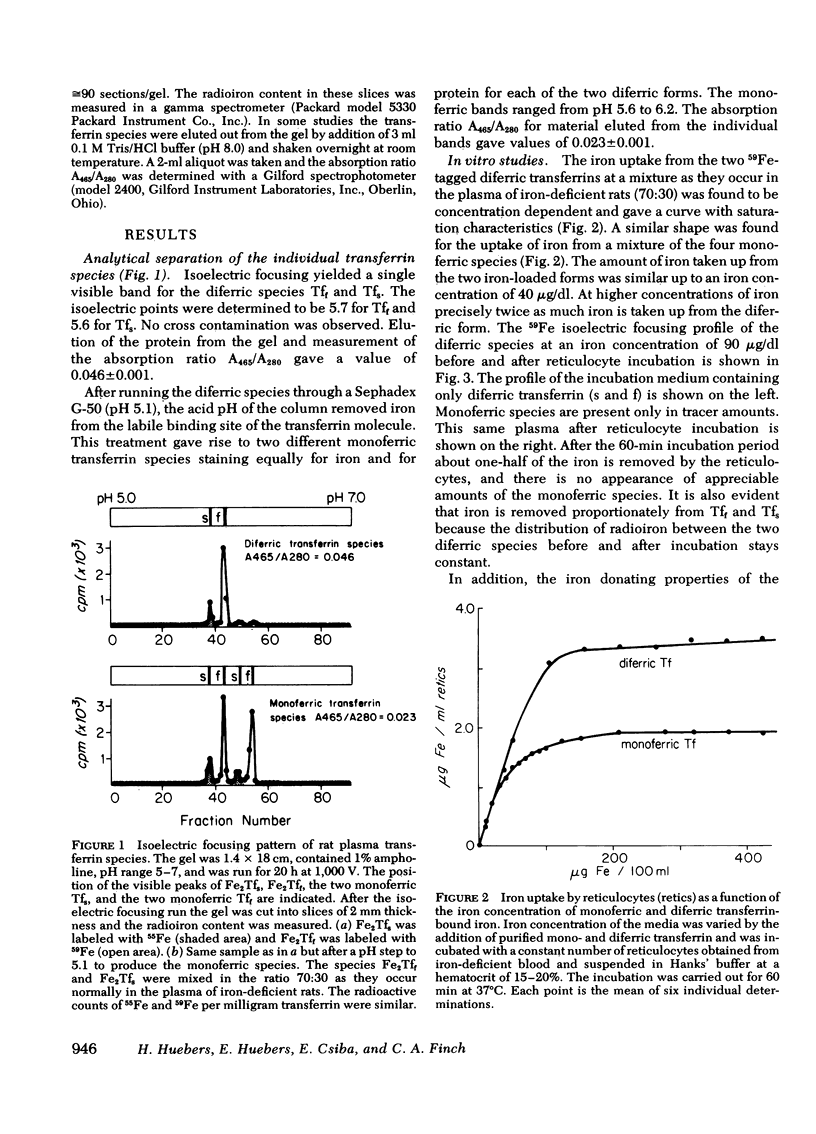
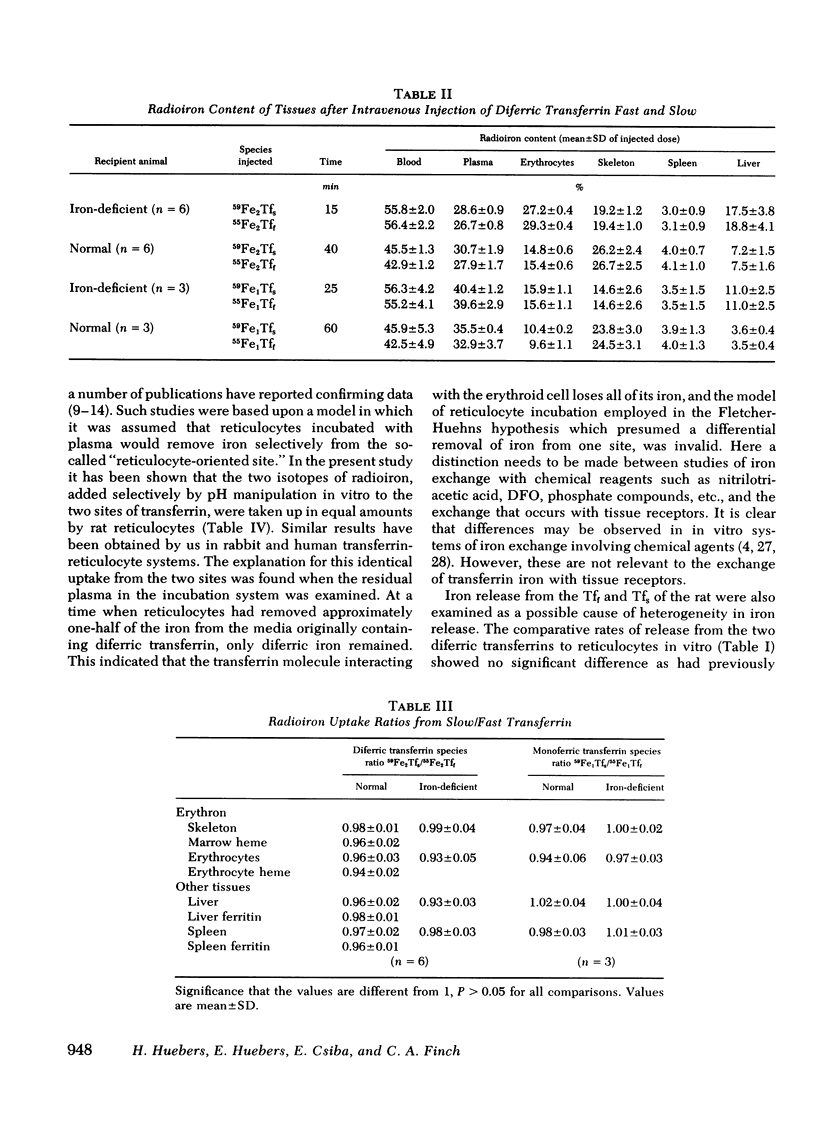
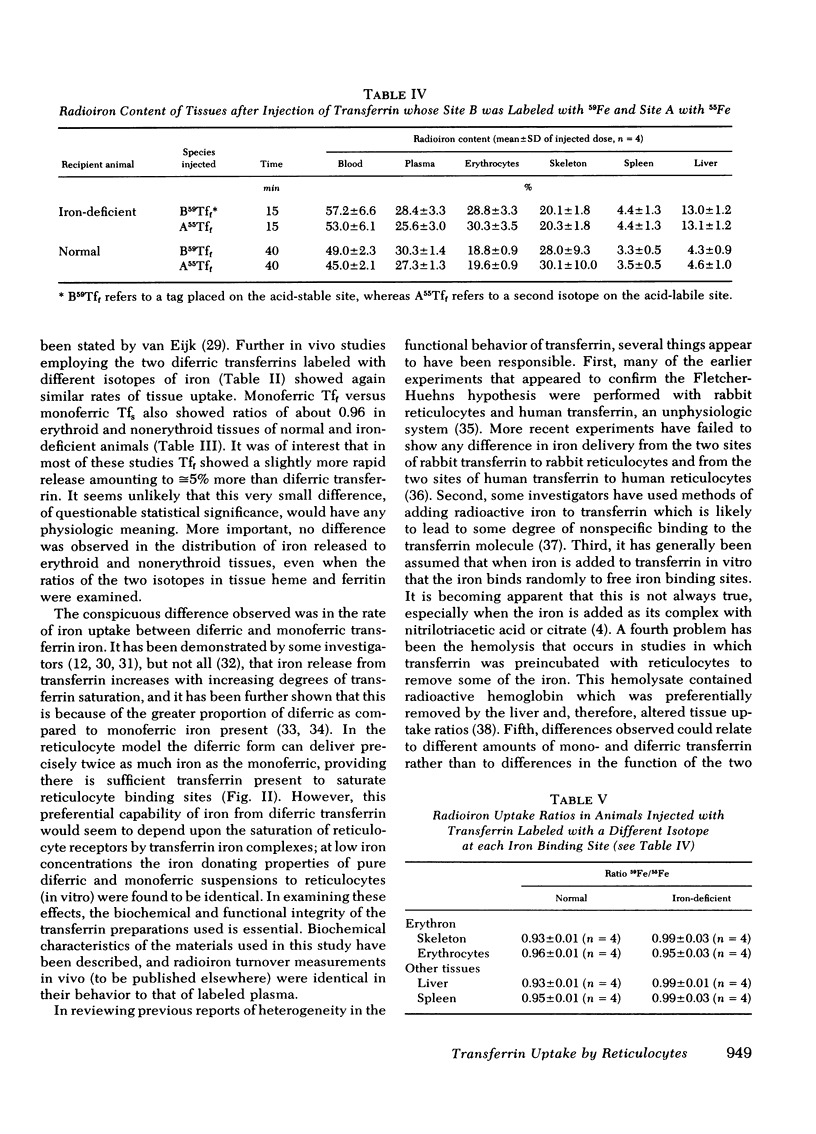
Abstract
Fast and slow rat transferrins were isolated by isoelectric focusing and prepared in their di- and monoferric forms. A comparison of the rates of iron release between fast and slow monoferric transferrins when incubated with reticulocytes or injected in vivo showed no significant difference in the behavior of the two isotransferrin species. Reticulocyte uptake of diferric transferrin resulted in the removal of both iron atoms from the transferrin molecule. A twofold greater iron uptake was observed from diferric as compared with monoferric iron, provided reticulocyte receptors were saturated. It is concluded that the two species of transferrin and their individual sites function similarly in their release of iron to tissue receptors.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Brown E. B. The iron-binding function of transferrin in iron metabolism. Semin Hematol. 1977 Jan;14(1):31–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awai M., Chipman B., Brown E. B. In vivo evidence for the functional heterogeneity of transferrin-bound iron. I. Studies in normal rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 May;85(5):769–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awai M., Chipman B., Brown E. B. In vivo evidence for the functional heterogeneity of transferrin-bound iron. II. Studies in pregnant rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 May;85(5):785–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates G. W., Schlabach M. R. The reaction of ferric salts with transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3228–3232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. B., Okada S., Awai M., Chipman B. In vivo evidence for the functional heterogeneity of transferrin-bound iron. III. Studies of transferrin at high and low iron saturation. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Oct;86(4):576–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. C., Chasteen N. D. Nonequivalence of the metal binding sites in vanadyl-labeled human serum transferrin. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4573–4577. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. C., Huebers H., Finch C. A. Effect of transferrin saturation on iron delivery in rats. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jul;235(1):R18–R22. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1978.235.1.R18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D., Marsaglia G., Eschbach J. W., Funk D. D., Finch C. A. Ferrokinetics: a biologic model for plasma iron exchange in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):197–205. doi: 10.1172/JCI106228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W., Ross K. D. Iron binding to conalbumin. Calorimetric evidence for two distinct species with one bound iron atom. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6026–6031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakins J. D., Brown D. A. An improved method for the simultaneous determination of iron-55 and iron-59 in blood by liquid scintillation counting. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1966 Jul;17(7):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(66)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch C. A., Deubelbeiss K., Cook J. D., Eschbach J. W., Harker L. A., Funk D. D., Marsaglia G., Hillman R. S., Slichter S., Adamson J. W. Ferrokinetics in man. Medicine (Baltimore) 1970 Jan;49(1):17–53. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197001000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J., Huehns E. R. Function of transferrin. Nature. 1968 Jun 29;218(5148):1211–1214. doi: 10.1038/2181211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J. The plasma clearance and liver uptake of iron from transferrin of low and high iron saturation. Clin Sci. 1971 Nov;41(5):395–402. doi: 10.1042/cs0410395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J. Variation in the availability of transferrin-bound iron for uptake by immature red cells. Clin Sci. 1969 Oct;37(2):273–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON A. H., LOUIS L. N. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF RAT TRANSFERRIN. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj0880409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganzoni A. M., Hahn D., Späti B. Plasma iron transport: absence of an uniform system. Blut. 1972 May;24(5):269–273. doi: 10.1007/BF01642011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn D., Baviera B., Ganzoni A. M. Functional heterogeneity of the transport iron compartment I. In vivo radioiron clearance from high and low saturated transferrin. Acta Haematol. 1975;53(5):285–291. doi: 10.1159/000208194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn D. Functional behaviour of transferrin. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr;34(2):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. C., Aisen P. Functional equivalence of the two iron-binding sites of human transferrin. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):821–823. doi: 10.1038/257821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebers H., Huebers E., Rummel W., Crichton R. R. Isolation and characterization of iron-binding proteins from rat intestinal mucosa. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):447–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABBE R. F., NISHIDA G. A new method of hemin isolation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):437–437. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S. Differences between human Fe1-transferrin molecules. Br J Haematol. 1975 Mar;29(3):511–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb01848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Finch C. A. The in vivo plasma clearance of iron from transferrins of low and high iron saturation. Clin Sci. 1970 Jun;38(6):783–793. doi: 10.1042/cs0380783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S. Iron uptake by rabbit reticulocytes. Br J Haematol. 1973 Mar;24(3):343–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lestas A. N. The effect of pH upon human transferrin: selective labelling of the two iron-binding sites. Br J Haematol. 1976 Mar;32(3):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pootrakul P., Christensen A., Josephson B., Finch C. A. Role of transferrin in determining internal iron distribution. Blood. 1977 Jun;49(6):957–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. M., Gibson J. F. Electron paramagnetic resonance evidence for a distinction between the two iron-binding sites in transferrin and in conalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8031–8035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHADE A. L. IRON UPTAKE BY ERYTHROPOIETIC AND OTHER TISSUES FROM "NATIVE" SERUM SIDEROPHILIN AND FROM ISOLATED "PURIFIED" SIDEROPHILIN. Farmaco Sci. 1964 Feb;19:185–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarberg K., Eng M., Huebers H., Marsaglia G., Finch C. Plasma radioiron kinetics in man: explanation for the effect of plasma iron concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1559–1561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eijk H. G., Van Noort W. L. Isolation of rat transferrin using CNBr-activated sepharose 4B. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1976 Oct;14(10):475–478. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1976.14.1-12.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zschocke R. H., Bezkorovainy A. Structure and function of transferrins. II. Transferrin and iron metabolism. Arzneimittelforschung. 1974 May;24(5):726–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


