Abstract
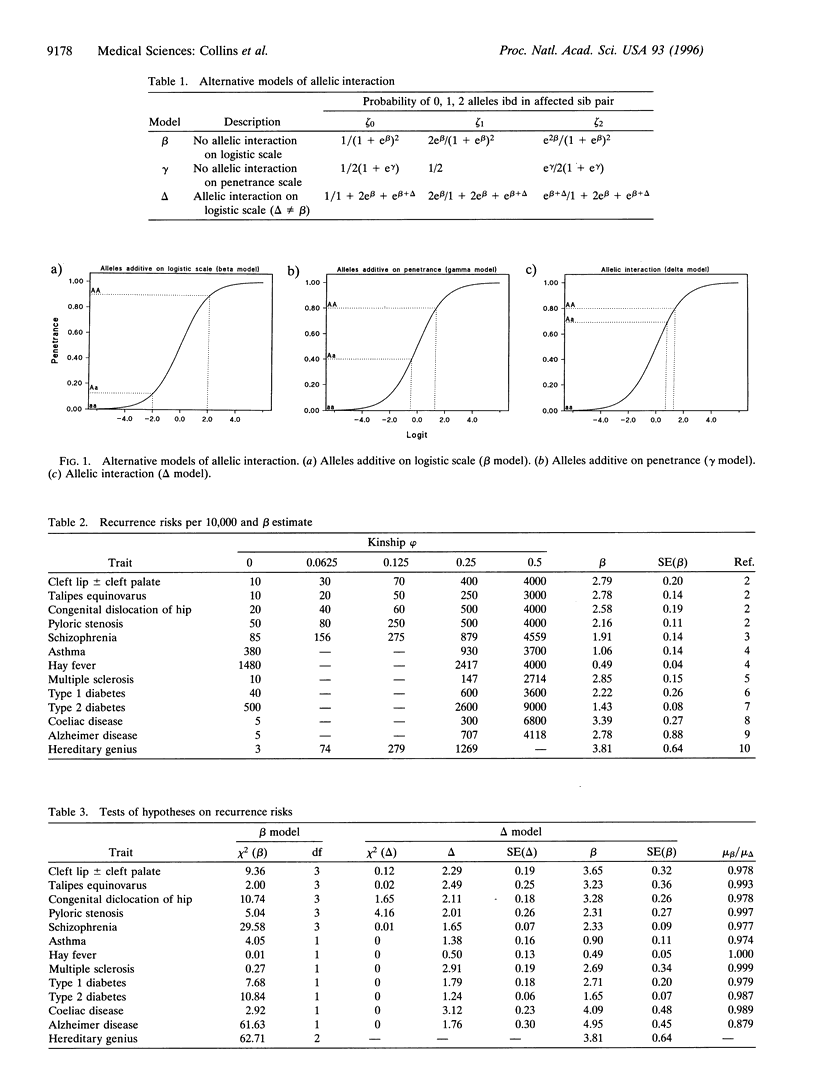
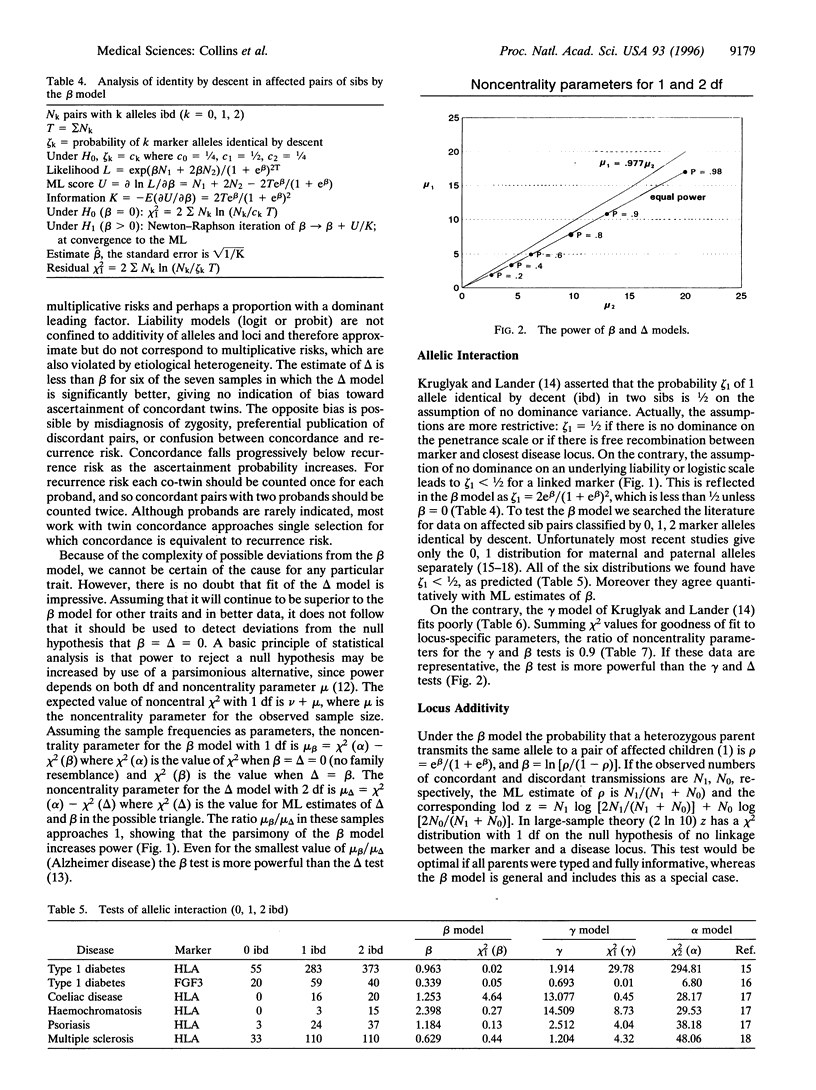
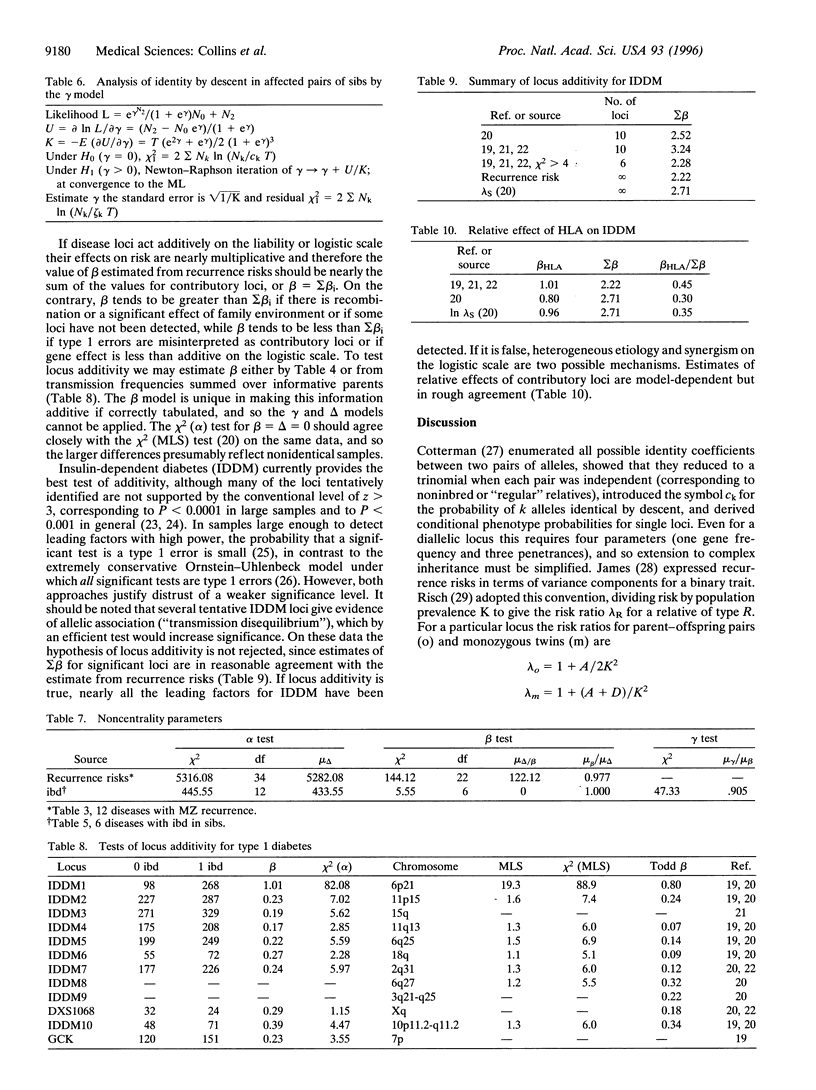
Theoretical advantages of nonparametric logarithm of odds to map polygenic diseases are supported by tests of the beta model that depends on a single logistic parameter and is the only model under which paternal and maternal transmissions to sibs of specified phenotypes are independent. Although it does not precisely describe recurrence risks in monozygous twins, the beta model has greater power to detect family resemblance or linkage than the more general delta model which describes the probability of 0, 1, or 2 alleles identical by descent (ibd) with two parameters. Available data on ibd in sibs are consistent with the beta model, but not with the equally parsimonious but less powerful gamma model that assumes a fixed probability of 1/2 for 1 allele ibd. Additivity of loci on the liability scale is not disproven. A simple equivalence extends the beta model to multipoint analysis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter C. O. Genetics of common disorders. Br Med Bull. 1969 Jan;25(1):52–57. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeman J. B., Cucca F., Hearne C. M., Cornall R. J., Reed P. W., Rønningen K. S., Undlien D. E., Nisticò L., Buzzetti R., Tosi R. Linkage disequilibrium mapping of a type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene (IDDM7) to chromosome 2q31-q33. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):80–85. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. L., Kawaguchi Y., Bennett S. T., Copeman J. B., Cordell H. J., Pritchard L. E., Reed P. W., Gough S. C., Jenkins S. C., Palmer S. M. A genome-wide search for human type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):130–136. doi: 10.1038/371130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Bulman D. E., Sadovnick A. D., Paty D. W., Warren S., Hader W., Murray T. J., Seland T. P., Duquette P., Grey T. A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1638–1642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. L., Tobias R., Magnus T. A locus on chromosome 15q26 (IDDM3) produces susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):189–194. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto L., Habita C., Beressi J. P., Delepine M., Besse C., Cambon-Thomsen A., Deschamps I., Rotter J. I., Djoulah S., James M. R. Genetic mapping of a susceptibility locus for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus on chromosome 11q. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):161–164. doi: 10.1038/371161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. W. Frequency in relatives for an all-or-none trait. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Jul;35(1):47–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1956.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Lander E. S. Complete multipoint sib-pair analysis of qualitative and quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;57(2):439–454. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E., Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs M. L. Emperic risks for genetic counseling in families with allergy. J Pediatr. 1972 Jan;80(1):26–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80448-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E. Logarithm of odds (lods) for linkage in complex inheritance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3471–3476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Rao D. C. Hereditary genius: a centennial problem in resolution of cultural and biological inheritance. Soc Biol. 1980 Spring;27(1):48–52. doi: 10.1080/19485565.1980.9988402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos P., A'Hern R., Heaton D. A., Millward B. A., Risley D., Pyke D. A., Leslie R. D. The significance of the concordance rate for type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes in identical twins. Diabetologia. 1988 Oct;31(10):747–750. doi: 10.1007/BF00274777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Thomson G., Motro U., Louis E. J., Hudes E. The affected sib method. IV. Sib trios. Ann Hum Genet. 1985 Oct;49(Pt 4):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. C., Keats B. J., Morton N. E., Yee S., Lew R. Variability of human linkage data. Am J Hum Genet. 1978 Sep;30(5):516–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Gottesman I. I., Lew R. Path analysis of qualitative data on pairs of relatives: application to schizophrenia. Hum Hered. 1981;31(6):325–333. doi: 10.1159/000153233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. Corrections to "Linkage strategies for genetically complex traits. III. The effect of marker polymorphism on analysis of affected relative pairs". Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Sep;51(3):673–675. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N. Linkage strategies for genetically complex traits. I. Multilocus models. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;46(2):222–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab S. G., Albus M., Hallmayer J., Hönig S., Borrmann M., Lichtermann D., Ebstein R. P., Ackenheil M., Lerer B., Risch N. Evaluation of a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p by multipoint affected sib-pair linkage analysis. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):325–327. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A. Genetic analysis of type 1 diabetes using whole genome approaches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8560–8565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


