Abstract
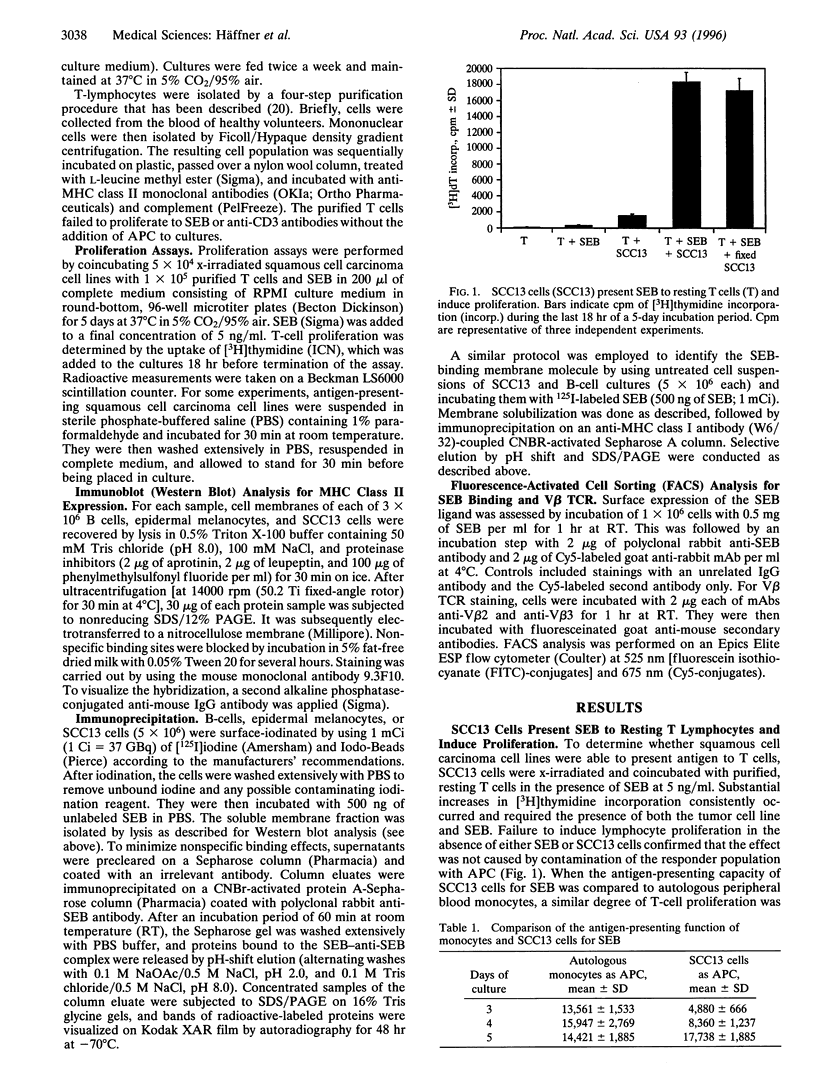
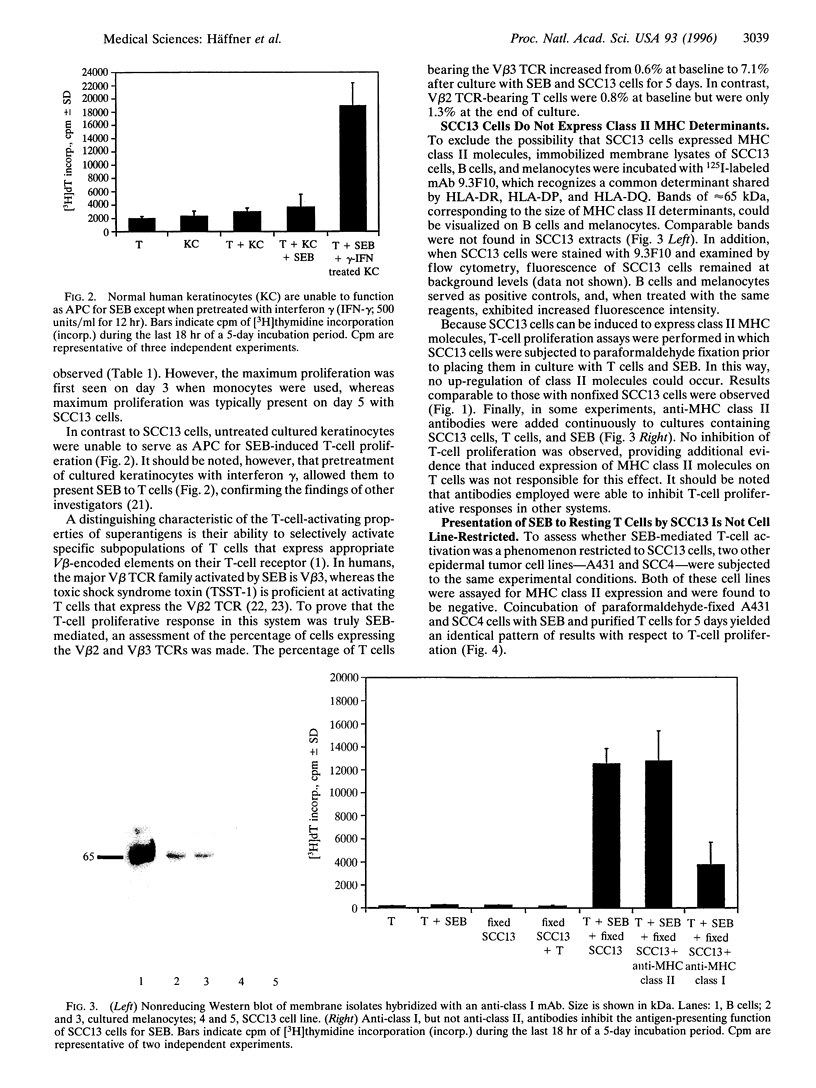
Superantigens, such as staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), elicit a strong proliferative response in T cells when presented in the context of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules. We observed a similar T-cell response, when MHC class II-negative epidermal cell lines were employed as antigen-presenting cells. Immunoprecipitation studies indicated that the ligand to which SEB bound had a molecular mass of 46 kDa. Radiolabeled SEB could be immunoprecipitated from isolated membrane proteins on the SCC13 epidermal cell line with a monoclonal antibody directed against the MHC class I molecule, and transfection of the K-562 cell line with MHC class I molecules showed a 75% increased SEB-binding capacity compared with the nontransfected MHC class I- and class II-negative counterpart. In functional studies, antibodies to the MHC class I molecule inhibited T-cell proliferation by at least 50%. From these studies, we conclude that MHC class I molecules on malignant squamous cell carcinomas serve as ligands for SEB, which, given the appropriate costimulatory signals, is sufficient to allow for superantigen-induced T-cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF
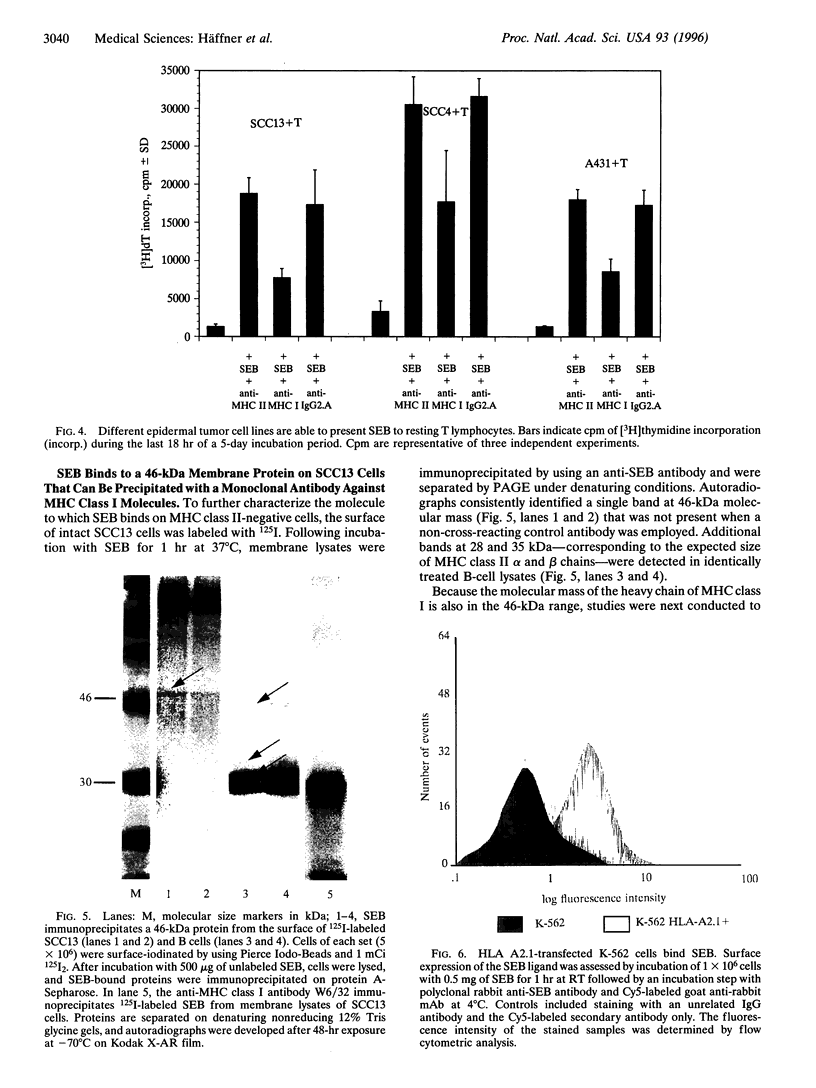
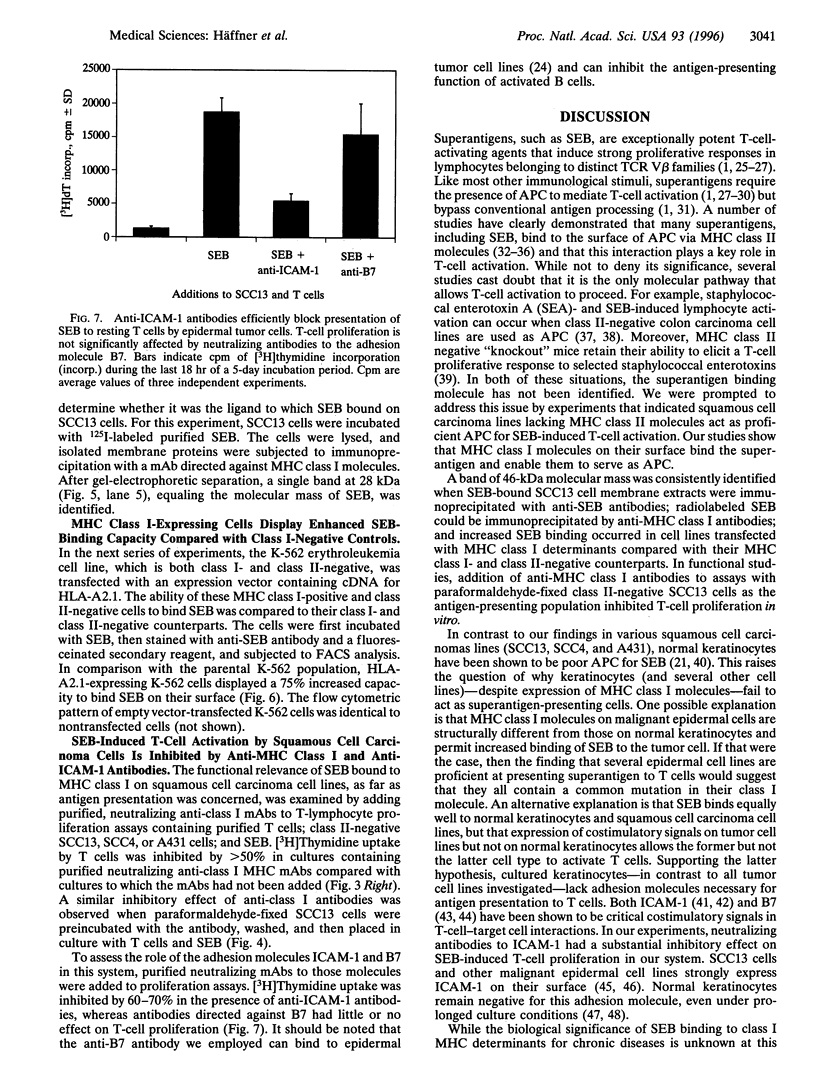

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya K. R., Passalacqua E. F., Jones E. Y., Harlos K., Stuart D. I., Brehm R. D., Tranter H. S. Structural basis of superantigen action inferred from crystal structure of toxic-shock syndrome toxin-1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):94–97. doi: 10.1038/367094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery A. C., Markowitz J. S., Grusby M. J., Glimcher L. H., Cantor H. Activation of T cells by superantigen in class II-negative mice. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 1;153(11):4853–4861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bette M., Schäfer M. K., van Rooijen N., Weihe E., Fleischer B. Distribution and kinetics of superantigen-induced cytokine gene expression in mouse spleen. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1531–1539. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankson J. N., Morse S. S. The CD28/B7 pathway costimulates the response of primary murine T cells to superantigens as well as to conventional antigens. Cell Immunol. 1994 Aug;157(1):306–312. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Herman A., DiGiusto D., Wade T., Marrack P., Kappler J. Residues of the variable region of the T-cell-receptor beta-chain that interact with S. aureus toxin superantigens. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):471–473. doi: 10.1038/346471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Herman A., DiGiusto D., Wade T., Marrack P., Kappler J. Residues of the variable region of the T-cell-receptor beta-chain that interact with S. aureus toxin superantigens. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):471–473. doi: 10.1038/346471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Kotzin B., Herron L., Callahan J., Marrack P., Kappler J. Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin "superantigens" with human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8941–8945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellabona P., Peccoud J., Kappler J., Marrack P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Superantigens interact with MHC class II molecules outside of the antigen groove. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90388-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Abrahmsén L., Björk P., Lando P. A., Hedlund G., Forsberg G., Brodin T., Gascoigne N. R., Förberg C., Lind P. Monoclonal antibody-superantigen fusion proteins: tumor-specific agents for T-cell-based tumor therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8945–8949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Akerblom E., Lando P. A., Kalland T. Monoclonal antibody-targeted superantigens: a different class of anti-tumor agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9287–9291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Sundstedt A., Björklund M., Hedlund G., Kalland T. Superantigen-induced cytokines suppress growth of human colon-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1993 May 28;54(3):482–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Dohlsten M., Lindvall M., Sjögren H. O., Carlsson R. Binding of staphylococcal enterotoxin A to HLA-DR on B cell lines. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3151–3157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Gjörloff A., Hedlund G., Hedman H., Lundgren E., Kalland T., Sjögren H. O., Dohlsten M. Stimulation of human naive and memory T helper cells with bacterial superantigen. Naive CD4+45RA+ T cells require a costimulatory signal mediated through the LFA-1/ICAM-1 pathway. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):1993–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Mittrücker H. W. Evidence for T cell receptor-HLA class II molecule interaction in the response to superantigenic bacterial toxins. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1331–1333. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming T. E., Mirando W. S., Trefzer U., Tubesing K. A., Elmets C. A. In situ expression of a B7-like adhesion molecule on keratinocytes from human epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Nov;101(5):754–758. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D. High-affinity binding of staphylococcal enterotoxins A and B to HLA-DR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):221–223. doi: 10.1038/339221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascoigne N. R., Ames K. T. Direct binding of secreted T-cell receptor beta chain to superantigen associated with class II major histocompatibility complex protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):613–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatto H., Viac J., Richard M. H., Lizard G., Charveron M., Schmitt D. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression on normal human keratinocytes by retinoic acid: comparison of cultured keratinocytes and skin explants. Skin Pharmacol. 1994;7(3):109–117. doi: 10.1159/000211284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goronzy J. J., Oppitz U., Weyand C. M. Clonal heterogeneity of superantigen reactivity in human V beta 6+ T cell clones. Limited contributions of V beta sequence polymorphisms. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):604–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Pullen A. M. Superantigens: mechanism of T-cell stimulation and role in immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:745–772. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Labrecque N., Thibodeau J., Marrack P., Kappler J. W., Sekaly R. P. Identification of the staphylococcal enterotoxin A superantigen binding site in the beta 1 domain of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9954–9958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann T., Romero P., Sartoris S., Paiola F., Accolla R. S., Maryanski J. L., MacDonald H. R. Staphylococcal enterotoxin-dependent lysis of MHC class II negative target cells by cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2504–2512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imberti L., Sottini A., Bettinardi A., Puoti M., Primi D. Selective depletion in HIV infection of T cells that bear specific T cell receptor V beta sequences. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.1948066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Brown J. H., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Chi Y. I., Stauffacher C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of a human class II histocompatibility molecule complexed with superantigen. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):711–718. doi: 10.1038/368711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageshita T., Yoshii A., Kimura T., Kuriya N., Ono T., Tsujisaki M., Imai K., Ferrone S. Clinical relevance of ICAM-1 expression in primary lesions and serum of patients with malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4927–4932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Pullen A., Callahan J., Choi Y., Herman A., White J., Potts W., Wakeland E., Marrack P. Consequences of self and foreign superantigen interaction with specific V beta elements of the murine TCR alpha beta. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 1):401–407. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R., Long E. O. Identification of HLA-DR1 beta chain residues critical for binding staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):415–424. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer T. Costimulatory receptors for the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B on human vascular endothelial cells and T cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Oct;56(4):458–463. doi: 10.1002/jlb.56.4.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krutmann J., Athar M., Mendel D. B., Khan I. U., Guyre P. M., Mukhtar H., Elmets C. A. Inhibition of the high affinity Fc receptor (Fc gamma RI) on human monocytes by porphyrin photosensitization is highly specific and mediated by the generation of superoxide radicals. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11407–11413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando P. A., Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Akerblom E., Kalland T. T cell killing of human colon carcinomas by monoclonal-antibody-targeted superantigens. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1993;36(4):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01740903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando P. A., Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Brodin T., Sansom D., Kalland T. Co-stimulation with B7 and targeted superantigen is required for MHC class II-independent T-cell proliferation but not cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1993 Oct;80(2):236–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Walsh P., Giorno R., Norris D. A. A potential role for superantigens in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Mar;100(3):225–228. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12468941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litton M. J., Sander B., Murphy E., O'Garra A., Abrams J. S. Early expression of cytokines in lymph nodes after treatment in vivo with Staphylococcus enterotoxin B. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Sep 30;175(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. P., Noble W. C., Camp R. D. Superantigenic exotoxin-secreting potential of staphylococci isolated from atopic eczematous skin. Br J Dermatol. 1993 Jun;128(6):631–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb00257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miele M. E., Bennett C. F., Miller B. E., Welch D. R. Enhanced metastatic ability of TNF-alpha-treated malignant melanoma cells is reduced by intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1, CD54) antisense oligonucleotides. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Sep;214(1):231–241. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Mitra R. S., Green J., Zheng X. G., Shimizu Y., Thompson C., Turka L. A. Accessory cell function of keratinocytes for superantigens. Dependence on lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1/intercellular adhesion molecule-1 interaction. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2148–2159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi H., Tanaka T., Takahara J., Kotb M. CD28 delivers costimulatory signals for superantigen-induced activation of antigen-presenting cell-depleted human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3207–3214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontzer C. H., Irwin M. J., Gascoigne N. R., Johnson H. M. T-cell antigen receptor binding sites for the microbial superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7727–7731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Radbruch A. Distinct antigen presenting cell-derived signals induce TH cell proliferation and expression of effector cytokines. Int Immunol. 1992 Jan;4(1):43–51. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Stern L. J., Ottenhoff T. H., Engel I., Owen M. J., Lamb J. R., Klausner R. D., Wiley D. C. Binary and ternary complexes between T-cell receptor, class II MHC and superantigen in vitro. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):324–327. doi: 10.1038/369324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu S., Krinock R. A., Matsumura T., Sussman J. J., Fox B. A., Chang A. E., Terman D. S. Stimulation of tumor-draining lymph node cells with superantigenic staphylococcal toxins leads to the generation of tumor-specific effector T cells. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1277–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange P., Skov L., Baadsgaard O. Interferon gamma-treated keratinocytes activate T cells in the presence of superantigens: involvement of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Feb;102(2):150–154. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokura Y., Yagi H., Hashizume H., Yagi J., Furukawa F., Takigawa M. Accessory cell ability of Langerhans cells for superantigen is resistant to ultraviolet-B light. Photochem Photobiol. 1994 Aug;60(2):147–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1994.tb05082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M. A., Beachey E. H., Majumdar G., Kotb M. Metabolically active antigen presenting cells are required for human T cell proliferation in response to the superantigen streptococcal M protein. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(3):155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallgren A., Festin R., Gidlöf C., Dohlsten M., Kalland T., Tötterman T. H. Efficient killing of chronic B-lymphocytic leukemia cells by superantigen-directed T cells. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1230–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Seventer G. A., Newman W., Shimizu Y., Nutman T. B., Tanaka Y., Horgan K. J., Gopal T. V., Ennis E., O'Sullivan D., Grey H. Analysis of T cell stimulation by superantigen plus major histocompatibility complex class II molecules or by CD3 monoclonal antibody: costimulation by purified adhesion ligands VCAM-1, ICAM-1, but not ELAM-1. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):901–913. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]