Abstract
Centromere DNA from 11 of the 16 chromosomes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae have been analyzed and reveal three sequence elements common to each centromere, referred to as conserved centromere DNA elements (CDE). The adenine-plus-thymine (A + T)-rich central core element, CDE II, is flanked by two short conserved sequences, CDE I (8 base pairs [bp]) and CDE III (25 bp). Although no consensus sequence exists among the different CDE II regions, they do have three common features of sequence organization. First, the CDE II regions are similar in length, ranging from 78 to 86 bp measured from CDE I to the left boundary of CDE III. Second, the base composition is always greater than 90% A + T. Finally, the A and T residues in these segments are often arranged in runs of A and runs of T residues, sometimes with six or seven bases in a stretch. We constructed insertion, deletion, and replacement mutations in the CDE II region of the centromere from chromosome III, CEN3, designed to investigate the length and sequence requirements for function of the CDE II region of the centromere. We analyzed the effect of these altered centromeres on plasmid and chromosome segregation in S. cerevisiae. Our results show that increasing the length of CDE II from 84 to 154 bp causes a 100-fold increase in chromosome nondisjunction. Deletion mutations removing segments of the A + T-rich CDE II DNA also cause aberrant segregation. In some cases partial function could be restored by replacing the deleted DNA with fragments whose primary sequence or base composition is very different from that of the wild-type CDE II DNA. In addition, we found that identical mutations introduced into different positions in CDE II have very similar effects.
Full text
PDF

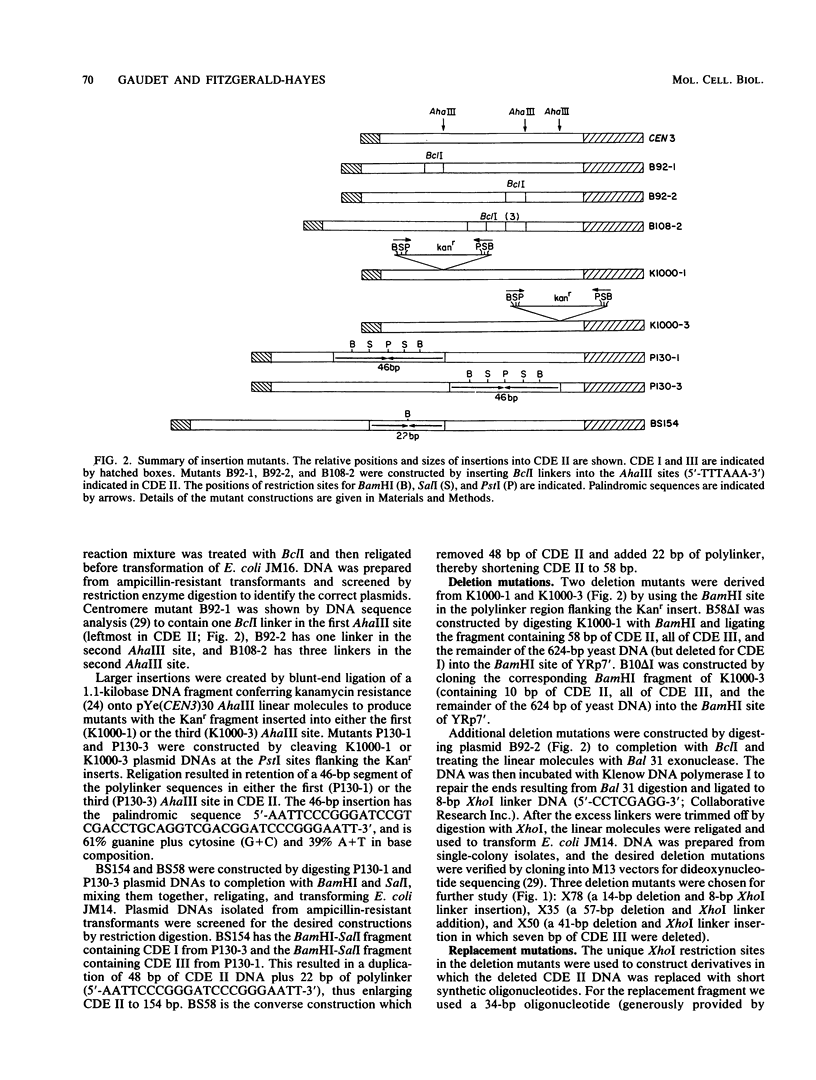

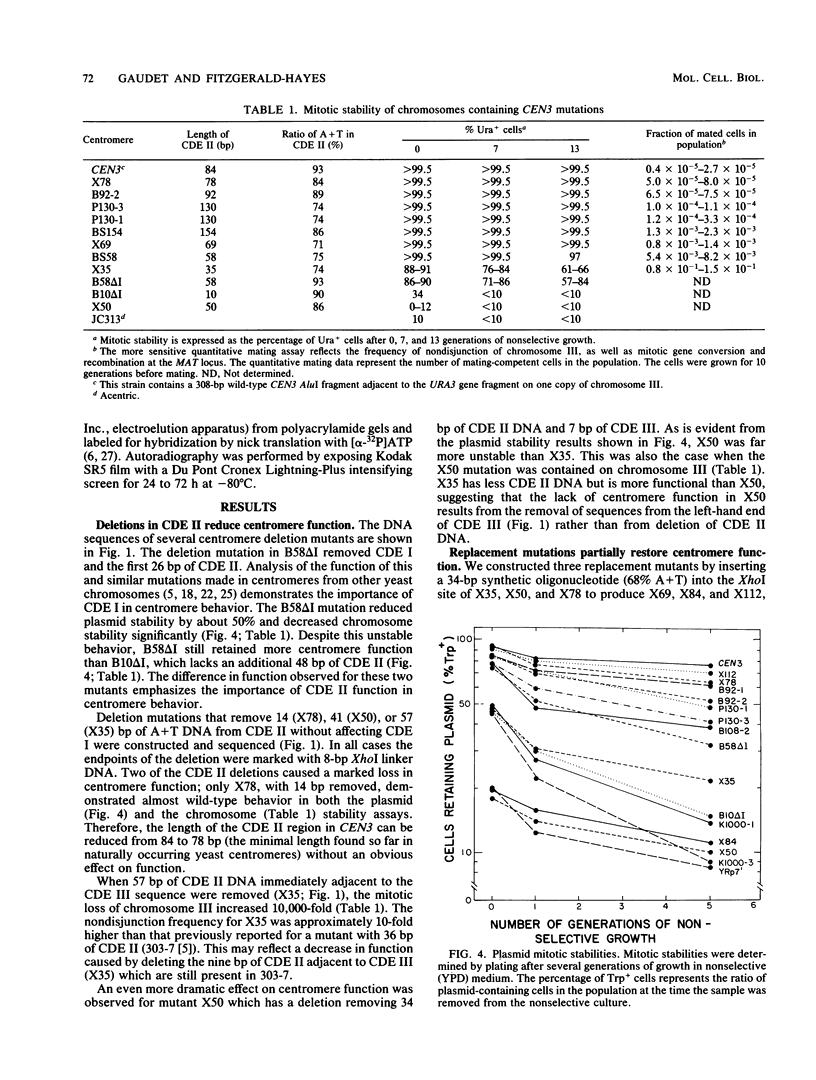



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C. Heteronomous DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4141–4155. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. S., Amaya E., Carbon J., Clarke L., Hill A., Yeh E. Chromatin conformation of yeast centromeres. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1559–1568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. S., Carbon J. Yeast centromere DNA is in a unique and highly ordered structure in chromosomes and small circular minichromosomes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. S., Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Carbon J. Structural analysis and sequence organization of yeast centromeres. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1175–1185. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon J., Clarke L. Structural and functional analysis of a yeast centromere (CEN3). J Cell Sci Suppl. 1984;1:43–58. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1984.supplement_1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinault A. C., Carbon J. Overlap hybridization screening: isolation and characterization of overlapping DNA fragments surrounding the leu2 gene on yeast chromosome III. Gene. 1979 Feb;5(2):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Genomic substitutions of centromeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):23–28. doi: 10.1038/305023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Isolation of a yeast centromere and construction of functional small circular chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):504–509. doi: 10.1038/287504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutcher S. K., Hartwell L. H. The role of S. cerevisiae cell division cycle genes in nuclear fusion. Genetics. 1982 Feb;100(2):175–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Buhler J. M., Cooper T. G., Carbon J. Isolation and subcloning analysis of functional centromere DNA (CEN11) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome XI. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Clarke L., Carbon J. Nucleotide sequence comparisons and functional analysis of yeast centromere DNAs. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Pridmore D., Hegemann J. H., Thomas M., Davis R. W., Philippsen P. Functional selection and analysis of yeast centromeric DNA. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao C. L., Carbon J. High-frequency transformation of yeast by plasmids containing the cloned yeast ARG4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3829–3833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D., Kent J. C., Hartwell L. H. Genetic analysis of the mitotic transmission of minichromosomes. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Martinson H. G. Nucleosomes will not form on double-stranded RNa or over poly(dA).poly(dT) tracts in recombinant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6869–6888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maine G. T., Surosky R. T., Tye B. K. Isolation and characterization of the centromere from chromosome V (CEN5) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann C., Davis R. W. Structure and sequence of the centromeric DNA of chromosome 4 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):241–245. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew J., Diehl B., Fitzgerald-Hayes M. Single base-pair mutations in centromere element III cause aberrant chromosome segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):530–538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nucleotide sequence of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzeri L., Landonio L., Stotz A., Philippsen P. Role of conserved sequence elements in yeast centromere DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1867–1874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03862.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzeri L., Philippsen P. Centromeric DNA from chromosome VI in Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Mann C., Davis R. W. Centromeric DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):157–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90427-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. S., Harvey S. C. Computer graphics program to reveal the dependence of the gross three-dimensional structure of the B-DNA double helix on primary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):381–387. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]