Abstract
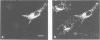
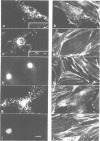
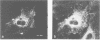
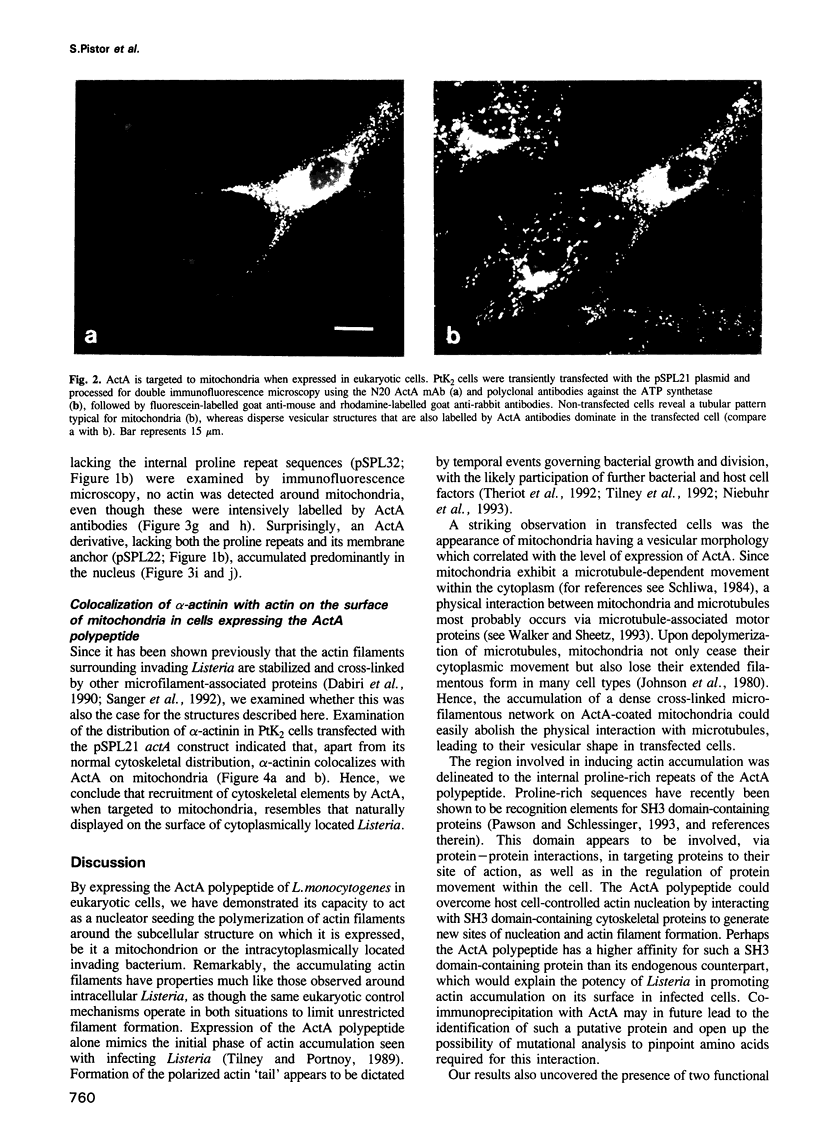
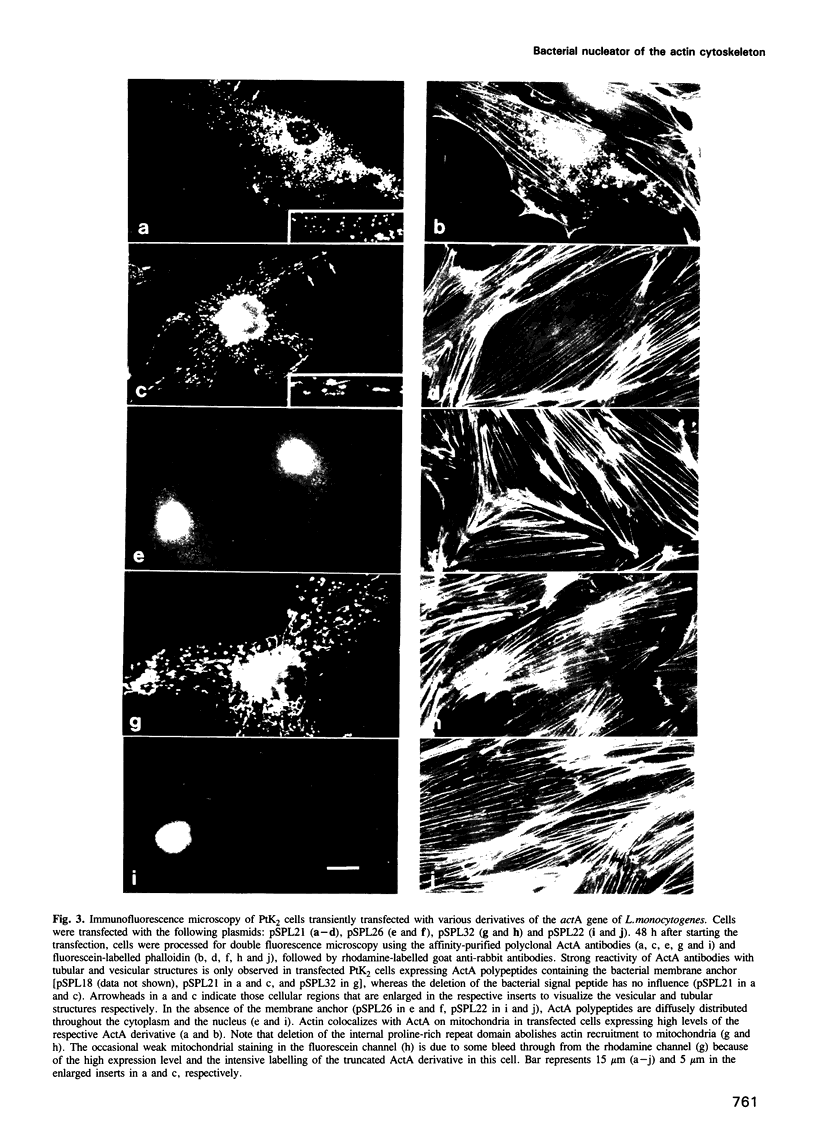
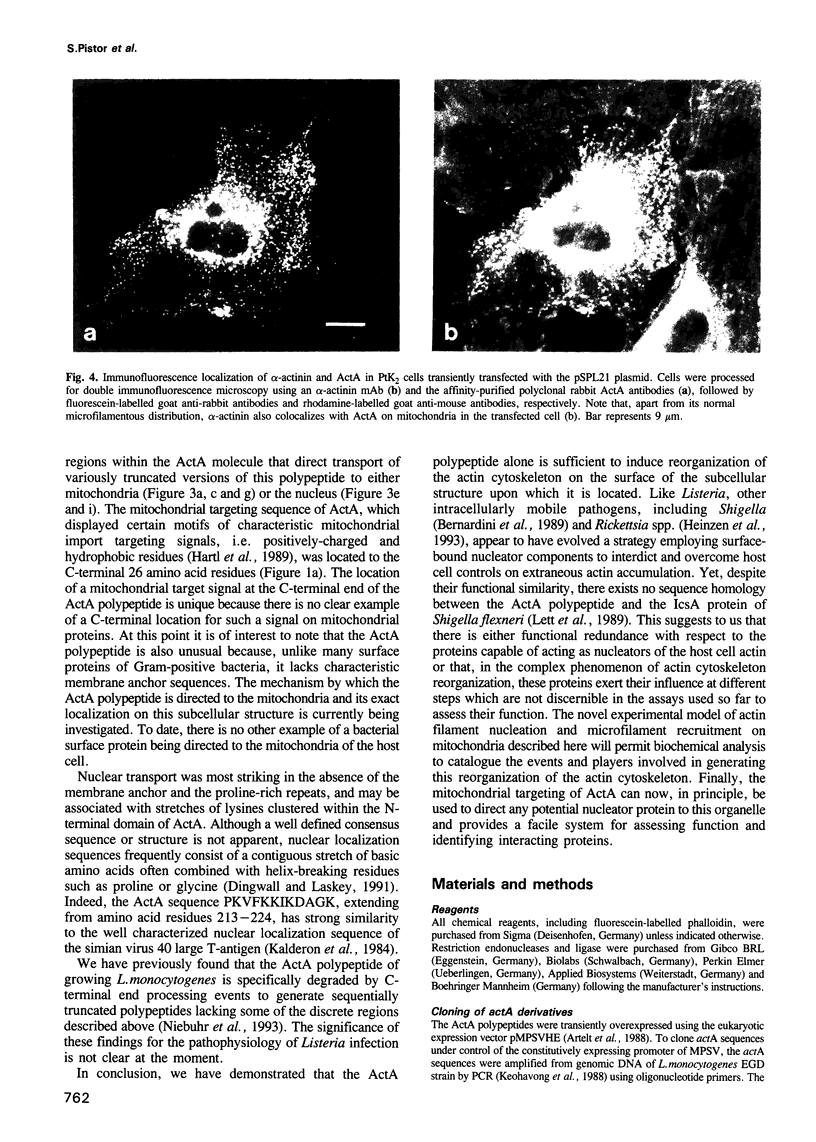
Listeria monocytogenes, a facultative intracellular pathogen, employs actin and other microfilament-associated proteins to move through the host cell cytoplasm. Isogenic mutants of L. monocytogenes lacking the surface-bound ActA polypeptide no longer interact with cytoskeletal elements and are, as a consequence, non-motile (Domann et al., 1992, EMBO J., 11, 1981-1990; Kocks et al., 1992, Cell, 68, 521-531). To investigate the interaction of ActA with the microfilament system in the absence of other bacterial factors, the listerial actA gene was expressed in eukaryotic cells. Immunofluorescence studies revealed that the complete ActA, including its C-terminally located bacterial membrane anchor, colocalized with mitochondria in transfected cells. When targeted to mitochondria, the ActA polypeptide recruited actin and alpha-actinin to these cellular organelles with concomitant reorganization of the microfilament system. Removal of the internal proline-rich repeat region of ActA completely abrogated interaction with cytoskeletal components. Our results identify the ActA polypeptide as a nucleator of the actin cytoskeleton and provide the first insights into the molecular nature of such controlling elements in microfilament organization.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artelt P., Morelle C., Ausmeier M., Fitzek M., Hauser H. Vectors for efficient expression in mammalian fibroblastoid, myeloid and lymphoid cells via transfection or infection. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri G. A., Sanger J. M., Portnoy D. A., Southwick F. S. Listeria monocytogenes moves rapidly through the host-cell cytoplasm by inducing directional actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6068–6072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Wehland J., Rohde M., Pistor S., Hartl M., Goebel W., Leimeister-Wächter M., Wuenscher M., Chakraborty T. A novel bacterial virulence gene in Listeria monocytogenes required for host cell microfilament interaction with homology to the proline-rich region of vinculin. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1981–1990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Pfanner N., Nicholson D. W., Neupert W. Mitochondrial protein import. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):1–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzen R. A., Hayes S. F., Peacock M. G., Hackstadt T. Directional actin polymerization associated with spotted fever group Rickettsia infection of Vero cells. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1926-1935.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Pocklington M. J., Orr E. The F1 ATP synthetase beta-subunit: a major yeast novobiocin binding protein. J Cell Sci. 1990 Aug;96(Pt 4):675–682. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.4.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. V., Walsh M. L., Chen L. B. Localization of mitochondria in living cells with rhodamine 123. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):990–994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Wang C. C., Cha R. S., Thilly W. G. Enzymatic amplification and characterization of large DNA fragments from genomic DNA. Gene. 1988 Nov 15;71(1):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Hellio R., Gounon P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. Polarized distribution of Listeria monocytogenes surface protein ActA at the site of directional actin assembly. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jul;105(Pt 3):699–710. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.3.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett M. C., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Sakai T., Makino S., Yamada M., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. virG, a plasmid-coded virulence gene of Shigella flexneri: identification of the virG protein and determination of the complete coding sequence. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):353–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.353-359.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr K., Chakraborty T., Rohde M., Gazlig T., Jansen B., Köllner P., Wehland J. Localization of the ActA polypeptide of Listeria monocytogenes in infected tissue culture cell lines: ActA is not associated with actin "comets". Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2793–2802. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2793-2802.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W., Southwick F. S. Host cell actin assembly is necessary and likely to provide the propulsive force for intracellular movement of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3609–3619. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3609-3619.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. The rate of actin-based motility of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes equals the rate of actin polymerization. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):257–260. doi: 10.1038/357257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., DeRosier D. J., Weber A., Tilney M. S. How Listeria exploits host cell actin to form its own cytoskeleton. II. Nucleation, actin filament polarity, filament assembly, and evidence for a pointed end capper. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):83–93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Tilney M. S. The wily ways of a parasite: induction of actin assembly by Listeria. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Apr;1(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90021-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., Sheetz M. P. Cytoplasmic microtubule-associated motors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:429–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. A., Ogryzko E. P., Corben E. B., Zhidkova N. I., Patel B., Price G. J., Spurr N. K., Koteliansky V. E., Critchley D. R. Complete sequence of human vinculin and assignment of the gene to chromosome 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5667–5671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]