Abstract
Background
The relationship between fish health and muscle growth is critical for continued expansion of the aquaculture industry. The effect of immune stimulation on the expression of genes related to the energy balance of fish is poorly understood. In mammals immune stimulation results in major transcriptional changes in muscle, potentially to allow a reallocation of amino acids for use in the immune response and energy homeostasis. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of immune stimulation on fish muscle gene expression.
Results
Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) primary muscle cell cultures were stimulated with recombinant (r)IL-1β, a major proinflammatory cytokine, for 24 h in order to simulate an acute immune response. The transcriptomic response was determined by RNA hybridization to a 4 × 44 K Agilent Atlantic salmon microarray platform. The rIL-1β stimulation induced the expression of genes related to both the innate and adaptive immune systems. In addition there were highly significant changes in the expression of genes related to regulation of the cell cycle, growth/structural proteins, proteolysis and lipid metabolism. Of interest were a number of IGF binding proteins that were differentially expressed, which may demonstrate cross talk between the growth and immune systems.
Conclusion
We show rIL-1β modulates the expression of not only immune related genes, but also that of genes involved in processes related to growth and metabolism. Co-stimulation of muscle cells with both rIGF-I and rIL-1β demonstrates cross talk between these pathways providing potential avenues for further research. This study highlights the potential negative effects of inflammation on muscle protein deposition and growth in fish and extends our understanding of energy allocation in ectothermic animals.
Keywords: Transcriptomics, Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), Muscle cell culture, Inflammation, Catabolism, Cell cycle, IGF binding proteins
Background
Muscle growth involves a tightly controlled balance between protein synthesis and degradation [1]. Protein synthesis is driven by the growth hormone (GH)/Insulin like growth factor (IGF)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway [2-5], whereas protein degradation occurs via a number of pathways including ubiquitin proteasome [6-8], lysosomal [9], apoptotic [10] and the calcium dependant calpains [11]. These processes and the pathways underlying their regulation have been examined in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) [12], rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) [13-16] and other fish [17,18]. The anabolic effects of the GH/IGF system have also been studied in ectothermic animals including Atlantic salmon [12,19,20], rainbow trout [21,22] and other teleosts [23]. The GH/IGF system has been seen to activate the mTOR pathway thus directing protein synthesis, and is highly conserved in teleosts [2-4].
In mammals the key signals involved in stimulating anabolic activity are free amino acids, GH and IGF [24], whereas catabolic signals include nutrient depletion, hormones such as cortisol and transcription factors such as forkhead box O (FOXOs) [25]. The actions of many of these key signals have been seen to be conserved in salmonid fish [2,12,22]. Despite being initiated by different signals, catabolism and anabolism share many aspects of downstream signalling machinery, providing the possibility of intracellular cross talk between these two processes [26]. In mammals undergoing acute inflammatory responses, muscle tissue goes into immediate catabolic state [27,28] where muscle fibres are broken down releasing free amino acids, likely to be used for liver protein synthesis of acute phase serum proteins. As skeletal muscle is the principal body store of proteins, this tissue is the main target for catabolism and release of free amino acids [29]. In mammals the inflammatory response leads to a loss of skeletal muscle mass in both acute and chronic inflammatory situations [30]. The current consensus in higher vertebrates is that this increase in muscle atrophy can be mediated by proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) [26,31], IL-6 [27,32,33] and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) [26,27,32]. Several different processes have been identified by which proinflammatory cytokines can negatively affect muscle mass. IL-1β and TNFα receptors, on the surface of the cells, signal via conserved signal transduction pathways and alter gene expression, which in muscle tissue normally induces genes involved in protein degradation resulting in the release of free amino acids [28,31,34-36]. In parallel this cytokine signalling competes with and decreases the effects of IGF-I signalling, specifically during downstream signal transduction, hence reducing the anabolic hormone effect. Such intracellular receptor crosstalk between cytokines and anabolic hormones can lead to a state of endocrine resistance whereby no increase in the amount of ligand present will increase the hormonal effects [26,37,38]. This cytokine induced hormone resistance can result in a condition known as cachexia, one aspect of which is a chronic increase in proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFα and IL-1β [39,40]. The effects of cachexia are a loss of body mass, especially skeletal muscle protein, and it is thought that the ability of cytokines to cause hormone resistance is one of the primary mediators of cachexia. This condition differs from simple weight loss since the loss of body mass will continue despite feeding [26,39].
Transcriptional responses to various triggers of protein catabolism have been examined in salmonid fish, including starvation [41], starvation and refeeding [42], or following extensive anorexic migrations [18] and vitellogenesis [14,43]. However to date only a limited number of investigations have addressed the effects of infection or immune stimulation on muscle growth in fish [44,45]. Previously a cachexia model in rainbow trout was developed by chronic stimulation with lipopolysaccharides (LPS) [44], mimicking sepsis and chronic background infection. In these fish, muscle protein content was decreased, but levels of MyoD and myosin were unaffected indicating that while muscle accretion was altered, the mechanisms may be different to those known in mammals. In general the response was much less dramatic than is observed in mammals, probably reflecting the different control of amino acid reallocation in ectothermic fish.
Proinflammatory cytokines, which include IL-1β, are the primary mediators of the innate immune system [46] and show a rapid response at the transcriptional level following recognition of pathogens including bacterial and viral products [47]. IL-1β is secreted as the mature form following cleavage of the precursor molecule by interleukin 1 converting enzyme (ICE). The mature soluble protein binds to the IL-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1) receptor which then recruits the IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) and initiates the signal cascade [47,48]. The signalling cascade activates pathways that positively regulate the activity of transcription factor nuclear factor-κβ (NFκB) and the mitogen activated protein kinases p38 (MAPK p38) and c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) [26,48,49]. It is through the activation of these pathways that IL-1β is thought to negatively affect anabolism while stimulating catabolism [26,34,37]. Whilst there is some controversy as to how IL-1β is processed in fish [50-52], nevertheless a functional mature peptide has been produced in several species [53] and the receptor genes have been cloned [54,55].
This paper investigates the effects of acute proinflammatory stimulation on the transcriptome of Atlantic salmon primary myocyte cells. We hypothesise that the inflammatory stimuli will cause significant changes in the expression of genes related to immune function, protein metabolism and other cellular processes. Further to this, we hypothesize that co-incubation of cell cultures with IGF-I as well as rIL-1β will lead to an attenuation of the metabolic actions of inflammation.
Results
Cell culture and stimulation
Primary muscle cell cultures were assessed for differentiation and purity by light microscopy at 4× and 10× magnification (Data not shown). Nine grams of white skeletal muscle pooled from six fish provided sufficient cells to reach confluence when evenly split between two 6 well plates. Prior to performing the microarray analysis, confirmation that the cells responded to rIL-1β was carried out by real time PCR using IL-1β itself as a marker gene since it is known to increase in expression in response to rIL-1β stimulation. IL-1β expression was significantly increased (541 fold) in the stimulated samples compared to the control samples.
Microarray analysis
Following filtering and quality control 27458 probes were retained for statistical analysis. Of these 7649 were significantly altered in expression at P < 0.05 following correction for multiple tests. We further filtered this set of genes by retaining those with a fold change of >2 leaving a differentially regulated set of 2504 genes for analysis (Table 1, full list of genes Additional file 1: Table S1). Within the gene set 1209 features were increased and 1295 features decreased in expression. The gene with the highest up-regulation is the cytokine TNFα2 with a 216 fold increase, whilst aquaporin 1 was the most decreased in expression with a 125 fold reduction in expression. Confirmation of microarray expression was conducted using seven key genes analysed with realtime PCR (Additional file 2: Figure S1) where a highly significant correlation (r2 = 0.8763 & P < 0.001) between qPCR and microarray data was found.
Table 1.
Microarray analysis showing the numbers of transcripts found to be differentially expressed following stimulation of primary muscle cells by rIL-1β compared to unstimulated cells with various P value (corrected by Benjamini Hochberg FDR) and Fold change (FC) cutoffs
| P all | P < 0.05 | P < 0.02 | P < 0.01 | P < 0.005 | P < 0.001 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC all |
27458 |
7649 |
3945 |
1912 |
591 |
0 |
| FC > 1.1 |
21039 |
7592 |
3938 |
1910 |
591 |
0 |
| FC > 1.5 |
7430 |
4752 |
3039 |
1630 |
554 |
0 |
| FC > 2.0 |
3205 |
2504 |
1884 |
1167 |
455 |
0 |
| FC > 3.0 |
1275 |
1131 |
956 |
695 |
317 |
0 |
| Expected by chance | 382 | 78 | 19 | 2 | 0 |
In order to better understand the changes in whole cell transcriptomic output, gene ontology analysis was used to indicate the biological processes that were modulated by the IL-1β stimulation. From the 2504 features retained for analysis, 2196 (88%) were annotated to a functional protein and 1945 (78%) were assigned at least one gene ontology (GO) identifier for biological process, enabling further assessment of biological function. These proportions reflect the annotation of all features on the microarray slide. Statistical analysis for enrichment for biological processes resulted in 1195 biological process GO terms being identified. The nature of GO analysis means that many of these are overlapping and only the non-redundant major groupings are presented (Figure 1). Observation of both the GO analysis and manual assignment identification of functions was used to assign genes to functional groups. The differentially expressed genes could be defined as belonging to a number of distinct functional classes, especially immune response, proteolysis, growth regulation and structural proteins, cell cycle and lipid metabolism. The directional expression changes indicated how these processes were being affected, with a general increase in the expression of immune related and protein metabolism genes, whereas growth, structural proteins and cell cycle showed a negative trend, with a majority of genes being down regulated in expression. A complex response was found for genes encoding lipid metabolism proteins, indicting major transcriptional changes relating to lipid mobilisation.
Figure 1.
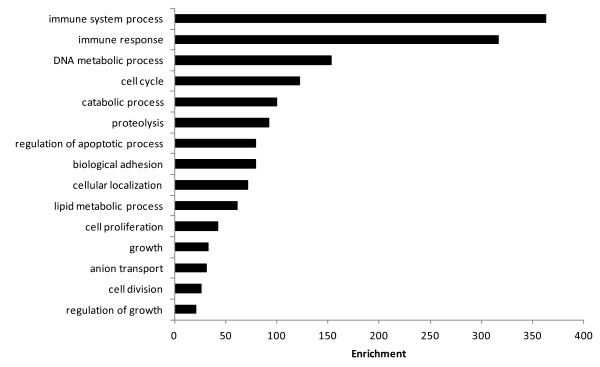
Bar chart showing the 15 Gene ontologies found to be most highly statistically enriched in response to rIL-1β stimulation of muscle cells in vitro. Gene ontology enrichment carried out using GOEAST, GOslimming of the subsequent list performed with REVIGO.
Immune response genes
There was a clear increase in genes related to immune function (Table 2) most notably in the high increase of expression of mRNAs encoding proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNFα (1/2) as well as chemokines such as IL-8. Transcription factors involved in IL-1β signalling were also increased in expression with subunits of NFκB and its inhibitor, MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2, MAPK activated jun-B and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein all being up regulated. Components of the IL-1β receptor machinery were also increased including IL-1 receptor accessory protein, IL-1 receptor kinase and an IL-1 receptor antagonist protein mRNA (Table 2). Other innate immune related genes were also increased including complement components, C-type lectins and the antimicrobial proteins hepcidin and ferritin. Both these latter two genes have roles in iron binding. Several negative regulators of inflammation were also found to be increased including two suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) genes, SOCS 1 and 3, the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, and as mentioned earlier an IL-1 antagonist (nIL-1 F).
Table 2.
Differential expression of genes related to the immune response
| Gene ID 1 | Annotation 2 | Mean fold change± SE 3 | Identity 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ssa#S24188435 |
AY929386 |
216.3 ± 58.8 |
TNFα 2 |
| Omy#gi185133433 |
NM_001124347 |
197.9 ± 79.1 |
IL-1B |
| Ssa#STIR00083_4 |
AY929385 |
99.2 ± 17.9 |
TNFα 1 |
| Omy#gi13235345 |
AJ279069 |
93.3 ± 15.4 |
IL-8 |
| Ssa#S34822137 |
AM397592 |
29.7 ± 5.1 |
Complement c3 |
| Ssa#STIR04816 |
BT047247 |
25.5 ± 13.1 |
Hepcidin |
| Omy#S37211068 |
EF175381 |
20.7 ± 1.1 |
Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2b |
| Ssa#STIR08688 |
TC65065 |
17.9 ± 4.9 |
Ferritin |
| Ssa#S21512941 |
AY572832 |
16.1 ± 0.2 |
C type lectin receptor A |
| Ssa#STIR35259 |
NM_001124618 |
13.8 ± 0.9 |
Complement protein component c7-1 |
| Ssa#STIR23928 |
NM_001124410.1 |
13.3 ± 10.8 |
Complement factor H precursor |
| Ssa#S43134841_S |
NM_001123611 |
9.5 ± 2.5 |
CD4-like protein |
| Ssa#STIR00084_4 |
DW569632 |
8.5 ± 0.3 |
NF-kappa-b inhibitor alpha |
| Ssa#S18892257 |
AJ505008 |
3.9 ± 0.3 |
IL-1 receptor accessory protein |
| Ssa#STIR14647 |
TC73172 |
3.9 ± 0.0 |
MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 |
| Ssa#S30276405 |
DW563373 |
3.9 ± 0.2 |
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 |
| Ssa#S35660755 |
EG895473 |
3.4 ± 0.3 |
NF-kappa-B p100 subunit |
| Ssa#S35667643 |
EG902361 |
3.4 ± 0.2 |
Complement c1q-like protein 4 |
| Ssa#S31992293 |
DY720890 |
3.2 ± 0.2 |
IL-10 receptor beta chain precursor |
| Omy#gi197927463 |
NM_001124396 |
3.0 ± 0.2 |
IL-1 receptor antagonist |
| Ssa#KSS392 |
NM_001141766 |
2.9 ± 0.3 |
IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 |
| Ssa#CB516003 |
CB516003 |
2.8 ± 0.3 |
NF-kappa-B 1 p105 subunit |
| Ssa#KSS3660 |
BT059477 |
2.8 ± 0.3 |
NF-kappa-B inhibitor epsilon |
| Ssa#STIR08793 |
TC65192 |
2.8 ± 0.1 |
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 |
| Ssa#STIR00087_4 |
DW555246 |
2.7 ± 0.2 |
IL-10 |
| Ssa#STIR12117 |
TC69580 |
2.3 ± 0.1 |
Transcription factor jun-B |
| Omy#S18157537 |
BX883008 |
2.1 ± 0.1 |
Interleukin-6 receptor subunit alpha precursor |
| Ssa#DW006091 |
DW006091 |
2.1 ± 0.2 |
MHC class i antigen |
| Ssa#TC106540 |
TC106540 |
−2.4 ± 0.1 |
TNF receptor-associated factor 6 |
| Ssa#STIR08822 |
TC65229 |
−2.6 ± 0.1 |
IL-15 |
| Ssa#S18849636_S |
BT071912.1 |
−2.6 ± 0.2 |
Complement C4-1 |
| Ssa#S35693513 |
EG928231 |
−3.3 ± 0.8 |
Complement component 6 precursor |
| Ssa#S35687715 | EG922433 | −22.7 ± 8.3 | Complement factor D precursor |
List of selected mRNAs associated with the immune response found to be increased or decreased in expression in response to rIL-1β stimulation. Genes were assigned to the table based upon both their GO identifier and previous knowledge of their functions. Genes with greatest fold differences in expression are presented, the genes that are lower in expression are denoted by (-) value. The genes shown were significant at p < 0.05 following t- tests with Benjamini-Hochberg FDR and greater than 2-fold change. 1Indicates the unique code for the feature on the microarray, 2Accession number of the cDNA sequence, accession numbers beginning with TC are for oligos from the TIGR Atlantic Salmon Gene Index. 3Fold change, in the case of oligos that featured multiple times in the gene list the one with the highest fold change is reported. 4Identity of the probe target as determined by BLASTX and BLASTN searches.
Proteolysis
Genes related to protein metabolism were modulated by the IL-1β stimulation including those involved in both synthesis and degradation (Table 3). The largest group of protein metabolism genes found to be increased in expression were those related to proteolysis, specifically the ubiquitin proteasome pathway (UBP). Several E3 ubiquitin ligases, ubiquitin like proteins and four 20S proteasome subunits all increased in expression. Other genes encoding proteolytic proteins found to be increased in expression included collagenase 3 and a cytosolic dipeptidase. A number of proteases were decreased in expression including a subunit of calpain 1, serine protease htra1 and 35, cystatin B and ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 T.
Table 3.
Differential expression of genes related to proteolysis
| Gene ID 1 | Annotation 2 | Mean fold change± SE 3 | Identity 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ssa#CL13Contig1 |
CL13Contig1 |
10.0 ± 1.8 |
Collagenase 3 |
| Ssa#S30266930 |
DW553898 |
8.3 ± 0.4 |
Angiotensinogen |
| Ssa#CK884742 |
CK884742 |
3.4 ± 0.5 |
Cytosolic non-specific dipeptidase |
| Ssa#S35528810 |
EG815188 |
3.2 ± 0.1 |
Ubiquitin-like protein 1 |
| Ssa#S18890005 |
CB515535 |
2.8 ± 0.2 |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF144A-A |
| Ssa#DW564916 |
DW564916 |
2.7 ± 0.4 |
Ubr5 protein |
| Ssa#CL300Ctg1 |
CL300Contig1 |
2.4 ± 0.1 |
Proteasome subunit beta type-6 precursor |
| Ssa#KSS4965 |
KSS4965 |
2.3 ± 0.1 |
Proteasome subunit beta type 7b |
| Ssa#STIR04015 |
BT048053 |
2.2 ± 0.1 |
Proteasomebeta type 8 |
| Ssa#S30295323 |
DW582287 |
2.2 ± 0.1 |
Proteasome subunit alpha type-6 |
| Ssa#S35509463 |
EG795841 |
2.0 ± 0.0 |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CHFR |
| Ssa#S35533557 |
EG819935 |
−2.1 ± 0.1 |
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 T |
| Ssa#S35507555 |
EG793933 |
−2.1 ± 0.2 |
Calpain small subunit 1 |
| Ssa#S35530808 |
EG817186 |
−2.1 ± 0.1 |
Cystatin-B |
| Ssa#S31992074 |
DY720671 |
−3.8 ± 0.2 |
Ubiquitin- containing phd and ring finger 1 |
| Ssa#S30242447 |
NM_001141717 |
−3.9 ± 0.2 |
Serine protease htra1 |
| Ssa#S35564994 | EG851372 | −16.2 ± 0.9 | Protease, serine, 35 |
List of selected mRNAs related to proteolysis found to be increased or decreased in expression in response to rIL-1β stimulation. Genes were assigned to the table based upon both their GO identifier and previous knowledge of their functions. Genes with greatest fold differences in expression are presented, the genes that are lower in expression are denoted by (-) value. The genes shown were significant at p < 0.05 following t- tests with Benjamini-Hochberg FDR and greater than 2-fold change. 1Indicates the unique code for the feature on the microarray, 2 Accession number of the cDNA sequence, accession numbers beginning with TC are for oligos from the TIGR Atlantic Salmon Gene Index. 3Fold change, in the case of oligos that featured multiple times in the gene list the one with the highest fold change is reported. 4Identity of the probe target as determined by BLASTX and BLASTN searches.
Growth regulation and structural proteins
An interesting group of genes that can be regarded as controllers of anabolic signalling were also modulated. Most notable were the IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs), where IGFBP-6 was found increased in expression following the inflammatory stimulus whereas IGFBPs -4, 5 and rP1 decreased in expression (Table 4). Genes controlling muscle cell differentiation were also changed in expression including the transcriptional repressor yin-yang 1 (YY1) which showed an up regulation and myogenic regulatory factor 5 (MyF5) which was down regulated (Table 4). Structural protein encoding mRNAs showed a marked tendency to be down regulated, as seen with the collagens and the myosins, β-actin, and troponin (Table 4).
Table 4.
Differential expression of genes for growth regulation & structural proteins
| Gene ID 1 | Annotation 2 | Mean fold change± SE 3 | Identity 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ssa#S30261281 |
DW548249 |
17.2 ± 2.5 |
IGF binding protein 6 |
| Ssa#S22669043 |
AY462105 |
4.6 ± 0.2 |
Growth hormone receptor isoform 1 precursor |
| Ssa#S35518234 |
EG804612 |
2.9 ± 0.2 |
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta |
| Ssa#DW566454 |
DW566454 |
2.6 ± 0.4 |
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 2 |
| Ssa#STIR16259 |
TC75448 |
2.3 ± 0.1 |
YY1 transcription factor |
| Ssa#STIR03019 |
BT049051 |
−2.1 ± 0.0 |
Regulator of g-protein signaling 18 |
| SsaHomCont3_080 |
SsaHomContl3 |
−2.2 ± 0.3 |
Beta-actin |
| Ssa#S30278631 |
DW565599 |
−2.2 ± 0.1 |
Collagen alpha 2 type VI |
| Omy#TC165689 |
TC165689 |
−2.4 ± 0.2 |
Collagen alpha 2 type V preproprotein |
| Ssa#S18891260 |
CB515159 |
−2.4 ± 0.4 |
Type I collagen alpha 2 chain |
| Ssa#S26643985 |
DQ163908 |
−2.5 ± 0.2 |
Growth hormone receptor isoform 2 precursor |
| Ssa#S35580189 |
EG866567 |
−2.5 ± 0.0 |
Collagen alpha 1 type II isoform 1 precursor |
| Ssa#STIR17006 |
TC76573 |
−2.6 ± 0.2 |
Growth arrest-specific 1 |
| Ssa#CA041082 |
CA041082 |
−2.8 ± 0.2 |
Transforming growth factor, beta receptor III |
| Ssa#S35580645 |
EG867023 |
−2.8 ± 0.2 |
Vascular endothelial growth factor D |
| Ssa#CA037592 |
CA037592 |
−2.8 ± 0.2 |
Myosin IB |
| Ssa#S31998683 |
DY727280 |
−2.8 ± 0.2 |
Laminin, beta 1 |
| Ssa#S35563089 |
EG849467 |
−2.9 ± 0.3 |
Collagen alpha 1 type V |
| Ssa#S31977813 |
DY706603 |
−3.1 ± 0.1 |
Myosin phosphatase-Rho interacting protein isoform 1 |
| Ssa#STIR25506 |
TC89337 |
−3.1 ± 0.1 |
Type i keratin s8 |
| Ssa#S46924879 |
EU861009.1 |
−3.4 ± 0.1 |
IGF binding protein 5 |
| Ssa#S32004569 |
DY733166 |
−3.5 ± 0.5 |
Corticotropin releasing factor precursor |
| Ssa#STIR05529 |
BT046528 |
−3.5 ± 0.2 |
Collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 |
| Ssa#TC91867 |
TC91867 |
−4.2 ± 0.3 |
Collagen alpha 1 type XI isoform A preproprotein |
| Ssa#S35504964 |
EG791342 |
−4.6 ± 0.5 |
Troponin I, slow skeletal muscle |
| Ssa#STIR00115_3 |
BT045917 |
−4.8 ± 0.6 |
Tropomyosin-1 alpha chain |
| Ssa#STIR11900 |
TC69277 |
−5.2 ± 0.4 |
Myosin ic |
| Ssa#S37580916 |
EF432866 |
−5.4 ± 0.7 |
IGF binding 7 precursor |
| Ssa#S37580919 |
EF432861 |
−7.9 ± 0.4 |
IGF binding protein 4 |
| Ssa#S35582593 |
EG868971 |
−10.9 ± 5.3 |
Collagen alpha 1 type X precursor |
| Ssa#STIR30922 | TC97553 | −27.9 ± 2.7 | Myf5 protein |
List of selected mRNAs related to growth regulation & structural proteins found to be increased or decreased in expression in response to rIL-1β stimulation. Genes were assigned to the table based upon both their GO identifier and previous knowledge of their functions. Genes with greatest fold differences in expression are presented, the genes that are lower in expression are denoted by (-) value. The genes shown were significant at p < 0.05 following t- tests with Benjamini-Hochberg FDR and greater than 2-fold change. 1Indicates the unique code for the feature on the microarray, 2 Accession number of the cDNA sequence, accession numbers beginning with TC are for oligos from the TIGR Atlantic Salmon Gene Index. 3Fold change, in the case of oligos that featured multiple times in the gene list the one with the highest fold change is reported. 4Identity of the probe target as determined by BLASTX and BLASTN searches.
Cell cycle and DNA metabolism
The expression of genes regulating the cell cycle was clearly altered, with the majority of them being reduced in expression (Table 5). Five cyclins (A2, B1/2, E1/2), two cyclin dependent kinases, and several cell division cycle proteins were all reduced in expression. However, two cyclins (D1 and G2) were increased in expression. DNA metabolism genes were also generally decreased in expression, including several minichromosome maintenance complex components, DNA replication complex and DNA replication licensing factor mcm2.
Table 5.
Differential expression of genes related to the cell cycle & DNA replication
| Gene ID 1 | Annotation 2 | Mean fold change± SE 3 | Identity 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ssa#S30294618 |
DW581582 |
2.4 ± 0.3 |
Cyclin D1 |
| Ssa#S31971283 |
DY700073 |
2.4 ± 0.2 |
Cell division cycle associated 4 isoform 14 |
| Ssa#S35549130 |
EG835508 |
2.2 ± 0.1 |
Cyclin G2 |
| Ssa#S30291070 |
DW578034 |
−2.0 ± 0.1 |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 isoform 1 |
| Ssa#STIR18340 |
TC78544 |
−2.1 ± 0.1 |
Cyclin B1 |
| Omy#S19711047 |
CR367942 |
−2.1 ± 0.2 |
Cyclin B2 |
| Ssa#S35661746 |
EG896464 |
−2.2 ± 0.2 |
Cell cycle progression 1 isoform 2 |
| Ssa#S35547210 |
EG833588 |
−2.2 ± 0.1 |
Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 22 |
| Ssa#TC109012 |
TC109012 |
−2.6 ± 0.2 |
Cyclin E1 isoform 1 |
| Ssa#KSS3754 |
NM_001173741 |
−2.8 ± 0.2 |
Minichromosome maintenance complex component 4 |
| Ssa#STIR12008 |
TC69433 |
−3.0 ± 0.1 |
Cell division control protein 2 |
| Ssa#TC103697_S |
TC103697 |
−3.0 ± 0.1 |
DNA replication licensing factor mcm2 |
| Ssa#S30290620 |
DW577584 |
−3.2 ± 0.1 |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| Ssa#S35659383 |
EG894101 |
−3.3 ± 0.1 |
Cyclin A2 |
| Ssa#S18888540 |
CB514505 |
−4.2 ± 0.3 |
Minichromosome maintenance complex component 2 |
| Ssa#S35699881 |
EG934599 |
−4.4 ± 0.1 |
Minichromosome maintenance complex component 3 |
| Ssa#S35664683 |
EG899401 |
−4.8 ± 0.4 |
DNA replication complex GINS protein PSF1 |
| Ssa#S30295467 |
DW582431 |
−5.1 ± 0.6 |
Spindle pole body component 24 homolog |
| Ssa#STIR15543 |
TC74419 |
−5.3 ± 0.5 |
Minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 |
| Ssa#S18890448 |
CB516667 |
−6.7 ± 0.6 |
Minichromosome maintenance complex component 5 |
| Ssa#S30277130 |
DW564098 |
−10.6 ± 0.4 |
Cell division cycle associated 7 isoform 1 |
| Omy#S19711255 |
CR367985 |
−14.7 ± 8.7 |
Cyclin E2 |
| Omy#S34311297 | CU069027 | −15.1 ± 2.8 | Cell division cycle 6 protein |
List of selected mRNAs related to the cell cycle & DNA replication found to be increased or decreased in expression in response to rIL-1β stimulation. Genes were assigned to the table based upon both their GO identifier and previous knowledge of their functions. Genes with greatest fold differences in expression are presented, the genes that are lower in expression are denoted by (-) value. The genes shown were significant at p < 0.05 following t- tests with Benjamini-Hochberg FDR and greater than 2-fold change. 1Indicates the unique code for the feature on the microarray, 2Accession number of the cDNA sequence, accession numbers beginning with TC are for oligos from the TIGR Atlantic Salmon Gene Index. 3Fold change, in the case of oligos that featured multiple times in the gene list the one with the highest fold change is reported. 4Identity of the probe target as determined by BLASTX and BLASTN searches.
Lipid and sterol metabolism
Finally, stimulation with rIL-1β caused changes in the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism (Table 6). These included the increase in expression of several cholesterol transport proteins such as apolipoprotein (Apo) L3 and lipoprotein lipase. However there was also a down regulation in other similar genes such as Apo A1 binding protein and Apo B and a down regulation of proteins involved in sterol synthesis.
Table 6.
Differential expression of genes related to lipid and sterol metabolism
| Gene ID 1 | Annotation 2 | Mean fold change± SE 3 | Identity 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ssa#S18890165 |
CB515874 |
23.2 ± 2.2 |
Creatine kinase, ubiquitous mitochondrial precursor |
| Ssa#STIR00012_4 |
AY848944 |
13.3 ± 1.1 |
Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 |
| Ssa#S30259776 |
DW546744 |
8.7 ± 0.3 |
Sphingomyelin synthase 1 |
| Ssa#STIR22551 |
TC84899 |
6.3 ± 0.2 |
Lipoprotein lipase |
| Ssa#TC105353 |
TC105353 |
5.5 ± 1.0 |
Mecr protein |
| Ssa#STIR12701 |
TC70393 |
3.6 ± 0.1 |
Retinol dehydrogenase 3 |
| Ssa#STIR31819 |
TC98944 |
3.5 ± 0.3 |
Glucose-6-phosphate-1-dehydrogenase |
| Ssa#S48420588 |
NM_001173773 |
3.2 ± 0.7 |
Myotubularin |
| Ssa#S31962884 |
DY691674 |
2.9 ± 0.1 |
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5B, mitochondrial |
| Ssa#S31963491 |
DY692281 |
2.8 ± 0.1 |
PPAR-alpha interacting complex protein 285 isoform 1 |
| Ssa#KSS1976 |
KSS1976 |
2.8 ± 0.2 |
78 kDa glucose-regulated protein |
| Ssa#S35587721 |
EG874099 |
2.7 ± 0.2 |
Apolipoprotein-L3 |
| Ssa#S30242761 |
DW538822 |
2.6 ± 0.2 |
Glycolipid transfer protein |
| Ssa#S32012431 |
DY741028 |
2.3 ± 0.1 |
StAR-related lipid transfer domain containing 3 |
| Ssa#CL50Contig2 |
CL50Contig2 |
2.3 ± 0.1 |
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A |
| Ssa#S32007249 |
DY735846 |
2.1 ± 0.2 |
Adipose differentiation-related protein |
| Ssa#STIR13627 |
TC71700 |
−2.0 ± 0.2 |
Cox18 cytochrome c oxidase assembly homolog |
| Ssa#CA043659 |
CA043659 |
−2.1 ± 0.2 |
Apolipoprotein B precursor |
| Ssa#DW564686 |
DW564686 |
−2.1 ± 0.1 |
Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 |
| Ssa#STIR21893 |
TC83911 |
−2.2 ± 0.1 |
Creatine kinase b-type |
| Ssa#S35679641 |
EG914359 |
−2.5 ± 0.1 |
Lipid phosphate phosphohydrolase 1 |
| Ssa#STIR22405 |
TC84675 |
−2.6 ± 0.1 |
Lipase a |
| Ssa#S30285553 |
DW572521 |
−2.6 ± 0.1 |
Lipid phosphate phosphohydrolase 2 |
| Ssa#S30246050 |
DW542111 |
−2.9 ± 0.3 |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-2 |
| Ssa#TC108704 |
TC108704 |
−3.8 ± 0.2 |
Lipocalin precursor |
| Ssa#STIR21285 |
TC82989 |
−4.9 ± 0.3 |
Glutamine synthetase |
| Ssa#S35523399 |
EG809777 |
−5.2 ± 0.5 |
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein, plasma |
| Ssa#STIR22650 | TC85053 | −5.2 ± 1.4 | Apolipoprotein a-i binding protein |
List of selected mRNAs related to the lipid & sterol metabolism found to be increased or decreased in expression in response to rIL-1β stimulation. Genes were assigned to the table based upon both their GO identifier and previous knowledge of their functions. Genes with greatest fold differences in expression are presented, the genes that are lower in expression are denoted by (-) value. The genes shown were significant at p < 0.05 following t- tests with Benjamini-Hochberg FDR and greater than 2-fold change. 1Indicates the unique code for the feature on the microarray, 2Accession number of the cDNA sequence, accession numbers beginning with TC are for oligos from the TIGR Atlantic Salmon Gene Index. 3Fold change, in the case of oligos that featured multiple times in the gene list the one with the highest fold change is reported. 4Identity of the probe target as determined by BLASTX and BLASTN searches.
Temporal response and interaction of IGF and IL-1β
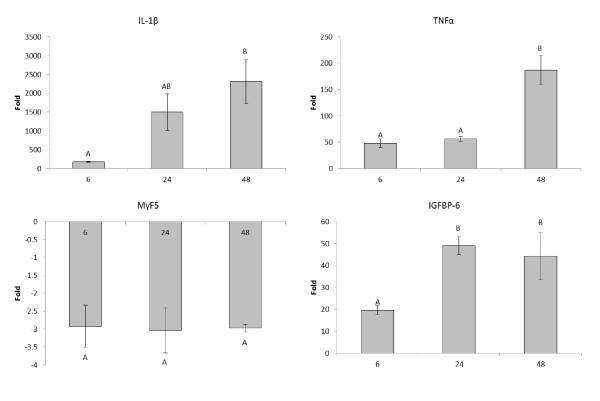
To assess the effect of time of rIL-1β stimulation on primary myocytes on gene expression, rIL-1β stimulation was performed at 6, 24 and 48 h and four key marker genes from the microarray analysis (IL-1β, TNFα, MyF5 and IGFBP-6) were examined by real time PCR (Figure 2). IL-1β was highly increased in expression at all-time points but it was at 48 h that the highest increase in expression was found. TNFα also showed the greatest fold increase at 48 h however this was more due to a reduction in the control expression seen at 48 h, than an increase in the stimulated cells. MyF5 was consistently down regulated at all time points with no increase in effect seen after 6 h. Finally IGFBP-6 was increased at all 3 times, but with a maximum fold increase at 24 h and 48 h.
Figure 2.
Graph showing the fold effects of rIL-1β stimulation compared to control on the expression of genes involved in the immune response and growth after 6, 24 and 48 h stimulation. Statistics were carried out using a one way ANOVA. Time points that do not share a letter are statistically different from each other. All mRNAs examined here were significantly altered in expression at all time points relative to the unstimulated control.
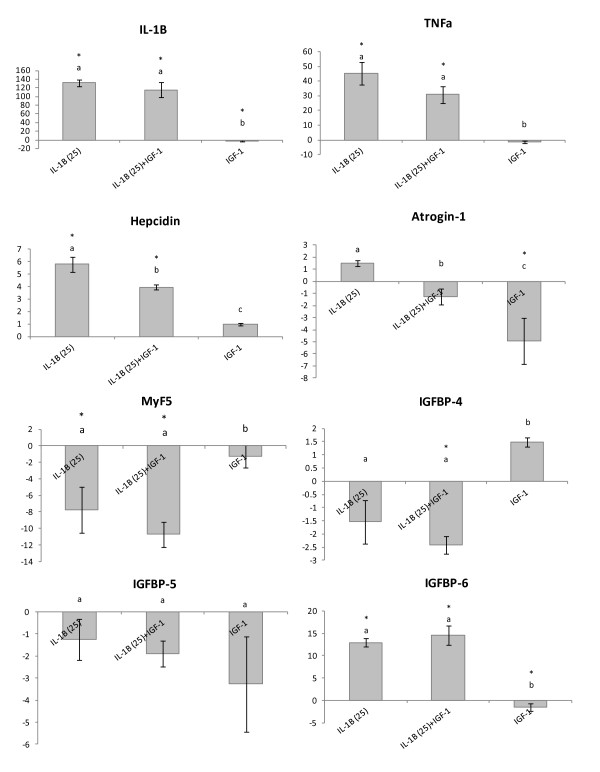
To assess the interaction between rIL-1β and rIGF-I primary myocyte cultures were stimulated with rIL-1β (25 ng/ml), rIGF-I (100nM), rIL-1β (25 ng/ml) + rIGF-I (100nM) or maintained as control. These stimulations were carried out for both 6 h and 24 h to determine if rIL-1β interfered with early effects that IGF-I may have on the cell cultures. The genes analysed were chosen to represent the immune response (IL-1β, TNFα and hepcidin) and protein metabolism/growth (atrogin-1, MyF5, IGFBPs-4, 5 & 6).
At 6 h co-stimulation of cells there was an up regulation of IL-1β and TNFα expression in response to rIL-1β stimulation, and this was not significantly altered by co-incubation with rIL-1 β + rIGF-I (Figure 3). Hepcidin was also found to be up regulated in response to rIL-1β (5.8 fold), with co-incubation with rIL-1β + rIGF-I reducing the magnitude of this increase ~30% (Figure 3). Regarding the expression of the IGFBPs, there was no effect of any treatment on the expression of IGFBP-5. IGFBP-6 was up regulated in response to rIL-1β (13.0 fold) and this effect was not altered by co-incubation with rIGF-I. However, stimulation with just rIGF-I led to a significant reduction in the expression of IGFBP-6 (Figure 3). Curiously IGFBP-4 was found to be significantly down regulated in response to co-incubation with rIL-1β + rIGF-I (-2.4 fold) but not by either treatment alone. MyF5 was found to be down regulated in response to rIL-1β (-7.8 fold) and this effect was not significantly altered by co-incubation (-10.7 fold) (Figure 3). Lastly, atrogin-1 was found to be significantly down regulated in response to stimulation with rIGF-I (-4.9 fold) but unaltered by rIL-1β treatment (Figure 3). Co-incubation with rIL-1β + rIGF-I however ablated the rIGF-I effect.
Figure 3.
Fold change of genes involved in both the immune response and growth in response to 6 h stimulation with either rIL-1β (25 ng/ml), rIL-1β (25 ng/ml) + rIGF(100nM), or rIGF(100nM). * represents a significant difference from control, bars which share a letter are not significantly different. All fold changes were calculated compared to unstimulated control samples. Comparative gene expression was measured with qPCR.
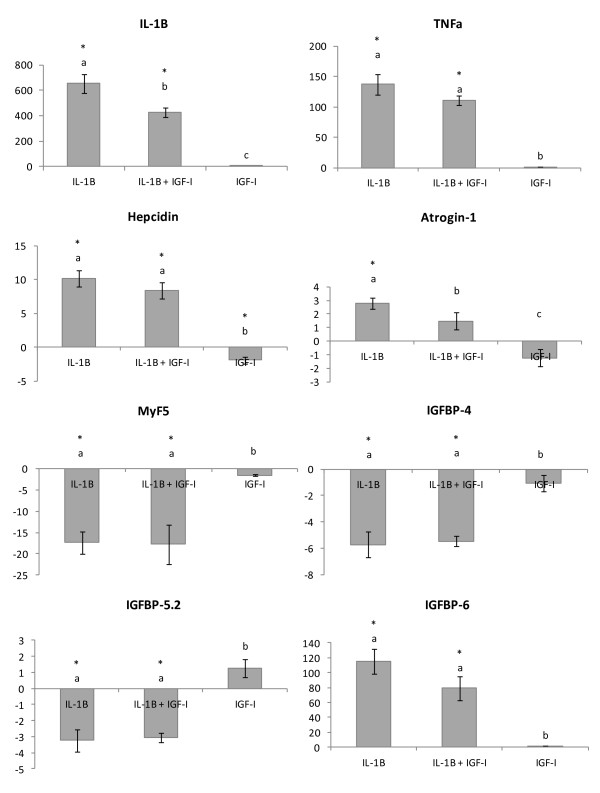
At 24 h co-stimulation of cells with rIL-1β + rIGF-I significantly reduced the expression of IL-1β relative to cells only stimulated with rIL-1β, from 654 fold to 427 fold (Figure 4). No significant effect of co-incubation of rIL-1β + rIGF-I was found on the expression of TNFα or hepcidin (Figure 4). Additionally co-incubation did not alter the expression of MyF5 or any of the IGFBPs. While rIL-1β alone significantly increased the expression of atrogin-1 (2.8 fold) this increase was not found in cells co-incubated with rIL-1β + rIGF-I (Figure 4). However the co-incubated cells had significantly increased expression of atrogin-1 compared to cells stimulated with just rIGF-I. rIGF-I alone also significantly reduced the expression of hepcidin (-1.9 fold) but had no effect on the other genes. All the genes tested that were also hybridised with sufficient intensity on the microarray showed the same direction and similar magnitude of response in this cell culture experiment.
Figure 4.
Fold change of genes involved in both the immune response and growth in response to 24 h stimulation with either rIL-1β (25 ng/ml), rIL-1β (25 ng/ml) + rIGF(100nM), or rIGF(100nM). * represents a significant difference from control, bars which share a letter are not significantly different. All fold changes were calculated compared to unstimulated control samples. Comparative gene expression was measured with qPCR.
Discussion
Regulation of muscle mass is under the control of a multitude of regulators related to both anabolic and catabolic processes. We hypothesised that the muscle cells would respond to the inflammatory stimulus by signalling the induction of inflammatory responsive genes in addition to other pathways related to protein metabolism for release of free amino acids as occurs during the acute phase response [56], or for gluconeogenesis and energy reallocation. Our approach of using primary cells to examine the transcriptomic responses of muscle cells stimulated with IL-1β avoids complex host and cell type responses observed during in vivo experiments. The response to the recombinant cytokine resulted in a large panel of genes that were significantly modulated being both increased and decreased in expression. Using gene ontology enrichment analysis for biological processes five key enriched processes were revealed: immune function, protein catabolism, IGF and growth regulation, cell cycle and lipid metabolism.
Immune response
The immune genes up regulated included several proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-8, indicating that stimulated myocytes are capable of synthesising these cytokines and are undergoing a proinflammatory response. The response to IL-1β is extremely rapid in other cell types in fish [57,58] and it is likely that within 24 h these molecules will have been secreted into the medium. Several genes in the inflammatory signalling cascade were induced including NFκB subunits p100 and p105, and the NFκb inhibitor (IκB), as seen during inflammation in other cell types [58]. Under normal conditions IκB binds to NFκB to inactivate it but IκB is phosphorylated by IκB kinase (IKK) and subsequently ubiquitinated and destroyed by the proteasome [59,60]. A related key signalling molecule up regulated was MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2, central to the MAPK pathways involved in IL-1β signalling [61], and with additional roles in the regulation of IGF signalling [26]. Another important transcription factor up regulated was the MAPK activated jun-B which increases transcription of IL-1β responsive genes generally at AP-1 responsive sites [62]. Interestingly, although jun-B may be associated with inflammatory signalling, it also has a role in maintaining muscle mass and its over expression in mammals can induce hypertrophy [63], indicting complex regulation of transcriptional machinery. In parallel to this, several genes encoding proteins that have roles as anti-inflammatory factors were activated; these include two suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS 1 and 3), IL-10 and an IL-10 receptor chain. SOCS proteins are often co-regulated during inflammation to prevent cellular damage and are negative regulators of cytokine signalling and function that interferes with signal transduction from cytokine receptors. The SOCS genes have been characterised in salmonid fish [64] and are increased in expression following stimulation with several different cytokines including IL-1β, TNFα and IL-6. Other immune related genes such as hepcidin, ferritin, C type lectin and the complement system were also significantly increased in expression. Both hepcidin and ferritin control iron availability and have antimicrobial actions with ferritin sequestering iron to reduce availability to microbes [65], whereas hepcidin also has direct antimicrobial properties and is often described as an antimicrobial peptide [66-68]. C-type lectins recognise carbohydrate moieties and are often induced by proinflammatory signals [58,69], to regulate a variety of immune processes including the complement system [70-72]. There was also activation of some genes that are components of the adaptive immune system, such as major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and CD4-like protein, but at the time point we examined the predominant immune gene response was by molecules of the innate defences.
Protein catabolic processes
A major proteolytic pathway in muscle is the ubiquitin proteasome pathway, which in mammals is believed to be responsible for the majority of muscle protein degradation initiated by a number of different stimuli including inflammation in mammals [30]. This pathway has also been seen to be activated in salmonid fish during muscle atrophy induced by food deprivation [45,73,74], hormonal changes [75], with some evidence of several components being modulated during immune responses [45,76]. The end product of proteolysis is the release of free amino acids for de novo protein synthesis or for the oxidation of the amino acids and gluconeogenesis. Following the inflammatory stimulus, several components of the UBP were increased in expression in myocytes. Several ubiquitin E3 ligases, which initiate the targeting of proteins for degradation and a number of proteasome subunits from the catalytic core of the proteasome (β subunits 6, 7 and 8 and α subunit 6), were increased in expression. We hypothesise that these changes would result in increased protein degradation and reduced muscle growth releasing free amino acids, which in vivo would be reallocated to other organs, such as the liver as occurs in mammals [77,78]. Although the predominant proteolytic genes modulated were related to the UBP system, cystatin B, an inhibitor of the acidic lysosomal cathepsins was down regulated, possibly indicating an increase in cathepsin bioavailability and activity [79]. In addition the calcium dependant protease calpain subunit 1 was down regulated following the IL-1β stimulation. This protease has roles in positive regulation of myofusion inhibiting the differentiation of myocyte cells [80,81] and this may indicate a reduction of muscle cell differentiation.
Other proteases observed to be increased included collagenase 3, that is increased in expression in NFkB mediated inflammation in mammals [82-84] and during vitellogenesis induced muscle atrophy in salmonids [43]. Angiotensinogen, the precursor of both angiotensin I & II, was also increased in expression, and is known to interfere with the actions and production of IGF-I, which in mammals is mediated by the NFκB pathway in collaboration with protein kinase C [85,86].
In general there was a clear effect of rIL-1β on the expression of genes related to catabolism as evidenced by a transcriptomic shift towards muscle catabolism by the increase in mRNAs related to protein degradation and the down regulation of protein degradation related genes that have positive effects on growth.
IGFBPs
The IGF system is instrumental in the control of protein synthesis and growth in both mammals and fish [87]. The activity of IGF is under tight control, often by a family of IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs), which have recently been characterised in salmonid fish [88]. They function by either stabilising the IGF or by competitively binding the IGF to prevent attachment to the IGF receptor [87] and thus reducing the anabolic effects of IGF on the cells.
We found several IGFBP encoding mRNAs were modulated by the proinflammatory stimulus. IGFBP-6 is thought to have a binding preference for IGF-II but also binds IGF-I [89]. These direct effects on the activity of both IGFs might drive the cells away from high levels of protein synthesis and anabolism towards a state of catabolism [90,91]. Previous studies indicate IGFBP-6 expression is associated with the inhibition of cell proliferation in both fish [12] and mammals [89,92]. Additionally IGFBP-6 expression is reduced during resumption of growth following starvation [20,93]. These findings tend to indicate that IGFBP-6 expression has a negative relationship with growth due to the ability of IGFBP-6 to act as a negative regulator of IGF-I & II activity, thus making an increase in the expression of IGFBP-6 a potential marker of inflammation induced catabolism in salmon muscle.
Other IGFBPs 4, 5 and rP1 were all decreased in expression following the inflammatory stimulus. In salmonids IGFBP-4 expression in muscle is increased by anabolic stimuli such as refeeding after starvation [20,93] and is positively related to the expression of the promyogenic transcription factors MyoD and MyF5 in vitro[12]. IGFBP-5 can potentiate the effects of IGF-I especially with regard to bone [94] and muscle differentiation [90]. In rainbow trout IGFBP-5 increased in expression in muscle during refeeding after starvation [93] and, in Atlantic salmon primary myocytes, the expression of IGFBP-5 decreased during cell proliferation suggesting this protein is associated with entry to cell cycle [12]. Together these results suggest the IGFBPs are responding in a coordinated fashion to reduce IGF signalling and altering the balance between anabolic and catabolic pathways.
Growth regulation and structural proteins
Many transcription factors involved in growth regulation were altered. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta was increased, and is a transcription factor with multiple functions, that is positively related to myostatin expression in mammals [95]. In rainbow trout muscle it is increased during energy reallocation caused by vitellogenesis [43] indicating a blocking of muscle growth. A second key transcription factor, NFκB, is often associated solely with immune function but also negatively regulates myogenesis via the transcriptional repressor YY1 [34,96]. Both of these molecules were increased in this experiment by IL-1β. YY1 is likely to be a mediator of NFκB induced muscle growth inhibition, achieving this by silencing myofibrillar promoters in myoblasts [34,96]. MyF5, a muscle specific transcription factor, regulates muscle cell differentiation [3,97] and a reduction in its expression level in this experiment fits with our anticipated reduction of muscle growth markers in response to rIL-1β stimulation. Additionally we found a general decrease in expression of mRNAs coding for muscle structural proteins such as collagens, myosins, actin and keratin, consistent with the hypothesis that the muscle cells are undergoing a reduction in growth in response to immune stimulation, as previously shown in mammals [98].
Cell cycle
The cell cycle is largely mediated through the actions of cyclin/cyclin dependent kinase complexes [99]. In the salmon myocytes multiple cyclins were modulated by IL-1β stimulation strongly suggesting cell cycle activity is being altered. For example, cyclin D1 expression was increased and functions in combination with cyclin dependent kinases to initiate and progress through the G1 phase of the cell cycle [99,100]. The increase of cyclin D1 may be related to NFκB mediated arrest of muscle growth by preventing myocyte differentiation [101]. Cyclin G2 was also increased and may inhibit entry into the cell cycle [102,103].
The remaining cyclins A2, B (1 and 2) and E (1 and 2) were all decreased in expression. Cyclin A2 is a rate limiting factor during S-phase and DNA synthesis and entry to mitosis [104], whereas cyclins E1 and E2 are responsible for the transition from G1 to S phases and initiation of DNA replication [105]. Cyclins B1 & B2 have roles during the S-phase and the M-phase and are crucial for maintenance of the mitotic state [106]. Several other cyclin related kinases, cell division proteins and minichromosome maintenance complex components were generally down regulated indicating a major reduction in cell cycle activity and DNA metabolism in these primary muscle cells under an inflammatory stimulus.
Lipid and sterol metabolism
A final group of genes found to be altered were those related to lipid and sterol metabolism, here several cholesterol transport proteins were increased in expression including Apo L3, glycolipid transfer protein and lipoprotein lipase. Apo-L3 is known to be a TNF-α inducible protein and its expression is known to be involved in the activation of the NFκB signalling pathway activated by cytokines in mammals [107]. The increase in the lipoprotein lipase could reflect an increased breakdown of lipoproteins for immune or cellular processes; this gene is under the control of many different signals in mammals including insulin, nutritional state and cytokines [108]. Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2, a gene known in mammals to be inducible by a variety of inflammatory substances [109], was also increased as a result of the rIL-1β stimulation. Apo A1 binding protein and Apo B were reduced in expression as well as several other sterol synthesis proteins. These results indicate that lipid metabolism is being actively changed in these myocytes under the inflammatory stimulus, resulting in complex changes in transcription of their mRNAs. Many of these changes could be mediated through intracellular crosstalk with the IGF/insulin pathway(s) [26,110].
Interaction between IGF-I and IL-1β
Results from the microarray clearly indicated genes involved in the IGF regulation were being modulated by IL-1β, especially a number IGF binding proteins. We performed additional experiments to address if transcripts altered by inflammation would be modulated by IGF-1, a hormone which drives cells towards an anabolic status. Atrogin -1 a key gene involved in protein degradation was reduced in expression by incubation of cells with rIGF-1 as previously reported, conversely it is increased following incubation with IL-1β as occurs in mammals [31]. When cells were co-incubation with rIL-1β and rIGF-I an almost total inhibition of the atrogin-1 down regulation was found, suggesting the proinflammatory signal is blocking the anabolic effect of IGF-1. IL-1β alone results in an increase in atrogin -1 expression at 24 h as found in mammalian cells stimulated by proinflammatory cytokines [111]. The co-stimulation also decreased the magnitude of the response of the antimicrobial peptide hepcidin, highlighting an alternative allocation of resources depending on the signalling the muscle cells are receiving. Together these results show how anabolic signals may attenuate transcription of immune defence molecules and that proinflammatory signals can increase catabolic effects in the cells.
Conclusions
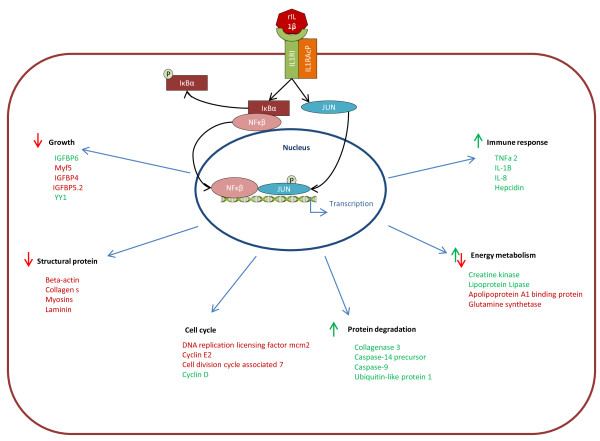
Muscle tissue is a complex and dynamic organ and is generally the only protein storage organ in the body; hence it needs to be able to control the synthesis of proteins and release of amino acids via degradation under a variety of environmental and physiological conditions. Muscle does respond to immune insults in fish, [45,76] but to date these responses have not been examined in an in vitro system removing the mileu of cytokines and hormones. Here we show a direct effect of a proinflammatory cytokine on primary muscle cells that induces not only immune genes, but also alters the wider transcriptome indicating increased catabolism, lipid mobilization and decreased cell proliferation with a large role potentially for the IGFBPs (Figure 5). Subsequent experiments demonstrate that both IL-1β and IGF-1 exert disparate effects on mechanisms that regulate growth and other physiological responses as highlighted by their interaction of expression on atrogin-1. These findings will direct future research into the control of muscle mass in ectothermic animals, particularly in relation to health and nutrition.
Figure 5.
Model of the proposed actions of rIL-1β on gene expression and physiology of muscle cells in vitro. rIL-1β is recognised by its receptor and an accessory protein, this then sets off a signal cascade resulting in the activation of NFκβ and JUN which in turn result in changes in gene expression and physiology. The proposed changes in physiology are shown in black. Green arrows show a positive effect on this aspect of physiology and red arrows show a negative effect. A sample of genes related to each aspect of physiology is shown in either red (up regulation) or green (down regulation).
Methods
Myosatellite isolation and stimulation
Atlantic salmon (mean weight of 25 g and mean length of 12 cm) were used for skeletal muscle myosatellite cell extraction, as previously described [112-114]. For each muscle extraction 6 fish were used (~1.5 g tissue from each fish), this was to remove any individual fish effects. No experimental procedures were carried out on the fish and fish maintenance was in line with national ethical guidelines in an experimental facility at University of Aberdeen, UK. Fish were maintained in freshwater and fed a commercial diet at 1.5% body weight per day. Fish were killed using a schedule one method and muscle tissue from above the mid line of the fish was removed sterilely with scalpel and forceps. This pooled muscle (approx 9 g) was placed into a pre-weighed flask containing 30 ml of Leibovitz L15 medium (Gibco) + penicillin/streptomycin 1% (Pen/Strep, Gibco, Penicillin 10,000 units/ml, streptomycin 10,000 μg/ml) (L15 + P/S). The muscle was diced into small blocks (2 mm3) using sterile procedures and the diced muscle then centrifuged (300 g, 5 min) and the supernatant removed. The tissue was digested in collagenase (0.2%) at 11°C for 1 h. Following digestion the cell suspension was centrifuged (300 g, 5 min) and washed before being centrifuged again (300 g, 5 min). This pellet was digested in trypsin (0.1%) at 11°C for 30 min. The cell suspension was again centrifuged (300 g, 40 sec) and the remaining supernatant was added to L15 + P/S plus 10% foetal calf serum (FCS, Sigma) before being passed through a 200 μm nylon mesh. The suspension was centrifuged (300 g, 15 min), the supernatant was removed and 12 ml of L15 + P/S + 10% FCS were added. Finally the contents of this tube were added to two 6 well plates. Prior to plating laminin (mouse laminin, Sigma-Aldrich) was applied to the well surfaces 24 h before the cells were plated out, at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. Cell cultures were then left for 1 h for microsatellite cells to bind to the surface before the medium was first changed and cells allowed to differentiate at 22°C, with the medium being changed every 2 days.
Stimulation of cells
Cells were cultured for 4 days to allow cellular differentiation, this was observed using light microscopy. Morphology typical of satellite cells and time taken to reach confluence in our system was approximately 6 days. The cells were found to exhibit the typical growth pattern previously observed for muscle satellite cells as described in Bower & Johnston (2010) [12]. Initially cells were mono-nucleic before beginning to proliferate and differentiate into spindle shaped cells, a small number of which were beginning to fuse together by day 4. For the microarray experiment stimulations, the medium was removed and 1 ml of new medium (with 0.5% FCS) containing either 10 μl recombinant trout IL-1β protein (rIL-1β) to achieve a concentration of 25 ng/ml or a non-stimulated control with 10 μl PBS. The concentration of IL-1β has previously been determined to be optimal in salmonid cell lines [58]. The cells were then stimulated for 24 h before RNA extraction was carried out.
Subsequent experiments were carried out to further investigate the effects of rIL-1β at different time points and to investigating the effects of the anabolic hormone IGF-I on rIL-1β actions. For these experiments the same procedure was carried out with the only alterations being the length of time the cells were stimulated and in some cases the addition of 100nM of recombinant human IGF-I (rIGF-I) (Sigma). For these experiments the cells were cultured in the stimulant for either 6, 24 or 48 h as specified.
Study design and sample replicates
Cells cultures were generated from six individual fish, this allowed purification of sufficient cells for two six well plates. For the microarray four of these wells were used as biological replicates and stimulated with rIL1β and the remaining four were mock stimulated as described above. RNA extractions were performed and the stimulated samples were kept separate whereas the control unstimulated samples were pooled to have a single common reference prior to mRNA amplification and labelling (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
The experimental design carried out for the microarray experiment. Cells were genereated from six individual fish, these cells were pooled and plated onto six well plates. RNA extracted from four biological replicates stimulated with rIL-1β stimulation were kept separate. For control wells, RNA was pooled to generate a common reference RNA sample.
RNA extraction
For microarray experiments RNA was isolated using the RNAeasy extraction kit (Qiagen) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. For all other samples RNA was isolated using Trizol (Sigma) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. In both cases the RNA was resuspended in 50 μl of nuclease free water and concentration measured by Nanodrop ND1000 (LabTech). The quality of the RNA was assessed using an Agilent Bioanalyzer RNA 6000 Nano Kit as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Microarray hybridization and analysis
Microarray analysis of the samples was carried out using a custom-designed Agilent microarray platform with 4 × 44 K probes per slide (Salar_2; Agilent Design ID:025520) as previously described [115]. The microarray platform design is available at array express accession number A-MEXP-2065.
To produce labelled template for hybridisations aRNA was generated using a MessageAMP II aRNA Amplification Kit (Ambion) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly 1 μg of total RNA was reverse transcribed to create first strand cDNA. This was then used in the synthesis of second strand cDNA and this product was purified using the supplied reagents and columns. Finally the in vitro transcription to synthesise amino allyl modified aRNA was carried out to incorporate amino allyl dUTP in to the aRNA after a 14 h incubation at 37°C and the product purified using the supplied reagents and columns.
For incorporation of flouresence dye 3 μg of aRNA in a volume of 10 μl was denatured at 70°C for 2 min, and to this was added 3 μl of NaHCO3 and 2 μl Cy dye (Cy3 or Cy5 mono-reactive dye pack, Amersham, resuspended in DMSO). The dye was allowed to incorporate for 1 h in the dark before excess dye was removed using a DyeEx spin column purification kit (Qiagen). Confirmation of dye incorporation and aRNA recovery was by nanodrop spectrometry. Agilent microarrays were hybridised according to the manufacturer’s instructions as described by [115]. Briefly 825 ng cDNA of each labelled template was fragmented in the dark and made up to a final volume of 20 μl with nuclease free dH2O. After fragmentation, 57 μl of 2XGEx hybridisation buffer (Agilent) was added to each sample which was then briefly mixed and spun down before being stored on ice in preparation for loading 103 μl onto each microarray. Four biological replicates of rIL-1β stimulated cells aRNA were labelled with Cy3 dye and a control consisting of four biological replicates of control cells aRNA was labelled with Cy5 dye. Each rIL-1β stimulated aRNA was hybridised against the control. Hybridisations were carried out in a microarray hybridisation oven (Agilent) overnight (18 h) at 65°C. Following hybridisation the slides were washed in the gene expression wash buffers 1 and 2 (Agilent) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The slides were scanned using a GenePix personal 4100A scanner (axon Instruments) at a resolution of 5 μm. Files saved as *. TIF files were extracted using feature extraction software v9.5.3 (Agilent) and background correction and normalization were carried out within this program. Statistical analysis was performed using the Genespring GX analysis platform (version 9.5, Agilent Technologies). Significant differences between IL-1β stimulated cells and control cells were established by t-test analysis (P < 0.05) followed by correction for multiple tests (Benjamini Hochberg FDR post hoc test). Further filtering was carried out to maintain only those genes that showed a ≥2 fold difference in expression as a result of the stimulation. The raw hybridisations data have been deposited at ArrayExpress under accession number (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpres, E-MTAB-1692).
Gene ontology (GO) enrichment was carried out on all features with associated GO identifiers using GOEAST software [116]. Fishers exact test was used within the GOEAST program to determine if the GO identifiers occurred significantly more often in a group than would be expected by chance. The output from GOEAST was entered into the software REVIGO [117] to remove redundant GOs.
Gene expression analysis by real time PCR
For cDNA synthesis total RNA (500 ng) was added to 1 μl of oligo-dT17 (500 ng μl-1) and RNase/DNase free water (Sigma-Aldrich) up to a volume of 11 μl, then denatured for 3 min at 70°C and cooled on ice. To each of these denatured RNA samples was added 1 μl of Bioscript reverse transcriptase enzyme (10000U μl, Bioline), 5 μl of 5x reaction buffer, 1 μl of deoxynucleoside triphosphate mix (12.5 mM each, Bioline) and 7 μl of RNase/DNase free water (Sigma-Aldrich) and the mix incubated at 42°C for 1.5 h in a final volume of 25 μl. The cDNA was diluted 4-fold to 100 μl in 1x TE. (Sigma-Aldrich). qPCR amplifications were performed using 3 μl cDNA, 2x Sybr Green PCR master mix (Biorad) and gene specific primers (Table 7) at 10 μM, with a final reaction volume of 20 μl in 96 well plates in an Opticon real time PCR machine. A typical qPCR cycle used was an initial denaturation for 5 min at 95°C followed by 30-40 cycles of 30 sec at 94°C, 30 sec at 55°C, 30 sec at 72°C, and a final 5 sec at 80°C in which the machine read the plate. The number of cycles used was varied depending upon the expression level of the gene under study. The annealing and measuring temperature was also varied depending upon the primers being used. To calculate the relative quantities of the gene of interest in each sample the standard curve method of relative quantification was used. A dilution series of cDNA diluted 1, 10, 100 and 1000 times was run in each plate to provide a standard curve which was used to calculate primer efficiency to ensure efficiency between 1.8 and 2. Next a linear regression was applied to the standard curve with the subsequent formulas being used to interpolate the relative amount of the gene of interest in the samples [118]. Negative control PCRs were run on all plates. For normalization three “house keeping genes” previously found to be stable during immune reactions in fish, namely elongation factor 1α, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT1) and RNA polymerase 1 (RPL1) were used. The arbitrary units of each individual house keeping gene were normalized to give an average value of 100 to account for different expression levels of the genes, a geometric mean of the arbiatry units of the three housekeeping genes was taken and used for normalization of genes of interest. None of these three genes were found to show any difference in expression over the experiment. For the comparison between microarray expression and qPCR one way T-tests were used to establish if a difference between stimulated and control samples was significant at P ≤ 0.05. For the subsequent qPCR experiments significant differences were established using one way ANOVAs with a Fishers post hoc test to control for multiple testing. Statistics were performed on log transformed arbitrary units. Fold was calculated by division of experimental sample arbitrary units by the average of the control. In the case of negative fold changes below 1, the number was inverted to give a negative fold change.
Table 7.
Primers used for qPCR
| Name 1 | Accession 2 | Sequence 5′ to 3′ | bp 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF-1α |
AF498320.1 |
F |
CAAGGATATCCGTCGTGGCA |
327 |
| |
|
R |
ACAGCGAAACGACCAAGAGG |
|
| RPL1 |
CB516726 |
F |
ACTATGGCTGTCGAGAAGGTGCT |
118 |
| |
|
R |
TGTACTCGAACAGTCGTGGGTCA |
|
| HPRT1 |
EG866745 |
F |
CCGCCTCAAGAGCTACTGTAAT |
255 |
| |
|
R |
GTCTGGAACCTCAAACCCTATG |
|
| IL-1β |
AJ223954.1 |
F |
GCTGGAGAGTGCTGTGGAAGAACATATAG |
179 |
| |
|
R |
CCTGGAGCATCATGGCGTG |
|
| Hepcidin |
NM_001140849.1 |
F |
CATTGAAAATCGTGCATTGG |
150 |
| |
|
R |
AGGCCTTCATTCTCGGTTTT |
|
| IGFBP-6 |
DQ190459.2 |
F |
GCTCAATAGTGTTCTGCGTGG |
118 |
| |
|
R |
CTTGGAGGAACGACACTGCTT |
|
| TNFα1 |
NM_001123589.1 |
F |
TGTGTGGCGTCCTCTTAGTAGCAGCTT |
101 |
| |
|
R |
CTCCATTTTGTCCTGCATCGTTGC |
|
| IGFBP-4 |
EU861007 |
F |
TGTCGTGCTGAGCTGCAGAG |
129 |
| |
|
R |
TGGCTGGCACTGCTTGGCAT |
|
| IGFBP-5.2 |
EU861009 |
F |
TTCTCCAGAGGAAGCTATGTTAG |
170 |
| |
|
R |
TCAAGGCTGCTGACAGAGTG |
|
| Myf5 |
TC97553 |
F |
CGCATACCGCTTTTACTTCC |
245 |
| |
|
R |
TGATCATGAGAAACGTGAAGC |
|
| High choriolytic enzyme |
TC63579 |
F |
ATCAATGGGGCTCATCTCAG |
239 |
| |
|
R |
ATGAGCAAACACGCAGTGAC |
|
| Atrogin-1 |
GU456729.1 |
F |
CGAGTGCTTCCAGGAGAATCTG |
384 |
| R | GTCTGAAGGAGCTCCTTGATGG |
List of primers used in qPCR, all primers were checked to ensure that they had an efficiency of between 1.8 & 2.0. All except for Atrogin 1 were used for qPCR confirmation of the microarray.1Identity of the gene, 2 Accession number of the cDNA sequence, 3Size of PCR product produced by the primers.
Availability of supporting data
The microarray data is submitted to Array express public archive (E-MTAB-1692). Other supporting data is as supplementary files attached to this paper.
Competing interests
The authors do not have any competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
NJP performed the cell culture stimulations, microarray data analysis, real time PCR and wrote the manuscript. LT carried out the microarray hybridizations CJS and SAMM conceived and designed the experiment and drafted the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
The genes shown were significant at p < 0.05 following t- tests & Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and greater than 2-fold change. 1Indicates the unique code for the feature on the microarray, 2Accession number of the cDNA sequence. 3Fold-change for genes higher or lower expressed in cells stimulated with rIL-1β compared to control. 4Regulation of fold change. 5Identity of the probe target as determined by BLASTX & BLASTN search.
Scatter plot showing comparative expression of genes from the microarray (n = 4) and qPCR (n = 4). The mean value was used in situations where a gene appeared multiple times on the microarray. Regression analysis found the expression levels for these 8 genes were significantly correlated between microarray and qPCR (p = 0.001).
Contributor Information
Nicholas J Pooley, Email: r02njp9@abdn.ac.uk.
Luca Tacchi, Email: ltacchi@unm.edu.
Christopher J Secombes, Email: c.secombes@abdn.ac.uk.
Samuel AM Martin, Email: sam.martin@abdn.ac.uk.
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by BBSRC studentship for NJP at the University of Aberdeen. We thank Dr Jun Zou for providing the recombinant IL-1β protein used for stimulations.
References
- Pallafacchina G, Blaauw B, Schiaffino S. Role of satellite cells in muscle growth and maintenance of muscle mass. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2012. pp. 1–7. In Press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Seiliez I, Panserat S, Lansard M, Polakof S, Plagnes-Juan E, Surget A, Dias K, Larquier M, Kaushik S, Skiba-Cassy S. Dietary carbohydrate-to-protein ratio affects TOR signaling and metabolism-related gene expression in the liver and muscle of rainbow trout after a single meal. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300:R733–R743. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00579.2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston IA, Bower NI, Macqueen DJ. Growth and the regulation of myotomal muscle mass in teleost fish. J Exp Biol. 2011;214:1617–1628. doi: 10.1242/jeb.038620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skiba-Cassy S, Lansard M, Panserat S, Médale F. Rainbow trout genetically selected for greater muscle fat content display increased activation of liver TOR signaling and lipogenic gene expression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;297:R1421–R1429. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00312.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N, Sonenberg N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1926–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.1212704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao PR, Kim HJ, Lecker SH. Ubiquitin-protein ligases in muscle wasting. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:2088–2097. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht E, Aguado C, Cárcel J, Esteban I, Esteve JM, Ghislat G, Moruno JF, Vidal JM, Sáez R. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian cells: recent developments. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66:2427–2443. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0030-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldo P, Sandri M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6:25–39. doi: 10.1242/dmm.010389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller S, Dennemärker J, Reinheckel T. Specific functions of lysosomal proteases in endocytic and autophagic pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1824;2012:34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Yuan J. Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene. 2008;27:6194–6206. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y, Sorimachi H. Calpains: an elaborate proteolytic system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1824;2012:224–236. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower NI, Johnston IA. Transcriptional regulation of the IGF signaling pathway by amino acids and insulin-like growth factors during myogenesis in Atlantic salmon. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin SAM, Blaney S, Bowman AS, Houlihan DF. Ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent proteolysis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effect of food deprivation. Pflügers Archiv Eur J Physiol. 2002;445:257–266. doi: 10.1007/s00424-002-0916-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem M, Kenney PB, Rexroad CE III, Yao J. Proteomic signature of muscle atrophy in rainbow trout. J Proteomics. 2010;73:778–789. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2009.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overturf K, Gaylord TG. Determination of relative protein degradation activity at different life stages in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;152:150–160. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2008.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiliez I, Panserat S, Skiba-Cassy S, Fricot A, Vachot C, Kaushik S, Tesseraud S. Feeding status regulates the polyubiquitination step of the ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent proteolysis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) muscle. J Nutr. 2008;138:487–491. doi: 10.1093/jn/138.3.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Requeni P, de Vareilles M, Kousoulaki K, Jordal A-EO, Conceição LEC, Rønnestad I. Whole body proteome response to a dietary lysine imbalance in zebrafish Danio rerio. Comp Biochem Physiol D Genomics Proteomics. 2011;6:178–186. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2011.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mommsen TP. Salmon spawning migration and muscle protein metabolism: the August Krogh principle at work. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;139:383–400. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2004.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevrøy EM, Azpeleta C, Shimizu M, Lanzén A, Kaiya H, Espe M, Olsvik PA. Effects of short-term starvation on ghrelin, GH-IGF system, and IGF-binding proteins in Atlantic salmon. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2011;37:217–232. doi: 10.1007/s10695-010-9434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower NI, Li X, Taylor R, Johnston IA. Switching to fast growth: the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system in skeletal muscle of Atlantic salmon. J Exp Biol. 2008;211:3859–3870. doi: 10.1242/jeb.024117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil C, Lebret V, Gabillard J-C. The IGF/IGFBP system in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) adipose tissue: expression related to regional localization and cell type. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2011;37:843–852. doi: 10.1007/s10695-011-9482-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland BM, Weber GM. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin, and leucine on protein turnover and ubiquitin ligase expression in rainbow trout primary myocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010;298:R341–R350. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00516.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amaral IPG, Johnston IA. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signalling and genome-wide transcriptional regulation in fast muscle of zebrafish following a single-satiating meal. J Exp Biol. 2011;214:2125–2139. doi: 10.1242/jeb.053298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons DR. Role of IGF-I in skeletal muscle mass maintenance. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20:349–356. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell DS, Baehr LM, van den Brandt J, Johnsen SA, Reichardt HM, Furlow JD, Bodine SC. The glucocorticoid receptor and FOXO1 synergistically activate the skeletal muscle atrophy-associated MuRF1 gene. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;295:E785–E797. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00646.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor JC, McCusker RH, Strle K, Johnson RW, Dantzer R, Kelley KW. Regulation of IGF-I function by proinflammatory cytokines: at the interface of immunology and endocrinology. Cell Immunol. 2008;252:91–110. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2007.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabler NK, Spurlock ME. Integrating the immune system with the regulation of growth and efficiency. J Anim Sci. 2008;86:E64–E74. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost RA, Nystrom GJ, Jefferson LS, Lang CH. Hormone, cytokine, and nutritional regulation of sepsis-induced increases in atrogin-1 and MuRF1 in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292:E501–E512. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00359.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N, Yoshikawa N, Ito N, Maruyama T, Suzuki Y, Takeda S, Nakae J, Tagata Y, Nishitani S, Takehana K, Sano M, Fukuda K, Suematsu M, Morimoto C, Tanaka H. Crosstalk between glucocorticoid receptor and nutritional sensor mTOR in skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2011;13:170–182. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker SH, Goldberg AL, Mitch WE. Protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in normal and disease states. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1807–1819. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006010083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W, Moylan JS, Chambers MA, Smith J, Reid MB. Interleukin-1 stimulates catabolism in C2C12 myotubes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297:C706–C714. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00626.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale MJ. Mechanisms of cancer cachexia. Physiol Rev. 2009;89:381–410. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00016.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad F, Zaldivar F, Cooper DM, Adams GR. IL-6-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. J Appl Physiol. 2005;98:911–917. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01026.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkar N, Wang J, Ladner KJ, Wang H, Dahlman JM, Carathers M, Acharyya S, Rudnicki MA, Hollenbach AD, Guttridge DC. IKK/NF-κB regulates skeletal myogenesis via a signaling switch to inhibit differentiation and promote mitochondrial biogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2008;180:787–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200707179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttridge DC. NF-κB-induced loss of MyoD messenger RNA: Possible role in muscle decay and cachexia. Science. 2000;289:2363–2366. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5488.2363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY, Pestell RG, Baldwin AS Jr. NF-κ B controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:5785–5799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.8.5785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams GR. Insulin-like growth factor I signaling in skeletal muscle and the potential for cytokine interactions. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42:50–57. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181b07d12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broussard SR, McCusker RH, Novakofski JE, Strle K, Shen W-H, Johnson RW, Freund GG, Dantzer R, Kelley KW. Cytokine-hormone interactions: tumor necrosis factor α impairs biologic activity and downstream activation signals of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor in myoblasts. Endocrinology. 2003;144:2988–2996. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D, Zheng H, Zhou Y, Tang X, Yu B, Li J. Association of IL-1beta gene polymorphism with cachexia from locally advanced gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acharyya S, Ladner KJ, Nelsen LL, Damrauer J, Reiser PJ, Swoap S, Guttridge DC. Cancer cachexia is regulated by selective targeting of skeletal muscle gene products. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:370–378. doi: 10.1172/JCI20174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin SAM, Douglas A, Houlihan DF, Secombes CJ. Starvation alters the liver transcriptome of the innate immune response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) BMC Genomics. 2010;11:418. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower NI, Taylor RG, Johnston IA. Phasing of muscle gene expression with fasting-induced recovery growth in Atlantic salmon. Front Zool. 2009;6:18. doi: 10.1186/1742-9994-6-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem M, Kenney PB, Rexroad CE III, Yao J. Microarray gene expression analysis in atrophying rainbow trout muscle: a unique nonmammalian muscle degradation model. Physiol Genomics. 2006;28:33–45. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00114.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen KA, Sealey WM, Overturf K. The effects of chronic immune stimulation on muscle growth in rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;144:520–531. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2006.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacchi L, Bickerdike R, Secombes CJ, Pooley NJ, Urquhart KL, Collet B, Martin SAM. Ubiquitin E3 ligase atrogin-1 (Fbox-32) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): sequence analysis, genomic structure and modulation of expression. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2010;157:364–373. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood. 2011;117:3720–3732. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-273417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allantaz F, Chaussabel D, Banchereau J, Pascual V. Microarray-based identification of novel biomarkers in IL-1-mediated diseases. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:623–632. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam S, Stansberg C, Cunningham C. The interleukin 1 receptor family. Dev Comp Immunol. 2004;28:415–428. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2003.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W-N, Luo S-F, Lee C-W, Wang C-C, Wang J-S, Yang C-M. Involvement of MAPKs and NF-κB in LPS-induced VCAM-1 expression in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal. 2007;19:1258–1267. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis MIR, do Vale A, Pereira PJB, Azevedo JE, dos Santos NMS. Caspase-1 and IL-1β processing in a teleost fish. PLoS One. 2012;7:e50450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angosto D, López-Castejón G, López-Muñoz A, Sepulcre MP, Arizcun M, Meseguer J, Mulero V. Evolution of inflammasome functions in vertebrates: Inflammasome and caspase-1 trigger fish macrophage cell death but are dispensable for the processing of IL-1β. Innate Immun. 2012;18:815–824. doi: 10.1177/1753425912441956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtech LN, Scharping N, Woodson JC, Hansen JD. Roles of inflammatory caspases during processing of zebrafish interleukin-1β in Francisella noatunensis infection. Infect Immun. 2012;80:2878–2885. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00543-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M, Bird S, van Zwieten R, Secombes CJ, Wang T. Cloning of the IL-1β3 gene and IL-1β4 pseudogene in salmonids uncovers a second type of IL-1β gene in teleost fish. Dev Comp Immunol. 2012;38:431–446. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2012.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison RN, Young ND, Nowak BF. Description of an Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) type II interleukin-1 receptor cDNA and analysis of interleukin-1 receptor expression in amoebic gill disease-affected fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012;32:1185–1190. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2012.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Castejón G, Sepulcre MP, Roca FJ, Castellana B, Planas JV, Meseguer J, Mulero V. The type II interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1RII) of the bony fish gilthead seabream Sparus aurata is strongly induced after infection and tightly regulated at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:2772–2780. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass DJ. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy signaling pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:1974–1984. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S, Zou J, Crampe M, Peddie S, Scapigliati G, Bols N, Cunningham C, Secombes CJ. The production and bioactivity of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) recombinant IL-1β. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001;81:1–14. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2427(01)00328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin SAM, Zou J, Houlihan DF, Secombes CJ. Directional responses following recombinant cytokine stimulation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) RTS-11 macrophage cells as revealed by transcriptome profiling. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:150. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. The IκB kinase (IKK) complex as a critical regulator of immune responses. Int Congr Ser. 2005;1285:97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sun SC, Ganchi PA, Ballard DW, Greene WC. NF-kB controls expression of inhibitor IkBa: Evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science. 1993;259:1912–1915. doi: 10.1126/science.8096091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T, Sasaki M, Elia AJ, Chio IIC, Hamada K, Fukunaga R, Mak TW. Combined deficiency for MAP kinase-interacting kinase 1 and 2 (Mnk1 and Mnk2) delays tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:1–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008136107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomard T, Michaud H-A, Tempé D, Thiolon K, Pelegrin M, Piechaczyk M. An NF-κB-dependent role for JunB in the induction of proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-activated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffaello A, Milan G, Masiero E, Carnio S, Lee D, Lanfranchi G, Goldberg AL, Sandri M. JunB transcription factor maintains skeletal muscle mass and promotes hypertrophy. J Cell Biol. 2010;191:101–113. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201001136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T, Gorgoglione B, Maehr T, Holland JW, Vecino JLG, Wadsworth S, Secombes CJ. Fish suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS): gene discovery, modulation of expression and function. J Signal Transduc. 2011;2011:905813. doi: 10.1155/2011/905813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn AM, Hershko C. Ferritin Synthesis in Inflammation. Br J Haematol. 1977;37:7–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Domenico I, Zhang TY, Koening CL, Branch RW, London N, Lo E, Daynes RA, Kushner JP, Li D, Ward DM, Kaplan J. Hepcidin mediates transcriptional changes that modulate acute cytokine-induced inflammatory responses in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:2395–2405. doi: 10.1172/JCI42011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi J, Camus AC. Hepcidins in amphibians and fishes: Antimicrobial peptides or iron-regulatory hormones? Dev Comp Immunol. 2006;30:746–755. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2005.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuesta A, Meseguer J, Esteban MA. The antimicrobial peptide hepcidin exerts an important role in the innate immunity against bacteria in the bony fish gilthead seabream. Mol Immunol. 2008;45:2333–2342. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewart K, Johnson SC, Ross NW. Lectins of the innate immune system and their relevance to fish health. ICES J Mar Sci. 2001;58:380–385. doi: 10.1006/jmsc.2000.1020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Magnadóttir B. Innate immunity of fish (overview) Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006;20:137–151. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2004.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasta GR, Nita-Lazar M, Giomarelli B, Ahmed H, Du S, Cammarata M, Parrinello N, Bianchet MA, Amzel LM. Structural and functional diversity of the lectin repertoire in teleost fish: relevance to innate and adaptive immunity. Dev Comp Immunol. 2011;35:1388–1399. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2011.08.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne CJ, Gerwick L, Fujiki K, Nakao M, Yano T. Immune-relevant (including acute phase) genes identified in the livers of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, by means of suppression subtractive hybridization. Dev Comp Immunol. 2001;25:205–217. doi: 10.1016/S0145-305X(00)00057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salem M, Silverstein J, Rexroad CE III, Yao J. Effect of starvation on global gene expression and proteolysis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) BMC Genomics. 2007;8:328. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescan P-Y, Montfort J, Rallière C, Le Cam A, Esquerré D, Hugot K. Dynamic gene expression in fish muscle during recovery growth induced by a fasting-refeeding schedule. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:438. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland BM, Weber GM. Effects of sex steroids on indices of protein turnover in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) white muscle. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2011;174:132–142. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2011.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacchi L, Bickerdike R, Secombes CJ, Martin SAM. Muscle-specific RING finger (MuRF) cDNAs in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and their role as regulators of muscle protein degradation. Mar Biotechnol (New York, N.Y.) 2012;14:35–45. doi: 10.1007/s10126-011-9385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benanti JA. Coordination of cell growth and division by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23:492–498. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2012.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Floc’h N, Melchior D, Obled C. Modifications of protein and amino acid metabolism during inflammation and immune system activation. Livest Prod Sci. 2004;87:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.livprodsci.2003.09.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Riccio M, Di Giaimo R, Pianetti S, Palmieri PP, Melli M, Santi S. Nuclear localization of cystatin B, the cathepsin inhibitor implicated in myoclonus epilepsy (EPM1) Exp Cell Res. 2001;262:84–94. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.5085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C, Gersch RP, Hawke TJ, Hadjiargyrou M. Silencing of Mustn1 inhibits myogenic fusion and differentiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;298:C1100–C1108. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00553.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyen C, Goudenege S, Poussard S, Sassi AH, Brustis J-J, Cottin P. Involvement of micro-calpain (CAPN 1) in muscle cell differentiation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:728–743. doi: 10.1016/S1357-2725(03)00265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y-A, Choi HM, Lee S-H, Hong S-J, Yang H-I, Yoo MC, Kim KS. Hypoxia differentially affects IL-1β-stimulated MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in an HIF-1α-dependent manner. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012;51:443–450. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Z, Yang H, Bau B, Söder S, Aigner T. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NFκB on IL-1β-induced effects on collagen type II, MMP-1 and 13 mRNA expression in normal articular human chondrocytes. Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:900–903. doi: 10.1007/s00296-006-0114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak PP, Firestein GS. NF-κB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:7–11. doi: 10.1172/JCI11830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink M, Price SR, Chrast J, Bailey JL, Anwar A, Mitch WE, Delafontaine P. Angiotensin II induces skeletal muscle wasting through enhanced protein degradation and down-regulates autocrine insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 2001;142:1489–1496. doi: 10.1210/en.142.4.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell ST, Wyke SM, Tisdale MJ. Mechanism of induction of muscle protein degradation by angiotensin II. Cell Signal. 2006;18:1087–1096. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan C, Ren H, Gao S. Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF receptors, and IGF-binding proteins: Roles in skeletal muscle growth and differentiation. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2010;167:344–351. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macqueen DJ, Garcia de la Serrana D, Johnston IA. Evolution of ancient functions in the vertebrate insulin-like growth factor system uncovered by study of duplicated salmonid fish genomes. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:1060–1076. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach LA. IGFBP-6 five years on; not so “forgotten”? Growth Horm IGF Res. 2005;15:185–192. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2005.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi A, Sakuma K, Fujikawa T, Morita I. Expression of specific IGFBPs is associated with those of the proliferating and differentiating markers in regenerating rat plantaris muscle. J Physiol Sci. 2013;63:71–77. doi: 10.1007/s12576-012-0227-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan C, Xu Q. Roles of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins in regulating IGF actions. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2005;142:44–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2004.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iosef C, Vilk G, Gkourasas T, Lee K-J, Chen BPC, Fu P, Bach LA, Lajoie G, Gupta MB, Li SSC, Han VK. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 (IGFBP-6) interacts with DNA-end binding protein Ku80 to regulate cell fate. Cell Signal. 2010;22:1033–1043. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabillard J-C, Kamangar BB, Montserrat N. Coordinated regulation of the GH/IGF system genes during refeeding in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) J Endocrinol. 2006;191:15–24. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin P, Xu Q, Duan C. Paradoxical actions of endogenous and exogenous insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 revealed by RNA interference analysis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:32660–32666. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401378200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen DL, Cleary AS, Hanson AM, Lindsay SF, Reed JM. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-δ expression is increased in fast skeletal muscle by food deprivation and regulates myostatin transcription in vitro. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010;299:R1592–R1601. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00247.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L, Wang L, Lu L, Jiang P, Sun H, Wang H. A novel target of microRNA-29, Ring1 and YY1-binding protein (Rybp), negatively regulates skeletal myogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:25255–25265. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.357053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinits Y, Osborn DPS, Hughes SM. Differential requirements for myogenic regulatory factors distinguish medial and lateral somitic, cranial and fin muscle fibre populations. Development. 2009;136:403–414. doi: 10.1242/dev.028019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Gilbert A, Gomes M, Baracos V, Bailey J, Price SR, Mitch WE, Goldberg AL. Multiple types of skeletal muscle atrophy involve a common program of changes in gene expression. FASEB J. 2004;18:39–51. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0610com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehrs C, Acebron SP. Mitotic and mitogenic Wnt signalling. EMBO J. 2012;31:2705–2713. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein EA, Assoian RK. Transcriptional regulation of the cyclin D1 gene at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:3853–3857. doi: 10.1242/jcs.039131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkar N, Guttridge D. NF-κB signaling: A Tale of Two Pathways in Skeletal Myogenesis. Physiol Rev. 2010;90:495–511. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00040.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G, Bernaudo S, Fu G, Lee DY, Yang BB, Peng C. Cyclin G2 is degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and mediates the antiproliferative effect of activin receptor-like kinase 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:4968–4979. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-03-0259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-gac L, Marqués M, García Z, Campanero MR, Carrera AC. Control of cyclin G2 mRNA expression by forkhead transcription factors: novel mechanism for cell cycle control by phosphoinositide 3-kinase and forkhead. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:2181–2189. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2181-2189.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan J, Nakade K, Huang Y-C, Zhu Z-W, Masuzaki S, Hasegawa H, Murata T, Yoshiki A, Yamaguchi N, Lee C-H, Yang W-C, Tsai E-M, Obata Y, Yokoyama KK. Suppression of cell-cycle progression by Jun dimerization protein-2 (JDP2) involves downregulation of cyclin-A2. Oncogene. 2010;29:6245–6256. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T, Geisen C. Cyclin E. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:1424–1439. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2003.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong D, Ferrell J. The roles of cyclin A2, B1, and B2 in early and late mitotic events. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:3149–3161. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-05-0393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhollebeke B, Pays E. The function of apolipoproteins L. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63:1937–1944. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6091-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H, Eckel RH. Lipoprotein lipase: from gene to obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;297:E271–E288. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90920.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said FA, Werts C, Elalamy I, Couetil J, Jacquemin C, Hatmi M. TNF-α, inefficient by itself, potentiates IL-1β-induced PGHS-2 expression in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells: requirement of NF-kB and p38 MAPK pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 2002;136:1005–1014. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vraskou Y, Roher N, Díaz M, Antonescu CN, MacKenzie SA, Planas JV. Direct involvement of tumor necrosis factor-α in the regulation of glucose uptake in rainbow trout muscle cells. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300:R716–R723. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00514.2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehoux M, Gobier C, Lause P, Bertrand L, Ketelslegers J-M, Thissen J-P. IGF-I does not prevent myotube atrophy caused by proinflammatory cytokines despite activation of Akt/Foxo and GSK-3β pathways and inhibition of atrogin-1 mRNA. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292:E145–E150. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00085.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vegusdal A, Østbye TK, Tran T, Gjøen T, Ruyter B. B-oxidation, esterification and secretion of radiolabeled fatty acids in cultivated Atlantic Salmon skeletal muscle cells. Lipids. 2004;39:649–658. doi: 10.1007/s11745-004-1278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschak TW, Stickland NC. The growth of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) myosatellite cells in culture at two different temperatures. Experientia. 1995;51:260–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01931109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koumans JTM, Akster HA, Dulos GJ, Osse JWM. Myosatellite cells of Cyprinus carpio (Teleostei) in vitro: isolation, recognition and differentiation. Cell Tissue Res. 1990;261:173–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00329450. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tacchi L, Bickerdike R, Douglas A, Secombes CJ, Martin SAM. Transcriptomic responses to functional feeds in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011;31:704–715. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2011.02.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Q, Wang X-J. GOEAST: a web-based software toolkit for Gene Ontology enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W358–W363. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N, Šmuc T. REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS One. 2011;6:e21800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookout AL, Cummins CL, Kramer MF, Pesola JM, Mangelsdorf DJ. High-Throughput Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2006;Supplement:15.8.1–15.8.28. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1508s73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The genes shown were significant at p < 0.05 following t- tests & Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and greater than 2-fold change. 1Indicates the unique code for the feature on the microarray, 2Accession number of the cDNA sequence. 3Fold-change for genes higher or lower expressed in cells stimulated with rIL-1β compared to control. 4Regulation of fold change. 5Identity of the probe target as determined by BLASTX & BLASTN search.
Scatter plot showing comparative expression of genes from the microarray (n = 4) and qPCR (n = 4). The mean value was used in situations where a gene appeared multiple times on the microarray. Regression analysis found the expression levels for these 8 genes were significantly correlated between microarray and qPCR (p = 0.001).