Abstract
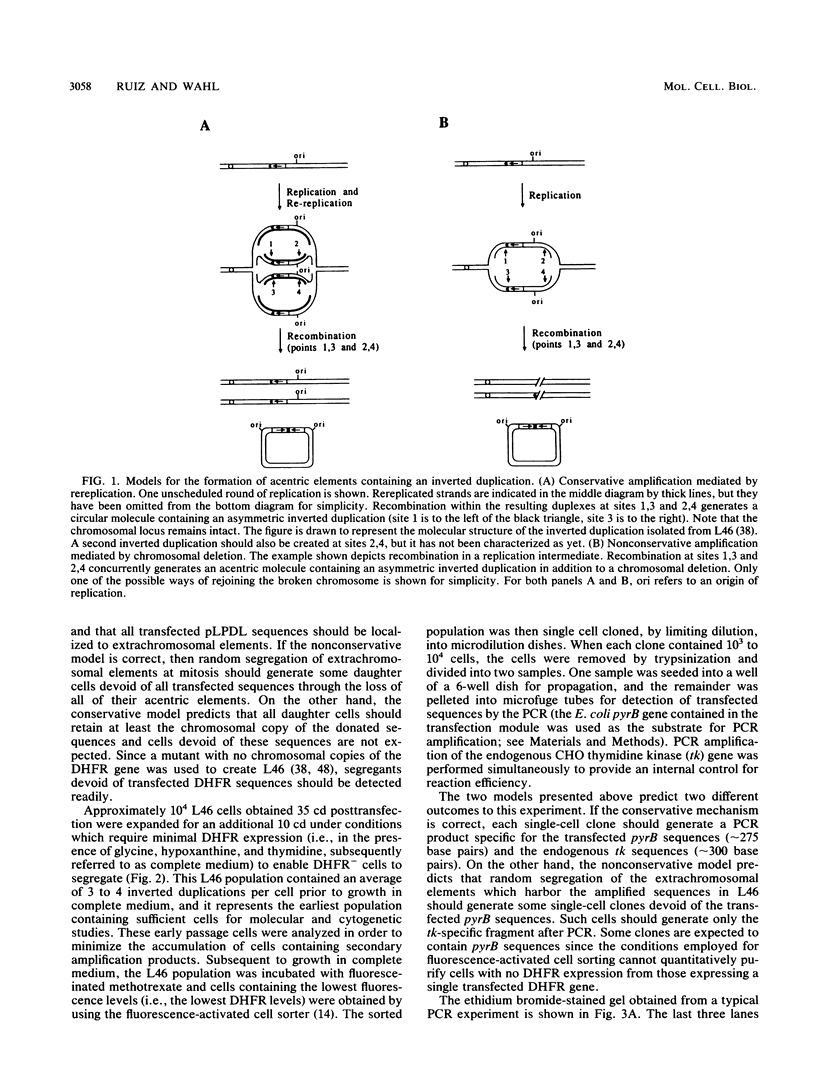
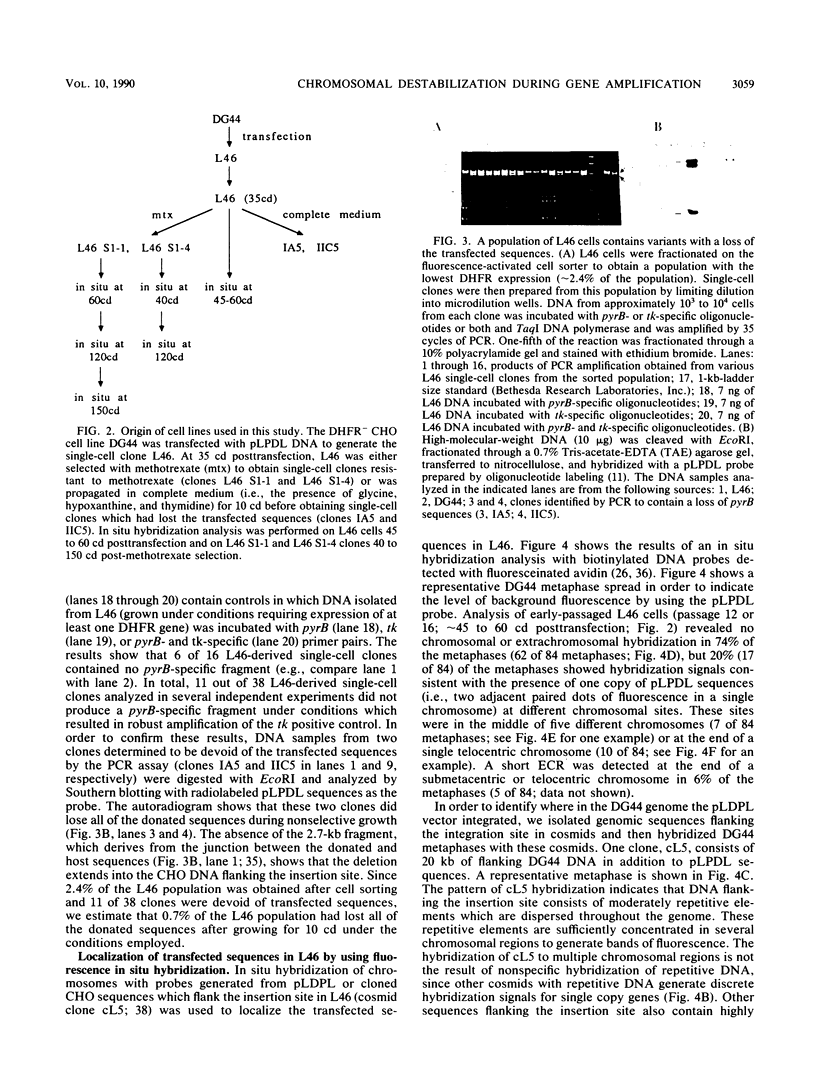
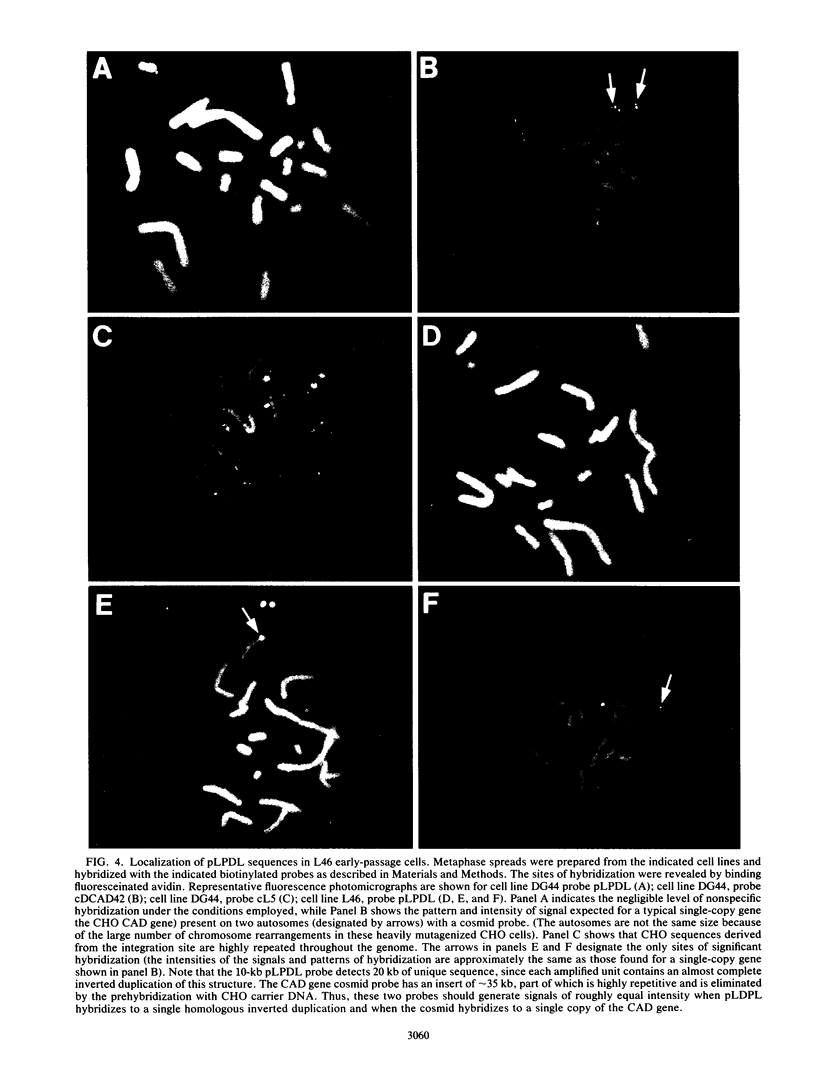
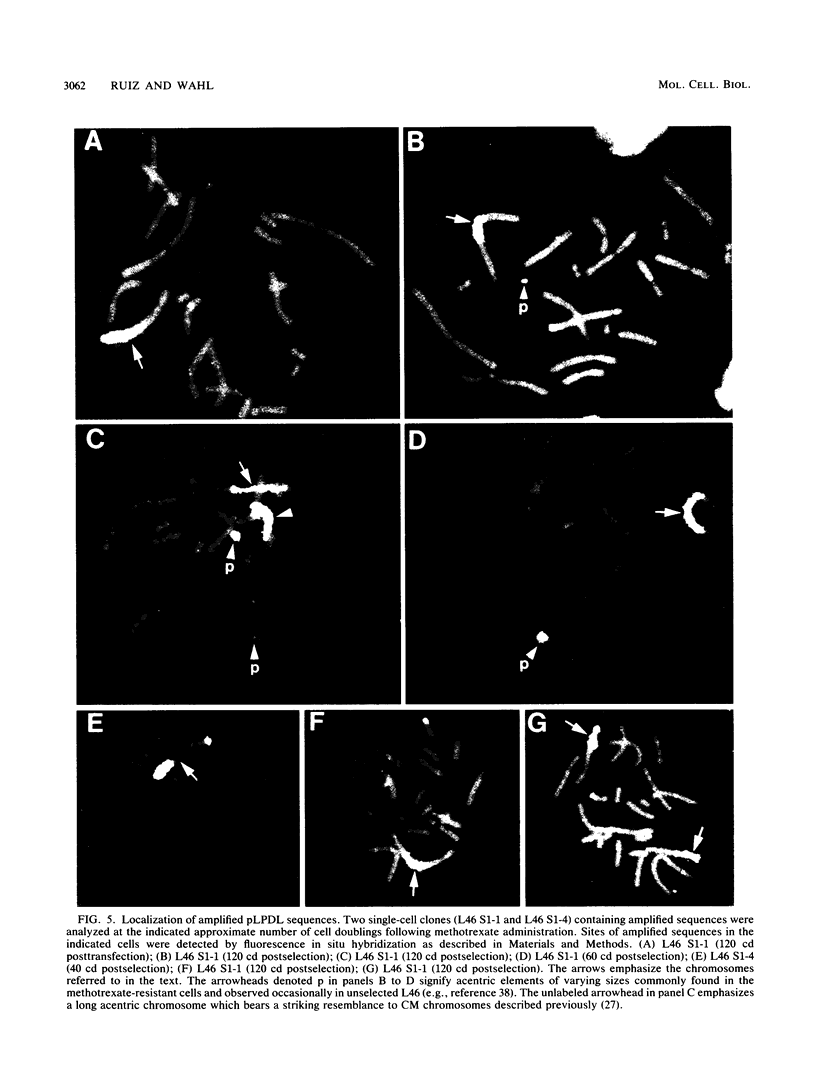
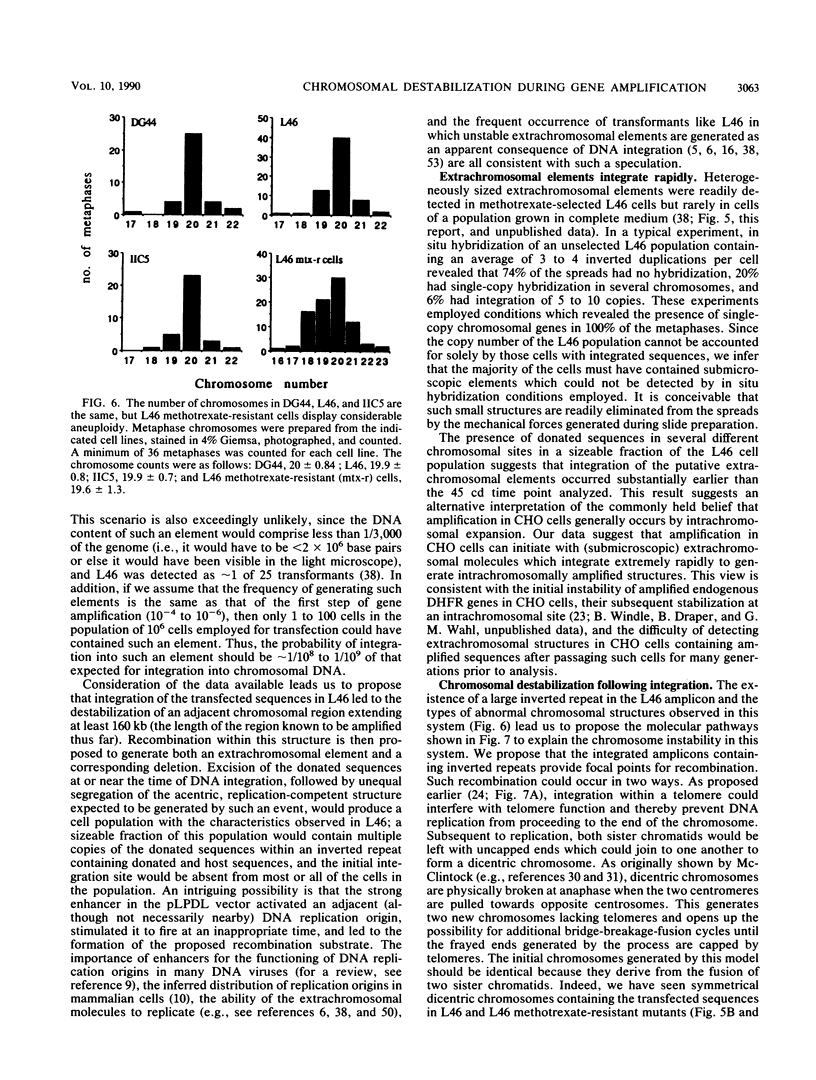
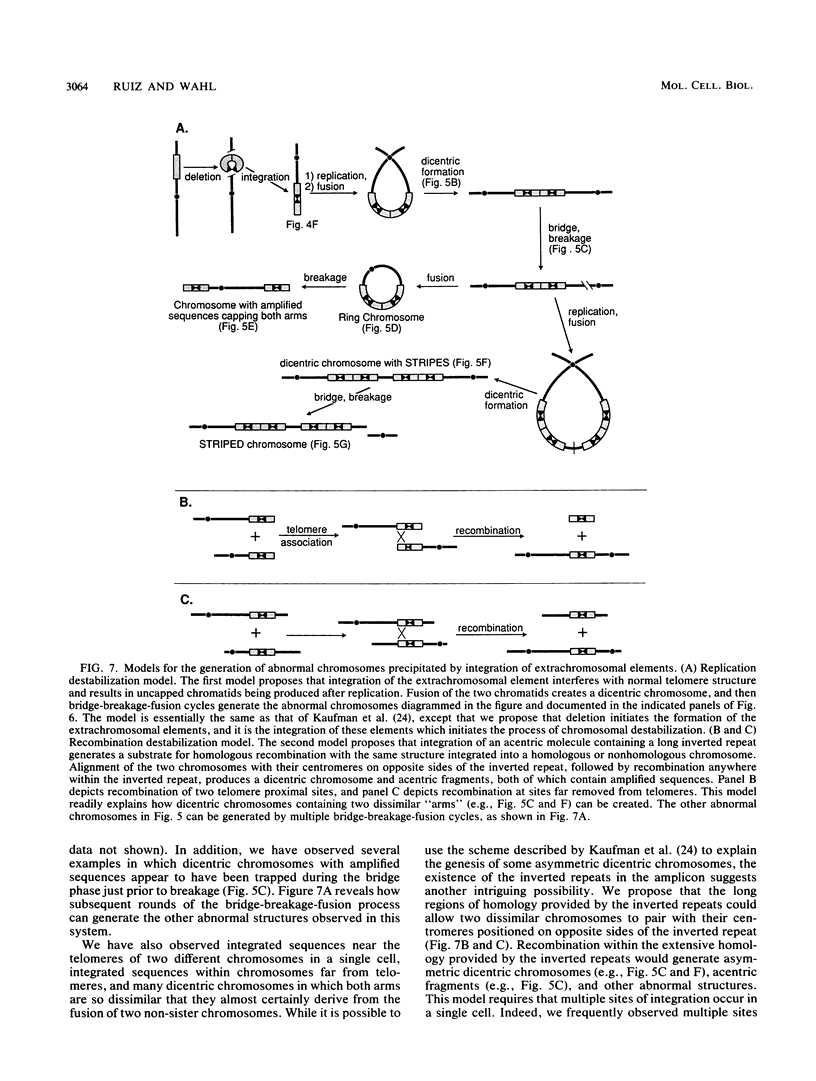
Acentric extrachromosomal elements, such as submicroscopic autonomously replicating circular molecules (episomes) and double minute chromosomes, are common early, and in some cases initial, intermediates of gene amplification in many drug-resistant and tumor cell lines. In order to gain a more complete understanding of the amplification process, we investigated the molecular mechanisms by which such extrachromosomal elements are generated and we traced the fate of these amplification intermediates over time. The model system consists of a Chinese hamster cell line (L46) created by gene transfer in which the initial amplification product was shown previously to be an unstable extrachromosomal element containing an inverted duplication spanning more than 160 kilobases (J. C. Ruiz and G. M. Wahl, Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:4302-4313, 1988). In this study, we show that these molecules were formed by a process involving chromosomal deletion. Fluorescence in situ hybridization was performed at multiple time points on cells with amplified sequences. These studies reveal that the extrachromosomal molecules rapidly integrate into chromosomes, often near or at telomeres, and once integrated, the amplified sequences are themselves unstable. These data provide a molecular and cytogenetic chronology for gene amplification in this model system; an early event involves deletion to generate extrachromosomal elements, and subsequent integration of these elements precipitates a cascade of chromosome instability.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A., Sedat J. W. Three-dimensional architecture of a polytene nucleus. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):676–681. doi: 10.1038/302676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt-Jovin D. J., Robert-Nicoud M., Zarling D. A., Greider C., Weimer E., Jovin T. M. Left-handed Z-DNA in bands of acid-fixed polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock C. J., Tyler-Smith C. Gene amplification in methotrexate-resistant mouse cells. II. Rearrangement and amplification of non-dihydrofolate reductase gene sequences accompany chromosomal changes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):219–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Gaudray P., Moore C. M., Needham-Vandevanter D. R., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Double minute chromosomes can be produced from precursors derived from a chromosomal deletion. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1525–1533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Gaudray P., De Rose M. L., Emery J. F., Meinkoth J. L., Nakkim E., Subler M., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Characterization of an episome produced in hamster cells that amplify a transfected CAD gene at high frequency: functional evidence for a mammalian replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1740–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherif D., Lavialle C., Modjtahedi N., Le Coniat M., Berger R., Brison O. Selection of cells with different chromosomal localizations of the amplified c-myc gene during in vivo and in vitro growth of the breast carcinoma cell line SW 613-S. Chromosoma. 1989 Jan;97(4):327–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00371974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancis B. M., Holmquist G. P. Telomere replication and fusion in eukaryotes. J Theor Biol. 1979 May 21;78(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg H. J., Huberman J. A. Eukaryotic chromosome replication. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:245–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M., Fried M. Large inverted duplications are associated with gene amplification. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Trotter J., Wahl G. M. Fluorescent methotrexate labeling and flow cytometric analysis of cells containing low levels of dihydrofolate reductase. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6285–6292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulotto E., Saito I., Stark G. R. Structure of DNA formed in the first step of CAD gene amplification. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2115–2121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N. Unstable expression and amplification of a transfected oncogene in confluent and subconfluent cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1456–1464. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudkov A. V., Chernova O. B., Kazarov A. R., Kopnin B. P. Cloning and characterization of DNA sequences amplified in multidrug-resistant Djungarian hamster and mouse cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Nov;13(6):609–619. doi: 10.1007/BF01534481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Allshire R. C. Human telomeres: fusion and interstitial sites. Trends Genet. 1989 Oct;5(10):326–331. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heartlein M. W., Latt S. A. Amplified inverted duplications within and adjacent to heterologous selectable DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1697–1716. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P., Dancis B. Telomere replication, kinetochore organizers, and satellite DNA evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4566–4570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Debatisse M., Buttin G., de Saint Vincent B. R. A hotspot for novel amplification joints in a mosaic of Alu-like repeats and palindromic A + T-rich DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2401–2408. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Debatisse M., Buttin G., de Saint Vincent B. R. The multicopy appearance of a large inverted duplication and the sequence at the inversion joint suggest a new model for gene amplification. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):407–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02828.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T. Amplification and loss of dihydrofolate reductase genes in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1069–1076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A., Latt S. A. Evolution of chromosomal regions containing transfected and amplified dihydrofolate reductase sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):699–711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Smithies O. Recombinant fragment assay for gene targetting based on the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8887–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. C., Alitalo K., Schwab M., George D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evolution of karyotypic abnormalities and C-MYC oncogene amplification in human colonic carcinoma cell lines. Chromosoma. 1985;92(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00327240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney J. E., Hamlin J. L. Isolation of the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain from methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):569–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCLINTOCK B. Chromosome organization and genic expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:13–47. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):792–801. doi: 10.1126/science.15739260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Killary A. M., Fournier R. E., Wahl G. M. Unstable and stable CAD gene amplification: importance of flanking sequences and nuclear environment in gene amplification. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1415–1424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Ledbetter D. H., Hejtmancik J. F., Caskey C. T. In vitro translation of hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase mRNA: characterization of a mouse neuroblastoma cell line that has elevated levels of hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6977–6980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Meuth M. DNA amplification--deletion in a spontaneous mutation of the hamster aprt locus: structure and sequence of the novel joint. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8361–8371. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passananti C., Davies B., Ford M., Fried M. Structure of an inverted duplication formed as a first step in a gene amplification event: implications for a model of gene amplification. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1697–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz J. C., Choi K. H., von Hoff D. D., Roninson I. B., Wahl G. M. Autonomously replicating episomes contain mdr1 genes in a multidrug-resistant human cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz J. C., Wahl G. M. Formation of an inverted duplication can be an initial step in gene amplification. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4302–4313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Groves R., Giulotto E., Rolfe M., Stark G. R. Evolution and stability of chromosomal DNA coamplified with the CAD gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2445–2452. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Stark G. R. Charomids: cosmid vectors for efficient cloning and mapping of large or small restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8664–8668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5989–5992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen S., Hittelman W. N., Teeter L. D., Kuo M. T. Model for the formation of double minutes from prematurely condensed chromosomes of replicating micronuclei in drug-treated Chinese hamster ovary cells undergoing DNA amplification. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6731–6737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Hiorns L. R., Spurr N., Kurkinen M., Barlow D., Hogan B. L., Dalgleish R. Chromosomal assignments of the genes coding for human types II, III, and IV collagen: a dispersed gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3330–3334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Debatisse M., Giulotto E., Wahl G. M. Recent progress in understanding mechanisms of mammalian DNA amplification. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J., Meltzer P., Rosenblum M., Harsh G., Kinzler K., Mashal R., Feinberg A., Vogelstein B. Evidence for rearrangement, amplification, and expression of c-myc in a human glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):470–473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Käs E., Carothers A. M., Chasin L. A. Deletion of the diploid dihydrofolate reductase locus from cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90422-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hoff D. D., Needham-VanDevanter D. R., Yucel J., Windle B. E., Wahl G. M. Amplified human MYC oncogenes localized to replicating submicroscopic circular DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4804–4808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Robert de Saint Vincent B., DeRose M. L. Effect of chromosomal position on amplification of transfected genes in animal cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):516–520. doi: 10.1038/307516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M. The importance of circular DNA in mammalian gene amplification. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1333–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Vitto L., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Single-copy and amplified CAD genes in Syrian hamster chromosomes localized by a highly sensitive method for in situ hybridization. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):308–319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bliek A. M., Lincke C. R., Borst P. Circular DNA of 3T6R50 double minute chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4841–4851. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





