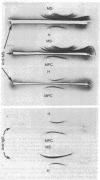
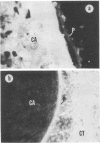
Abstract
We have shown that lymphocyte-myeloma cell hybridization can be used to produce large amounts of extremely high-titer specific antibodies against type I collagen, a macromolecule normally of low immunogenicity. In a passive hemagglutination assay the antibody had a high titer against chicken type I collagen but showed no activity against chicken type II or rat type I collagen. By using a two-step fluorescence histochemical procedure on sections of embryonic chicken tibia, strong fluorescence was observed in the perichondrium and surrounding connective tissue (known to contain type I collagen) but not over the cartilage (characterized by type II collagen). When used in conjunction with Staphylococcus aureus as a solid phase immunoadsorbant, the antibody was shown to bind to labeled collagen synthesized in vitro by embryonic chicken calvaria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balian G., Click E. M., Hermodson M. A., Bornstein P. Structure of rat skin collagen alpha 1-CBB. Amino acid sequence of the hydroxyl amine-produced fragment HA2. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 26;11(20):3798–3806. doi: 10.1021/bi00770a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beil W., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Chicken antibodies to soluble rat collagen. I. Characterization of the immune response by precipitation and agglutination methods. Immunochemistry. 1972 Aug;9(8):779–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P. Comparative sequence studies of rat skin and tendon collagen. I. Evidence for incomplete hydroxylation of individual prolyl residues in the normal proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3082–3093. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. L., Yaeger J. A., Tanzer M. L. Isolation and partial characterization of procollagen fractions produced by a clonal strain of calf dermatosparactic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):785–799. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Immunochemistry of collagens and procollagens. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1976;7:61–99. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363707-9.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Martin G. R., Muller P. K., Timpl R., Kuhn K. Simultaneous synthesis of types I and III collagen by fibroblasts in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4037–4040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Margulies D. H., Scharff M. D. A simple method for polyethylene glycol-promoted hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Mar;3(2):231–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01551818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. Collagen biology: structure, degradation, and disease. Harvey Lect. 1974;68:351–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay E. D., Linsenmayer T. F., Trelstad R. L., von der Mark K. Origin and distribution of collagens in the developing avian cornea. Curr Top Eye Res. 1979;1:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Little C. D. Embryonic neural retina collagen: in vitro synthesis of high molecular weight forms of type II plus a new genetic type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3235–3239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Smith G. N., Jr, Hay E. D. Synthesis of two collagen types by embryonic chick corneal epithelium in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):39–43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Toole B. P., Trelstad R. L. Temporal and spatial transitions in collagen types during embryonic chick limb development. Dev Biol. 1973 Dec;35(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Kuehl W. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic cell hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1652–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Harosi F. I., Leder P. Differentiation in erythroleukemic cells and their somatic hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):98–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundar Raj C. V., Church R. L., Klobutcher L. A., Ruddle F. H. Genetics of the connective tissue proteins: assignment of the gene for human type I procollagen to chromosome 17 by analysis of cell hybrids and microcell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4444–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Solomon E. Assignment of a type I collagen structural gene to human chromosome 7. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):548–549. doi: 10.1038/272548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Linsenmayer T. F. Newer knowledge of skeletogenesis: macromolecular transitions in the extracellular matrix. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977 Nov-Dec;(129):258–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelstad R. L., Kang A. H., Toole B. P., Gross J. Collagen heterogeneity. High resolution separation of native ( 1(I) 2 2 and ( 1(II) 3 and their component chains. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6469–6473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark H., von der Mark K., Gay S. Study of differential collagen synthesis during development of the chick embryo by immunofluorescence. I. Preparation of collagen type I and type II specific antibodies and their application to early stages of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1976 Feb;48(2):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]