Abstract
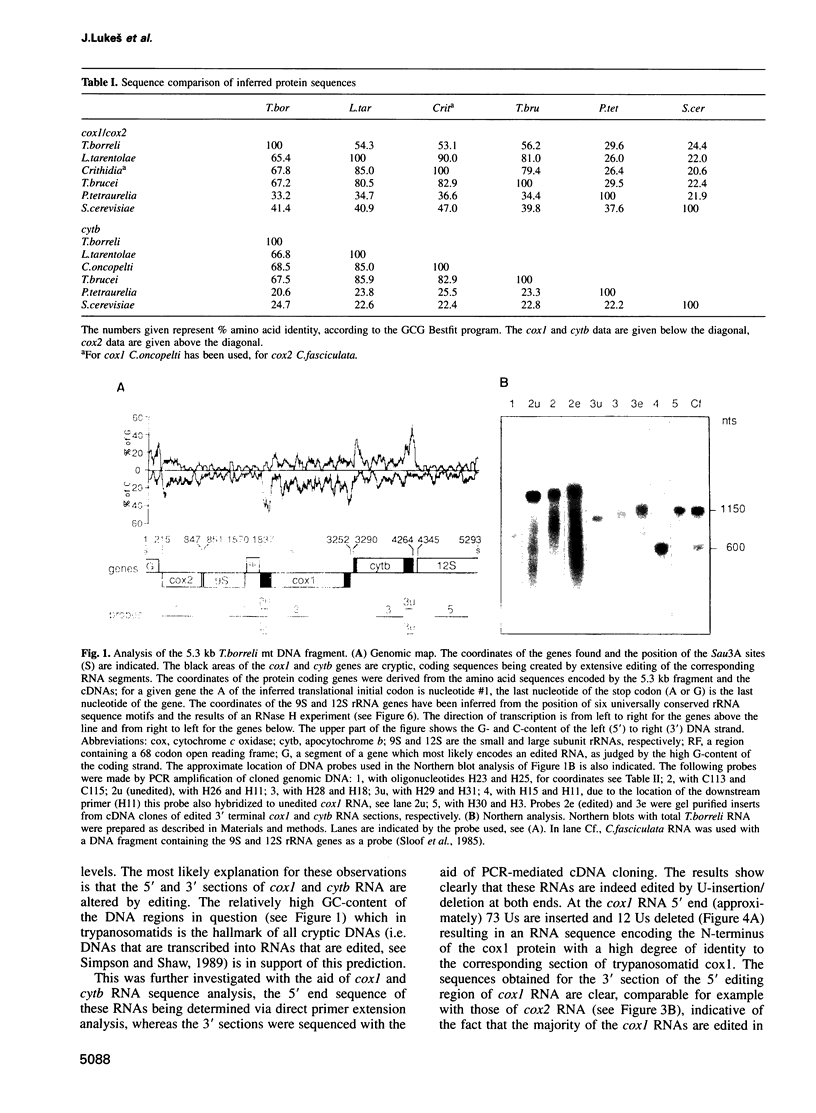
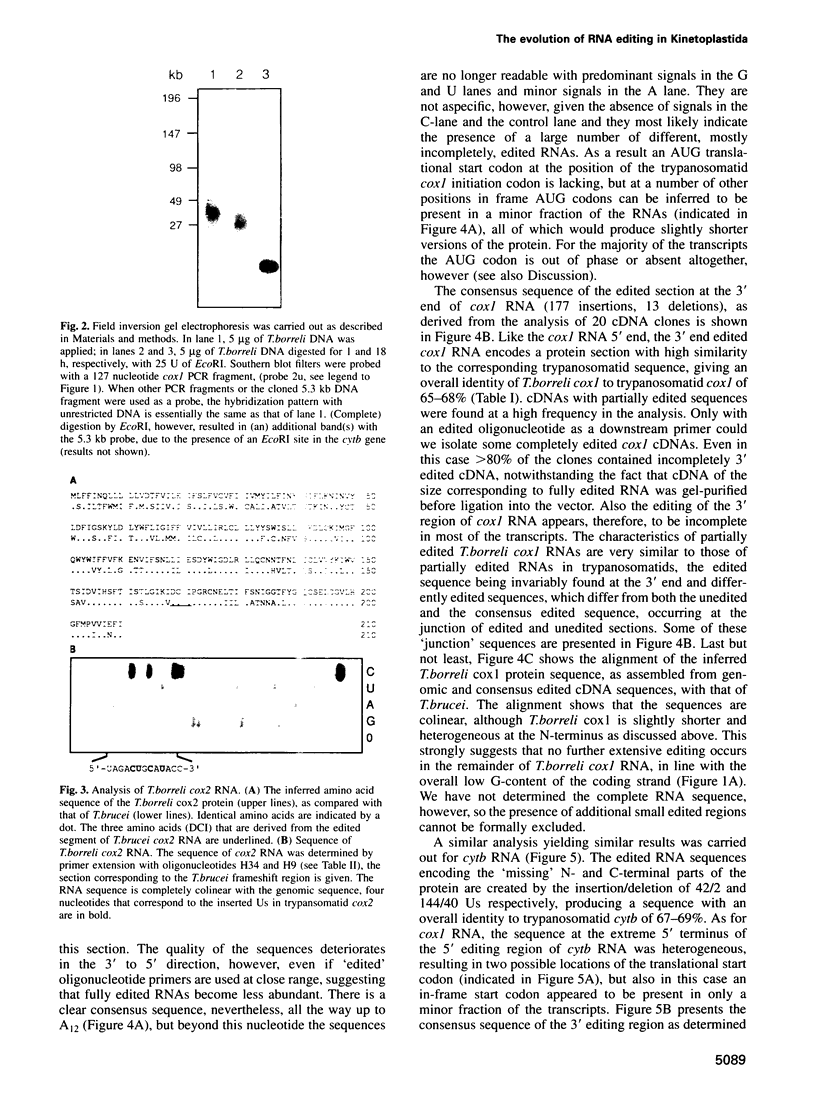
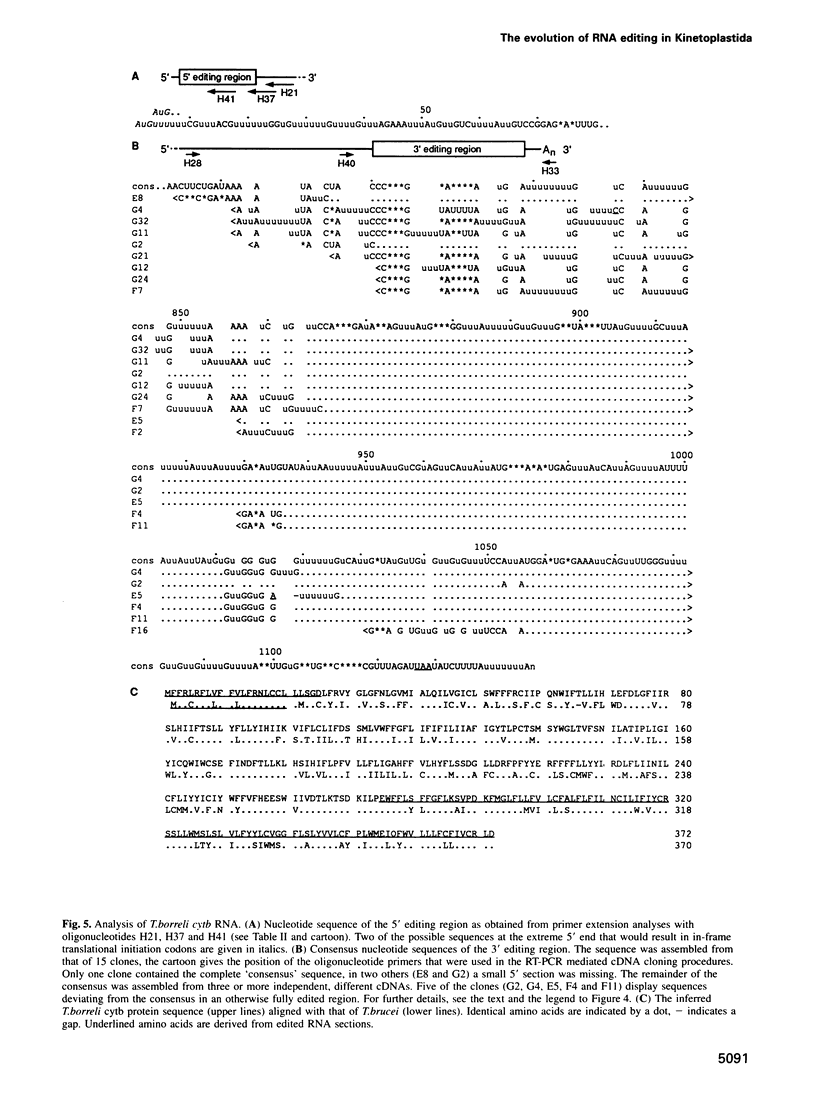
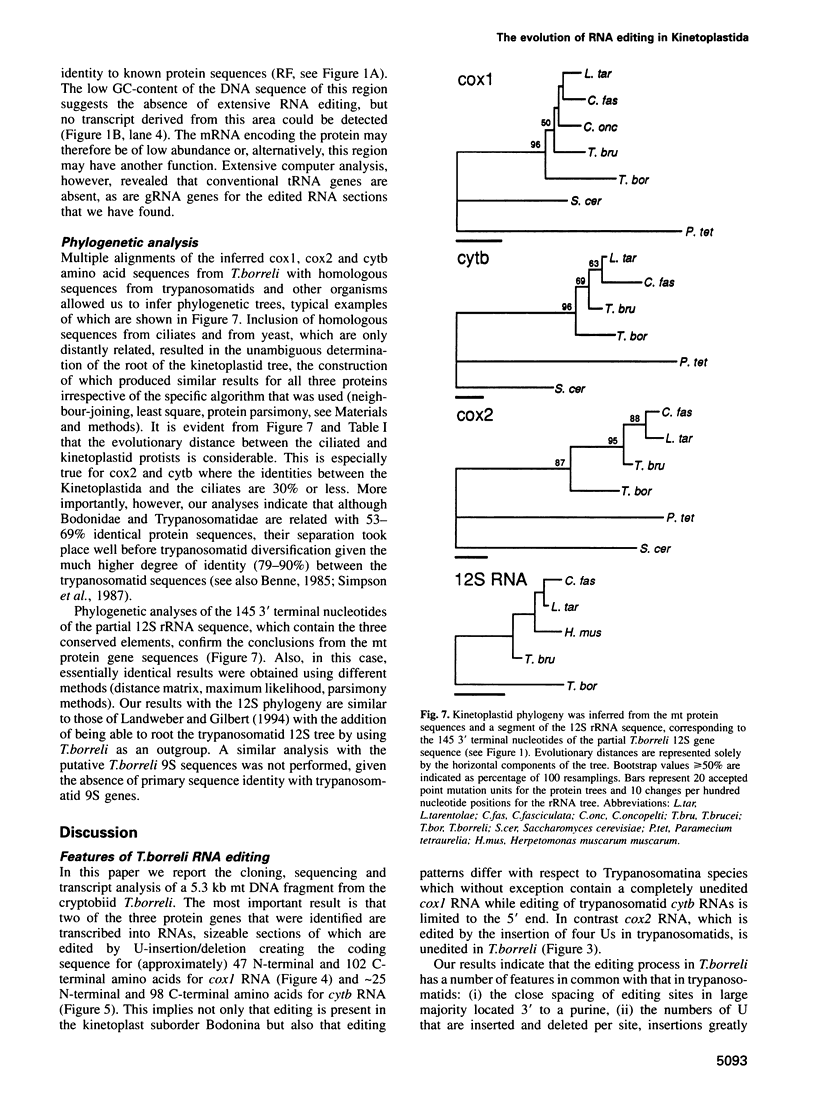
In mitochondria of Kinetoplastida belonging to the suborder Trypanosomatina, the nucleotide sequence of transcripts is post-transcriptionally edited via insertion and deletion of uridylate residues. In order to shed more light on the evolutionary history of this process we have searched for editing in mitochondrial RNAs of Trypanoplasma borreli, an organism belonging to the suborder Bodonina. We have cloned and sequenced a 5.3 kb fragment derived from a 37 kb mitochondrial DNA molecule which does not appear to be a part of a network structure and have found genes encoding cytochrome c oxidase (cox) subunit 1, cox 2 and apocytochrome (cyt) b, and genes encoding the small and large subunit mitoribosomal RNAs. The order in which these genes occur is completely different from that of trypanosomatid maxicircle genes. The 5' and 3' termini of both the cytb and cox1 gene are cryptic, the protein coding sequences being created by extensive insertion/deletion of Us in the corresponding mRNA sections. Phylogenetic analyses of the protein and ribosomal RNA sequences demonstrated that the separation between T.borreli and Trypanosomatina was an early event, implying that U-insertion/deletion processes are ancient. Different patterns of editing have persisted in different lineages, however, since editing of cox1 RNA and of relatively small 3'-terminal RNA sections is not found in trypanosomatids. In contrast, cox2 RNA which is edited in trypanosomatids by the insertion of four Us, is unedited in T.borreli.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arts G. J., van der Spek H., Speijer D., van den Burg J., van Steeg H., Sloof P., Benne R. Implications of novel guide RNA features for the mechanism of RNA editing in Crithidia fasciculata. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1523–1532. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R. Guide RNA tails of the unexpected. Curr Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):425–427. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R. RNA editing in mitochondria of Leishmania tarentolae and Crithidia fasciculata. Semin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;4(4):241–249. doi: 10.1006/scel.1993.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R. RNA editing in trypanosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 1;221(1):9–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R. RNA editing in trypanosomes: is there a message? Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum B., Bakalara N., Simpson L. A model for RNA editing in kinetoplastid mitochondria: "guide" RNA molecules transcribed from maxicircle DNA provide the edited information. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90735-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum B., Sturm N. R., Simpson A. M., Simpson L. Chimeric gRNA-mRNA molecules with oligo(U) tails covalently linked at sites of RNA editing suggest that U addition occurs by transesterification. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90087-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Fase-Fowler F. The maxi-circle of Trypanosoma brucei kinetoplast DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 22;565(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P. Why kinetoplast DNA networks? Trends Genet. 1991 May;7(5):139–141. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90374-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braly P., Simpson L., Kretzer F. Isolation of kinetoplast-mitochondrial complexes from Leishmania tarentolae. J Protozool. 1974 Nov;21(5):782–790. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A. Bodo caudatus medRNA and 5S rRNA genes: tandem arrangement and phylogenetic analyses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1053–1058. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91838-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. RNA editing: world's smallest introns? Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):667–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90494-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covello P. S., Gray M. W. On the evolution of RNA editing. Trends Genet. 1993 Aug;9(8):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Abraham J. M., Stuart K. Extensive editing of the cytochrome c oxidase III transcript in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Jasmer D. P., Stuart K. Developmentally regulated addition of nucleotides within apocytochrome b transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes A. P., Nelson K., Beverley S. M. Evolution of nuclear ribosomal RNAs in kinetoplastid protozoa: perspectives on the age and origins of parasitism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11608–11612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Margoliash E. Construction of phylogenetic trees. Science. 1967 Jan 20;155(3760):279–284. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3760.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel A., Boeke J. D. Reverse transcriptase encoded by a retrotransposon from the trypanosomatid Crithidia fasciculata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9794–9798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Covello P. S. RNA editing in plant mitochondria and chloroplasts. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):64–71. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. RNA. Pan-editing in the beginning. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):288–288. doi: 10.1038/368288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajduk S. L., Harris M. E., Pollard V. W. RNA editing in kinetoplastid mitochondria. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):54–63. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajduk S. L., Siqueira A. M., Vickerman K. Kinetoplast DNA of Bodo caudatus: a noncatenated structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4372–4378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. E., Hajduk S. L. Kinetoplastid RNA editing: in vitro formation of cytochrome b gRNA-mRNA chimeras from synthetic substrate RNAs. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1091–1099. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90080-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M., Decker C., Sollner-Webb B., Hajduk S. Specific cleavage of pre-edited mRNAs in trypanosome mitochondrial extracts. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2591–2598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa M., Fujiwara M. Relative efficiencies of the maximum likelihood, maximum parsimony, and neighbor-joining methods for estimating protein phylogeny. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1993 Mar;2(1):1–5. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1993.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Brakenhoff J., De Vries B. F., Sloof P., Tromp M. C., Van Boom J. H., Benne R. The sequence of the gene for cytochrome c oxidase subunit I, a frameshift containing gene for cytochrome c oxidase subunit II and seven unassigned reading frames in Trypanosoma brucei mitochondrial maxi-circle DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7327–7344. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges P., Scott J. Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing: a new tier for the control of gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Feb;17(2):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., Schoutsen B., Borst P. Kinetoplast DNA in the insect trypanosomes Crithidia luciliae and Crithidia fasciculata. I. Sequence evolution and transcription of the maxicircle. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Teixeira S. M., Kirchhoff L. V., Donelson J. E. Transcription and editing of cytochrome oxidase II RNAs in Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1206–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koslowsky D. J., Bhat G. J., Perrollaz A. L., Feagin J. E., Stuart K. The MURF3 gene of T. brucei contains multiple domains of extensive editing and is homologous to a subunit of NADH dehydrogenase. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90265-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koslowsky D. J., Bhat G. J., Read L. K., Stuart K. Cycles of progressive realignment of gRNA with mRNA in RNA editing. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90528-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koslowsky D. J., Göringer H. U., Morales T. H., Stuart K. In vitro guide RNA/mRNA chimaera formation in Trypanosoma brucei RNA editing. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):807–809. doi: 10.1038/356807a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A., de la Cruz V. F., Ferreira P. C., Morel C., Simpson L. Evolution of parasitism: kinetoplastid protozoan history reconstructed from mitochondrial rRNA gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4779–4783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landweber L. F., Fiks A. G., Gilbert W. The boundaries of partially edited transcripts are not conserved in kinetoplastids: implications for the guide RNA model of editing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9242–9246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landweber L. F., Gilbert W. Phylogenetic analysis of RNA editing: a primitive genetic phenomenon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):918–921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landweber L. F., Gilbert W. RNA editing as a source of genetic variation. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):179–182. doi: 10.1038/363179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslov D. A., Avila H. A., Lake J. A., Simpson L. Evolution of RNA editing in kinetoplastid protozoa. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):345–348. doi: 10.1038/368345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslov D. A., Elgort M. G., Wong S., Pecková H., Lom J., Simpson L., Campbell D. A. Organization of mini-exon and 5S rRNA genes in the kinetoplastid Trypanoplasma borreli. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Sep;61(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90165-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslov D. A., Sturm N. R., Niner B. M., Gruszynski E. S., Peris M., Simpson L. An intergenic G-rich region in Leishmania tarentolae kinetoplast maxicircle DNA is a pan-edited cryptogene encoding ribosomal protein S12. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):56–67. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecková H., Lom J. Growth, morphology and division of flagellates of the genus Trypanoplasma (Protozoa, Kinetoplastida) in vitro. Parasitol Res. 1990;76(7):553–558. doi: 10.1007/BF00932559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read L. K., Fish W. R., Muthiani A. M., Stuart K. Maxicircle DNA and edited mRNA sequences of closely related trypanosome species: implications of kRNA editing for evolution of maxicircle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 25;21(17):4073–4078. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.17.4073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read L. K., Wilson K. D., Myler P. J., Stuart K. Editing of Trypanosoma brucei maxicircle CR5 mRNA generates variable carboxy terminal predicted protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1489–1495. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. M., Feagin J. E., Stuart K., Simpson L. Editing of kinetoplastid mitochondrial mRNAs by uridine addition and deletion generates conserved amino acid sequences and AUG initiation codons. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. M., Bakalara N., Simpson L. A ribonuclease activity is activated by heparin or by digestion with proteinase K in mitochondrial extracts of Leishmania tarentolae. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6782–6788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Neckelmann N., de la Cruz V. F., Simpson A. M., Feagin J. E., Jasmer D. P., Stuart K. Comparison of the maxicircle (mitochondrial) genomes of Leishmania tarentolae and Trypanosoma brucei at the level of nucleotide sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6182–6196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Shaw J. RNA editing and the mitochondrial cryptogenes of kinetoplastid protozoa. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90911-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloof P., Van den Burg J., Voogd A., Benne R., Agostinelli M., Borst P., Gutell R., Noller H. Further characterization of the extremely small mitochondrial ribosomal RNAs from trypanosomes: a detailed comparison of the 9S and 12S RNAs from Crithidia fasciculata and Trypanosoma brucei with rRNAs from other organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4171–4190. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B. RNA editing. Guides to experiments. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):743–744. doi: 10.1038/356743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Köhler M., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90568-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm N. R., Maslov D. A., Blum B., Simpson L. Generation of unexpected editing patterns in Leishmania tarentolae mitochondrial mRNAs: misediting produced by misguiding. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm N. R., Simpson L. Partially edited mRNAs for cytochrome b and subunit III of cytochrome oxidase from Leishmania tarentolae mitochondria: RNA editing intermediates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):871–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90197-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis R. H., Rubin H. Calcium protects DNase I from proteinase K: a new method for the removal of contaminating RNase from DNase I. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90519-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Spek H., Speijer D., Arts G. J., Van den Burg J., Van Steeg H., Sloof P., Benne R. RNA editing in transcripts of the mitochondrial genes of the insect trypanosome Crithidia fasciculata. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):257–262. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08103.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. mRNA splicing and autocatalytic introns: distant cousins or the products of chemical determinism? Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Cruz V. F., Lake J. A., Simpson A. M., Simpson L. A minimal ribosomal RNA: sequence and secondary structure of the 9S kinetoplast ribosomal RNA from Leishmania tarentolae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1401–1405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Cruz V. F., Simpson A. M., Lake J. A., Simpson L. Primary sequence and partial secondary structure of the 12S kinetoplast (mitochondrial) ribosomal RNA from Leishmania tarentolae: conservation of peptidyl-transferase structural elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2337–2356. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Spek H., Arts G. J., Zwaal R. R., van den Burg J., Sloof P., Benne R. Conserved genes encode guide RNAs in mitochondria of Crithidia fasciculata. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1217–1224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Spek H., van den Burg J., Croiset A., van den Broek M., Sloof P., Benne R. Transcripts from the frameshifted MURF3 gene from Crithidia fasciculata are edited by U insertion at multiple sites. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2509–2514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







