Abstract
A cell line producing monoclonal antibodies directed against the core region of Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide has been established. These antibodies were inhibited by lipopolysaccharide preparations of both O-group 1 vibrios and some non-O-group 1 vibrios as detected in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-inhibition experiments. Coagglutination experiments with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies adsorbed to protein A-carrying staphylococci were performed. All V. cholerae strains tested, regardless of serotype, were agglutinated when mixed with staphylococci coated with the monoclonal antibodies, whereas staphylococci coated with group-specific (O1) polyclonal antibodies only agglutinated with O-group 1 vibrios.
Full text
PDF


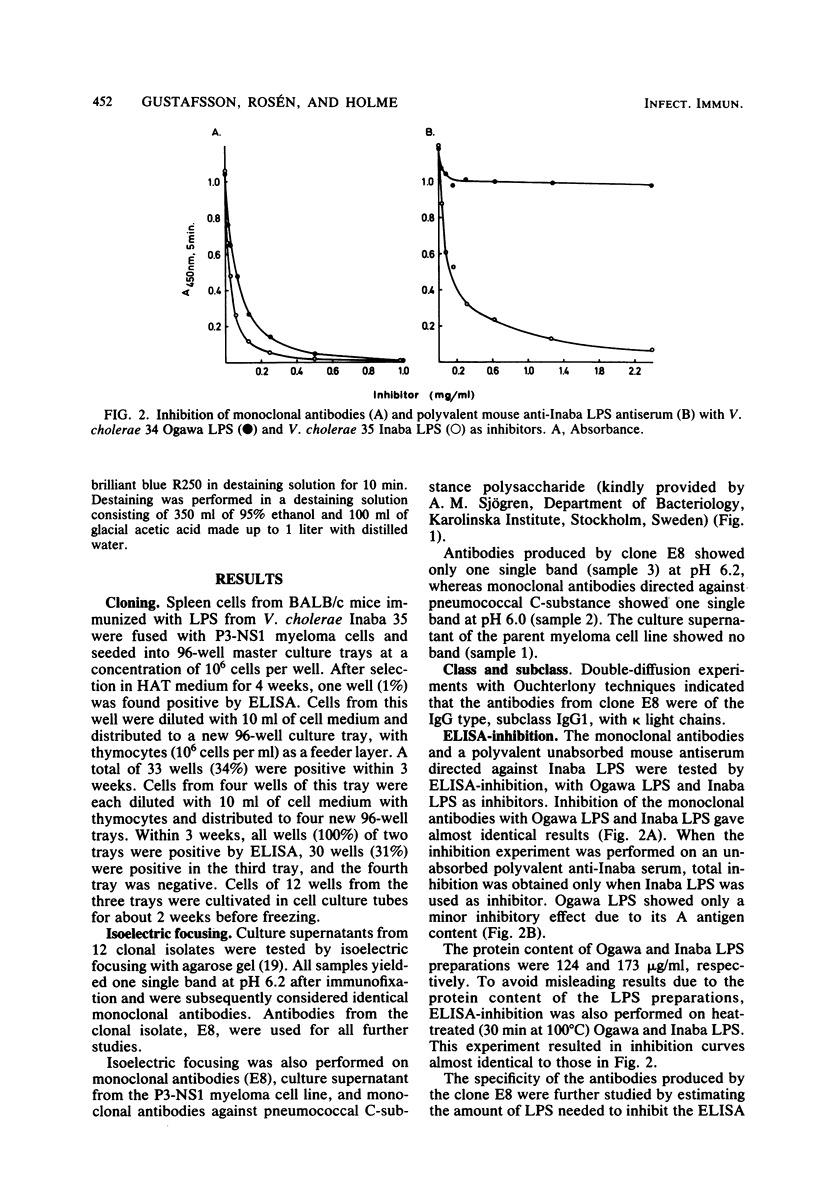


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boorsma D. M., Streefkerk J. G. Periodate or glutaraldehyde for preparing peroxidase conjugates? J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(3):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatsune K., Kondo S. Lipopolysaccharides of R mutants isolated from Vibria cholerae. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):77–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1850077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Jann K., Beyaert G. O. 2-Amino-2,6-dideoxy-d-glucose (D-quinovosamine): a constituent of the lipopolysaccharides of Vibrio cholerae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 3;37(3):531–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson P. E., Lindberg A. A., Lindberg B., Wollin R. Structural studies on the hexose region of the core in lipopolysaccharides from Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):571–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Unger P., Gustafsson B., Holme T. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O-antigen. Carbohydr Res. 1982 Mar 1;100:341–349. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Unger P., Holme T., Holmgren J. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O-antigen. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Jan;68(1):C14–C16. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Lostrom M. E., Tam M. R., Stone M. R., Burnette W. N. The isolation of hybrid cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies against the p15(E) protein of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin S. Immunochemical studies of the lipopolysaccharides of Vibrio cholerae: constitution of O specific side chain and core polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):211–215. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.211-215.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. W., Korsch M. J., Jackson G. D. Immunochemical studies to the O-antigens of vibrio cholerae. Partial characterization of an acid-labile antigenic determinant. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1973 Apr;51(2):229–235. doi: 10.1038/icb.1973.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. W. The 4-amino sugars present in the lipopolysaccharides of vibro cholerae and related vibrios. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 6;542(3):378–384. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K. Somatic antigen variation in Vibrio cholerae. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1971 Apr;24(2):93–100. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.24.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Sakazaki R. Additional serovars and inter-O antigenic relationships of Vibrio cholerae. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1977 Oct;30(5):275–277. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.30.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Sakazaki R. R antigen of vibrio cholerae. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1973 Aug;26(4):155–160. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.26.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A., Fleck D. G., Perkins M., Oladehin B. A microplate enzyme-immunoassay for toxoplasma antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Feb;29(2):150–153. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Draper C., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for chagas' disease. Lancet. 1975 Feb 22;1(7904):426–428. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



