Abstract
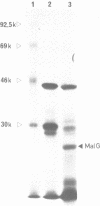
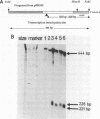
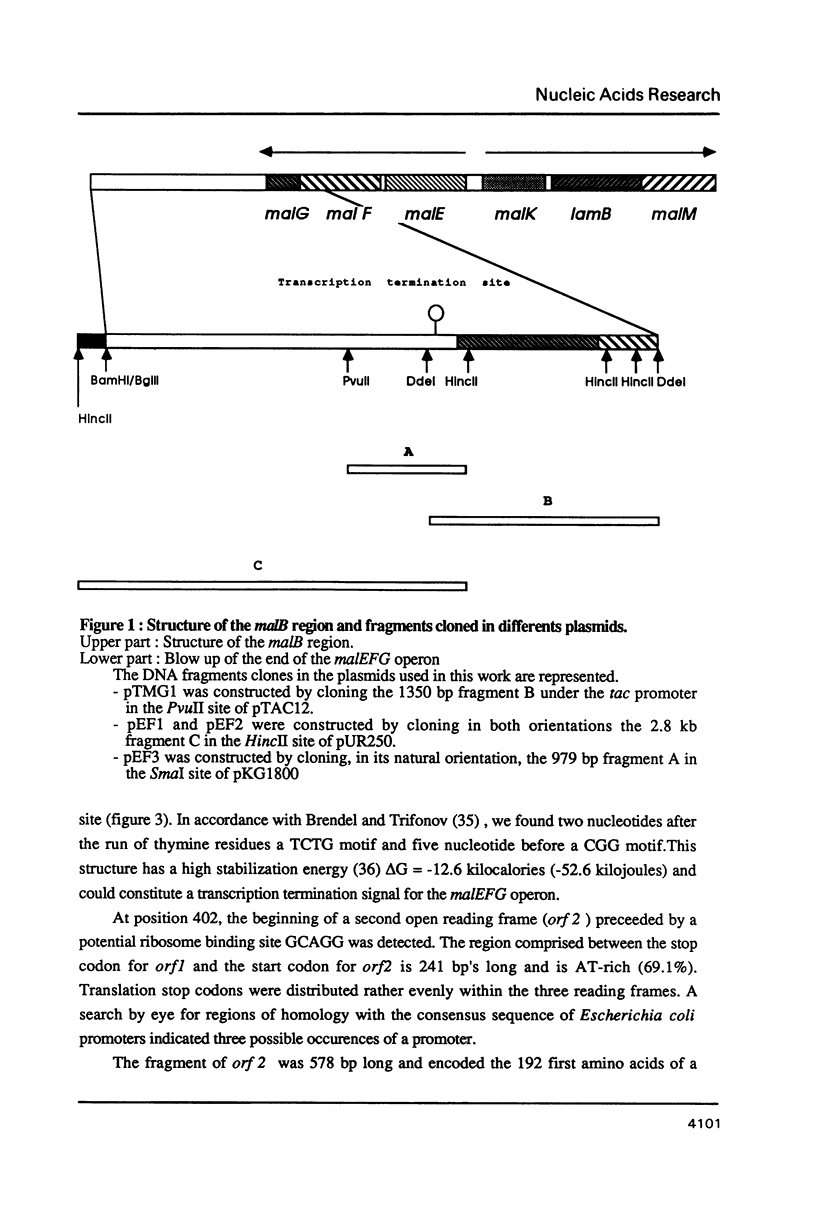
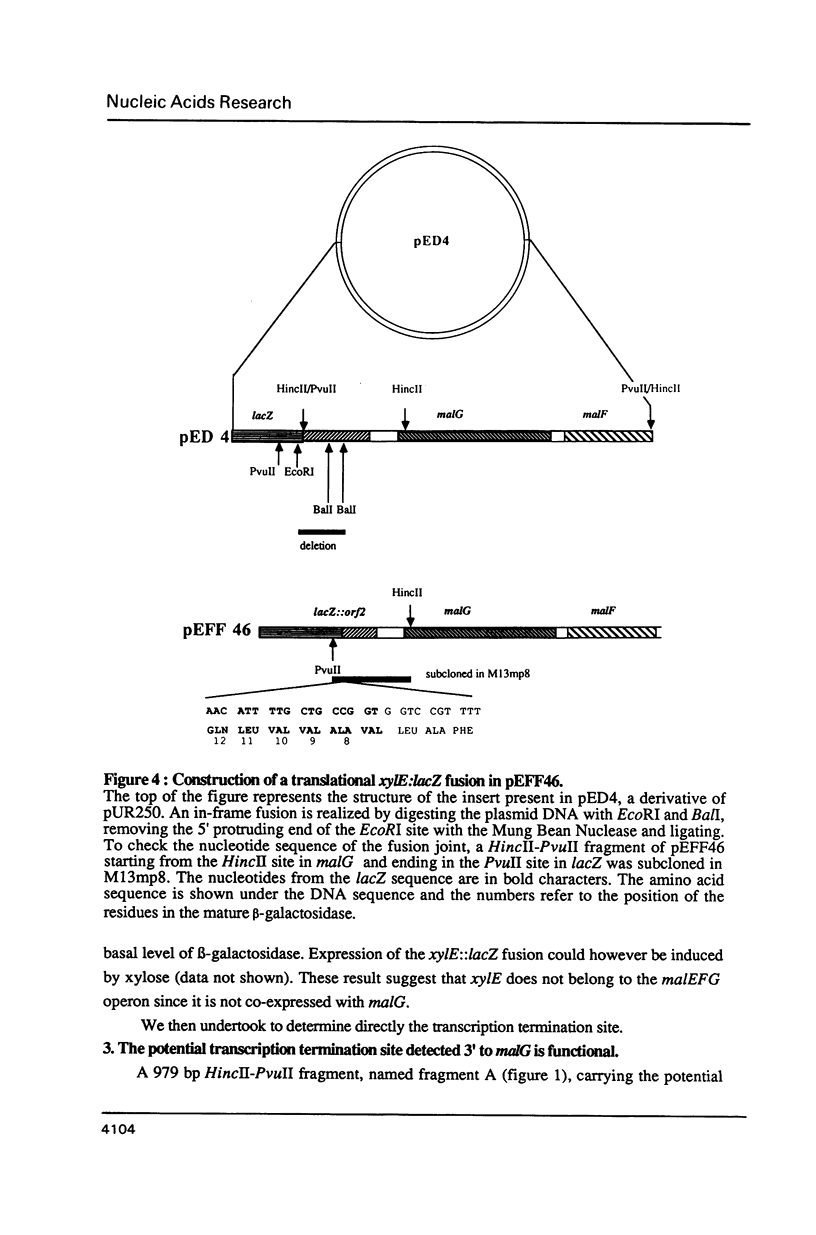
The nucleotide sequence of a 981 bp's HincII-PvuII DNA fragment containing the 3' end of the malEFG operon in E. coli was determined. This sequence displayed a putative Rho-independent transcription termination site localized 87 bp's after the stop codon of malG. When cloned into plasmid pKG1800, the HincII-PvuII fragment containing this structure acted as a strong transcription termination signal. By S1 mapping, we demonstrated that the 3' end of the malEFG transcript coincided with the putative transcription termination site. One short open reading frames orf1 (123 bp) and and the beginning of another one orf2 were localized after malG. The transcription termination site is localized within orf1. Consequently malG is the last gene of the malEFG operon. orf2 corresponds exactly to the 5' part of the xylE gene reported independently (Davis & Henderson, 1987) as the gene coding for the XylE protein, the xylose-proton symport of Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Brosius J., Ptashne M. Vectors bearing a hybrid trp-lac promoter useful for regulated expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Trifonov E. N. A computer algorithm for testing potential prokaryotic terminators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4411–4427. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F. High-sensitivity S1 mapping with single-stranded [32P]DNA probes synthesized from bacteriophage M13mp templates. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément J. M., Hofnung M. Gene sequence of the lambda receptor, an outer membrane protein of E. coli K12. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassa E., Hofnung M. Sequence of gene malG in E. coli K12: homologies between integral membrane components from binding protein-dependent transport systems. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2287–2293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Henderson P. J. The cloning and DNA sequence of the gene xylE for xylose-proton symport in Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13928–13932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duplay P., Bedouelle H., Fowler A., Zabin I., Saurin W., Hofnung M. Sequences of the malE gene and of its product, the maltose-binding protein of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10606–10613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Muir M., Lee K. S., Maris D. Substrate specificity of the Escherichia coli maltodextrin transport system and its component proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 7;860(1):44–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90496-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Beckwith J. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for malF protein, an inner membrane component of the maltose transport system of Escherichia coli. Repeated DNA sequences are found in the malE-malF intercistronic region. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10896–10903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Nikaido H., Hofnung M. Sequence of the malK gene in E.coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7449–7458. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Rousset J. P., Charbit A., Perrin D., Hofnung M. malM, a new gene of the maltose regulon in Escherichia coli K12. I. malM is the last gene of the malK-lamB operon and encodes a periplasmic protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge R., Boos W. Maltose and lactose transport in Escherichia coli. Examples of two different types of concentrative transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):443–478. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M. Divergent operons and the genetic structure of the maltose B region in Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):169–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann O., Szmelcman S. Active transport of maltose in Escherichia coli K12. Involvement of a "periplasmic" maltose binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchal C., Greenblatt J., Hofnung M. malB region in Escherichia coli K-12: specialized transducing bacteriophages and first restriction map. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1109–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1109-1119.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. pUR 250 allows rapid chemical sequencing of both DNA strands of its inserts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5765–5772. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H. A., Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Labeling of proteins with beta-galactosidase by gene fusion. Identification of a cytoplasmic membrane component of the Escherichia coli maltose transport system. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):168–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H. A. The maltose-maltodextrin transport system of Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Jan;133A(1):153–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Brickman E., Bassford P. J., Jr, Casadaban M. J., Shuman H. A., Schwartz V., Guarente L., Schwartz M., Beckwith J. R. Structure of the malB region in Escherichia coli K12. II. Genetic map of the malE,F,G operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 24;174(3):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00267797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Hofnung M. Maltose transport in Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of the bacteriophage lambda receptor. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):112–118. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.112-118.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Schwartz M., Ferenci T. Escherichia coli mutants impaired in maltodextrin transport. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.1-13.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]