Abstract
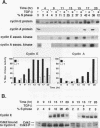
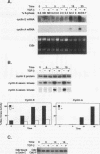
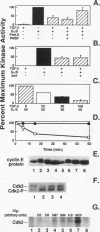
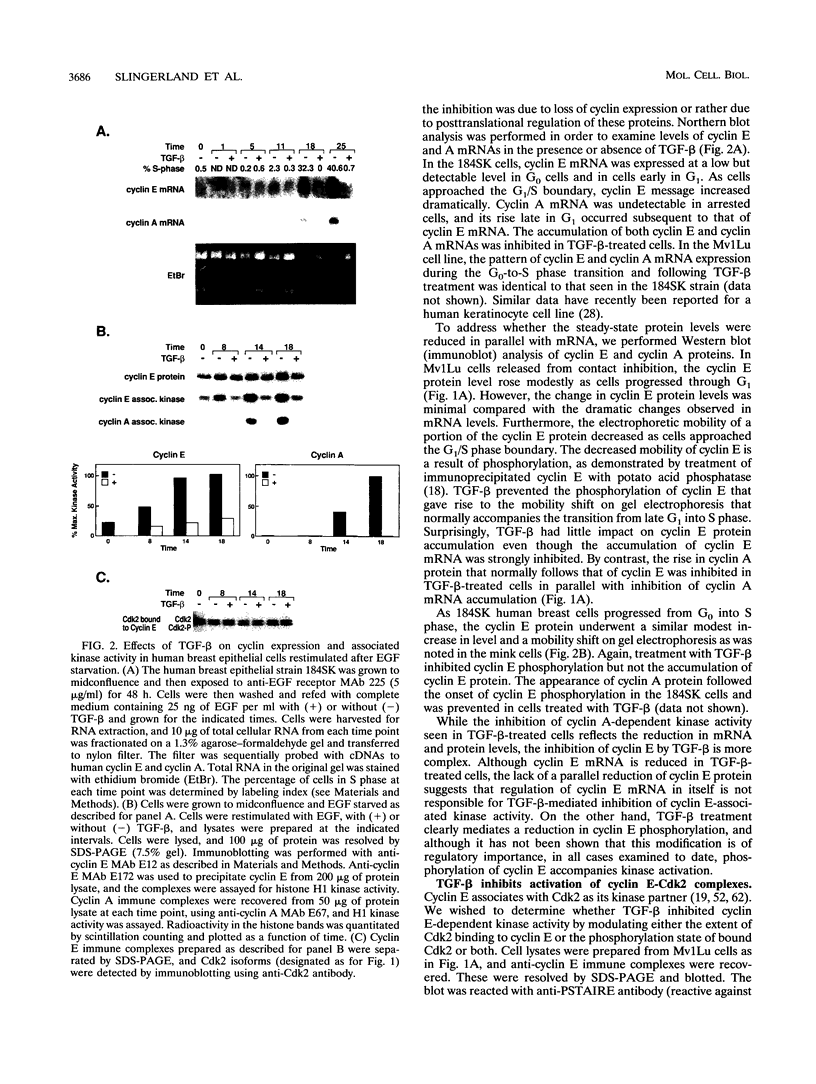
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) is a potent inhibitor of epithelial cell growth. Cyclins E and A in association with Cdk2 have been shown to play a role in the G1-to-S phase transition in mammalian cells. We have studied the effects of TGF-beta-mediated growth arrest on G1/S cyclins E and A. Inhibition of cyclin A-associated kinase by TGF-beta is primarily due to a decrease in cyclin A mRNA and protein. By contrast, while TGF-beta inhibits accumulation of cyclin E mRNA, the reduction in cyclin E protein is minimal. Instead, we find that the activation of cyclin E-associated kinase that normally accompanies the G1-to-S phase transition is inhibited. A novel inhibitor of cyclin-Cdk complexes was detected in TGF-beta-treated cell lysates. Inhibition is mediated by a heat-stable protein that targets both Cdk2 and Cdc2 kinases. In G0-arrested cells, a similar inhibitor of Cdk2 kinase was detected. These data suggest the existence of an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases induced under different conditions to mediate antiproliferative responses.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlakha R. C., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Wright D. A., Rao P. N. Evidence for the presence of inhibitors of mitotic factors during G1 period in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1707–1713. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga C. L., Tandon A. K., Von Hoff D. D., Osborne C. K. Transforming growth factor beta: potential autocrine growth inhibitor of estrogen receptor-negative human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 15;48(14):3898–3904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Lukas J., Marcote M. J., Pagano M., Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):812–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D., Durkacz B., Nurse P. Functionally homologous cell cycle control genes in budding and fission yeast. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):706–709. doi: 10.1038/300706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Site-specific mutagenesis of cdc2+, a cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein R., Lee W. H. Molecular genetics of the retinoblastoma suppressor gene. Crit Rev Oncog. 1991;2(3):211–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Herskowitz I. Identification of a gene necessary for cell cycle arrest by a negative growth factor of yeast: FAR1 is an inhibitor of a G1 cyclin, CLN2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):999–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. DAF1, a mutant gene affecting size control, pheromone arrest, and cell cycle kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4675–4684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorée M. Control of M-phase by maturation-promoting factor. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;2(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90018-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Brizuela L., Potashkin J., Beach D. Identification of p34 and p13, human homologs of the cell cycle regulators of fission yeast encoded by cdc2+ and suc1+. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Kaufmann W. K., Wilson S. J., Tlsty T. D., Lees E., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Reed S. I. p53-dependent inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase activities in human fibroblasts during radiation-induced G1 arrest. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Lees E., Reed S. I. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1958–1961. doi: 10.1126/science.1329201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Richman R., Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Lodgson N., Harper J. W. CDK2 encodes a 33-kDa cyclin A-associated protein kinase and is expressed before CDC2 in the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2907–2911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Spottswood M. R. A new human p34 protein kinase, CDK2, identified by complementation of a cdc28 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a homolog of Xenopus Eg1. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2653–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Whitehouse L. L., Livingston D. M. TGF beta inhibition of Cdk4 synthesis is linked to cell cycle arrest. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1009–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filmus J., Kerbel R. S. Development of resistance mechanisms to the growth-inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor-beta during tumor progression. Curr Opin Oncol. 1993 Jan;5(1):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y., Weinberg R. A. Transforming growth factor beta effects on expression of G1 cyclins and cyclin-dependent protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10315–10319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwin B. I., Spillare E., Forrester K., Lehman T. A., Kispert J., Welsh J. A., Pfeifer A. M., Lechner J. F., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. Mutant p53 can induce tumorigenic conversion of human bronchial epithelial cells and reduce their responsiveness to a negative growth factor, transforming growth factor beta 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2759–2763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiara J. B., Richardson H. E., Sugimoto K., Henze M., Lew D. J., Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. A cyclin B homolog in S. cerevisiae: chronic activation of the Cdc28 protein kinase by cyclin prevents exit from mitosis. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90417-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Cosson M. P., Evans J. A., Gibbons B. H., Houck B., Martinson K. H., Sale W. S., Tang W. J. Potent inhibition of dynein adenosinetriphosphatase and of the motility of cilia and sperm flagella by vanadate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard F., Strausfeld U., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cyclin A is required for the onset of DNA replication in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1169–1179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Rosenblatt J., Morgan D. O. Cell cycle regulation of CDK2 activity by phosphorylation of Thr160 and Tyr15. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3995–4005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris J., Golemis E., Chertkov H., Brent R. Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Culotti J., Pringle J. R., Reid B. J. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. Science. 1974 Jan 11;183(4120):46–51. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4120.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Unger M. W. Unequal division in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its implications for the control of cell division. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):422–435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosobuchi M., Stampfer M. R. Effects of transforming growth factor beta on growth of human mammary epithelial cells in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;25(8):705–713. doi: 10.1007/BF02623723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe P. H., Draetta G., Leof E. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 inhibition of p34cdc2 phosphorylation and histone H1 kinase activity is associated with G1/S-phase growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1185–1194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Kahn S. M., Tomita N., Zhang Y. J., Lu S. H., Weinstein I. B. Amplification and expression of the human cyclin D gene in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2980–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyomarsi K., Pardee A. B. Redundant cyclin overexpression and gene amplification in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Wang X. F., Weinberg R. A., Cheifetz S., Massagué J. Absence of TGF-beta receptors and growth inhibitory responses in retinoblastoma cells. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):196–199. doi: 10.1126/science.2895499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K. Transformation of cells by an inhibitor of phosphatases acting on phosphotyrosine in proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Cross F., Fisher A., Schumacher J., Leguellec K., Philippe M., Roberts J. M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D., Yamashita K., Harper J. W., Elledge S., Nishimoto T., Morgan D. O., Franza B. R., Roberts J. M. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.1388288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Ohtsuki M., Polyak K., Roberts J. M., Massagué J. Negative regulation of G1 in mammalian cells: inhibition of cyclin E-dependent kinase by TGF-beta. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):536–539. doi: 10.1126/science.8475385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Rogers T., Maizel A., Sharma S. Loss of transforming growth factor beta 1 receptors and its effects on the growth of EBV-transformed human B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):998–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Cavadore J. C., Nurse P., Doree M. Purification of MPF from starfish: identification as the H1 histone kinase p34cdc2 and a possible mechanism for its periodic activation. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90963-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Growth inhibition by TGF-beta linked to suppression of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Weis M. B., Massagué J. Concomitant loss of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta receptor types I and II in TGF-beta-resistant cell mutants implicates both receptor types in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18518–18524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammie G. A., Fantl V., Smith R., Schuuring E., Brookes S., Michalides R., Dickson C., Arnold A., Peters G. D11S287, a putative oncogene on chromosome 11q13, is amplified and expressed in squamous cell and mammary carcinomas and linked to BCL-1. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A., Gautier J., Lohka M., Hollingsworth R., Moreno S., Nurse P., Maller J., Sclafani R. A. Mammalian growth-associated H1 histone kinase: a homolog of cdc2+/CDC28 protein kinases controlling mitotic entry in yeast and frog cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3860–3868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léopold P., O'Farrell P. H. An evolutionarily conserved cyclin homolog from Drosophila rescues yeast deficient in G1 cyclins. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1207–1216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90043-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Laiho M., Ralph D. A., Weis F. M., Zentella A. Transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Surv. 1992;12:81–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:597–641. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui T., Wakefield L. M., Lechner J. F., LaVeck M. A., Sporn M. B., Harris C. C. Type beta transforming growth factor is the primary differentiation-inducing serum factor for normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2438–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):701–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon J. B., Richards W. L., del Campo A. A., Song M. K., Thorgeirsson S. S. Differential effects of transforming growth factor-beta on proliferation of normal and malignant rat liver epithelial cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1986 Sep;46(9):4665–4671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D. An inhibitor of p34CDC28 protein kinase activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):216–219. doi: 10.1126/science.8421781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D., Jones C. A., Reed S. I. Dual regulation of the yeast CDC28-p40 protein kinase complex: cell cycle, pheromone, and nutrient limitation effects. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):927–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Enders G. H., Wu C. L., Su L. K., Gorka C., Nelson C., Harlow E., Tsai L. H. A family of human cdc2-related protein kinases. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2909–2917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Pietenpol J. A., Pittelkow M. R., Holt J. T., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factor beta 1 regulation of c-myc expression, pRB phosphorylation, and cell cycle progression in keratinocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Nomoto S., Yasuda H., Reed S. I., Matsumoto K. Cloning of a human cDNA encoding a CDC2-related kinase by complementation of a budding yeast cdc28 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Genetic control of cell size at cell division in yeast. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):547–551. doi: 10.1038/256547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Roberts J. M. Cyclin-dependent regulation of G1 in mammalian fibroblasts. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1908–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.8384376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris J., Le Guellec R., Couturier A., Le Guellec K., Omilli F., Camonis J., MacNeill S., Philippe M. Cloning by differential screening of a Xenopus cDNA coding for a protein highly homologous to cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1039–1043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Gartner A., Horecka J., Ammerer G., Herskowitz I. FAR1 links the signal transduction pathway to the cell cycle machinery in yeast. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):747–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90254-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott J. R., Rai R., Carter B. L. A bifunctional gene product involved in two phases of the yeast cell cycle. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):391–393. doi: 10.1038/298391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Kato J. Y., Solomon M. J., Sherr C. J., Massague J., Roberts J. M., Koff A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):9–22. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. G1-specific cyclins: in search of an S-phase-promoting factor. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90279-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Hadwiger J. A., Lörincz A. T. Protein kinase activity associated with the product of the yeast cell division cycle gene CDC28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Wittenberg C. Mitotic role for the Cdc28 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5697–5701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Gossen M., Bujard H., Reed S. I. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1669–1679. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. New class of transforming growth factors potentiated by epidermal growth factor: isolation from non-neoplastic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5339–5343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C. L., Wong E., Petty E. M., Bale A. E., Tsujimoto Y., Harris N. L., Arnold A. PRAD1, a candidate BCL1 oncogene: mapping and expression in centrocytic lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9638–9642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., De Bondt H., Jancarik J., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Purification and crystallization of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 20;230(4):1317–1319. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. D., Pittelkow M. R., Wille J. J., Jr, Scott R. E., Moses H. L. Reversible inhibition of normal human prokeratinocyte proliferation by type beta transforming growth factor-growth inhibitor in serum-free medium. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):2068–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M. R., Pan C. H., Hosoda J., Bartholomew J., Mendelsohn J., Yaswen P. Blockage of EGF receptor signal transduction causes reversible arrest of normal and immortal human mammary epithelial cells with synchronous reentry into the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Sep;208(1):175–188. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Robitsch H., Price C., Schuster T., Fitch I., Futcher A. B., Nasmyth K. The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90416-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takehara K., LeRoy E. C., Grotendorst G. R. TGF-beta inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation: alteration of EGF binding and EGF-induced growth-regulatory (competence) gene expression. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Wright P. S., Hamaguchi J., Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Nurse P., Bradbury E. M. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Characterization of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6731–6737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Lees E., Faha B., Harlow E., Riabowol K. The cdk2 kinase is required for the G1-to-S transition in mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1593–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. Conservation of function and regulation within the Cdc28/cdc2 protein kinase family: characterization of the human Cdc2Hs protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4064–4068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg C., Sugimoto K., Reed S. I. G1-specific cyclins of S. cerevisiae: cell cycle periodicity, regulation by mating pheromone, and association with the p34CDC28 protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90361-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie F. S., Dawson T., Bond J. A., Goretzki P., Game S., Prime S., Wynford-Thomas D. Correlated abnormalities of transforming growth factor-beta 1 response and p53 expression in thyroid epithelial cell transformation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;76(1-3):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90255-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Connolly T., Futcher B., Beach D. Human D-type cyclin. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90100-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita M., Fukada S., Yoshikuni M., Bulet P., Hirai T., Yamaguchi A., Lou Y. H., Zhao Z., Nagahama Y. Purification and characterization of maturation-promoting factor in fish. Dev Biol. 1992 Jan;149(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90259-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaswen P., Smoll A., Peehl D. M., Trask D. K., Sager R., Stampfer M. R. Down-regulation of a calmodulin-related gene during transformation of human mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7360–7364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterberg A. Control of mammalian cell proliferation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;2(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterberg A., Larsson O. Kinetic analysis of regulatory events in G1 leading to proliferation or quiescence of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5365–5369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zindy F., Lamas E., Chenivesse X., Sobczak J., Wang J., Fesquet D., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Cyclin A is required in S phase in normal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1144–1154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91851-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]