Full text
PDF
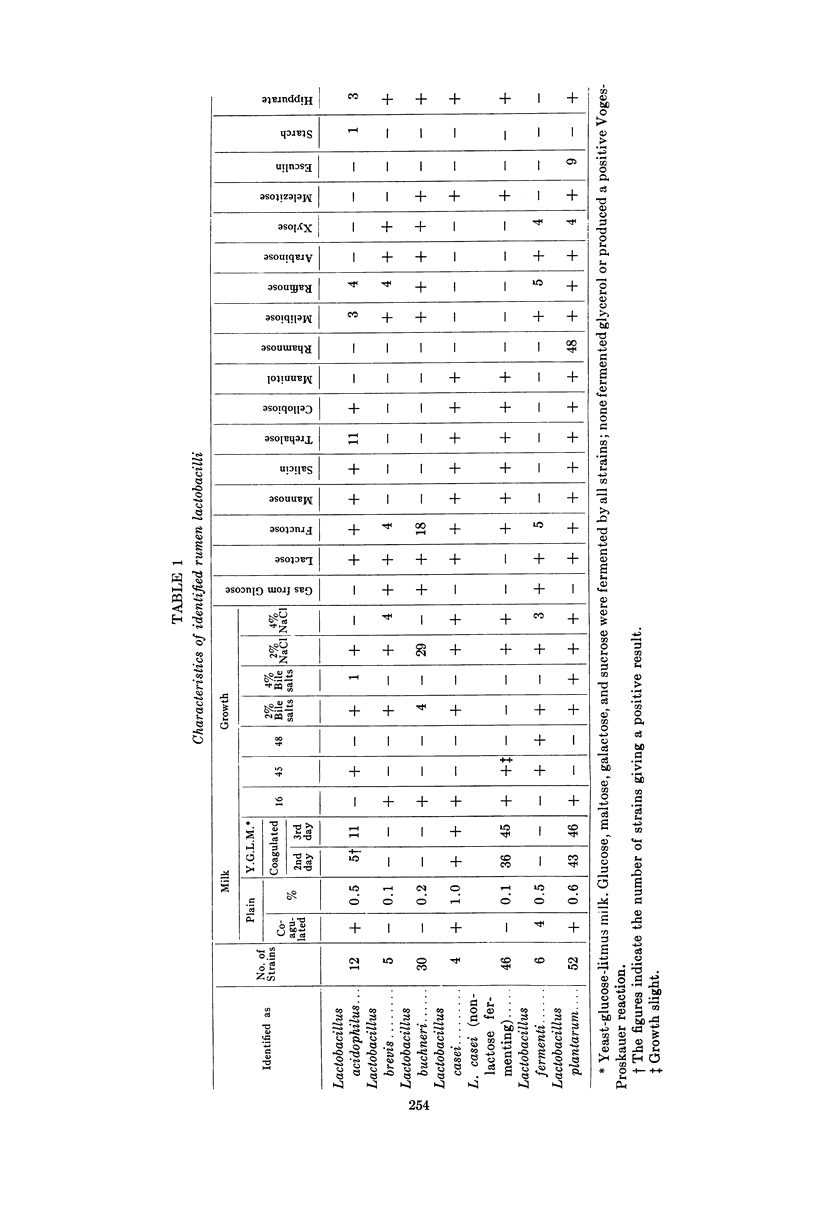
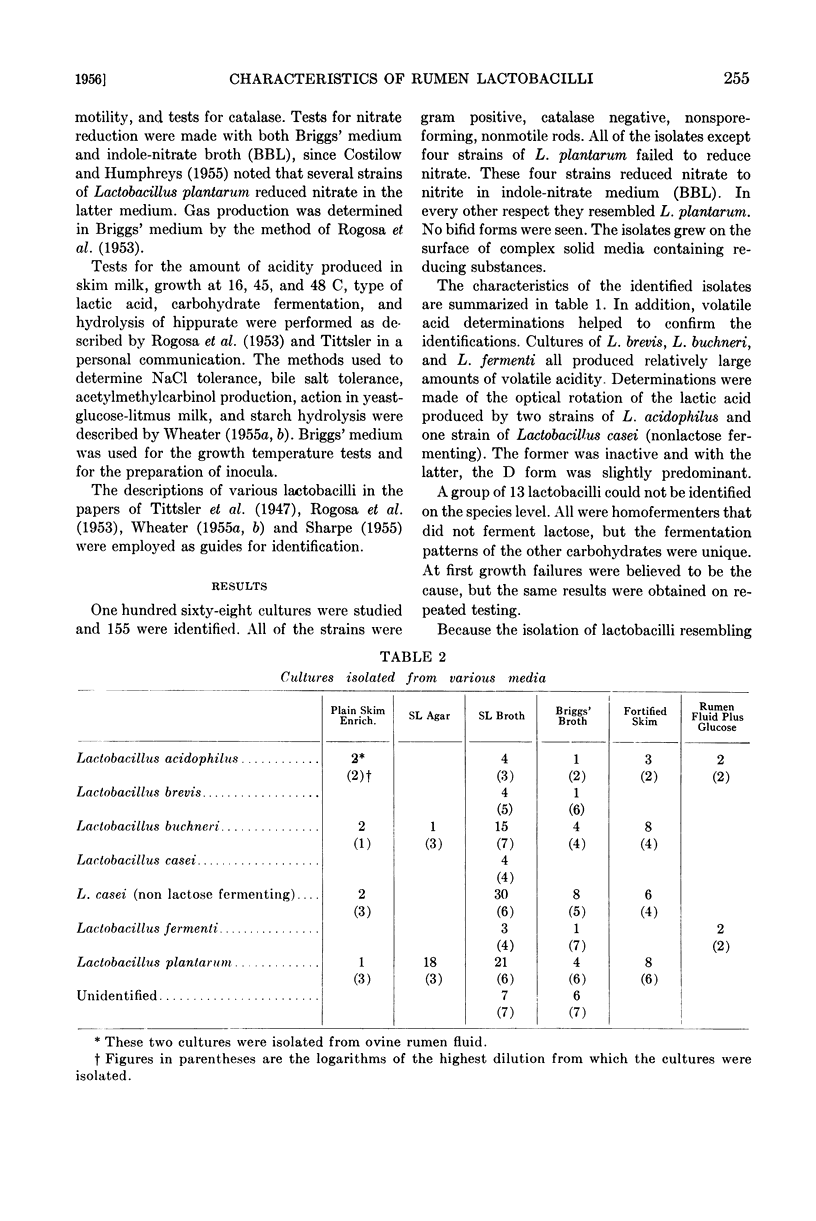



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRIGGS M. The classification of Lactobacilli by means of physiological tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Oct;9(2):234–248. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-2-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTILOW R. N., HUMPHREYS T. W. Nitrate reduction by certain strains of Lactobacillus plantarum. Science. 1955 Feb 4;121(3136):168–168. doi: 10.1126/science.121.3136.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON A. P., Jr, HANSEN P. A. A motile Lactobacillus from the cecal feces of turkeys. J Bacteriol. 1950 Mar;59(3):444–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.3.444-446.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUHTANEN C. N., GALL L. S. Rumen organisms. II. Two lactate utilizers and six miscellaneous types. J Bacteriol. 1953 May;65(5):554–559. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.5.554-559.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt G. A., Rettger L. F. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MEMBERS OF THE LACTOBACILLUS GENUS, WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON LACTOBACILLI OF SOIL AND GRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1930 Jul;20(1):61–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.20.1.61-83.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN S. O., OXFORD A. E. Relationships between viable saccharolytic bacteria in rumen and abomasum of the young calf and kid. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Feb;12(1):140–146. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-1-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN S. O., OXFORD A. E. Studies of some presumptive lactobacilli isolated from the rumens of young calves. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):83–90. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL A. W. The occurrence and distribution of amino-acid decarboxylases within the genus Lactobacillus. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Apr;8(2):224–232. doi: 10.1099/00221287-8-2-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M., MITCHELL J. A., WISEMAN R. F. A selective medium for the isolation and enumeration of oral lactobacilli. J Dent Res. 1951 Oct;30(5):682–689. doi: 10.1177/00220345510300051201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M., WISEMAN R. F., MITCHELL J. A., DISRAELY M. N., BEAMAN A. J. Species differentiation of oral lactobacilli from man including description of Lactobacillus salivarius nov spec and lactobacillus Cellobiosus nov spec. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jun;65(6):681–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.6.681-699.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARPE M. E. A serological classification of lactobacilli. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Feb;12(1):107–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEATER D. M. The characteristics of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Feb;12(1):123–132. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEATER D. M. The characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum, L. helveticus and L. casei. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Feb;12(1):133–139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


