Abstract
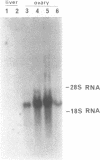
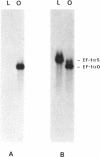
We have cloned cDNAs encoding two variants of the elongation factor for protein synthesis in Xenopus laevis, called EF-1 alpha. One of these (42Sp50) is expressed exclusively in immature oocytes. It is one of two protein components of a 42S RNP particle that is very abundant in previtellogenic oocytes. The 42S RNP particle consists of various tRNAs, 5S RNA, 42Sp50 and a 5S RNA binding protein (42Sp43). A major function served by 42Sp50 appears to be the storage of tRNAs for later use in oogenesis and early embryogenesis. The second EF-1 alpha variant (EF-1 alpha O) is expressed mainly in oocytes but transiently in early embryogenesis as well. Its mRNA cannot be detected after neurulation in somatic cells. EF-1 alpha O is closely related to a third EF-1 alpha (EF-1 alpha S), discovered originally by Krieg et al. (1). EF-1 alpha S is expressed at low levels in oocytes but actively in somatic cells. The latter two proteins are very similar to known eukaryotic EF-1 alpha from other organisms and presumably function in their respective cell types to support protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTH L. G., BARTH L. J. Differentiation of cells of the Rana pipiens gastrula in unconditioned medium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1959 Jun;7:210–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis H., Mairy M. Recherches biochimiques sur l'oogenèse. 1. Distribution intracellulaire du RNA dans les petits oocytes de Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):524–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis H., le Maire M. Biochemical research on oogenesis. Aminoacyl tRNA turns over in the 42-S particles of Xenopus laevis oocytes, but its ester bond is protected against hydrolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 18;149(3):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis H., le Maire M. Thesaurisomes, a novel kind of nucleoprotein particle. Subcell Biochem. 1983;9:263–297. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-3533-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda B. M., Roeder R. G. Association of a 5S gene transcription factor with 5S RNA and altered levels of the factor during cell differentiation. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovemann B., Richter S., Walldorf U., Cziepluch C. Two genes encode related cytoplasmic elongation factors 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) in Drosophila melanogaster with continuous and stage specific expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3175–3194. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho K. E., Darby M. K., Crawford E. T., Brown D. D. A finger protein structurally similar to TFIIIA that binds exclusively to 5S RNA in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90809-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M., Melton D. A. The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1-alpha (EF-1 alpha) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Coppard N. J., Brown R. S., Clark B. F., De Robertis E. M. 42S p48--the most abundant protein in previtellogenic Xenopus oocytes--resembles elongation factor 1 alpha structurally and functionally. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2409–2413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazabraud A., Wegnez M., Denis H. Biochemical research on oogenesis. RNA accumulation in the oocytes of teleosts. Dev Biol. 1975 Jun;44(2):326–332. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., le Maire M., Wegnez M., Denis H. Biochemical Research on oogenesis. Composition of the 42-S storage particles of Xenopus laevix oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):359–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Weeks D. L., Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Identification and cloning of localized maternal RNAs from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viel A., Djé M. K., Mazabraud A., Denis H., le Maire M. Thesaurin a, the major protein of Xenopus laevis previtellogenic oocytes, present in the 42 S particles, is homologous to elongation factor EF-1 alpha. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80295-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegnez M., Denis H. Biochemical research on oogenesis. Transfer RNA is fully charged in the 42-S storage particles of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- le Maire M., Denis H. Biochemical research on oogenesis. Binding of tRNA to the nucleoprotein particles of Xenopus laevis previtellogenic oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):654–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]