Abstract
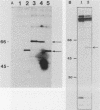
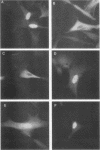
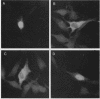
Transcriptional activation of gene expression by oncogenic proteins can lead to cellular transformation. It has recently been demonstrated that the protein encoded by the v-rel oncogene from reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T can transactivate gene expression from certain promoters in a cell-specific manner. We have examined the cytological location, transforming properties, and transactivation properties of proteins encoded by chimeric turkey v-rel/chicken c-rel genes. We found that whereas the v-rel protein was nuclear in both chicken embryo and rat fibroblasts, the presence of the C terminus of the c-rel protein inhibited nuclear localization of the rel protein in these fibroblasts. Cytoplasmic rel proteins containing C-terminal c-rel sequences transactivated gene expression from the polyomavirus late promoter as efficiently as did similar rel proteins located in the nucleus. These results indicate that the cellular location of rel proteins is not important for transactivation of gene expression and suggest that transactivation by rel proteins is indirect, perhaps by affecting an intracellular signal transduction pathway that eventually results in the alteration of gene expression. The transforming properties of the rel protein were unaltered by the presence of the c-rel C terminus, but, as previously reported for turkey c-rel sequences, substitution of chicken c-rel sequences for internal v-rel sequences reduced the transforming activity of the rel protein and eliminated the immortalization ability. However, all of the chimeric v/c-rel proteins were able to transactivate gene expression, indicating that transactivation does not correlate with transformation. These results suggest that transactivation may be necessary but is not sufficient for transformation by rel proteins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Bohmann D., Tsuchie H., Tjian R., Vogt P. K. v-jun encodes a nuclear protein with enhancer binding properties of AP-1. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):705–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Wilhelmsen K. C., Temin H. M. Structure and expression of c-rel, the cellular homolog to the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):104–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.104-113.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Temin H. M. High mutation rate of a spleen necrosis virus-based retrovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4387–4395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. B., Maldonado R. L., Bose H. R. Isolation and characterization of reticuloendotheliosis virus transformed bone marrow cells. Intervirology. 1974;3(5-6):342–352. doi: 10.1159/000149771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson K., Kang C. Y. Identification of the v-rel protein in REV-T transformed chicken bone marrow cells and expression in Cos1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):716–722. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80479-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. Different localization of the product of the v-rel oncogene in chicken fibroblasts and spleen cells correlates with transformation by REV-T. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. v-rel oncoproteins in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm transform chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):703–714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.703-714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Temin H. M. The v-rel oncogene encodes a cell-specific transcriptional activator of certain promoters. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B., Baichwal V. R. The transforming domain alone of the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus is toxic to cells when expressed at high levels. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2469–2475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2469-2475.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Donoghue D. J. Autocrine stimulation by the v-sis gene product requires a ligand-receptor interaction at the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):287–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Sauer M. K., Donoghue D. J. Deletions in the C-terminal coding region of the v-sis gene: dimerization is required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1304–1314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog N. K., Bose H. R., Jr Expression of the oncogene of avian reticuloendotheliosis virus in Escherichia coli and identification of the transforming protein in reticuloendotheliosis virus T-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):812–816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzer J. D., Lewis R. B., Wasmuth C. R., Bose H. R., Jr Hematopoietic cell transformation by reticuloendotheliosis virus: characterization of the genetic defect. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):462–474. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90536-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Sharp P. A. Transcription control by oncogenes. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The approaching era of the tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1539–1545. doi: 10.1126/science.3317834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S., Yaciuk P., Kmiecik T. E., Coussens P. M., Shalloway D. v-src mutations outside the carboxyl-coding region are not sufficient to fully activate transformation by pp60c-src in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):704–712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Roesel D. J., Kanner S. B., Parsons J. T. Transformation-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of a novel cellular protein in chicken cells expressing oncogenic variants of the avian cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):629–638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Copeland T. D., Simek S., Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. Detection and characterization of the protein encoded by the v-rel oncogene. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Setoyama C., de Crombrugghe B. Regulation of a collagen gene promoter by the product of viral mos oncogene. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):286–289. doi: 10.1038/314286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Witte O. N. A recombinant murine retrovirus expressing v-rel is cytopathic. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):182–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90671-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S. L., Stephens R. M., Rice N. R. Localization of the v-rel protein in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T-transformed lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):120–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.120-126.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. Detection and characterization of the protein encoded by the chicken c-rel protooncogene. Oncogene Res. 1988;2(2):103–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. p59v-rel, the transforming protein of reticuloendotheliosis virus, is complexed with at least four other proteins in transformed chicken lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4730–4736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4730-4736.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Rice N. R., Hiebsch R. R., Bose H. R., Jr, Gilden R. V. Nucleotide sequence of v-rel: the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6229–6233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylla B. S., Temin H. M. Activation of oncogenicity of the c-rel proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4709–4716. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarpley W. G., Temin H. M. The location of v-src in a retrovirus vector determines whether the virus is toxic or transforming. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2653–2660. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walro D. S., Herzog N. K., Zhang J., Lim M. Y., Bose H. R., Jr The transforming protein of avian reticuloendotheliosis virus is a soluble cytoplasmic protein which is associated with a protein kinase activity. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):433–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Imler J. L., Perez-Mutul J., Wasylyk B. The c-Ha-ras oncogene and a tumor promoter activate the polyoma virus enhancer. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):525–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Construction of a helper cell line for avian reticuloendotheliosis virus cloning vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2241–2249. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Encapsidation sequences for spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus, are between the 5' long terminal repeat and the start of the gag gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Temin H. M. Structure and dimorphism of c-rel (turkey), the cellular homolog to the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):521–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.521-529.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]