Abstract
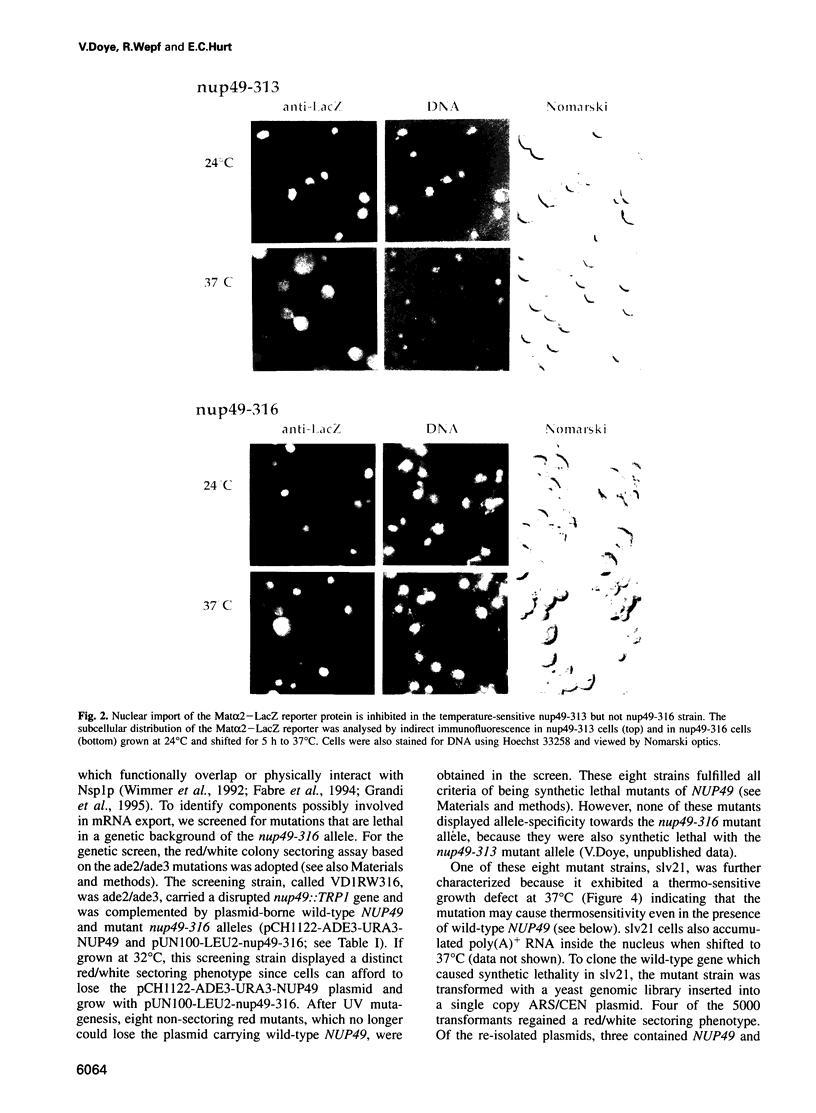
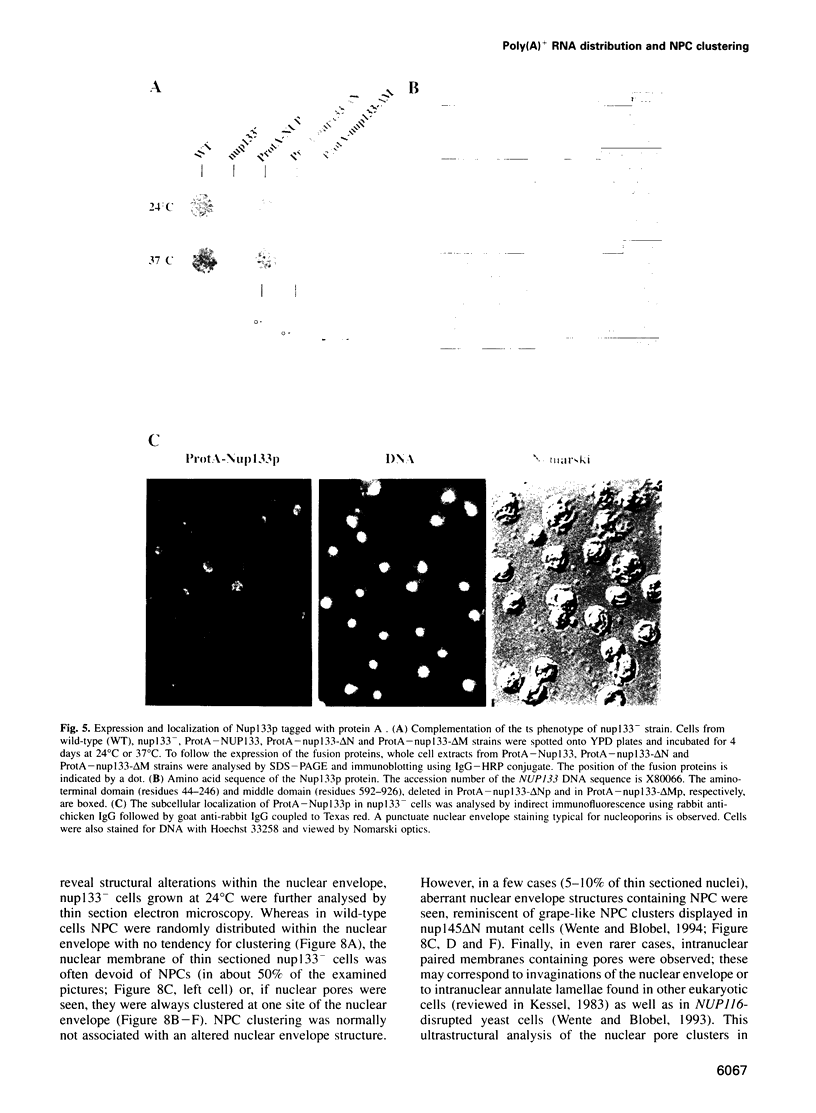
Temperature-sensitive nucleoporin nup49-316 mutant cells accumulate poly(A)+ RNA inside the nucleus when shifted to restrictive temperature. We performed a synthetic lethal screen with this mutant allele to identify further components of the mRNA export machinery. A synthetic lethal mutant slv21 was isolated, which exhibited a ts phenotype and showed nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA at 37 degrees C. The wild-type gene complementing slv21 was cloned and sequenced. It encodes a novel protein Nup133p which is located at the nuclear pore complex. NUP133 is not an essential gene, but cells in which NUP133 is disrupted grow slowly at permissive temperatures and stop growing at 37 degrees C. Concomitant with the growth inhibition, nup133- cells accumulate poly(A)+ RNA inside the nucleus whereas nuclear import of a karyophilic reporter protein is not altered. Strikingly, nup133- cells display extensive clustering of nuclear pore complexes at a few sites on the nuclear envelope. However, the nuclear pore clustering phenotype and intranuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA are not obligatorily linked, since an amino-terminally truncated Nup133p allows normal poly(A)+ RNA export, but does not complement the clustering phenotype of nup133- cells.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson R. P., Blobel G. On the attachment of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):746–754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Fleischmann M., Stagljar I., Cole C. N., Aebi M. Nuclear PRP20 protein is required for mRNA export. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):233–241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Yeast nuclear envelope proteins cross react with an antibody against mammalian pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2059–2067. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berben G., Dumont J., Gilliquet V., Bolle P. A., Hilger F. The YDp plasmids: a uniform set of vectors bearing versatile gene disruption cassettes for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991 Jul;7(5):475–477. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergès T., Petfalski E., Tollervey D., Hurt E. C. Synthetic lethality with fibrillarin identifies NOP77p, a nucleolar protein required for pre-rRNA processing and modification. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3136–3148. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossie M. A., Silver P. A. Movement of macromolecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus in yeast. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Oct;2(5):768–774. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Preparation of yeast cells for thin-section electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:602–608. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94044-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Kern H., Hurt E. C. Human nucleoporin p62 and the essential yeast nuclear pore protein NSP1 show sequence homology and a similar domain organization. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;55(1):17–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabauvalle M. C., Loos K., Scheer U. Identification of a soluble precursor complex essential for nuclear pore assembly in vitro. Chromosoma. 1990 Dec;100(1):56–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00337603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Fink G. R. The NUP1 gene encodes an essential component of the yeast nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):965–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. A family of versatile centromeric vectors designed for use in the sectoring-shuffle mutagenesis assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Boelens W. C., Wimmer C., Mattaj I. W., Hurt E. C. Nup145p is required for nuclear export of mRNA and binds homopolymeric RNA in vitro via a novel conserved motif. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Hurt E. C. Nuclear transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Meier E., Bradley P., Horecka J., Forbes D. J. A complex of nuclear pore proteins required for pore function. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):169–183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J. Structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:495–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Cantalejo J., Baladrón V., Esteban P. F., Santos M. A., Bou G., Remacha M. A., Revuelta J. L., Ballesta J. P., Jiménez A., del Rey F. The complete sequence of an 18,002 bp segment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome XI contains the HBS1, MRP-L20 and PRP16 genes, and six new open reading frames. Yeast. 1994 Feb;10(2):231–245. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. W., Allen T. D. High resolution scanning electron microscopy of the nuclear envelope: demonstration of a new, regular, fibrous lattice attached to the baskets of the nucleoplasmic face of the nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1429–1440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. W., Allen T. D. The nuclear pore complex: three-dimensional surface structure revealed by field emission, in-lens scanning electron microscopy, with underlying structure uncovered by proteolysis. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):261–274. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D., Michaud N. Pathways for the nuclear transport of proteins and RNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;1(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90065-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandi P., Doye V., Hurt E. C. Purification of NSP1 reveals complex formation with 'GLFG' nucleoporins and a novel nuclear pore protein NIC96. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3061–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05975.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greber U. F., Senior A., Gerace L. A major glycoprotein of the nuclear pore complex is a membrane-spanning polypeptide with a large lumenal domain and a small cytoplasmic tail. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guddat U., Bakken A. H., Pieler T. Protein-mediated nuclear export of RNA: 5S rRNA containing small RNPs in xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90665-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg E., Wozniak R. W., Blobel G. An integral membrane protein of the pore membrane domain of the nuclear envelope contains a nucleoporin-like region. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):513–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mattaj I. W. Transport of RNA between nucleus and cytoplasm. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;3(4):279–288. doi: 10.1016/1043-4682(92)90029-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Stepinski J., Darzynkiewicz E., Mattaj I. W. A cap binding protein that may mediate nuclear export of RNA polymerase II-transcribed RNAs. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1287–1295. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarmolowski A., Boelens W. C., Izaurralde E., Mattaj I. W. Nuclear export of different classes of RNA is mediated by specific factors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(5):627–635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.5.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Goldfarb D., Spitz L. M., Tartakoff A. M., Ohno M. Regulation of RNA processing and transport by a nuclear guanine nucleotide release protein and members of the Ras superfamily. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2929–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Zhao Y., Tartakoff A. M. A conditional yeast mutant deficient in mRNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel R. G. The structure and function of annulate lamellae: porous cytoplasmic and intranuclear membranes. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;82:181–303. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60826-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer D., Wozniak R. W., Blobel G., Radu A. The human CAN protein, a putative oncogene product associated with myeloid leukemogenesis, is a nuclear pore complex protein that faces the cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1519–1523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz J. E., Holm C. Cloning by function: an alternative approach for identifying yeast homologs of genes from other organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6629–6633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. D., Davis L. I., Fink G. R. NUP2, a novel yeast nucleoporin, has functional overlap with other proteins of the nuclear pore complex. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Feb;4(2):209–222. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMorrow I., Bastos R., Horton H., Burke B. Sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding a human nuclear pore complex protein, hnup153. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 1;1217(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutvei A., Dihlmann S., Herth W., Hurt E. C. NSP1 depletion in yeast affects nuclear pore formation and nuclear accumulation. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;59(2):280–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Fabre E., Dihlmann S., Herth W., Hurt E. C. Analysis of nucleo-cytoplasmic transport in a thermosensitive mutant of nuclear pore protein NSP1. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;62(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Kern H., Mutvei A., Horstmann H., Marshallsay B., Hurt E. C. NSP1: a yeast nuclear envelope protein localized at the nuclear pores exerts its essential function by its carboxy-terminal domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90063-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panté N., Aebi U. The nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):977–984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Dreyfuss G. Shuttling of pre-mRNA binding proteins between nucleus and cytoplasm. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):730–732. doi: 10.1038/355730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Blobel G., Wozniak R. W. Nup155 is a novel nuclear pore complex protein that contains neither repetitive sequence motifs nor reacts with WGA. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):1–9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt R., Holzenburg A., Buhle E. L., Jr, Jarnik M., Engel A., Aebi U. Correlation between structure and mass distribution of the nuclear pore complex and of distinct pore complex components. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):883–894. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Blobel G. Isolation of the yeast nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):771–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Hurt E., Doye V., Silver P. A. Reconstitution of nuclear protein transport with semi-intact yeast cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):785–798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severs N. J., Jordan E. G., Williamson D. H. Nuclear pore absence from areas of close association between nucleus and vacuole in synchronous yeast cultures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Mar;54(3):374–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R., Green M. R. Sequence-specific binding of transfer RNA by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Science. 1993 Jan 15;259(5093):365–368. doi: 10.1126/science.8420004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr C. M., D'Onofrio M., Park M. K., Hanover J. A. Primary sequence and heterologous expression of nuclear pore glycoprotein p62. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1861–1871. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukegawa J., Blobel G. A nuclear pore complex protein that contains zinc finger motifs, binds DNA, and faces the nucleoplasm. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90047-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. A temperature-sensitive NUP116 null mutant forms a nuclear envelope seal over the yeast nuclear pore complex thereby blocking nucleocytoplasmic traffic. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):275–284. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. NUP145 encodes a novel yeast glycine-leucine-phenylalanine-glycine (GLFG) nucleoporin required for nuclear envelope structure. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):955–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Rout M. P., Blobel G. A new family of yeast nuclear pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):705–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer C., Doye V., Grandi P., Nehrbass U., Hurt E. C. A new subclass of nucleoporins that functionally interact with nuclear pore protein NSP1. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5051–5061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Blobel G., Rout M. P. POM152 is an integral protein of the pore membrane domain of the yeast nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):31–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Blobel G. The single transmembrane segment of gp210 is sufficient for sorting to the pore membrane domain of the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1441–1449. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R., Basson M., D'Ari L., Rine J. Increased amounts of HMG-CoA reductase induce "karmellae": a proliferation of stacked membrane pairs surrounding the yeast nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):101–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. tRNA transport from the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell: carrier-mediated translocation process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6436–6440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]