Abstract
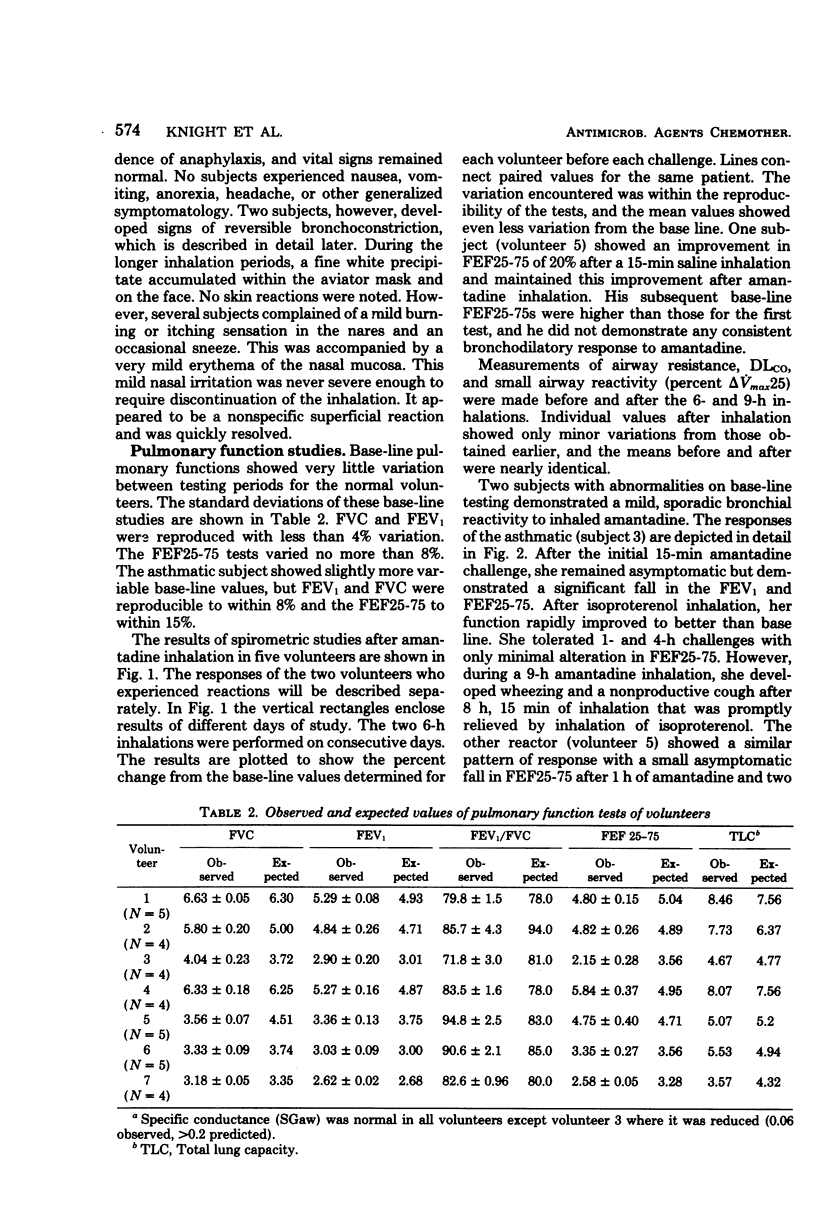
Seven well volunteers and three patients with a naturally occurring influenza A/USSR/77 (H1N1)-like infection were given amantadine by small-particle aerosol with a Collison generator modified for this purpose. Inhalation periods for the volunteers were increased on consecutive weekends from 15 min to 1 h, 4 h, 9 h, and 2 consecutive days of 6 h each. The particle size was 1.2-micrometer mass median diameter, and the concentration of inhaled aerosol ranged from 47 to 75 microgram/liter. Estimates of retained doses in 9 h were 74 to 149 mg. About two-thirds of the dose was recovered in the urine. Pulmonary function studies did not vary significantly from base-line values and were within a normal range for five of seven volunteers. Two volunteers with a moderate reduction in mid-maximal flow before exposure had a total of three episodes of coughing and wheezing associated with moderate reductions in mid-maximal flow values. These episodes cleared spontaneously or improved promptly after isoproterenol therapy. The patients with influenza tolerated the treatment well and recovered promptly.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURROWS B., KASIK J. E., NIDEN A. H., BARCLAY W. R. Clinical usefulness of the single-breath pulmonucy diffusing capacity test. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:789–806. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Hall W. J., Douglas R. G., Jr, Mudholkar G. S., Speers D. M., Patel K. Airway hyperreactivity and peripheral airway dysfunction in influenza A infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Aug;118(2):295–303. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F., Koski A., Johnson L. C. Spirometric standards for healthy nonsmoking adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jan;103(1):57–67. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. S., Stephen E. L., Spertzel R. O. Small-particle aerosols of antiviral compounds in treatment of type A influenza pneumonia in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A140–A144. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. Z., Knight V., Moore R., Larson E. W. Amantadine small-particle aerosol: generation and delivery to man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Jul;161(3):350–354. doi: 10.3181/00379727-161-40551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. W., Dominik J. W., Walker J. S., Larson E. W. Continuous aerosol therapy system using a modified Collison nebulizer. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):131–136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.131-136.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


