Abstract
A quantitative primate model of arterial thromboembolism has been characterized with respect to mechanism and usefulness in evaluating modifying variables. The model involved the kinetic measurements of 51Cr-platelets and 125I-fibrinogen consumption by femoral arteriovenous cannulae in chaired baboons.
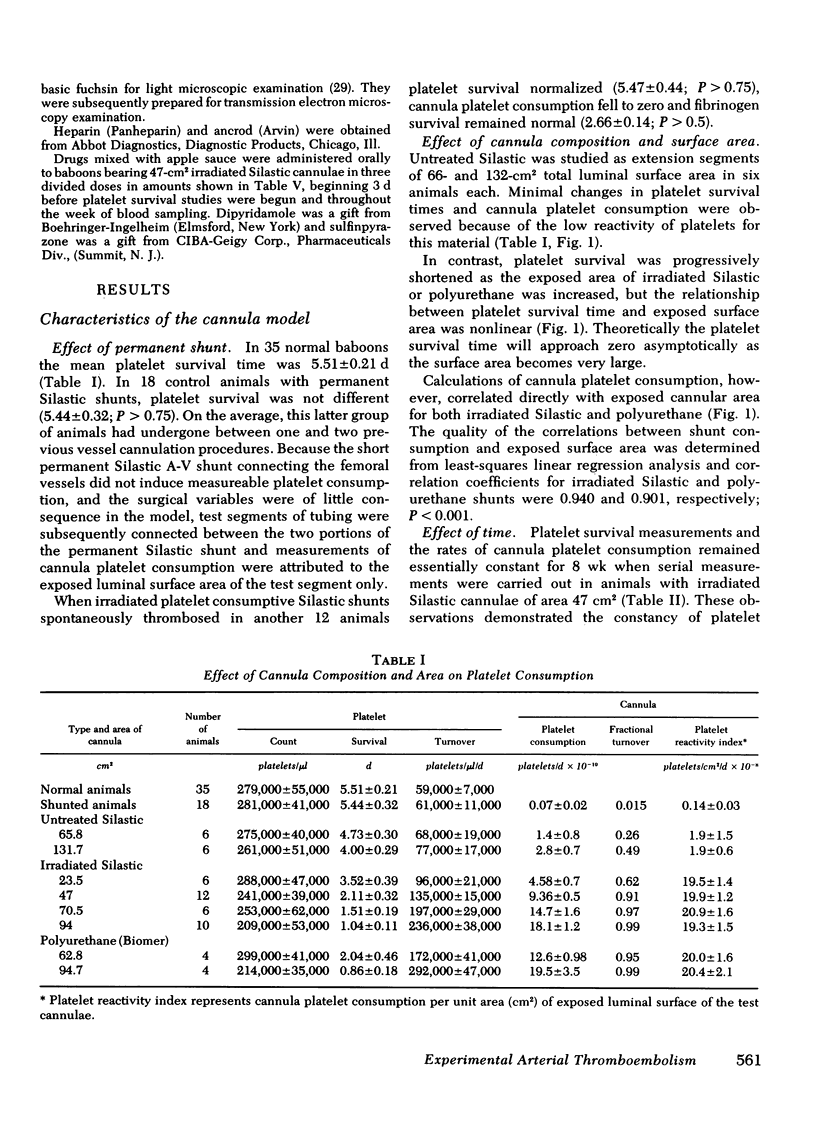
Cannula platelet consumption correlated directly with exposed cannular area for irradiated Silastic and polyurethane (correlation coefficients of 0.940 and 0.901, respectively; P < 0.001) and remained steady state for months. Nonirradiated Silastic was only minimally reactive with platelets. Despite increased rates of platelet consumption circulating fibrinogen was not measurably destroyed by any of the cannulae tested. Cannula platelet consumption was independent of cannula flow rate, platelet count, heparin anti-coagulation, and ancrod defibrinogenation.
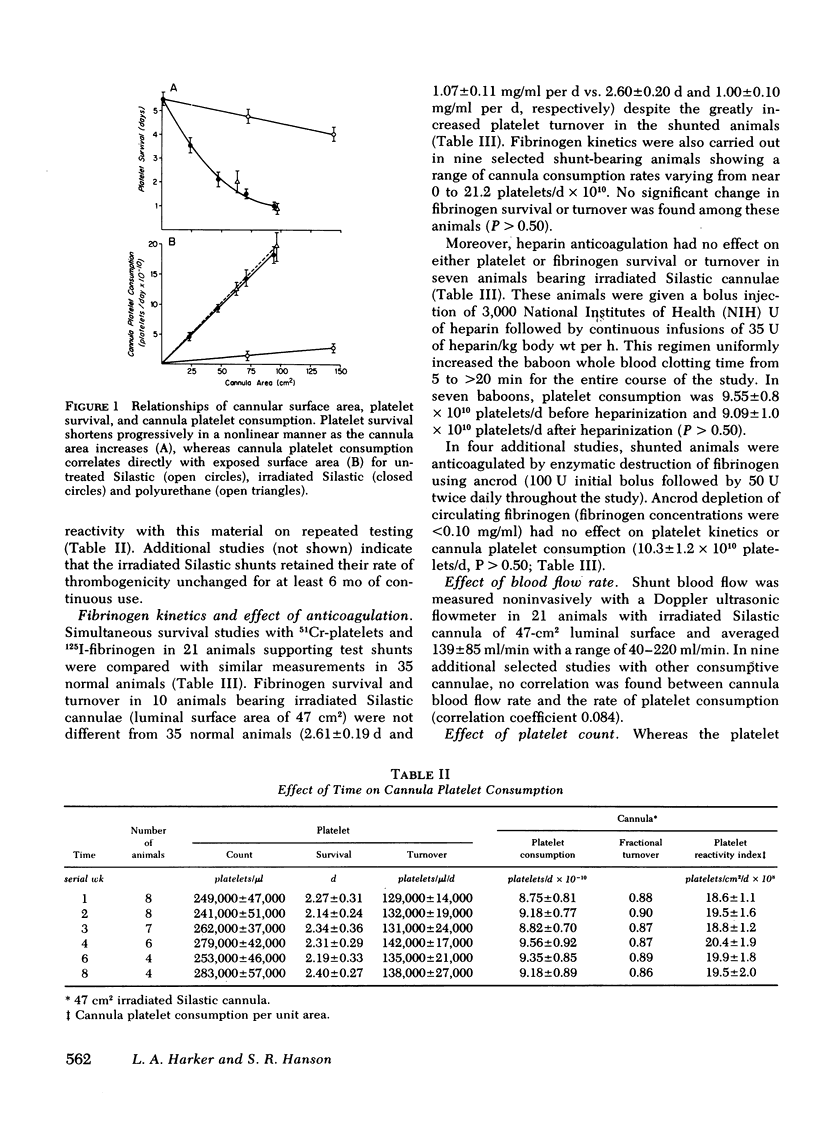
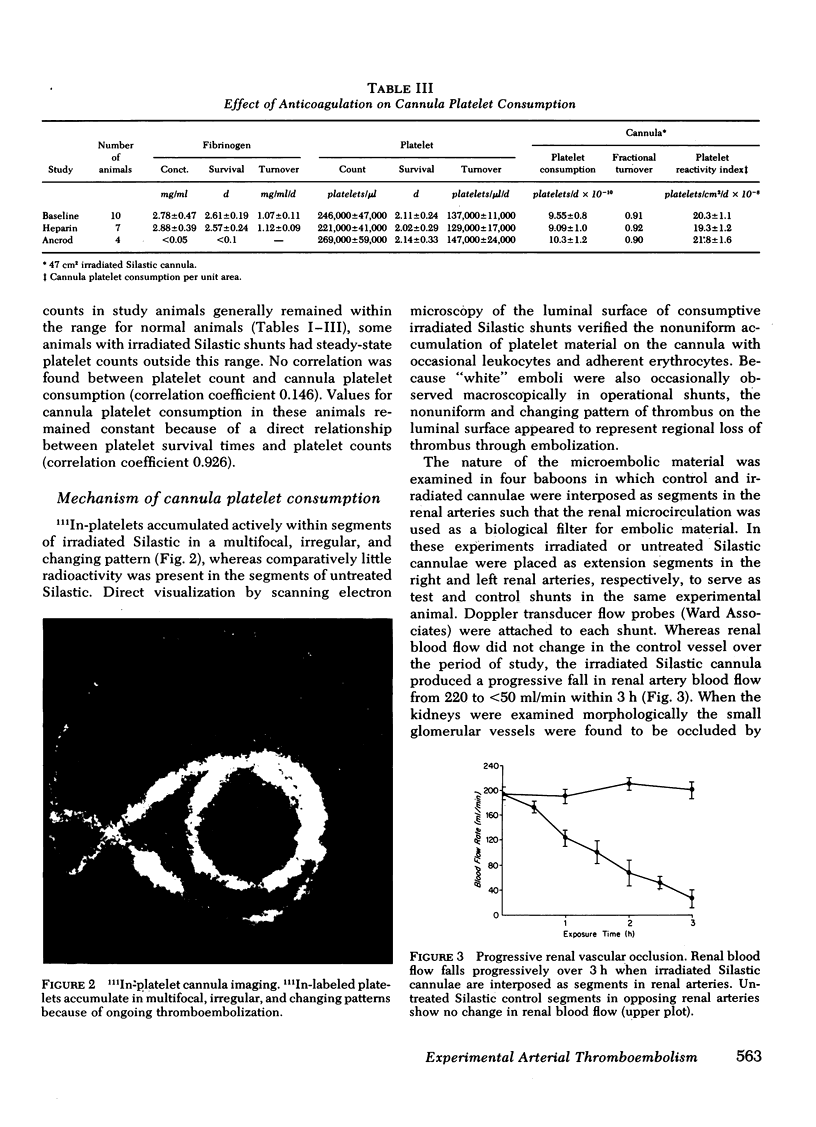
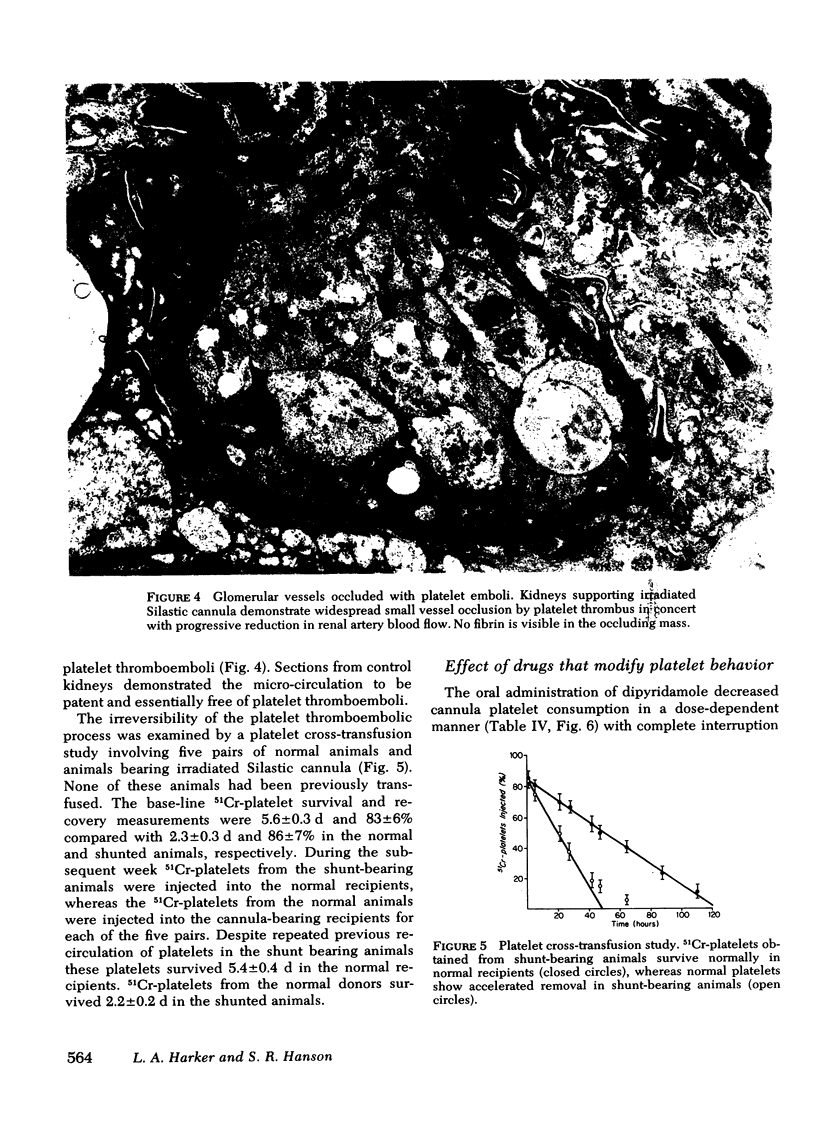
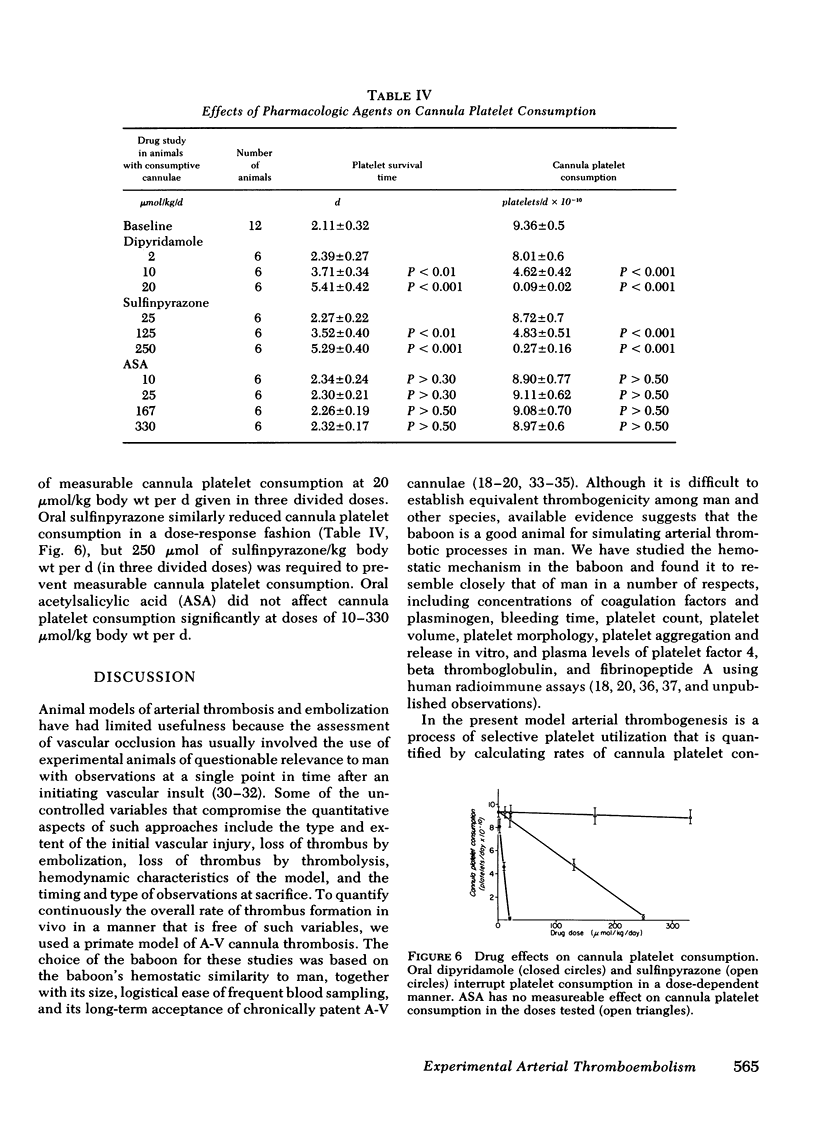
111In-platelet imaging of irradiated Silastic cannulae demonstrated luminal accumulation and subsequent embolization of irregular platelet masses. When irradiated Silastic cannulae were inserted as extension segments in the renal arteries of four animals the glomerular vessels became progressively occluded with nonfibrin-containing platelet thromboemboli. Nonirradiated Silastic cannulae in control arteries produced no significant vascular occlusion. Because the survival of platelets from animals with consumptive cannulae was not shortened in normal recipient animals we concluded that platelets were either irreversibly removed through thromboembolic consumption or unaffected in their viability.
Oral administration of dipyridamole and sulfinpyrazone decreased cannula platelet consumption in a dose-dependent manner with complete interruption at 20 and 250 μmol/kg body wt per d (in three divided doses), respectively, whereas oral acetylsalicylic acid (10-330 μmol/kg per d) had no measurable effect on cannula platelet consumption.
We conclude that this primate model simulates arterial thrombotic processes in man and that this model is suitable for the in vivo evaluation of biomaterials and of drugs that modify platelet behavior.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELSON E., RHEINGOLD J. J., PARKER O., BUENAVENTURA A., CROSBY W. H. Platelet and fibrinogen survival in normal and abnormal states of coagulation. Blood. 1961 Mar;17:267–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashford T. P., Frieiman D. G. The role of the endothelium in the initial phases of thrombosis. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1967 Feb;50(2):257–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner H. R., Muggli R., Tschopp T. B., Turitto V. T. Platelet adhesion, release and aggregation in flowing blood: effects of surface properties and platelet function. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Feb 29;35(1):124–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave J. P., Packham M. A., Guccione M. A., Mustard J. F. Inhibition of platelet adherence to a collagen-coated surface by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pyrimido-pyrimidine and tricyclic compounds, and lidocaine. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 May;83(5):797–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DORNHORST A. C. The interpretation of red cell survival curves. Blood. 1951 Dec;6(12):1284–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didisheim P. Animal models useful in the study of thrombosis and antithrombotic agents. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1972;1:165–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH J. E., MACFARLANE R. G., SANDERS A. G. THE STRUCTURE OF HAEMOSTATIC PLUGS AND EXPERIMENTAL THROMBI IN SMALL ARTERIES. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Oct;45:467–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON G. P., AKERS R. P., LUTZ B. R. White thrombo-embolism and vascular fragility in the hamster cheek pouch after anticoagulants. Blood. 1953 Feb;8(2):140–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg A. D., Aster R. H. Kinetic studies with 51-chromium-labeled platelet cohorts in rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jul;74(1):138–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin D. A., Bushberg J. T., Doherty P. W., Lipton M. J., Conley F. K., Diamanti C. I., Meares C. F. Indium-111-labeled autologous platelets for location of vascular thrombi in humans. J Nucl Med. 1978 Jun;19(6):626–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONOUR A. J., RUSSELL R. W. Experimental platelet embolism. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:350–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGUES J., LAPIERE M. NOUVELLES RECHERCHES SUR L'ACCOLEMENT DES PLAQUETTES AUX FIBRES DE COLLAG'ENE. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jul 31;11:327–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haerem J. W. Mural platelet microthrombi and major acute lesions of main epicardial arteries in sudden coronary death. Atherosclerosis. 1974 May-Jun;19(3):529–541. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(74)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton J. W., Matthews C. Similarities between baboon and human blood clotting. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Nov;21(6):1713–1716. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.6.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A. 189. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1978;4:321–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Ross R., Slichter S. J., Scott C. R. Homocystine-induced arteriosclerosis. The role of endothelial cell injury and platelet response in its genesis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):731–741. doi: 10.1172/JCI108520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Slichter S. J. Arterial and venous thromboembolism: kinetic characterization and evaluation of therapy. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1974 May 15;31(2):188–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Slichter S. J. Platelet and fibrinogen consumption in man. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 16;287(20):999–1005. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211162872001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Slichter S. J., Sauvage L. R. Platelet consumption by arterial prostheses: the effects of endothelialization and pharmacologic inhibition of platelet function. Ann Surg. 1977 Nov;186(5):594–601. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197711000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Slichter S. J., Scott C. R., Ross R. Homocystinemia. Vascular injury and arterial thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 12;291(11):537–543. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409122911101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Slichter S. J. Studies of platelet and fibrinogen kinetics in patients with prosthetic heart valves. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 10;283(24):1302–1305. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012102832402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haudenschild C., Baumgartner H. R., Studer A. Significance of fixation procedure for preservation of arteries. Experientia. 1972 Jul 15;28(7):828–831. doi: 10.1007/BF01923157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber J. D., Parker F., Odland G. F. A basic fuchsin and alkalinized methylene blue rapid stain for epoxy-embedded tissue. Stain Technol. 1968 Mar;43(2):83–87. doi: 10.3109/10520296809115048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen L., Rowsell H. C., Hovig T., Glynn M. F., Mustard J. F. Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation and myocardial infarction in swine. Lab Invest. 1967 Dec;17(6):616–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelton J. G., Hirsh J., Carter C. J., Buchanan M. R. Thrombogenic effect of high-dose aspirin in rabbits. Relationship to inhibition of vessel wall synthesis of prostaglandin I2-like activity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):892–895. doi: 10.1172/JCI109203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerker D. J., Harker L. A., Goodner C. J. Effects of somatostatin on hemostasis in baboons. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 4;293(10):476–479. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509042931004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Korbut R. Dipyridamole and other phosphodiesterase inhibitors act as antithrombotic agents by potentiating endogenous prostacyclin. Lancet. 1978 Jun 17;1(8077):1286–1289. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. A., Francis M. E. The estimation of blood platelet survival. II. The multiple hit model. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971;25(1):53–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Packham M. A. The role of blood and platelets in atherosclerosis and the complications of atherosclerosis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Jun 30;33(3):444–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOLE J. C., FRENCH J. E., CLIFF W. J. THE EARLY STAGES OF THROMBOSIS. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Nov;16:523–528. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.6.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. L., Harker L. A. Platelet and fibrinogen survival in coronary atherosclerosis. Response to medical and surgical therapy. Am J Cardiol. 1977 Apr;39(4):595–598. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(77)80171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman N. F., Wolf R. H., Mason R. G. Venous thrombosis on prosthetic surfaces. Evolution and blood coagulation studies in a nonhuman primate model. Am J Pathol. 1974 May;75(2):229–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Majerus P. W. The mechanism of the effect of aspirin on human platelets. I. Acetylation of a particulate fraction protein. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):624–632. doi: 10.1172/JCI108132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Acetylation of prostaglandin synthase by aspirin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3073–3076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon T. L., Hyers T. M., Gaston J. P., Harker L. A. Heparin pharmacokinetics: increased requirements in pulmonary embolism. Br J Haematol. 1978 May;39(1):111–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb07133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaet T. H., Erichson R. B. The vascular wall in the pathogenesis of thrombosis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1966;21:67–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele P., Carroll J., Overfield D., Genton E. Effect of sulfinpyrazone on platelet survival time in patients with transient cerebral ischemic attacks. Stroke. 1977 May-Jun;8(3):396–398. doi: 10.1161/01.str.8.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele P., Weily H., Davies H., Ppppas G., Genton E. Platelet survival time following aortic valve replacement. Circulation. 1975 Feb;51(2):358–362. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.51.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb R., Ragde H., Thomas E. D. Extracorporeal irradiation of the blood in baboons. Radiat Res. 1969 Apr;38(1):43–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. M., Harken D. E., Gorlin R. Pharmacologic control of thromboembolic complications of cardiac-valve replacement. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jun 24;284(25):1391–1394. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197106242842501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Studies of the metabolism and distribution of fibrinogen in healthy men with autologous 125-I-labeled fibrinogen. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):103–111. doi: 10.1172/JCI105314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakur M. L., Welch M. J., Joist J. H., Coleman R. E. Indium-LLL labeled platelets: studies on preparation and evaluation of in vitro and in vivo functions. Thromb Res. 1976 Oct;9(4):345–357. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. E., McDevitt E., Goldsmith E. I. Blood-clotting mechanisms of nonhuman primates. Choice of the baboon model to simulate man. J Med Primatol. 1972;1(3):132–141. doi: 10.1159/000460376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Tschopp T. B., Baumgartner H. R. Impaired interaction (adhesion-aggregation) of platelets with the subendothelium in storage-pool disease and after aspirin ingestion. A comparison with von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 25;293(13):619–623. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509252931301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]