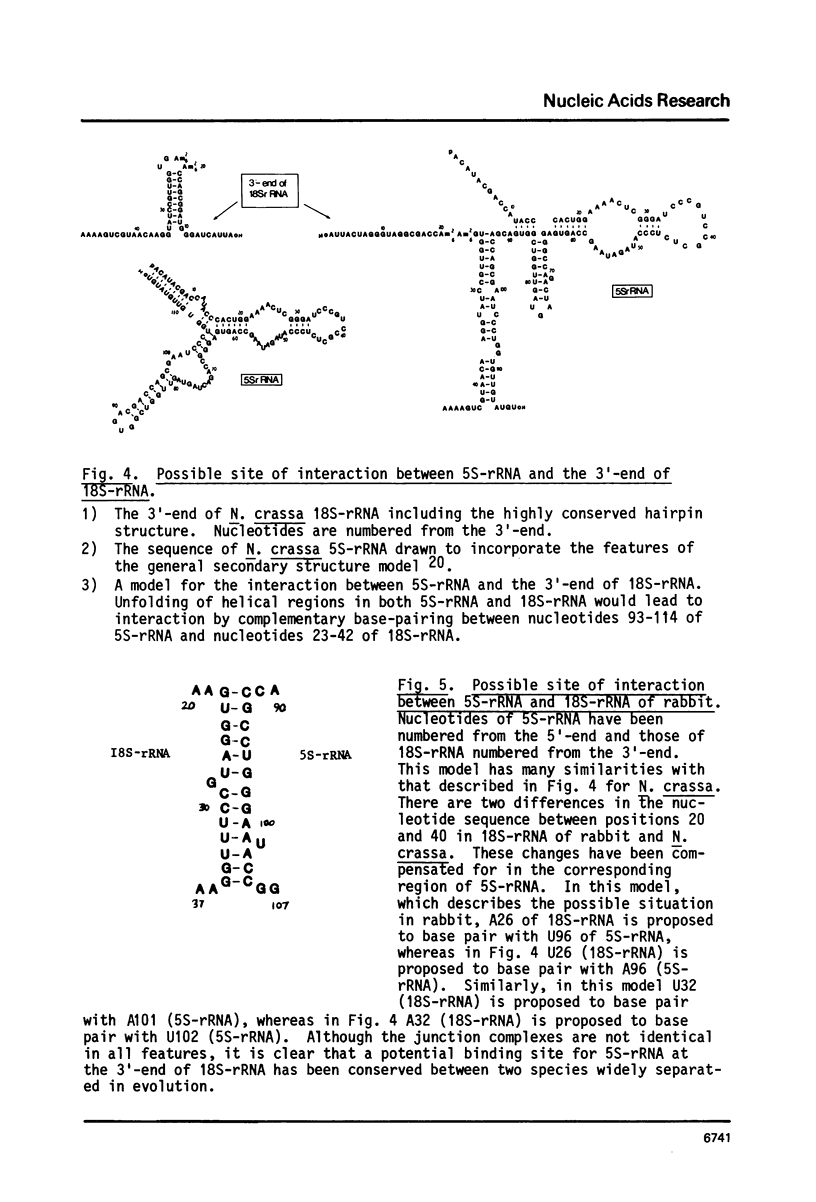




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azad A. A., Deacon N. J. Base-paired interaction, in vitro, between hen globin 9S mRNA and eukaryotic ribosomal RNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 14;86(3):568–576. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91751-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. A., Deacon N. J. The 3'-terminal primary structure of five eukaryotic 18S rRNAs determined by the direct chemical method of sequencing. The highly conserved sequences include an invariant region complementary to eukaryotic 5S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4365–4376. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. A. Intermolecular base-paired interaction between complementary sequences present near the 3' ends of 5S rRNA and 18S (16S) rRNA might be involved in the reversible association of ribosomal subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1913–1929. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. A., Lane B. G. Wheat-embryo ribonucleates. IV. Factors that influence the formation and stability of a complex between 5S rRNA and 18S rRNA. Can J Biochem. 1975 Mar;53(3):320–327. doi: 10.1139/o75-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Sabatini D. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kotecha S. Resistance of the peptidyltransferase centre of rabbit ribosomes to attack by nucleases and proteinases. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):199–214. doi: 10.1042/bj1900199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Pratt H., Huvos P., Higginson B., Hirst W. A study of the thermal stability of ribosomes and biologically active subribosomal particles. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;134(3):775–793. doi: 10.1042/bj1340775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Latil-Damotte M., Jourdan R. Sequence of the 3'-terminal portion of Drosophila melanogaster 18 S rRNA and of the adjoining spacer: comparison with corresponding prokaryotic and eukaryotic sequences. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Cox R. A. The nucleotide sequence at the 3'-end of Neurospora crassa 25S-rRNA and the location of a 5.8S-rRNA binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1111–1121. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. O. Dissociation of HeLa cells ribosomes by heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 15;30(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechulla B., Hahn U., McLaughlin L. W., Küntzel H. Nucleotide sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA from Aspergillus nidulans and Neurospora crassa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1445–1450. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Maden B. E. Nucleotide sequence of Xenopus laevis 18S ribosomal RNA inferred from gene sequence. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):205–208. doi: 10.1038/291205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols D. R., Hagenbuchle O., Gage L. P. Homology of the 3' terminal sequences of the 18S rRNA of Bombyx mori and the 16S rRNA of Escherchia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1109–1119. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of Crithidia fasciculata small ribosomal subunit RNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Yanofsky C., Driftmier K., Metzenberg R. L., Alzner-DeWeerd B., RajBhandary U. L. Dispersed 5S RNA genes in N. crassa: structure, expression and evolution. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):819–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Charldorp R., Van Knippenberg P. H. Sequence, modified nucleotides and secondary structure at the 3'-end of small ribosomal subunit RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1149–1158. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Steitz J. A. Complementary sequences 1700 nucleotides apart form a ribonuclease III cleavage site in Escherichia coli ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3593–3597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]