Abstract
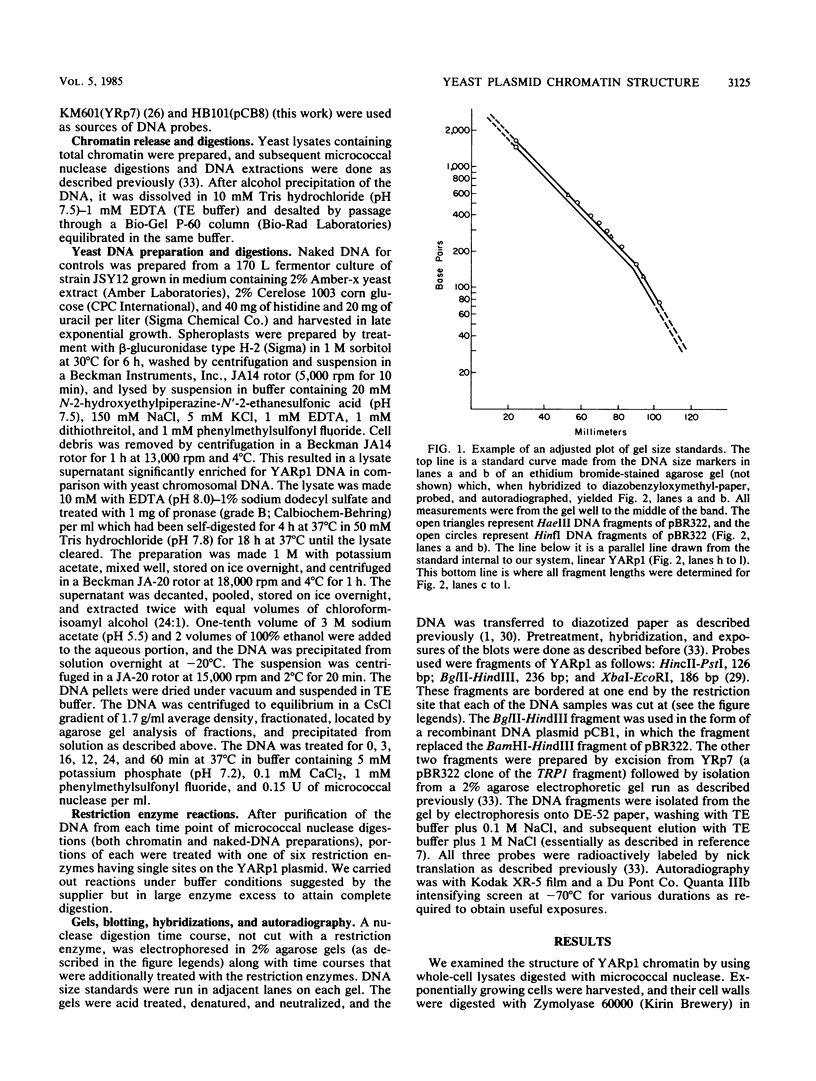
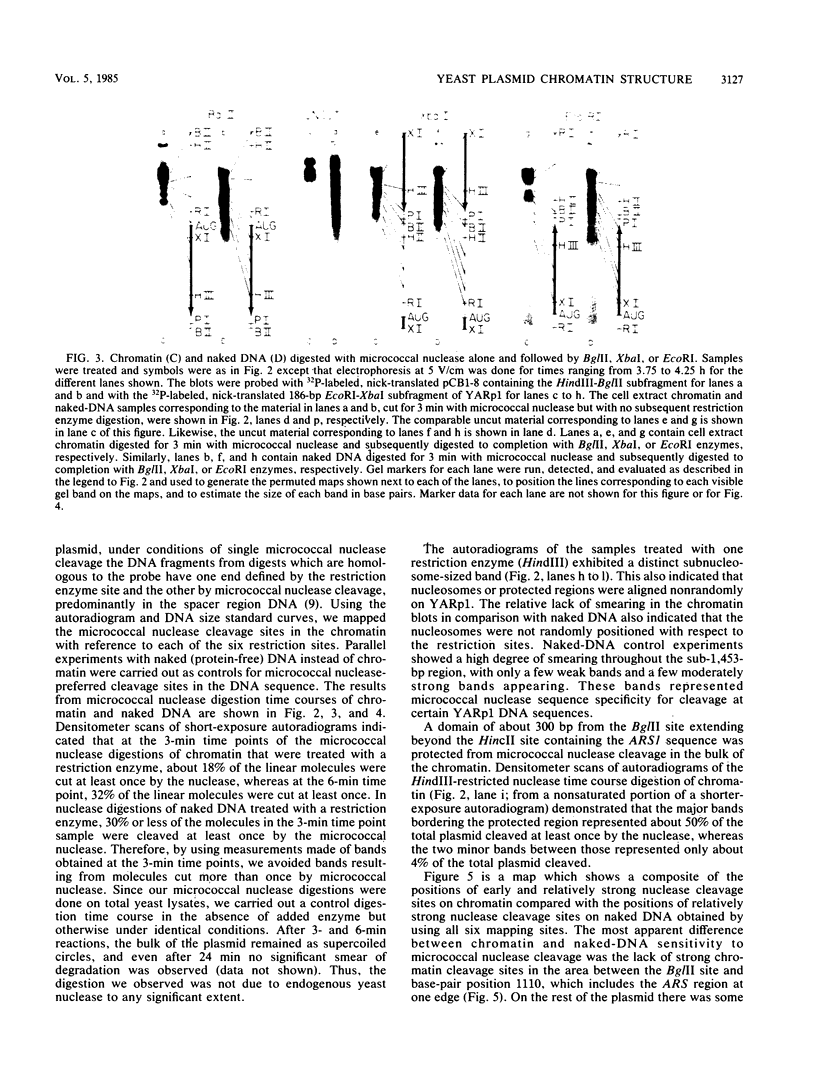
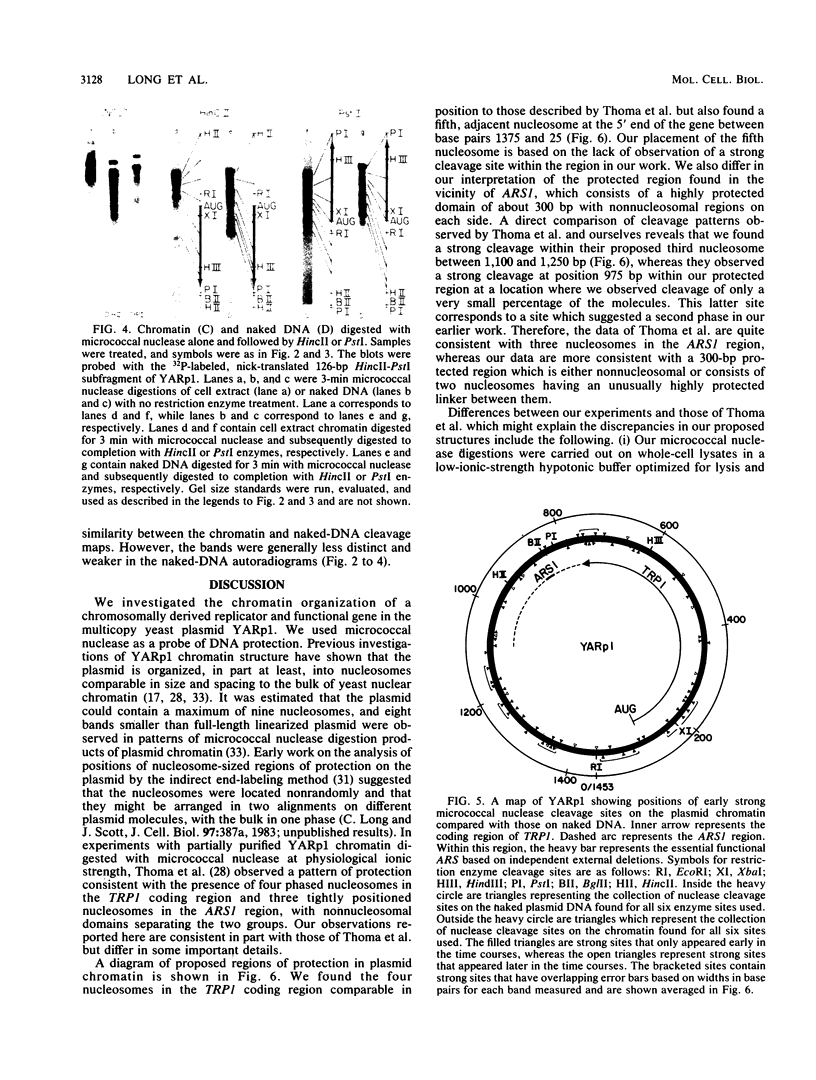
TRP1 RI circle (now designated YARp1, yeast acentric ring plasmid 1) is a 1,453-base-pair artificial plasmid composed exclusively of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomal DNA. It contains both the TRP1 gene and ARS1 (a DNA sequence that permits extrachromosomal maintenance of recombinant plasmids). This high-copy-number, relatively stable plasmid was shown to be organized into nucleosomes comparable to typical yeast chromatin, containing a possible maximum of nine nucleosomes per circle. Therefore, YARp1 can be used to examine the structure of chromatin of both a chromosomally derived replicator and a functional gene. By mapping regions of micrococcal nuclease cleavage in chromatin versus purified DNA, we located the positions of protected regions on the circle with reference to six unique restriction sites. Measurements made on patterns of early digestion products indicated that a region of approximately 300 base pairs in the vicinity of ARS1 was strongly resistant to micrococcal nuclease. The remainder of the plasmid appeared to be associated with five positioned nucleosomes and two nonnucleosomal, partially protected regions on the bulk of the molecules. After similar extents of digestion, naked DNA did not exhibit an equivalent pattern, although some hypersensitive cleavage sites matched sites found in the chromatin. These results are consistent with the interpretation that the protected domains are aligned with respect to a specific site or sites on the small circular chromatin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs J. D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):104–109. doi: 10.1038/275104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Replication and recombination functions associated with the yeast plasmid, 2 mu circle. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90487-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celniker S. E., Campbell J. L. Yeast DNA replication in vitro: initiation and elongation events mimic in vivo processes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90420-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celniker S. E., Sweder K., Srienc F., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. Deletion mutations affecting autonomously replicating sequence ARS1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2455–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L., Hice R. H., Chlebowicz-Sledziewska E. ARS replication during the yeast S phase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):831–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):115–122. doi: 10.1038/271115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Bloomer L. S. Nonrandom alignment of nucleosomes on 5S RNA genes of X. laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao C. L., Carbon J. High-frequency transformation of yeast by plasmids containing the cloned yeast ARG4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3829–3833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. The location of nucleosomes in chromatin: specific or statistical. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):579–580. doi: 10.1038/292579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Kovacic R. T., Van Holde K. E. Quantitative analysis of the digestion of yeast chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):463–471. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D. Organization of the GAL1-GAL10 intergenic control region chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8457–8474. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis C., Schedl P., Samal B., Worcel A. Chromatin structure of the 5S RNA genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):387–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Another potential artifact in the study of nucleosome phasing by chromatin digestion with micrococcal nuclease. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Georgiev G. P. Non-random cleavage of SV40 DNA in the compact minichromosome and free in solution by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. G., Fangman W. L. Nucleosome organization of the yeast 2-micrometer DNA plasmid: a eukaryotic minichromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6515–6519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen T. E., Cech T. R. Chromatin structure at the replication origins and transcription-initiation regions of the ribosomal RNA genes of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):933–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samal B., Worcel A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin structure of the histone genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Isolation and characterisation of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):39–43. doi: 10.1038/282039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Bergman L. W., Simpson R. T. Nuclease digestion of circular TRP1ARS1 chromatin reveals positioned nucleosomes separated by nuclease-sensitive regions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):715–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachau H. G., Igo-Kemenes T. Face to phase with nucleosomes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):597–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A., Scott J. F. Construction, replication, and chromatin structure of TRP1 RI circle, a multiple-copy synthetic plasmid derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):221–232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





