Abstract
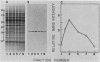
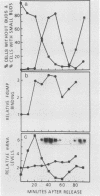
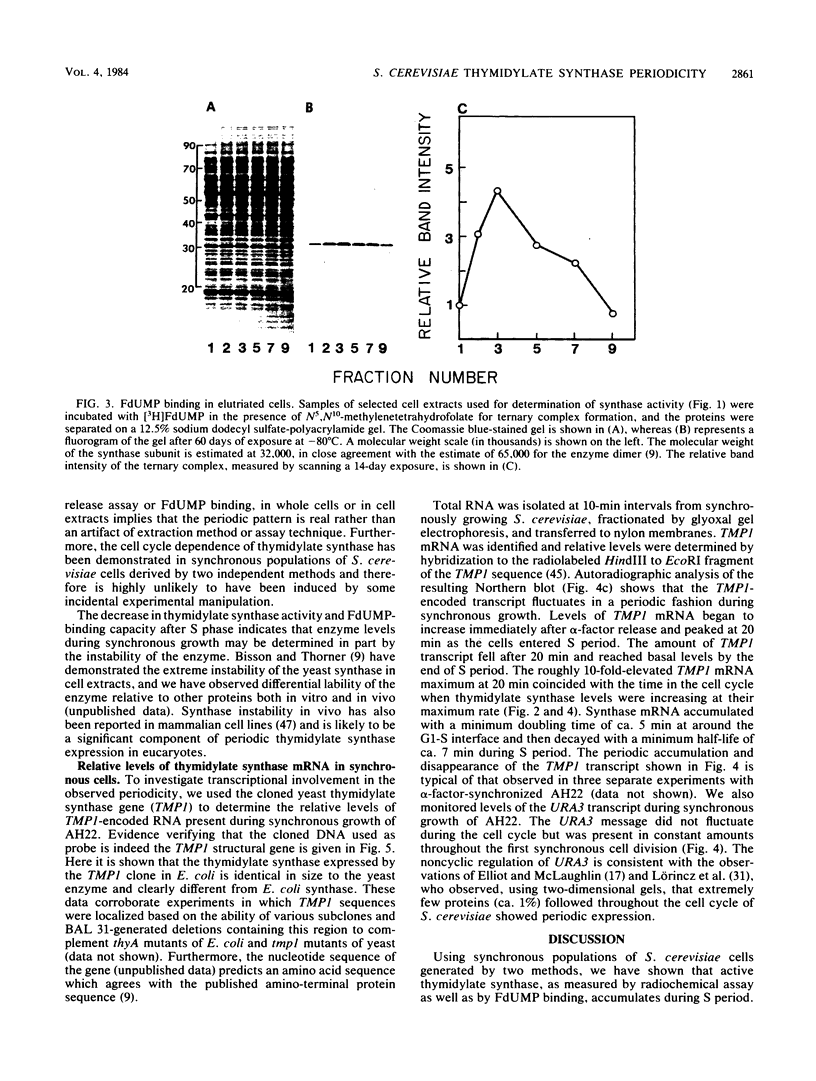
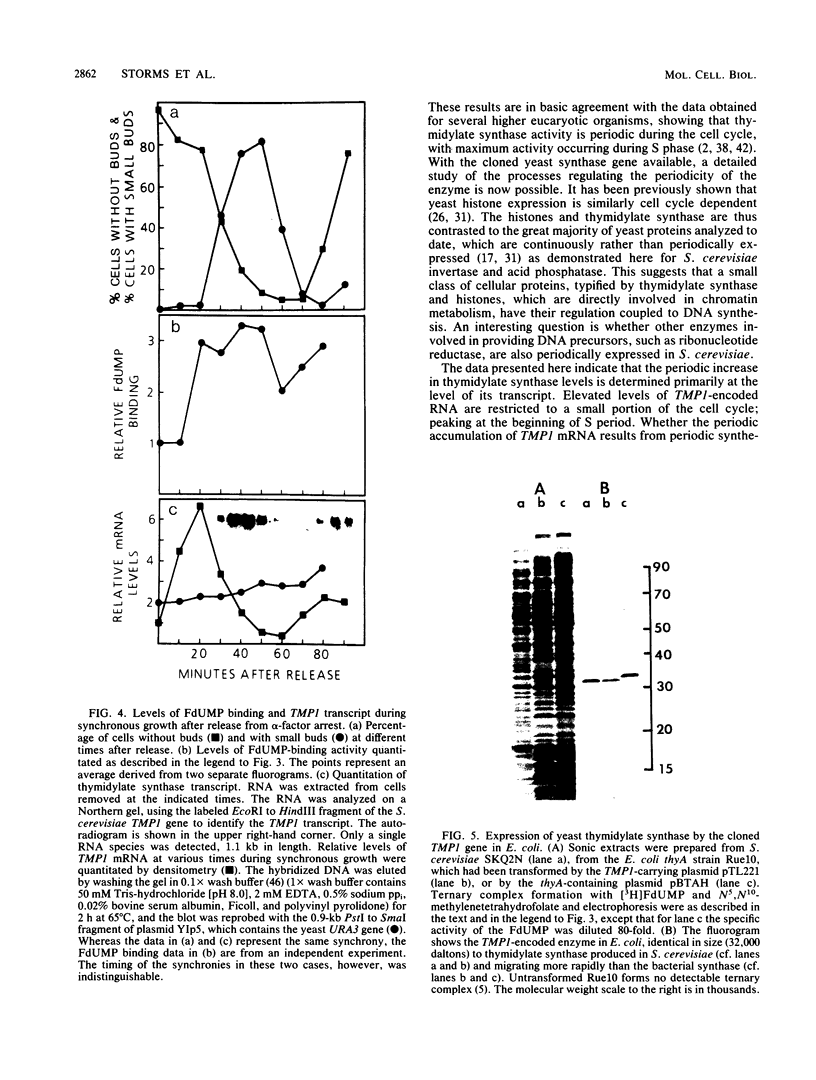
Synchronous populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, generated by two independent methods, have been used to show that thymidylate synthase, in contrast to the vast majority of cellular proteins thus far examined, fluctuates periodically during the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. The enzyme, as assayed by two different methods, accumulated during S period and peaked in mid to late S phase, and then its level dropped. These observations suggest that both periodic synthesis and the instability of the enzyme contribute to the activity profile seen during the cell cycle. Accumulation of thymidylate synthase is determined at the level of its transcript, with synthase-specific mRNA levels increasing at least 10-fold to peak near the beginning of S period and then falling dramatically to basal levels after the onset of DNA synthesis. This mRNA peak coincided with the time during the cell cycle when thymidylate synthase levels were increasing maximally and immediately preceded the peak of DNA synthesis, for which the enzyme provides precursor dTMP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G. N., Scaletta C., Vaughan J. H. Modified diphenylamine reaction for increased sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):547–549. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Maley G. F., Maley F. Characterization of the Escherichia coli thyA gene and its amplified thymidylate synthetase product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1858–1861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Moelleken A., Maley G. F., Maley F. Purification and properties of T4 phage thymidylate synthetase produced by the cloned gene in an amplification vector. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2045–2051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Thorner J. Mutations in the pho80 gene confer permeability to 5'-mononucleotides in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1982 Nov;102(3):341–359. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Thorner J. Thymidylate synthetase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification and enzymic properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12456–12462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L., Thorner J. Thymidine 5'-monophosphate-requiring mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are deficient in thymidylate synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.44-50.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel M., Fäth W. W. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae auxotrophic and conditionally auxotrophic for 5'-dTMP. Z Naturforsch C. 1974 Nov-Dec;29(11-12):733–738. doi: 10.1515/znc-1974-11-1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel M., Haynes R. H. Kinetics and genetic control of the incorporation of thymidine monophosphate in yeast DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;117(1):39–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00268835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Trimble R. B., Maley F. The effect of carbohydrate depletion on the properties of yeast external invertase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8691–8693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., Barner H. D. STUDIES ON UNBALANCED GROWTH IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Oct;40(10):885–893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.10.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. G., McLaughlin C. S. Rate of macromolecular synthesis through the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. G., McLaughlin C. S. The yeast cell cycle: coordination of growth and division rates. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:143–176. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLANT J., SPOTTSWOOD T. MEASUREMENT OF THE STABILITY OF THE REPRESSOR OF ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE SYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1591–1598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C. N., Elliott S. C. Fractionation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell populations by centrifugal elutriation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):97–100. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.97-100.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grivell A. R., Jackson J. F. Thymidine kinase: evidence for its absence from Neurospora crassa and some other micro-organisms, and the relevance of this to the specific labelling of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(2):307–317. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. II. Genes controlling DNA replication and its initiation. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Three additional genes required for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):966–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.966-974.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Defective DNA synthesis in permeabilized yeast mutants. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 8;234(49):171–172. doi: 10.1038/newbio234171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Osley M. A., Ludwig T. R., 2nd, McLaughlin C. S. Cell-cycle regulation of yeast histone mRNA. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hryniuk W. M., Bertino J. R. Growth rate and cell kill. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Nov 30;186:330–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. G., Haynes R. H. Isolation and characterization of yeast mutants auxotrophic for 2'-deoxythymidine 5'-monophosphate. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 10;168(2):141–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00431440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz A. T., Miller M. J., Xuong N. H., Geiduschek E. P. Identification of proteins whose synthesis is modulated during the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1532–1549. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALEY F., MALEY G. F. Nucleotide interconversions. II. Elevation of deoxycytidylate deaminase and thymidylate synthetase in regenerating rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2968–2970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenecourt B. S., Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Saccharomyces mutants with invertase formation resistant to repression by hexoses. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):233–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.233-238.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalgund L. G., Rossana C., Muench A. J., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of thymidylate synthetase gene expression in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7386–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Hereford L. Identification of a sequence responsible for periodic synthesis of yeast histone 2A mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7689–7693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi E., De Petrocellis B. Sea urchin thymidylate synthetase. Changes of activity during embryonic development. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Aug;101(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. M. Modifications of the diphenylamine reaction giving increased sensitivity and simplicity in the estimation of DNA. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode W., Scanlon K. J., Moroson B. A., Bertino J. R. Regulation of thymidylate synthetase in mouse leukemia cells (L1210). J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1305–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storms R. K., McNeil J. B., Khandekar P. S., An G., Parker J., Friesen J. D. Chimeric plasmids for cloning of deoxyribonucleic acid sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):73–82. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.73-82.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. R., Barclay B. J., Storms R. K., Friesen J. D., Haynes R. H. Isolation of the thymidylate synthetase gene (TMP1) by complementation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):437–442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washtien W. L. Increased levels of thymidylate synthetase in cells exposed to 5-fluorouracil. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;25(1):171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]