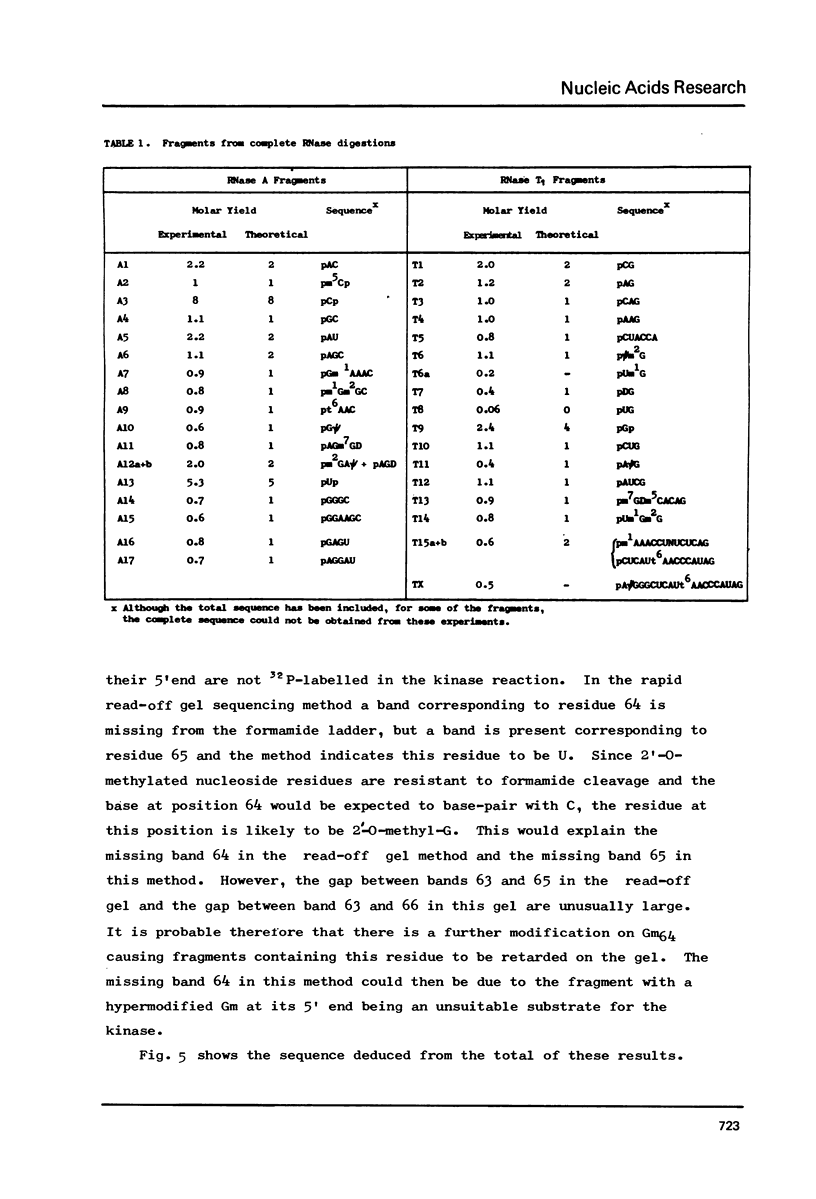
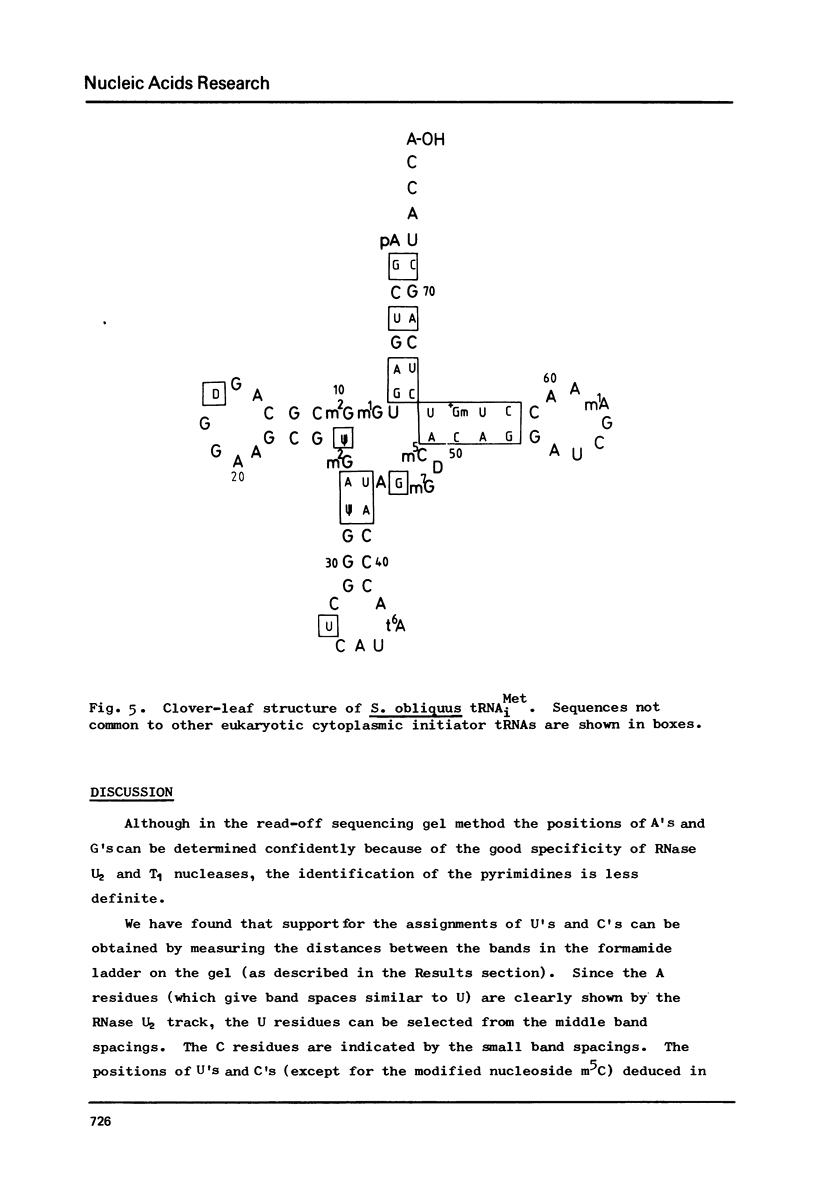
Abstract
The cytoplasmic initiator tRNA from the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus has been purified and its sequence shown to be p A G C U G A G-U m G m G C G C A G D G G A A G C G psi m G A psi G G G C U C A U t A A--C C C A U A G m G D m C A C A G G A U C G m A A A C C U Gm U C U C A--G C U A C C A-O H. The sequence has been deduced and confirmed using several different P-post labelling techniques. The sequence is similar to those of other eukaryotic cytoplasmic initiator tRNAs and it has the sequence G A U C in place of the usual G T psi C. Although it resembles lower eukaryotic species in having a U preceding the anticodon and a modified G in the T psi C stem, in overall homology it is closer to the higher eukaryotic than to the fungal initiator tRNAs.
Full text
PDF




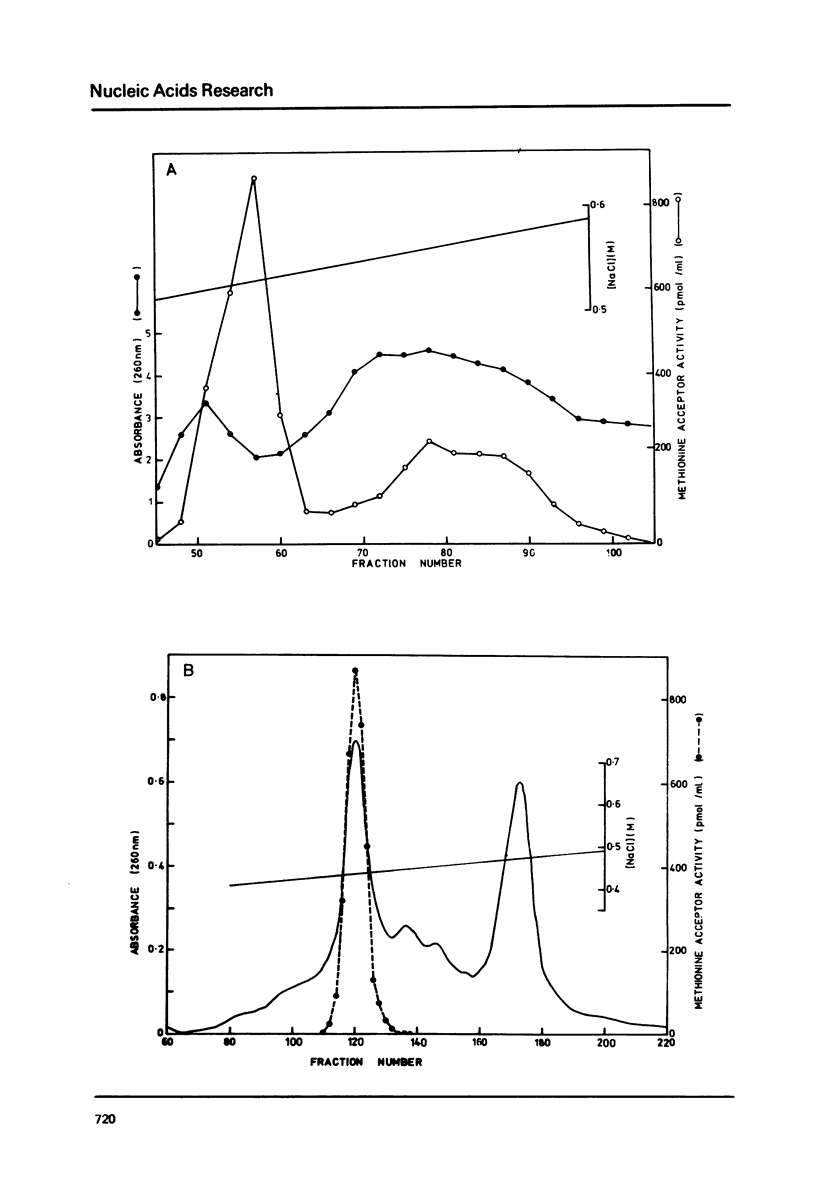
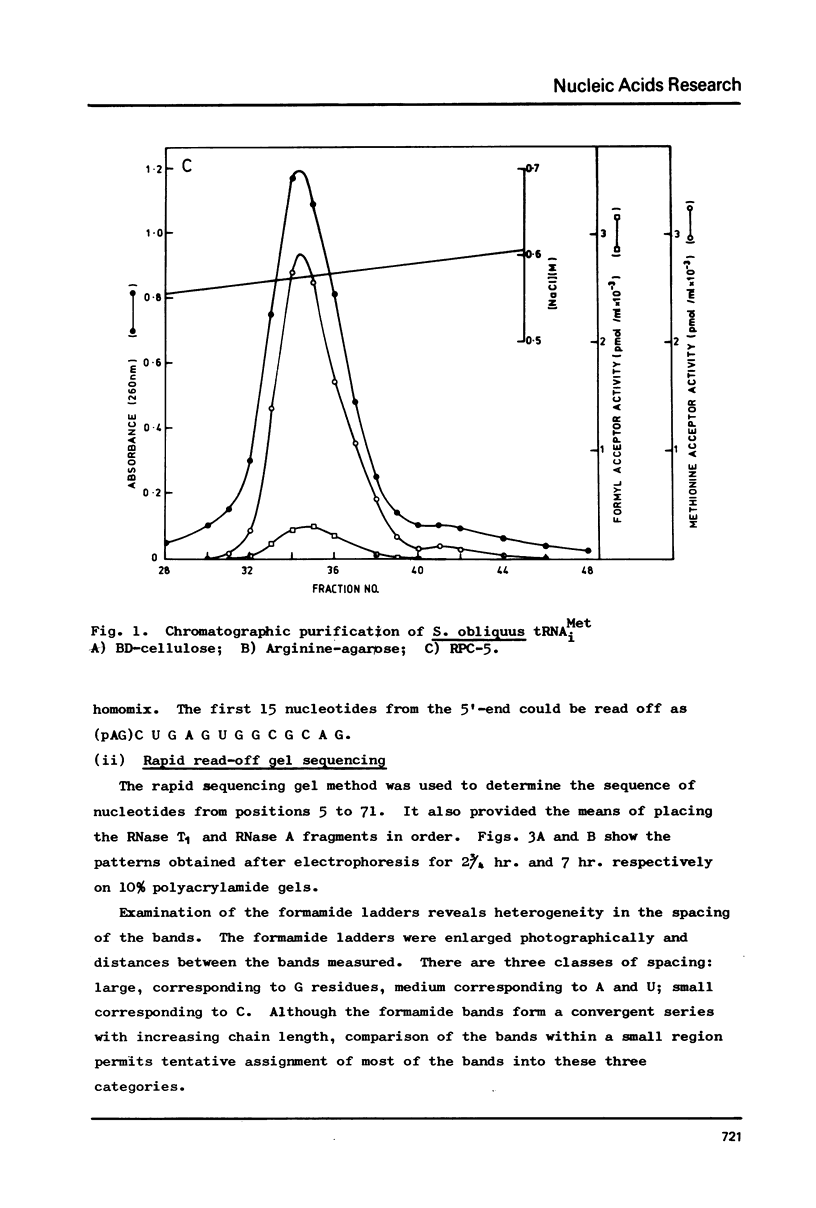






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Rhodes D., Guilley H., Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G. The nucleoside sequence of tyrosine tRNA from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):23–36. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Margoliash E. Construction of phylogenetic trees. Science. 1967 Jan 20;155(3760):279–284. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3760.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Grüter F., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):r1–r19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam I., Millward S., Blew D., von Tigerstrom M., Wimmer E., Tener G. M. The separation of soluble ribonucleic acids on benzoylated diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3043–3056. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Hecker L. I., Silberklang M., Schwartzbach S. D., RajBhandary U. L., Barnett W. E. Nucleotide sequence of Neurospora crassa cytoplasmic initiator tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4109–4131. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Roe B. A., Anandaraj M. P., RajBhandary U. L. Nucleotide sequence of human placenta cytoplasmic initiator tRNA. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Urquhart N., Smith M., RajBhandary U. L. Nucleotide sequence of salmon testes and salmon liver cytoplasmic initiator tRNA. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay F. T., Coultas C., Jones D. S. The use of a dipolar ion-exchanger for the fractionation of transfer ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):177–190. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Kato M., Sugisaki H., Nishimura S. Nucleotide sequence of starfish initiator tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3459–3469. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Alzner-Deweerd B., Heckman J. E., MacGee J., Tabor M. W., RajBhandary U. L. Sequence analysis of 5'[32P] labeled mRNA and tRNA using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jan;5(1):37–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L. W., Chiang G. H., Tseng W. C., Randerath K. Effects of 5-fluorouridine on modified nucleosides in mouse liver transfer RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):1075–1082. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. G., Reese C. B. Some aspects of the chemistry of N(1)- and N(6)-dimethylallyl derivatives of adenosine and adenine. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1968;14:1731–1738. doi: 10.1039/j39680001731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old J. M., Jones D. S. The aminoacylation of transfer ribonucleic acid. Inhibitory effects of some amino acid analogues with altered side chains. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):503–511. doi: 10.1042/bj1590503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. L., Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. Improved separation of transfer RNA's on polychlorotrifuoroethylene-supported reversed-phase chromatography columns. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 11;228(3):770–774. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90748-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Fornstedt N. Group fractionation of plasma proteins on dipolar ion exchangers. J Chromatogr. 1970 Sep 23;51(3):479–489. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96895-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath E., Yu C. T., Randerath K. Base analysis of ribopolynucleotides by chemical tritium labeling: a methodological study with model nucleosides and purified tRNA species. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jul;48(1):172–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Randerath E., Chia L. S., Nowak B. J. Base analysis of ribopolynucleotides by chemical tritium labeling: an improved mapping procedure for nucleoside trialcohols. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Donelson J. E., Coulson A. R., Kössel H., Fischer D. Use of DNA polymerase I primed by a synthetic oligonucleotide to determine a nucleotide sequence in phage fl DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. The use of nuclease P1 in sequence analysis of end group labeled RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4091–4108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Prochiantz A., Haenni A. L., Rajbhandary U. L. Studies on the sequence of the 3'-terminal region of turnip-yellow-mosaic-virus RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):465–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simsek M., RajBhandary U. L. The primary structure of yeast initiator transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):508–515. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Vassilenko S. A different approach to RNA sequencing. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):87–89. doi: 10.1038/274087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Székely M., Sanger F. Use of polynucleotide kinase in fingerprinting non-radioactive nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 14;43(3):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro-Matsumura S., Takemura S. The primary structure of cytoplasmic initiator transfer ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. J Biochem. 1979 Aug;86(2):335–346. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]