Abstract
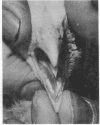
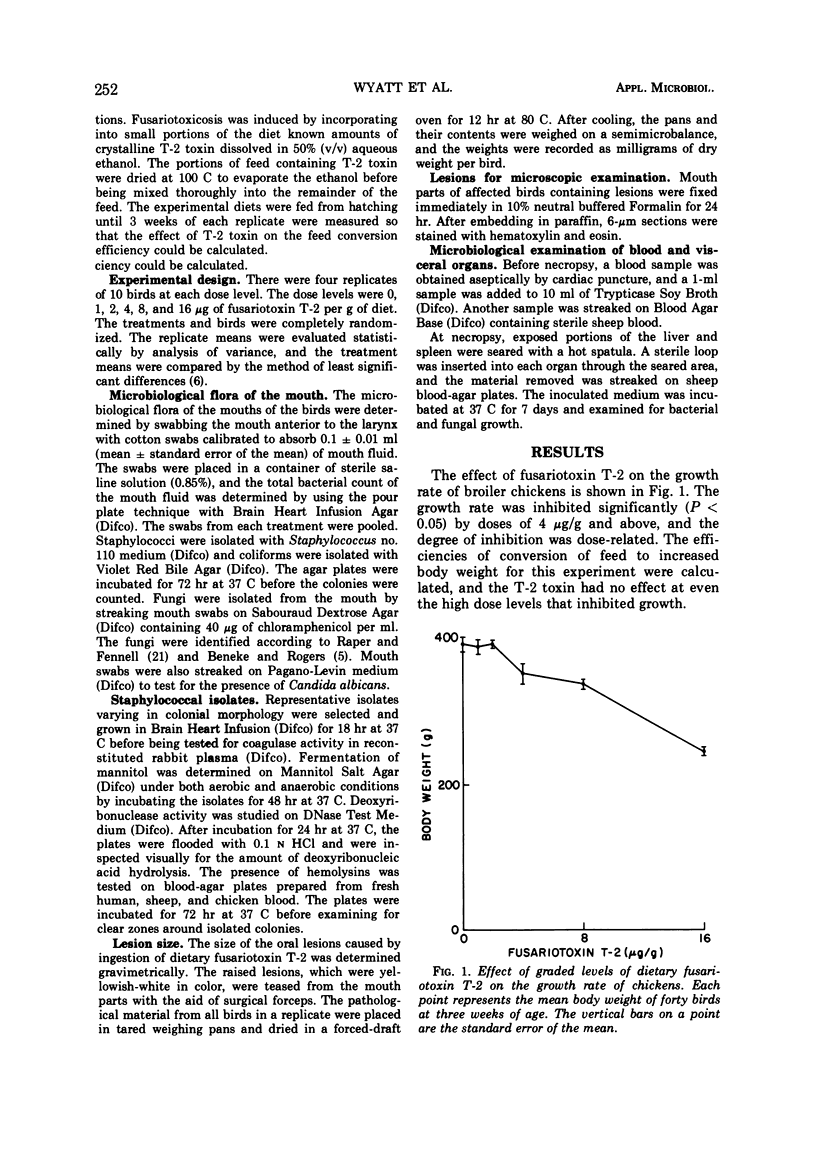
Fusariotoxin T-2 is a mycotoxin produced by Fusarium tricinctum which was implicated in moldy corn toxicosis of farm animals. Graded concentrations of dietary fusariotoxin T-2 (0, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16 μg/g, respectively) were given to groups of 40 chickens. Raised yellowish-white lesions on the mouth parts were produced by all concentrations, and the size of the lesions was dose-related. The growth rate was reduced significantly (P < 0.05) by concentrations of 4, 8, and 16 μg/g. The mouth fluid of the affected birds contained greatly increased numbers of bacteria, including Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli, which proved avirulent when inoculated into scarified tissue of control birds. Microscopy examinations of the lesions revealed a fibrinous surface layer, intermediate layers containing invaginations filled with rods and cocci, and a heavy infiltration of the underlying tissues with granular leukocytes. These data suggest that the role of fusariotoxin T-2 in field cases of moldy corn toxicosis should be reinvestigated since oral lesions were not mentioned in the original descriptions of the disease. However, the lesions bear some features of those characteristic of the third or septic angina stage of alimentary toxic aleukia, a nutritional toxicosis of humans produced by eating grains infested with F. tricinctum.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bamburg J. R., Riggs N. V., Strong F. M. The structures of toxins from two strains of Fusarium tricinctum. Tetrahedron. 1968 Apr;24(8):3329–3336. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4020(01)92631-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister H. R. T-2 toxin production by Fusarium tricinctum on solid substrate. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):739–742. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.739-742.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen C. M., Meronuck R. A., Nelson G. H., Behrens J. C. Effects on turkey poults of rations containing corn invaded by Fusarium tricinctum (Cda.) Sny. & Hans. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):177–179. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.177-179.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilgan M. W., Smalley E. B., Strong F. M. Isolation and partial characterization of a toxin from Fusarium tricinctum on moldy corn. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harry E. G. Some characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from the skin and upper respiratory tract of domesticated and wild (Feral) birds. Res Vet Sci. 1967 Oct;8(4):490–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Sakai K., Ueno Y., Tsunoda H., Enomoto M. Solaniol, a toxic metabolite of Fusarium solani. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):718–720. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.718-720.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER C. F. Endemic panmyelotoxicosis in the Russian grain belt. I. The clinical aspects of alimentary toxic aleukia (ATA); a comprehensive review. Mil Surg. 1953 Sep;113(3):173–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER C. F. Endemic panmyelotoxicosis in the Russian grain belt. II. The botany, phytopathology, and toxicology of Russian cereal food. Mil Surg. 1953 Oct;113(4):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasas W. F., Bamburg J. R., Smalley E. B., Strong F. M., Ragland W. L., Degurse P. E. Toxic effects on trout, rats, and mice of T-2 toxin produced by the fungus Fusarium tricinctum (Cd.) Snyd. et Hans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;15(2):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(69)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palyusik M., Szép I., Szöke F. Data on susceptibility to mycotoxins of day-old goslings. Acta Vet Acad Sci Hung. 1968;18(4):363–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pong R. S., Wogan G. N. Time course of alterations of rat liver polysome profiles induced by aflatoxin B 1 . Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Oct;18(10):2357–2361. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90350-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Hill C. H., Hamilton P. B. The effect of dietary modifications on aflatoxicosis in the broiler chicken. Poult Sci. 1971 May;50(3):768–774. doi: 10.3382/ps.0500768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]