1. Introduction
The cell surface displays a complex array of oligosaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. This diverse mixture of glycans contains a wealth of information, modulating a wide range of processes such as cell migration, proliferation, transcriptional regulation, and differentiation.1–5 Glycosylation is one of the most ubiquitous forms of post-translational modification, with more than 50% of the human proteome estimated to be glycosylated.6 Glycosylation adds another dimension to the complexity of cellular signaling and expands the ability of a cell to modulate protein function. The structural complexity of glycan modifications ranges from the addition of a single monosaccharide unit to polysaccharides containing hundreds of sugars in branched or linear arrays.7 This chemical diversity enables glycans to impart a vast array of functions, from structural stability and proteolytic protection to protein recognition and modulation of cell signaling networks.8,9–12
Emerging evidence suggests a pivotal role for glycans in regulating nervous system development and function. For instance, glycosylation influences various neuronal processes, such as neurite outgrowth and morphology, and may contribute to the molecular events that underlie learning and memory.7,13,14 Glycosylation is an efficient modulator of cell signaling and has been implicated in memory consolidation pathways.15–18 Genetic ablation of glycosylation enzymes often leads to developmental defects and can influence various organismal behaviors such as stress and cognition.19–24 Thus, the complexity of glycan functions help to orchestrate proper neuronal development during embryogenesis, as well as influence behaviors in the adult organism.
The importance of glycosylation is further highlighted by defects in glycan structures that often lead to human disease, as exhibited by congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG).25–29 These are usually inherited disorders resulting from defects in glycan biosynthesis, which are accompanied by severe developmental abnormalities, mental retardation, and difficulties with motor coordination. Such disorders highlight the importance of glycan biosynthesis in human health and development. Because therapeutic treatments are currently limited, investigations into the structure–activity relationships of glycans, as well as disease-associated alterations to glycan structure, are crucial for developing strategies to combat these diseases.
Understanding the structure–function relationships of glycans has been hampered by a lack of tools and methods to facilitate their analysis. In contrast to nucleic acids and proteins, oligosaccharides often have branched structures, and their biosynthesis is not template-encoded. As such, the composition and sequence of oligosaccharides cannot be easily predicted, and genetic manipulations are considerably less straightforward. Analytical techniques for investigating oligosaccharide composition, sequence, and tertiary structure are still undergoing development and are far from routine, unlike methods for DNA and protein analysis. Lastly, glycan structures are not under direct genetic control and, thus, are often heterogeneous. This heterogeneity complicates structure–function analyses by traditional biochemical approaches that rely on the isolation and purification of glycans from natural sources.
The problems associated with oligosaccharide analysis have hindered efforts to understand the biology of oligosaccharides yet have given chemists a unique opportunity to develop new methods to overcome these challenges. The development of chemical tools for the analysis of glycan structure and function is essential to advance our understanding of the roles of glycoconjugates in regulating diverse biological processes. In this review, we will highlight the emerging area of glyconeurobiology with an emphasis on current chemical approaches for elucidating the biological functions of glycans in the nervous system.
2. Sialic Acids
2.1. Structure
Sialic acids participate in a multitude of biologically interesting phenomena, including cell–cell recognition, adhesion, and intracellular signaling events.30–32 Originally known as neuraminic acid (Neu) and its derivatives, sialic acids are a family of α-keto acids containing a nine-carbon backbone.32 The most well-known members of the sialic acid family include N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), and deaminoneuraminic acid (KDN) (Figure 1). In addition to these basic forms, more than 50 distinct sialic acid structures have been identified in nature, arising from acetylation, methylation, lactylation, sulfation, and phosphorylation of the C-4, C-5, C-7, C-8, or C-9 hydroxyl groups.
Figure 1.

Common structures of sialic acid derivatives: neuraminic acid (Neu), N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), and deaminoneuraminic acid (KDN).
Sialic acids exist predominantly as terminal monosaccharides linked to galactose residues in glycan chains through α(2–3)- or α(2–6)-linkages. They can also form a ho-mopolymer of α(2–8)-linked sialic acid in mammals, termed polysialic acid (PSA).33,34 As discussed below, each glycoform dictates a unique function to the glycoproteins and glycolipids expressing these sugars. Sialic acids have historically received much attention due to their participation in cell–cell recognition events and the pathogenesis of diseases such as cancer,35–37 inflammatory disease,38–40 and viral infection.41–44 The development of sialic acid analogues as inhibitors or probes for biomedical research has led to significant advances in our understanding of this important family of carbohydrates. Here, we will discuss some of the roles of sialic acids in neurobiology and chemical approaches that have provided insight into their functions.
2.2. Neurobiological Functions
2.2.1. α(2–3)-Sialic Acid and Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein
Sialic acid is often expressed as α(2–3)-linked sialic acid in the nervous system, a carbohydrate motif recognized by the Siglec (sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin) family of proteins. Human Siglecs include at least 13 members, each containing a common V-set immunoglobulin domain that interacts with sialic acid.45 One interaction that has been extensively studied is the binding of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG; also known as Siglec-4) with α(2–3)-sialic acid. MAG is a 100-kDa integral membrane glycoprotein that is expressed myelinating glia cells.46,47 It is involved in regulating the formation and maintenance of myelin48 and has been suggested to inhibit nerve regeneration in the adult central nervous system (CNS).49–51 Mice deficient in MAG display delayed myelination,52 defects in the organization of periaxonal space,53 and subtle morphological abnormalities of myelin sheaths.52 The interactions of MAG with sialic acid-containing glycosphingolipids, known as gangliosides, have been extensively studied and have contributed to our understanding the role of MAG in myelin formation and neural regeneration.
MAG preferentially binds the glycan structure Neu5Acα-(2–3)Galβ(1–3)GalNAc,54 which is expressed on cell-surface gangliosides and O-glycans of glycoproteins.47 Gangliosides represent the major source of sialic acid expression in the brain. MAG binds with high affinity and specificity to the major brain gangliosides GD1a and GT1b, as well as the polysialoganglioside GQ1bα, a minor ganglioside expressed on cholinergic neurons (Figure 2). Digestion of gangliosides purified from bovine brain with neuraminidase, an enzyme that cleaves sialic acid residues, eliminated the binding of MAG to these gangliosides, demonstrating the importance of the sialic acid moiety in mediating MAG–ganglioside interactions.55–57
Figure 2.
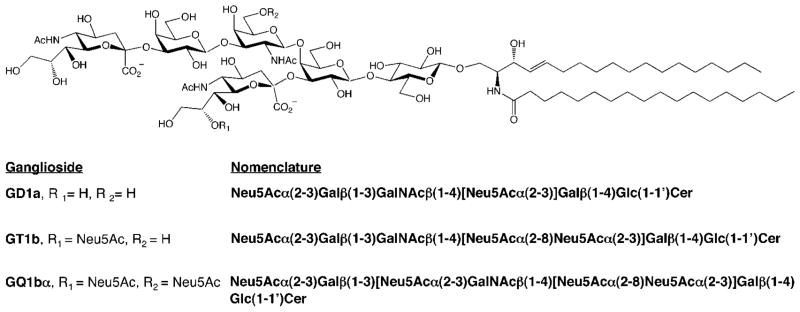
Structures of gangliosides that bind to MAG. Neu5Ac = N-acetylneuramic acid; Gal = galactose; GalNAc = N-acetylgalactosamine; Glc = glucose; Cer = ceramide.
Studies suggest that the association of MAG with sialic acid-containing gangliosides plays an important functional role in neuronal growth. The ability of MAG to inhibit neurite outgrowth in vitro is blocked by treatment of cerebellar granule neurons with neuraminidase or with the glucosyl-ceramide synthase inhibitor P4, which prevents synthesis of all glycosphingolipids.55 Moreover, mice lacking the glycosyltransferase gene GalNAcT (UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine: GM3/GD3 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase) do not express complex gangliosides such as GD1a and GT1b and, as a consequence, exhibit axon degeneration and gross dysmyeli-nation.58,59 These mice also display progressive behavioral abnormalities consistent with neurodegenerative disease, such as defects in balance, reflexes, and motor coordination.59 Thus, detailed knowledge of MAG and its interactions with sialylated glycans may enhance our understanding of myelinating disorders such as multiple sclerosis and provide opportunities to enhance axon regeneration after CNS injury or disease.
2.2.2. Polysialic Acid
In the brain, PSA is expressed primarily on the protein neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM).60–62 NCAM plays critical roles in both nervous system development and memory formation, regulating processes such as cell adhesion, axon targeting and fasciculation, neuronal migration, synaptic plasticity, and synaptogenesis.60,61,63–70 PSA–NCAM is highly expressed in the embryonic brain71–73 and is found in the adult brain in areas that retain a high degree of plasticity and neurogenesis, such as the hippocampus, olfactory bulb, and hypothalamus.74–77
Although the molecular mechanisms underlying PSA function are not well understood, PSA is thought to modulate cell–cell adhesion by attenuating homophilic NCAM–NCAM interactions. The large steric bulk and hydration shell of the carbohydrate chain increase the intercellular space by 10–15 μm, reducing trans NCAM–NCAM interactions across apposing cells.78 In addition, PSA modulates the interactions of NCAM with other proteins, such as heparan sulfate proteoglycans involved in the formation and remodeling of hippocampal synapses.79 The PSA chains on NCAM have also been proposed to play a role in some neuropsychiatric disorders. For example, expression of PSA–NCAM is significantly reduced in the hippocampus of schizophrenic patients and may contribute to the complex symptoms associated with the disease.80–82 Moreover, PSA has been implicated in the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease, as PSA–NCAM-positive granule cells are increased in the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s patients and are associated with disorganization of PSA-positive fibers.83 Finally, PSA may also regulate neuronal function through NCAM-independent mechanisms. For example, PSA has been suggested to act as a competitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor, an ionotropic glutamate channel involved in synaptic transmission,84 thereby preventing glutamate-induced excitotoxicity.85
Despite intriguing roles for sialic acid-containing glycans, the molecular mechanisms underlying their diverse functions in the brain remain largely unknown. As described below, chemical approaches to access and manipulate sialic acid structures have expanded our understanding of the neuro-biological roles of sialic acid and promise to continue to advance the field.
2.3. Chemical Neurobiology of Sialic Acid
2.3.1. Synthetic Sialic Acid Derivatives: Probing the Specificity of MAG Interactions
Synthetic sialic acid analogues have been used to elucidate the molecular determinants important for MAG-ganglioside interactions. The C-9 hydroxyl group represents a key recognition element: substitution of this group with hydrogen, halogen, or thiol groups attenuated the association of MAG with Neu5Ac (Figure 3, compounds 1–5). Interestingly, an amino group at C-9 enhanced binding to MAG by 3-fold, suggesting the importance of a hydrogen donor at this position (compound 6).86 The C-5 N-acetyl group of Neu5Ac was also found to be critical for MAG binding, although it is not always required for interaction with other Siglecs. Replacement of this group with an N-propanoyl, N-aminoacetyl, or N-thioacetyl moiety enhanced binding of sialic acid to MAG by up to 4-fold (compounds 7–9). The corresponding halogenated derivatives were all found to increase the binding to MAG (compounds 10–13), with the monofluorinated derivative achieving a 17-fold increase in potency. In contrast, amino substitution at the C-5 position significantly attenuated binding to MAG.86 Together, these studies highlight key interactions between MAG and the C-9 hydroxyl and C-5 N-acetyl groups of sialic acid.
Figure 3.
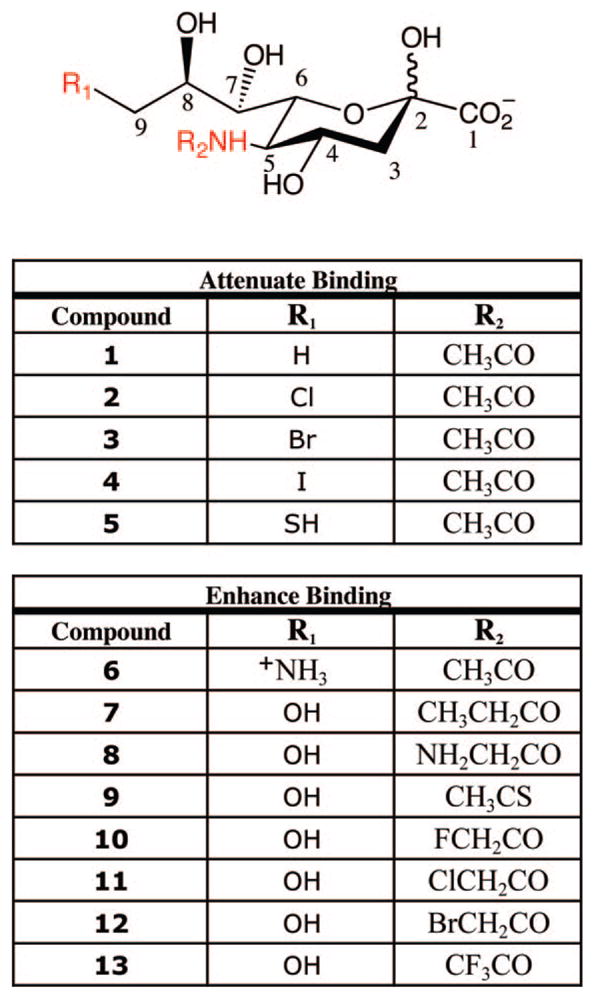
Synthetic sialic acid analogues tested for binding to MAG. Positions important for MAG interactions are shown in red.
In addition to probing monosaccharide variants, numerous oligosaccharide derivatives have been synthesized and tested for binding to MAG. These structures mimic naturally occurring ganglioside structures such as GD1a (Figure 2). Consistent with previous studies, substitution of the C-9 hydroxyl of Neu5Ac with a methyl group within the trisaccharide Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ(1–4)Glc attenuated binding to MAG by 5-fold, again highlighting the importance of the glycerol side chain.87 These results are consistent with an X-ray crystal structure of the Siglec sialoadhesin complexed with sialyllactose, in which the C-9 hydroxyl group of NeuAc forms a hydrogen bond with the amide backbone of Leu-107.88 Although these proteins are distinct, it is conceivable that their mode of binding to sialic acid would be conserved across Siglec family members. In contrast to C-9, the C-7 and C-4 hydroxyls do not appear to contribute substantially to the binding energy of MAG–sialic acid interactions.87 The C-7 deoxy derivative of Neu5Acα(2–3)-Gal(β(1–4)Glcβ-2-azidoethyl exhibited only slightly enhanced binding to MAG (1.5-fold), whereas the C-4 deoxy derivative showed slightly decreased binding (2-fold). However, both the C-7 and C-4 hydroxyls appeared to be critical for binding when placed in the context of a polyvalent array.57 Thus, valency and cell-surface presentation may reflect another facet of the complex regulation and specificity of Siglec–ganglioside interactions.
Synthetic oligosaccharide derivatives have also provided insight into the importance of specific glycosidic linkages and other residues within the structure. MAG was found to bind 5-fold better to α(2–3)-linked Neu5Ac than to α(2–6)-linked Neu5Ac in synthetic trisaccharides.87 Interestingly, replacement of Neu5Ac in a pentasaccharide structure with the naturally occurring sialic acid KDN led to a 6.5-fold increase in MAG binding,87 suggesting that other sialic acid forms may bind MAG in vivo. In addition to contacts with terminal sialic acid residues, internal sugars were also found to be important for MAG interactions. For instance, substitution of the C-4 hydroxyl group of galactose in Neu5Acα(2–3)-Galβ(1–4)Glc with a hydrogen atom enhanced binding to MAG by 2.3-fold. Changing this residue to GalNAc, adding an O-methyl substituent at C-6, or exchanging the ring oxygen to an N-methyl or N-butyl functionality decreased the potency of the trisaccharide.87 Modifications of the third glucose residue to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) also decreased the binding properties of the molecules. Various substitutions of the N-acetyl group, such as N-phthaloyl or N-octanoyl substituents, increased the potency of the compounds, which reflects the potential for a hydrophobic interaction with MAG at this site.87 Lastly, pentasaccharides of the structure Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ(1–4)AllNAcβ(1–3)-Galβ(1–4)Glcβ–2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl (AllNAc = N-acetyl-allosamine) were found to increase binding above the trisaccharide Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ(1–4)Glc by ~6-fold, suggesting even more extensive contacts between MAG and the interior residues of large glycan structures.87
Together, studies using synthetic analogues have illustrated how subtle perturbations to the sialic acid core structure can have significant effects on protein binding. As described below, such studies may facilitate the design of novel synthetic inhibitors of MAG function with therapeutic potential.
2.3.2. Development of MAG Antagonists with Therapeutic Potential
The importance of MAG–ganglioside interactions for nerve regeneration and myelination has inspired the design and synthesis of small molecules capable of disrupting those interactions. Such molecules have the potential to enhance nerve regeneration by blocking the inhibitory effects of MAG on neurite outgrowth. Below, we provide some examples of small molecule antagonists that exhibit activity in cellular regeneration models.
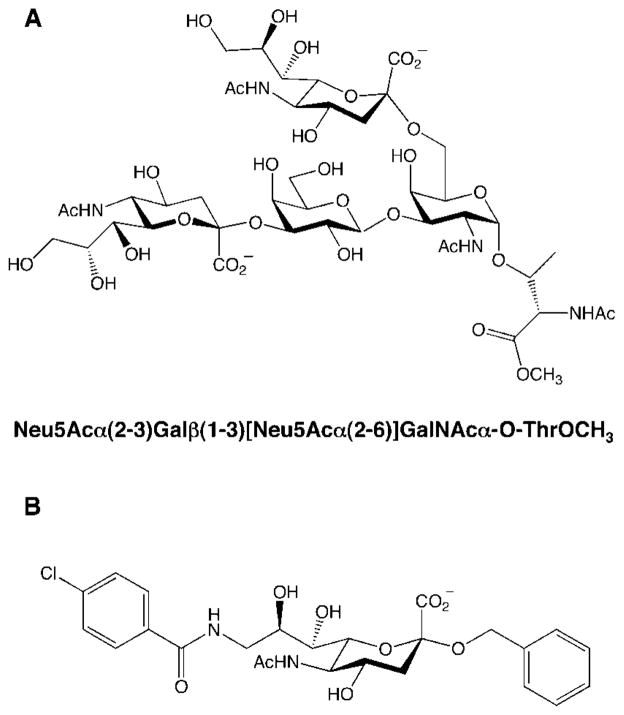
Paulson and co-workers examined the interactions of monovalent sialic acid derivatives with MAG and other Siglec family members.89 Over 25 derivatives representing most of the major sialic acid structures found on glycoproteins and glycolipids were tested. The most potent inhibitor of MAG–ganglioside interactions was the disialyl structure Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ (1–3)[Neu5Acα(2–6)]GalNAcα-O-ThrOCH3 (Figure 4A), which exhibited an IC50 value of 0.3 μM. This compound showed greater than 12000-fold enhanced potency relative to Neu5Ac for inhibiting MAG–sialic acid interactions.89
Figure 4.
Structure of (A) a potent disialyl MAG inhibitor and (B) a simplified mimic of the ganglioside GQ1bα with enhanced binding affinity to MAG relative to Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ(1–3)-GalNAc.
The disialyl structure above and other potent inhibitors such as Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ (1–3)GalNAc were subsequently tested for their ability to attenuate MAG-mediated inhibition of neurite outgrowth.90 When rat cerebellar granule neurons (CGN) are cultured on a substratum of myelin-extracted proteins, they project fasciculated axons and cluster together, leaving the majority of the substrata bare. This form of neuronal growth inhibition is mediated primarily by MAG. The sialosides relieved the MAG-dependent inhibition of CGN neurons, enhancing nerve regeneration in a dose-dependent manner and proportional to their relative binding affinities for MAG.90 The most potent compound, the disialyl structure, completely reversed the inhibition induced by MAG. Thus, synthetic glycans can effectively enhance neurite outgrowth in vitro and, when used in combination with other treatments, may provide a means to improve functional recovery after neuronal injury. The ability to compare various Siglec family members against a large number of sialoside structures has also revealed the specificity of Siglecs for different carbohydrate epitopes and may help to fine-tune the development of selective MAG antagonists.
Many oligosaccharide-based inhibitors are synthetically challenging to produce and can suffer from poor pharmacokinetics. As an alternative to this approach, Ernst and coworkers generated structurally simplified mimics of the ganglioside GQ1bα. In particular, the Gal and GalNAc residues in the trisaccharide Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ (1–3)GalNAc were replaced with an α-linked benzyl ether moiety, and aromatic residues were positioned on the glycerol side chain (Figure 4B). Despite its smaller size, this compound displayed a remarkable 1000-fold enhanced binding affinity relative to the trisaccharide Neu5Acα(2–3)Galβ (1–3)Gal-NAcβ-2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl. Although the compound was not tested in cellular regeneration assays, it was anticipated to have improved pharmacokinetic properties due to its lower molecular weight and favorable Clog P value.91–93 Similar approaches may yield additional therapeutic leads with the desired inhibitory potency and pharmacokinetics for the treatment of demyelinating disorders.
2.3.3. Synthetic Mimics of α(2–8)-Linked PSA for Nerve Regeneration
PSA expression is generally considered a permissive determinant in areas of neuronal growth and plasticity, making it a potential therapeutic target for neuronal regeneration. In fact, expression of PSA has been shown to promote functional recovery and provide a favorable environment for axonal regeneration in animal models of spinal cord injury.94,95 In these studies, PSA–NCAM was ectopically expressed in spinal cord astrocytes in vivo,94 or PSA-expressing Schwann cell grafts were employed.95 Although the use of PSA oligo- and polysaccharides may be viable alternatives, PSA isolated from natural sources is often heterogeneous in length and can be contaminated with other cell-surface glycans. In addition, PSA adopts a helical conformation96 and forms filament bundles,97 thus exhibiting different structural elements that may have distinct functions.
To circumvent these challenges, Rougon, Schachner, and co-workers screened a large peptide library to identify potential PSA mimetics.98 Two cyclic peptides were identified that recapitulated the properties of endogenous PSA. Both compounds stimulated the outgrowth and defasciculation of mouse dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons and promoted neuronal migration in vitro and in vivo. In addition, one peptide enhanced the migration of transplanted neuronal progenitor cells in the murine olfactory bulb in vivo via a pathway known to be regulated by PSA.98 Thus, synthetic mimics may provide novel alternatives to PSA for neuronal regeneration.
2.3.4. Metabolic Labeling To Remodel Cell-Surface Sialic Acid Interactions
The metabolic labeling of glycan chains with unnatural sugars has played a key role in expanding the knowledge of sialic acid function in the nervous system. Early studies by Reuttar and colleagues demonstrated that unnatural chemical functionalities could be incorporated into cell-surface sialylglycoconjugates by the addition of N-acetylmannosamine analogues (ManNAc; Figure 5A) to cells.99–103 ManNAc is the first committed intermediate in the sialic acid biosynthetic pathway, and the enzymes in this metabolic pathway are promiscuous for some unnatural substrates.104–106 As described below, the ability to alter the structures of sialylglycoconjugates has provided key insights into the roles of sialic acid in neuronal migration and proliferation.
Figure 5.
(A) Mannosamine derivatives used for metabolic labeling (R = H or Ac) and (B) chemoselective labeling reaction after treatment of cells with ManLev (R = biotin).
2.3.4.1. Metabolic Labeling of Neurons with Elongated N-Acyl Derivatives of Sialic Acid
Elongated N-acyl derivatives of ManNAc have been incorporated into sialylglycoconjugates of PC12 cells, oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, microglia, astrocytes, and neurons from cerebellar microex-plant cultures.101,107 In these studies, cells were treated with N-propanoylmannosamine (ManNProp), wherein the N-acetyl substituent of Neu5Ac is replaced with a longer N-propanoyl group (Figure 5A). ManNProp was found to stimulate the proliferation of microglia relative to cells treated with the natural sialic acid precursor, ManNAc.107 ManNProp also induced the migration of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, the precursors to oligodendrocyte cells, which play key roles in myelin formation and become functionally impaired in neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis.108–112 Interestingly, treatment with ManNProp prolonged expression of a sialylated ganglioside involved in cell migration, the A2B5 epitope,113 revealing a potential mechanism for its functional effects.
In other studies, Reutter and co-workers investigated whether ManNProp modulates signaling pathways within oligodendrocytes.114 Treatment of these cells with ManNProp and the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) induced GABA-dependent oscillations in intracellular calcium. Calcium is an important second messenger in the nervous system, and calcium oscillations are believed to contribute to a highly plastic signaling system underlying the communication between neurons and glia.114 Interestingly, ionotropic GABA receptors are modified by sialic acid,115,116 suggesting that extended N-acyl substituents may alter the functional properties of this receptor. However, ManNProp undoubtedly perturbs the expression of multiple sialylglycoconjugates at the cell surface, and direct evidence that altered sialylation of the GABA receptor is responsible for the observed response is lacking. In the future, it will be interesting to uncover the precise molecular mechanisms by which these modifications to sialic acid structure elicit their effects on intracellular signaling.
ManNProp has also been shown to promote neuronal growth in various contexts. For instance, ManNProp induced the neurite outgrowth of small rat CGN, PC12 cells, and chick DRG neurons.117,118 Moreover, treatment with Man-NProp promoted reestablishment of functional connections in the perforant pathway, which consists of projections from the entorhinal cortex into the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, in coculture experiments.117 Although the particular glycoconjugates responsible for these effects were not elucidated, several cytosolic proteins implicated in neurite outgrowth were found to be differentially expressed after the ManNProp treatment, including unc-33 like phosphoprotein (ULIP), various heat shock proteins, and 14-3-3ε, a protein that associates with both GABA receptors and the α(2–3)-sialyltransferase IV.117,119,120
Bertozzi and colleagues have explored the influence of various ManNAc derivatives on PSA biosynthesis. N-Butanoylmannosamine (ManNBut, Figure 5A), but not ManNProp, was shown to significantly inhibit PSA expression in a dose-dependent manner in the NT2 neuroblastoma cell line. Moreover, both human polysialytransferases responsible for PSA biosynthesis (STX and PST) displayed reduced kinetic efficiencies for transfer of ManNBut and ManNPent (Figure 5A), whereas ManNProp was transferred at a rate sufficient for biosynthesis.118,121 Thus, elongation of the N-acyl side chain of sialic acid may interfere with recognition of the growing PSA chain by polysialyltransferases. However, findings by Jennings and co-workers suggest that both ManNBut and ManNProp may be partially incorporated into sialylglycoconjugates, as detected by flow cytometry using a monoclonal antibody that recognizes N-propanoyl- and N-butanoyl-PSA.122,123 Consistent with an inhibitory effect on PSA biosynthesis, ManNBut blocked polysialylation of NCAM in both chick DRG neurons118 and NT2 cells124 and decreased the outgrowth of DRG neurons.118 The effects on neurite outgrowth were comparable to those elicited by treatment of cells with endoneuraminidase, an enzyme that cleaves PSA residues.
2.3.4.2. Metabolic Labeling with ManNGcPA
Metabolic labeling of neurons with unnatural sugars has also been exploited to alter protein recognition events at the cell surface. Treatment of neuroblastoma–glioma hybrid cells with the sialic acid metabolic precursor N-glycolylmannosamine pentaacetate (ManNGcPA; Figure 5A) converted cell-surface sialylglycoconjugates from expressing Neu5Ac to expressing Neu5Gc,125 a sialic acid form that is not normally found in humans.126 Whereas Neu5Ac sialylglycoconjugates displayed on neuronal cells bound efficiently to MAG, the binding of MAG to cells expressing Neu5Gc sialylglycoconjugates was significantly inhibited.127 These studies demonstrate the potential of metabolic labeling to serve as a useful tool for perturbing specific glycan–protein interactions.
2.3.4.3. Chemoselective Labeling of Sialylated Cell-Surface Glycoconjugates
The ability to incorporate unnatural sugar analogues into cell-surface glycoconjugates allows for the introduction of reactive chemical functionalities onto glycoproteins and glycolipids, such as ketone, azide, or alkyne groups. These functionalities allow for selective labeling of proteins with reporter groups such as affinity tags and fluorescent dyes or for the delivery of toxins.128–131 Bertozzi and co-workers have exploited N-levulinoylmannosamine (ManLev), which contains a ketone functionality appended to the N-acyl side chain (Figure 5A), to label neuroblastoma cells.129 Incubation of the cells with ManLev resulted in incorporation of the ketone moiety into sialylated glycans in a concentration-dependent manner. Subsequent reaction with a biotin hydrazide derivative (Figure 5B) enabled visualization of sialylglycans by fluorescence microscopy, revealing their presence along the cell body and neuronal processes.132 Although the specific sialyltransferases involved are not fully understood, ManLev was successfully incorporated into PSA, suggesting that α(2–8)-polysialyltransferases are capable of utilizing ketone-modified precursors for PSA synthesis.132 These studies provide a powerful means to modulate the structure of PSA and potentially other sialylglycans with a wide variety of chemical groups.
2.3.4.4. Summary of Sialic Acid Metabolic Labeling
Cumulatively, studies have demonstrated that unnatural ManNAc derivatives can be exploited to manipulate the structure of sialylated glycans on neuronal cell surfaces. These studies have revealed that subtle alterations in sialic acid structure can have striking consequences for PSA biosynthesis and biological phenomena such as neurite outgrowth, cell proliferation, and migration. In the future, these versatile chemical tools could be employed for visualization of dynamic neuronal processes in vivo, such as activity-dependent changes in the expression or localization of sialylglycans. The ability to engineer the glycan composition of cell surfaces and to selectively label sialylated glycans for imaging or other applications provides a powerful complementary approach to genetics and biochemistry.
3. α-L-Fucose
3.1. Structure and Biosynthesis
α-L-Fucose (6-deoxy-L-galactose; Fuc) is generally expressed as a terminal monosaccharide on N- and O-linked glycoproteins and glycolipids. As such, it often serves as an important molecular recognition element for proteins. Fucose is distinct from other naturally occurring sugars because it is a deoxyhexose sugar that exists exclusively in the L-configuration (Figure 6). A structurally diverse array of fucosylated glycans has been identified with fucose often linked to the C-2, C-3, C-4, or C-6 positions of the penultimate galactose in glycoconjugates or to the core GalNAc residue of N-linked glycans.1 O-Fucosylation, the direct modification of serine and threonine residues by fucose, has also been observed on epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeats of glycoproteins such as Notch, a protein involved in cell growth and differentiation.133 While fucose is not elongated in N-linked and O-linked glycans, O-fucose can be elongated by other sugars.1
Figure 6.

Structures of various fucose derivatives and 2-dGal.
Given the structural diversity of fucosylated glycans, it is perhaps not surprising that more than a dozen different human enzymes are involved in the formation of Fuc linkages.1 Two enzymes, FUT1 and FUT2, are dedicated to the synthesis of Fucα(1–2)Gal glycans, an epitope found on the ABO blood group antigens134–136 that has also been implicated in synaptic plasticity.13,137,138 A gene homologous to FUT1 and FUT2, called Sec1, contains translational frameshifts and stop codons that interrupt potential open reading frames and thus appears to be a pseudogene.134 FUT3 catalyzes the synthesis of both α(1–3)- and α(1–4)-fucosylated glycans and can transfer fucose to both Gal and GlcNAc in an oligosaccharide chain, whereas FUT4–7 form only α(1–3)-fucosylated glycans.139,140 FUT8 and FUT9 generate Fucα(1–6)GlcNAc structures, with FUT8 generally catalyzing attachment of this structure to the core asparagine residue of N-linked oligosaccharides141 and FUT9 catalyzing its attachment to a distal GlcNAc of polylactosamine chains.142 FUT10 and FUT11 are putative fucosyltransferases that are reported to synthesize α(1–3)-fucosylated glycans based on sequence homology, although no functional studies have yet been performed.1 Finally, POFUT1 and POFUT2, also known as O-fucosyltransferase 1 and O-fucosyltransferase 2, catalyze the direct fucosylation of serine and threonine residues within epidermal growth factor repeats.143,144
3.2. Neurobiological Functions
Fucosylated glycans play important roles in various physiological and pathological processes, including leukocyte adhesion,145,146 host–microbe interactions,147,148 and neuronal development.149,150 They are prevalent on the glycolipids of erythrocytes, where they form the ABO blood group antigens that distinguish specific blood types.136 Aberrant expression of fucosylated glycoconjugates has been associated with cancer,151–154 inflammation,145,155–157 and neoplastic processes.158,159 For instance, the fucosylated antigens, sialyl LewisX, sialyl LewisY, and sialyl LewisB, are up-regulated in certain cancers and have been associated with advanced tumor progression and poor clinical prognosis.160–163 Moreover, deficiency in fucose leads to a congenital disorder of glycosylation type IIc in humans, also known as leukocyte adhesion deficiency type II (LAD II). This disorder results in the impairment of leukocyte–vascular epithelium interactions and is characterized by immunodeficiency, developmental abnormalities, psychomotor difficulties, and deficits in mental capabilities.164
Although their roles in the brain are less well understood, fucosylated glycans have been implicated in neural development, learning, and memory. Here, we will highlight aspects of their biosynthesis and functional roles in the nervous system.
3.2.1. Neuronal Development
Fucose has been reported to play an important role in neural development. O-Fucosylation is essential for the activity of Notch, a transmembrane receptor protein that controls a broad range of cell-fate decisions during development., 165–169 Studies suggest that fucose modulates Notch signaling either by inducing a conformational change in the protein or by interacting directly with Notch ligands.168 Notch signaling is believed to be involved in neuronal progenitor maintenance, and governs the cell-fate decision between neuronal and glial lineages. Notch signaling may also contribute to the behavior of differentiated neurons and neuronal migration.170 Genetic deletion of the POFUT1 gene is embryonic lethal in mice and causes developmental defects similar to those observed upon deletion of Notch receptors, including abnormal vasculogenesis, somitogenensis, and neurogenesis.171,172 These studies demonstrate the importance of fucose in proper neuronal development and implicate Notch fucosylation as an important mediator of these events.
3.2.2. Learning and Memory
Multiple studies have suggested a role for fucosylation in learning and memory. For instance, the incorporation of fucose into glycoconjugates in the brain was significantly enhanced by task-dependent learning in both chicks and rats.173–176 Rats were trained in a brightness discrimination task, in which animals learned to enter a bright chamber while avoiding a dark one. Trained animals demonstrated an increase in [3H]-labeled fucose incorporation into glycoconjugates at synapses, the specialized sites of communication between neurons.175 Moreover, exogenous application of L-fucose or 2′-fucosyllactose (Figure 6) enhanced long-term potentiation (LTP), an electrophysiological model for learning and memory, both in vivo and in hippocampal slices.177,178
Fucose is highly enriched at neuronal synapses,13,179,180 where the majority of the fucosylated glycoconjugates exist as complex N-linked structures.181 Studies indicate that the activity of fucosyltransferases increases during synaptoge-nesis182 and upon passive-avoidance training in animals.183 Moreover, the cellular machinery involved in protein glycosylation can be found within dendrites,184,185 raising the intriguing possibility that local protein synthesis and fucosylation may be occurring at synapses in response to neuronal stimulation.
Further studies have specifically implicated Fucα(1–2)Gal linkages in neuronal communication processes. For instance, 2-deoxy-D-galactose (2-dGal; Figure 6), which competes with native galactose for incorporation into glycan chains and thus prevents the formation of Fucα(1–2)Gal linkages,186 has been shown to induce reversible amnesia in animals.138,186,187 In contrast, other small molecule sugars such as 2-deoxy-D-glucose, Gal, or Glc had no effect, suggesting a unique function for Fucα(1–2)Gal saccharides. 2-dGal has also been reported to interfere with the maintenance of LTP, both in vitro and in vivo.188,189 Furthermore, a monoclonal antibody specific for Fucα(1–2)Gal190 significantly impaired memory formation in animals, presumably by blocking formation of the Fucα(1–2)Gal epitope.137
3.3. Chemical Approaches for Studying L-Fucose
Despite intriguing evidence linking Fucα(1–2)Gal sugars to neuronal communication and memory storage, the molecular mechanisms by which these sugars exert their effects are not well understood. Recently, however, chemical tools have been developed that are beginning to shed light on the roles of Fucα(1–2)Gal lectins and glycoproteins in the brain.
3.3.1. Deoxygalactose Analogues
Hsieh-Wilson and co-workers investigated the effects of the amnesic compound 2-dGal and other fucosylation inhibitors on cultured hippocampal neurons. Inhibition of Fucα-(1–2)Gal linkages using 2-dGal led to stunted neurite outgrowth in young neurons lacking functional synapses (Figure 7).14 In contrast, 3-deoxy-D-galactose (3-dGal), which inhibits fucose incorporation at the C-3 position of galactose, had no effect on neurite growth, suggesting that specific fucose linkages are important for the neuritogenic activity. The effects of 2-dGal could be successfully rescued by the addition of excess D-Gal to the media, suggesting that the inhibition can be reversed by the de novo synthesis of Fucα(1–2)Gal sugars.
Figure 7.
Inhibition of Fucα(1–2)Gal linkages with 2-dGal leads to stunted neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neurons cultured for 4 days in vitro (DIV). D-Gal is able to rescue the effects of 2-dGal. 3-dGal has no effect. White bar indicates 45 μm. Images courtesy of C. Gama.
Interestingly, 2-dGal also exerted dramatic effects on the morphology of older neurons, even after axonal differentiation and synaptogenesis had begun to occur.13 Application of 2-dGal led to a remarkable retraction of dendrites and collapse of synapses, whereas 6-dGal had no effect. However, D-Gal was only partially able to rescue the effects of 2-dGal, which may reflect the decreased plasticity of older neurons. Thus, fucosylated glycans and, in particular, Fucα(1–2)Gal glycoconjugates appear to be important for modulating neuronal morphology and maintaining functional neuronal connections.
To gain insight into the molecular mechanisms involved, Hsieh-Wilson and co-workers sought to identify Fucα(1–2)Gal glycoproteins in the hippocampus.13 Using a gel-based mass spectrometry approach, they identified synapsins Ia and Ib as the predominant Fucα(1–2)Gal glycoproteins in older hippocampal cultures and in the adult rat brain. The synapsins are synaptic vesicle-associated proteins that play important roles in neurotransmitter release and synaptogenesis.191,192 Fucosylation of synapsin I was found to have significant effects on synapsin expression in neurons, protecting it from proteolytic degradation by the calcium-activated protease calpain. Moreover, studies using 2-dGal and synapsin I-deficient mice showed that synapsin fucosylation contributes to the profound effects of 2-dGal on neurite outgrowth and synapse formation. However, other unknown Fucα(1–2)Gal glycoproteins were also involved in the process. These studies provide the first evidence that Fucα(1–2)Gal glycoproteins are directly involved in neurite outgrowth and underscore the importance of identifying the Fucα(1–2)Gal proteome of the brain.
3.3.2. Glycopolymers and Imaging Probes
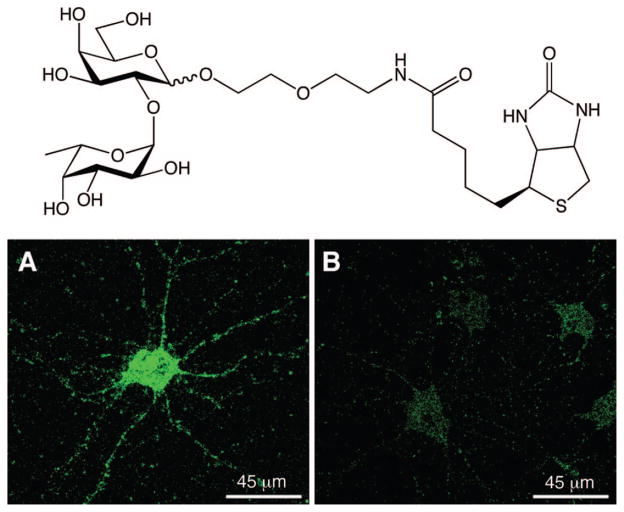
Fucose often occupies a terminal position on glycan chains, and as such, it serves as an important molecular recognition element for lectins. A well-studied example is the binding of L-selectin to the fucosylated glycan sialyl LewisX, an interaction known to be critical for leukocyte adhesion.1 To investigate whether Fucα(1–2)Gal lectins exist in the mammalian brain, a small molecule probe was designed and synthesized that contained the Fucα(1–2)Gal epitope and a biotin moiety for imaging potential lectin receptors in the brain (Figure 8).14 Rat hippocampal neurons were incubated with the small molecule probe, and the bound probe was visualized on the cells using a streptavidin–dye conjugate (Figure 8). Strong fluorescent staining of the cell body and neuronal processes was observed, consistent with the presence of fucose-binding lectin receptors.
Figure 8.
Chemical probe for imaging lectin receptors (top) and staining of hippocampal neurons in culture (bottom panels) with the probe demonstrating the presence of Fucα(1–2)Gal lectins along the cell body and neurites. Cells were treated with 3 mM of the imaging probe (A) or biotin (B), labeled with a streptavidin–dye conjugate, and imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Images courtesy of C. Gama.
To investigate whether the association of Fucα(1–2)Gal with these receptors would elicit a neuronal response, Hsieh-Wilson and colleagues treated cultured neurons with poly-acrylamide-based polymers displaying multiple copies of the Fucα(1–2)Gal epitope.14 The Fucα(1–2)Gal polymers promoted neurite outgrowth by more than 75%, and the potency of the compounds was dramatically enhanced with increasing polymer concentration or carbohydrate valency. Importantly, polymers bearing other carbohydrates moieties, such as GlcNAc, Gal, Fucα(1–3)GlcNAc, or only Fuc, had no appreciable effects, indicating that the observed neuritogenic activity was specific for Fucα(1–2)Gal. Together, these studies provide the first evidence that Fucα(1–2)Gal lectin receptors are found in the brain, and they identify a novel carbohydrate-mediated pathway for the regulation of neuronal growth. This work also highlights the power of chemical probes to explore the biological effects of specific glycans and their associated receptors. It will be important in the future to identify the lectins involved and to elucidate the specific mechanisms and pathways leading to neuronal growth.
3.3.3. Metabolic Labeling Using Alkynyl or Azido Fucose Analogues
Recently, the Bertozzi and Wong groups independently demonstrated that alkynyl- or azido-containing fucose analogues could be exploited to selectively label and image fucosylated glycans in mammalian cells.193,194 Their strategy exploits the fucose salvage pathway to convert unnatural fucose sugars into the corresponding GDP-fucose analogues, which then serve as donors for fucosyltransferases. Once the azido or alkynyl fucose analogue is incorporated into glycans, it can be reacted with fluorescent dyes, biotin, or peptides via Staudinger ligation or [3 + 2] azide–alkyne cycloaddition chemistry. Bertozzi and co-workers synthesized fucose derivatives with azido groups at the C-2, C-4, and C-6 positions.193 Only the C-6 azido fucose analogue (Figure 6) was successfully incorporated into the glycans of the Jurkat T lymphocyte cell line, consistent with earlier observations that some fucosyltransferases tolerate substitutions at the C-6 position of the pyranose ring. Wong and colleagues demonstrated that both azido- and alkynyl-modified fucose derivatives (Figure 6) could be incorporated into the glycans of hepatoma cells, allowing for fluorescent imaging of fucosylated glycoconjugates.194,195 Interestingly, the alkynyl fucose analogue was shown to be significantly less toxic to cells than the azido fucose analogue.194 Future application of these powerful approaches to neurons should facilitate proteomic studies to identify fucosylated glycoproteins and may allow for the dynamic imaging of protein fucosylation in vivo.
3.3.4. Summary of Fucosyl Oligosaccharides
Cumulatively, studies using chemical probes have revealed a role for fucosyl oligosaccharides and their associated lectins and glycoproteins in the regulation of neurite growth and synapse formation. These findings may shed light on behavioral and electrophysiological studies implicating Fucα(1–2)Gal in long-term memory storage. Alterations in neuronal morphology, such as dynamic changes in dendritic spine number and shape, occur during memory consolidation and LTP.196,197 One possibility is that the interaction between certain Fucα(1–2)Gal glycoproteins and lectins may promote the stabilization of synaptic connections that underlie learning and memory. In addition, fucosylation may exert its effects independently of lectins, by stabilizing fucosylated glycoproteins such as synapsin or modulating their functions. The continued development and application of chemical tools has tremendous potential to expand our understanding of the roles of fucosylated lectins and glycoproteins in the brain and may provide exciting opportunities to modulate neuronal communication processes.
4. O-GlcNAc Glycosylation
4.1. Structure and Biological Functions
O-GlcNAc glycosylation is the covalent attachment of β-N-acetylglucosamine to serine and threonine residues of proteins (Figure 9). Unlike other forms of glycosylation, O-GlcNAc is a dynamic, reversible modification found only on intracellular proteins, rendering it akin to protein phosphorylation. A wide range of proteins are O-GlcNAc-modified, including transcription factors, nuclear pore proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, and synaptic proteins.8,12,198,199–202 Several excellent reviews have described the functional roles of O-GlcNAc in transcription,203 apoptosis,204,205 signal transduction,199 nutrient sensing,206,207 and proteasomal degradation.206 O-GlcNAc glycosylation has also been implicated in the cellular stress response208,209 and is induced by oxidative, osmotic, metabolic, and chemical stress.8,206 Levels of O-GlcNAc glycosylation are altered in disease states such as cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease.201,204,207,210–215 Moreover, one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is the formation of neurofibrillary tangles by hyperphosphorylated tau protein,216 and several studies suggest that O-GlcNAc glycosylation negatively regulates the ability of tau to become phosphorylated.217,218 Thus, the investigation of O-GlcNAc function may provide insights into our understanding of critical cellular processes and diseases.
Figure 9.
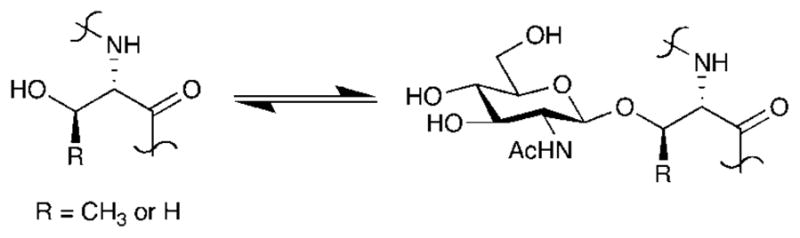
O-GlcNAc glycosylation.
4.2. Neurobiological Functions of O-GlcNAc
Emerging evidence indicates an important role for O-GlcNAc glycosylation in the nervous system. The enzymes that catalyze the addition and removal of O-GlcNAc, O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and O-GlcNAcase (OGA), are most highly expressed in the brain219 and are enriched in both pre- and postsynaptic nerve terminals.220 OGT expression is critical for cell survival,221 and neuronal-specific deletion of the OGT gene in mice leads to abnormal development, defects in motor coordination, and early neonatal death.222 Thus far, more than 50 neuronal proteins have been shown to be O-GlcNAc-modified, including proteins involved in transcription (e.g., CREB (cAMP-response element binding-protein), Sox2 (SRY box-containing gene 2), ATF-2 (activating transcription factor-2)), neuronal signaling (synGAP (synaptic Ras GTPase activating protein)), bassoon, the guanine nucleotide exchange factor PDZ-GEF, and synapsin I), synaptic plasticity (synaptopodin and δ-catenin), and neurodegenerative disease (tau and APP (β-amyloid precursor protein)).8,202,217,223–227 Finally, O-GlcNAc glycosylation levels are dynamically modulated by excitatory stimulation of the brain in vivo and upon activation of specific kinase pathways in cultured cerebellar neurons.223
Despite its importance, the functional roles of O-GlcNAc glycosylation are only beginning to be understood in the brain. A major challenge has been the difficulty of detecting and studying the modification in vivo. Similar to phosphorylation, O-GlcNAc is often dynamic, substoichiometric, targeted to subcellular compartments, and prevalent on low abundance regulatory proteins. The sugar is also both enzymatically and chemically labile. For example, mass spectrometry analyses to identify O-GlcNAc-modified proteins and map glycosylation sites are challenged by loss of the modification upon collision-induced dissociation (CID). The lack of a well-defined consensus sequence for OGT has precluded the determination of in vivo glycosylation sites based on primary sequence alone. Furthermore, the complexity of the nervous system and its unique technical challenges (e.g., postmitotic cells, multiple cell types, blood–brain barrier, complex organization) greatly complicates efforts to study O-GlcNAc glycosylation and necessitates the development of rapid, highly sensitive detection methods. Here, we describe chemical approaches undertaken to overcome these challenges and highlight how they have advanced our understanding of the roles of O-GlcNAc glycosylation in neuronal function and dysfunction.
4.3. Chemical Tools To Study O-GlcNAc Glycosylation
4.3.1. Chemoenzymatic Labeling of O-GlcNAc Proteins
4.3.1.1. Rapid, Sensitive Detection
Traditional methods for detecting O-GlcNAc-modified proteins often suffer from limited sensitivity and specificity. For instance, radiolabeling of the proteins using UDP-[3H]-galactose and β(1–4)-galactosyltransferase (GalT), an enzyme that transfers [3H]-galactose onto terminal GlcNAc groups of glycoproteins,228 can require weeks for visualization and lacks the sensitivity to detect certain O-GlcNAc-modified proteins. Lectins228 and antibodies229,230 are also effective methods, but they bind only a subset of the O-GlcNAc-modified proteins (usually those with multiple glycosylation sites) and have limited affinity and specificity.
In response, a chemoenzymatic approach for tagging O-GlcNAc proteins was developed by Hsieh-Wilson and coworkers that allows for more rapid and sensitive detection. An unnatural substrate for GalT was designed, in which a bioorthogonal ketone moiety was appended to the C-2 position of galactose (UDP-ketogalactose probe, Figure 10A).231 Studies by Qasba and colleagues had demonstrated that a mutant form of GalT (Y289L) tolerates minor substitutions at this position.232 Once transferred, the ketone moiety can be reacted with an aminooxy biotin derivative, thus permitting the sensitive detection of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins by chemiluminescence.231 Notably, this method enables the identification of O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins that elude detection using other methods. For example, detection of the glycoproteins α-crystallin and CREB was accomplished within minutes, whereas lectins and antibodies failed to detect the modification on these proteins and tritium labeling required more than a week to develop.231 Thus, this chemoenzymatic approach provides superior sensitivity relative to traditional methods and accelerates the identification of new O-GlcNAc-modified proteins.
Figure 10.
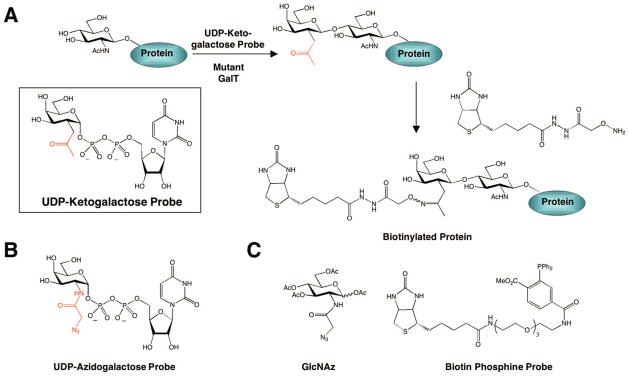
(A) Chemoenzymatic approach for tagging O-GlcNAc glycosylated proteins, (B) UDP–azidogalactose probe for [3 + 2] cycloaddition chemistry using the chemoenzymatic approach, and (C) GlcNAz and biotin phosphine probe for metabolic labeling of O-GlcNAc-modified protein using the Staudinger ligation.
4.3.1.2. Identification of O-GlcNAc-Glycosylated Proteins from Cells
Selective biotinylation of proteins using the chemoenzymatic approach also facilitates the parallel purification of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins from cell or tissue extracts by affinity chromatography.233 Previous methods have necessitated purification of individual proteins prior to analysis, a tedious and time-consuming process. Using the chemoenzymatic approach, the tagged O-GlcNAc proteins can be isolated in a single step by streptavidin affinity chromatography and interrogated for modification in parallel by Western blotting.233 This strategy was used to demonstrate that the AP-1 transcription factors c-Fos and c-Jun, as well as the activating transcription factor ATF-1, are O-GlcNAc-modified in HeLa cells.233 In addition, the identification of O-GlcNAc on CREB-binding protein (CBP) reveals a new class of O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins, the histone acetyltransferases (HAT). Thus, glycosylation can be readily investigated across structurally or functionally related proteins, as well as novel functional classes. Together, studies have revealed that a broad number of transcriptional components are O-GlcNAc-glycosylated,202,223,233 and O-GlcNAc may function as a general regulatory modification for the control of transcription.239,240
4.3.1.3. Proteome-Wide Analyses
When used in conjunction with high-throughput mass spectrometry, the chemoenzymatic approach can be exploited for proteome-wide analyses of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins.202 Proteins from cell lysates are chemoenzymatically labeled and pro-teolytically digested. The desired glycopeptides are then captured by avidin affinity chromatography and analyzed by HPLC in line with tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). The ketogalactose–biotin tag facilitates the isolation of O-GlcNAc glycopeptides from complex mixtures. This enrichment step is often crucial for detecting low-abundance post-translational modifications. The tag also provides a unique signature on the mass spectrometer, thus enabling unambiguous identification of O-GlcNAc-modified peptides and mapping of glycosylation sites to specific functional domains within a protein. Using this approach, Hsieh-Wilson, Peters, and colleagues reported the first proteome-wide identification of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins from the mammalian brain.202 Nearly 100 peptides were identified containing the mass spectrometry signature, and 34 of these peptides were successfully sequenced. The sequenced peptides identified 25 different proteins from rat brain. Of the proteins identified, only two proteins had been previously reported, and 23 were novel O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins, thus significantly expanding the repertoire of proteins known to be modified.
This method demonstrates the power of chemical-tagging approaches to accelerate the high-throughput identification of O-GlcNAc glycoproteins. Notably, many of the proteins identified have important functional roles in gene regulation, cytoskeletal dynamics, neuronal signaling, and synaptic plasticity. For example, synaptopodin, synGap, and shank2 (SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains protein 2) are critical for the regulation of dendritic spine formation.234–236 Synaptopodin and δ-catenin have important roles in learning and memory,234,237 and the guanine nucleotide exchange factor PDZ-GEF is involved in the assembly of signal transduction complexes at the synapse.238 Together, these studies suggest that O-GlcNAc glycosylation may play a role in mediating neuronal communication and signaling networks. Consistent with this observation, Burlingame and coworkers recently employed lectin weak-affinity chromatography in conjunction with mass spectrometry to identify 18 O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins from the postsynaptic density fraction of rat brain.224 The proteins represent multiple functional classes, and several proteins involved in synaptic vesicle cycling were found to be extensively O-GlcNAc-glycosylated, such as bassoon, piccolo, and synapsin I.224
While the chemoenzymatic approach has broad application to the study of O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins from cell and tissue extracts, O-GlcNAc proteins cannot be labeled in animals using this method. In addition, the determination of exact glycosylation sites is still difficult, because the ketogalactose–biotin moiety can be lost upon CID in the mass spectrometer. Instead, O-GlcNAc modification sites are mapped to short amino acid sequences within proteins, which still provides insight into the function of the modification. Despite these limitations, the chemoenzymatic labeling strategy is so powerful for in vitro analysis and proteomics that a variation of this approach is now commercially available for fluorescent labeling or biotinylation of O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins using [3 + 2] cycloaddition chemistry (Figure 10B).
4.3.2. Metabolic Labeling of O-GlcNAc Proteins
4.3.2.1. Incorporation of GlcNAz into O-GlcNAc Proteins
A complementary strategy that enables tagging of O-GlcNAcylated proteins in living cells involves metabolically labeling the proteins with unnatural GlcNAc derivatives. Bertozzi and colleagues demonstrated that N-(2-azidoacetyl)-glucosamine (GlcNAz, Figure 10C) is processed by enzymes in the hexosamine salvage pathway, resulting in incorporation of a bioorthogonal azide functionality into O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins.241 The azido group can be subsequently labeled with triarylphosphines via the Staudinger ligation. Using this approach, the authors demonstrated successful incorporation of GlcNAz into both nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins of cultured Jurkat T lymphocyte cells. In particular, selective labeling and detection of the nuclear pore protein p62, a known O-GlcNAc-modified protein with >10 glycosylation sites,242 was shown using a phosphine–FLAG probe. Although incomplete labeling of O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins limits the sensitivity of this approach relative to the chemoenzymatic strategy described above, metabolic labeling with GlcNAz sugars can be performed in living cells and might allow for the dynamic imaging of O-GlcNAc-glycosylated proteins in vivo.
4.3.2.2. Proteomic Analysis by Metabolic Labeling
Although metabolic labeling has not yet been applied to neurons, it represents another powerful chemical approach for the high-throughput identification of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins. Zhao and colleagues labeled O-GlcNAc proteins in the HeLa cervical cancer cell line with GlcNAz and tagged them with a biotin phosphine reagent (Figure 10C).243,244 Tryptic digestion of the affinity-captured proteins, followed by LC–MS/MS analysis, led to the identification of 199 putative O-GlcNAc-modified proteins. Because the presence of the GlcNAc moiety was inferred rather than detected directly, independent confirmation of the modification by immunoblotting was required and demonstrated on 23 of the 199 proteins.
While this method provides a powerful chemical tool for profiling O-GlcNAc-modified proteins, there are some limitations of this procedure for in vivo labeling in the brain. Most sugars do not cross the blood–brain barrier,245 and thus in vivo labeling with these molecules would entail invasive surgical procedures for intracranial administration rather than simple intraperitoneal injection. In addition, metabolic labeling is not quantitative, which may limit the sensitivity of detection as well as preclude the ability to monitor glycosylation dynamics. Despite these limitations, the approach has been successfully employed to investigate the O-GlcNAc proteome in both mammalian and insect cell lines.243,244 In the future, metabolic labeling could prove a useful tool for studying the O-GlcNAc proteome in cultured neurons.
4.3.3. Methods for Mapping Exact Glycosylation Sites
4.3.3.1. The β-Elimination Followed by Michael Addition with Dithiothreitol (BEMAD) Approach
The identification of O-GlcNAc modification sites within proteins is critical for elucidating the functions of O-GlcNAc in specific biological contexts. Nonetheless, the exact sites of glycosylation remain unknown for most proteins. Mapping glycosylation sites has been challenging due to the low abundance of the modification and the lability of the glycosidic linkage during fragmentation on a mass spectrometer, which can result in the loss of direct amino acid identification. Hart and co-workers showed that the labile GlcNAc moiety could be replaced with a more stable sulfide adduct by alkaline-induced β-elimination followed by Michael addition with dithiothreitol (BEMAD, Figure 11).246 The resulting sulfide adduct is not cleaved upon CID, thereby allowing sites of glycosylation to be more readily determined. However, a limitation of this approach is that it is often destructive to proteins,247,248 and selectivity controls must be performed to distinguish among O-GlcNAc, O-phosphate, and other O-linked carbohydrates.246 When biotin pentylamine is used in place of dithiothreitol, O-GlcNAc-modified peptides can be selectively biotinylated, enriched by affinity chromatography, and identified by LC–MS/MS analysis. This method has been successfully employed to identify novel O-GlcNAc sites on purified glycoproteins such as synapsin I and proteins from a purified rat brain nuclear pore complex.246 Further extension of BEMAD to complex mixtures for the high-throughput mapping of O-GlcNAc sites is an important future goal.
Figure 11.
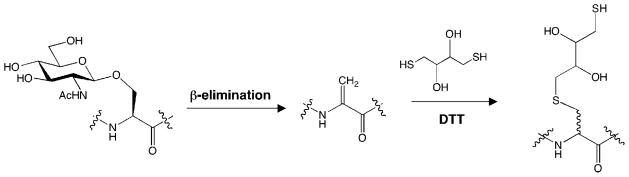
BEMAD approach for mapping O-GlcNAc glycosylation sites.
4.3.3.2. Electron Transfer Dissociation (ETD) and Electron Capture Dissociation (ECD) Coupled with Lectin Affinity Chromatography or Chemoenzymatic Labeling
Recently, the development of novel fragmentation methods for mass spectrometry has facilitated the identification of O-GlcNAc modification sites. Electron transfer dissociation (ETD) and electron capture dissociation (ECD) use thermal electrons to produce sequence specific-peptide fragmentation without the loss of labile post-translational modifications such as O-GlcNAc and O-phosphate.249 ECD has recently been used by Burlingame and co-workers to identify O-GlcNAc glycosylation sites following enrichment of the modified peptides by lectin weak-affinity chromatography.224 The authors were able to identify glycosylation sites on several neuronal proteins such as spectrin β2, shank2, bassoon, and piccolo.
While ECD requires the use of a Fourier transform mass spectrometer, ETD has the advantage of being performed in appropriately modified ion trap mass spectrometers, rendering the technology powerful and more accessible. Hsieh-Wilson, Coon, and colleagues have implemented ETD fragmentation to map glycosylation sites on neuronal proteins following chemoenzymatic labeling and enrichment by avidin affinity chromatography. The authors identified glycosylation sites on multiple proteins such as the neuron-specific transcriptional repressor BHC80, the transcriptional repressor p66β, the transcriptional coactivator SRC-1, and the zinc finger RNA-binding protein.223 With further methodological refinements and advances in database search algorithms for fragment ions, it is anticipated that ETD and ECD will become increasingly powerful tools for the study of O-GlcNAc glycosylation.
4.3.4. Monitoring O-GlcNAc Dynamics
Unlike most forms of protein glycosylation, O-GlcNAc glycosylation is reversible and dynamic. Several studies have shown that global O-GlcNAc levels in cells change within minutes of activation by specific extracellular stimuli.250,251 O-GlcNAc levels are also highly responsive to cellular glucose concentrations, as approximately 2–5% of all glucose is metabolized through the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway to generate UDP-GlcNAc.252–254 Furthermore, studies have suggested a potential interplay between O-GlcNAc glycosylation and phosphorylation in neurons. An inverse relationship between O-GlcNAc and O-phosphate was observed upon activation of protein kinase C (PKC) or cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) in the cytoskeletal protein fraction of cultured cerebellar neurons.255 As described below, recent quantitative proteomics studies have shown that O-GlcNAc glycosylation is dynamically induced by excitatory stimulation of the mammalian brain in vivo.223 Finally, O-GlcNAc glycosylation is known to be dysregulated in multiple disease states and is believed to contribute to the etiology of certain diseases, such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer.207,252,256,257
Despite considerable investigation, the specific proteins undergoing dynamic changes in glycosylation remain largely unknown. Moreover, the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways involved in the regulation of OGT and OGA are poorly understood. As such, there is a great need to develop chemical tools to monitor changes in glycosylation on specific proteins and at specific modification sites in both normal and disease states. We describe below some of the chemical approaches that have been developed to address these challenges.
4.3.4.1. FRET-Based Sensors
Mahal and colleagues developed a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based sensor to investigate O-GlcNAc glycosylation dynamics in living cells.258 Their approach uses two fluorophores, enhanced cyan and yellow fluorescent protein, separated by a known OGT substrate domain and the bacterial O-GlcNAc lectin GafD (Figure 12). Upon O-GlcNAc glycosylation of the substrate domain, the GafD domain binds the carbohydrate moiety, bringing the fluorophores into close proximity and leading to a concomitant increase in FRET. The authors detected a significant increase in FRET from HeLa cells transfected with the sensor construct upon treatment with glucosamine or the OGA inhibitor PUGNAc (O-(2-acet-amido-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranosylidene)amino-N-phenylcarbamate, Figure 14). 258 This biological sensor represents a promising tool for the investigation of O-GlcNAc glycosylation dynamics in response to a variety of cellular stimuli.
Figure 12.
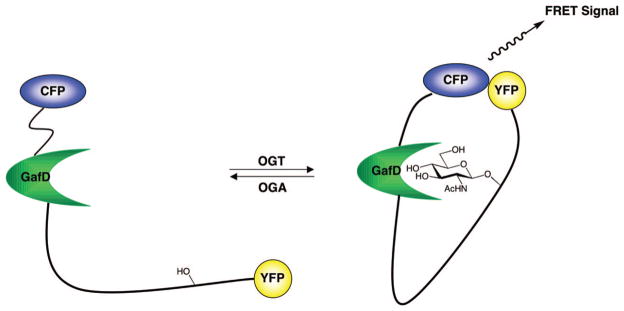
A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based sensor to detect O-GlcNAc glycosylation levels.
Figure 14.
Small-molecule OGA inhibitors.
4.3.4.2. The Quantitative Isotopic and Chemoenzymatic Tagging(QUIC-Tag)Approach for Quantitative Proteomics
Hsieh-Wilson, Peters, and co-workers developed a method to probe dynamic changes in O-GlcNAc glycosylation using quantitative mass spectrometry-based proteomics.223 Their QUIC-Tag approach (quantitative isotopic and chemoenzymatic tagging) involves chemoenzymatically labeling proteins from two different cell states (e.g., normal versus diseased; stimulated versus unstimulated) with the keto-galactose–biotin group as described above (Figure 13).223 After proteolytic digestion, the resulting peptides are isotopically labeled with either heavy or light isotope tags using reductive amination chemistry to distinguish the two populations. The peptides are subsequently combined, and the biotinylated O-GlcNAc peptides are captured using avidin chromatography. MS analysis reveals two ions for each glycosylated peptide (corresponding to each of the two isotopically labeled forms), and calculation of the peak areas measures the change in glycosylation level for each peptide. Importantly, as the observed peptides are sequenced using CID or ETD MS, the method identifies specific proteins undergoing dynamic changes in glycosylation and can be used to monitor changes at particular glycosylation sites within proteins.
Figure 13.

QUIC-Tag approach for quantifying dynamic changes in glycosylation.
This approach has advantages over other methods of O-GlcNAc detection. For instance, lectins and O-GlcNAc antibodies are typically used to detect only global changes in O-GlcNAc glycosylation by Western blotting and do not monitor individual glycosylation sites. Metabolic labeling using GlcNAz may alter the kinetic efficiency of O-GlcNAc transfer to protein substrates, as well as influx through the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway, which complicates efforts to quantify dynamic changes in response to cellular stimuli. In contrast, the QUIC-Tag approach is performed on denatured protein lysates and thus preserves the physiological glycosylation state of the protein without perturbing intra-cellular glycosylation pathways.
By this approach, O-GlcNAc glycosylation was found to be stimulated upon PUGNAc treatment of cortical neurons or kainic acid-induced excitatory stimulation of rodent brains in vivo.223 Robust changes in O-GlcNAc glycosylation were observed at specific sites on several proteins, whereas other modification sites remained unchanged, suggesting that O-GlcNAc is subject to complex regulation in neurons. For example, glycosylation of early growth response-1 (EGR-1), a transcription factor involved in long-term memory formation and cell survival,259,260 increased greater than 10-fold after kainic acid stimulation. Because the dynamic glycosylation site within EGR-1 lies within its transactivation domain, O-GlcNAc glycosylation may modulate the transcriptional activity of EGR-1 and modulate gene expression. Cumulatively, these studies indicate that O-GlcNAc glycosylation is reversible, subject to complex regulation, and induced by neuronal activity, which supports the notion that O-GlcNAc represents an important regulatory modification in the brain.
4.3.4.3. Stable Isotope Labeling with Amino Acids in Cell Culture(SILAC)Coupled with Affinity Chromatography
Recently, Hart and co-workers employed the SILAC (stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture) method for quantitative proteomics261 in conjunction with immunoaffinity chromatography to investigate the interplay between O-GlcNAc and phosphorylation in COS-7 kidney fibroblast cells.262 Cells from two different states were labeled with either heavy or light isotopes of arginine and combined. Proteins of interest were subsequently isolated by affinity chromatography using a general O-GlcNAc antibody, resolved by SDS–PAGE, proteolytically digested, and analyzed by LC–MS/MS.
Using this approach, Hart and colleagues investigated the effects of lithium inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) on O-GlcNAc glycosylation levels. GSK-3 is involved in multiple intracellular signaling cascades and is implicated in the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, and bipolar disorder, thus making it a desirable therapeutic target.263,264 The authors identified 10 proteins that were enriched after LiCl treatment, suggesting that they underwent increases in O-GlcNAc glycosylation. The increases in glycosylation were confirmed on four proteins by immunoprecipitation. Interestingly, many proteins exhibited no change, and 19 proteins showed decreases in glycosylation. These studies suggest that a complex interplay exists between O-phosphate and O-GlcNAc within signaling networks.
Although this approach works well for dividing cells, SILAC is not amenable to tissues and quiescent cells such as neurons. In addition, the method does not readily enable direct detection of the O-GlcNAc modification, and thus independent confirmation by immunoprecipitation is required. Nonetheless, this approach provides another powerful strategy to investigate the cellular dynamics of O-GlcNAc glycosylation.
4.3.4.4. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of OGT and OGA
Traditional genetic approaches have revealed insights into the functions of OGT and OGA in vivo. For example, genetic deletion of the OGT gene in mice has revealed that OGT is critical for cell survival, and neuron-specific deletion of OGT results in defects in mouse embryogenesis, loss of locomotor control, and neonatal death.221,222 Although such studies have revealed an important role for these enzymes in neural development, investigations into the functions of O-GlcNAc remain challenging, particularly in adult animals. The development of small-molecule inhibitors for OGT and OGA has been actively pursued to enable direct temporal and spatial control over OGT and OGA activity.
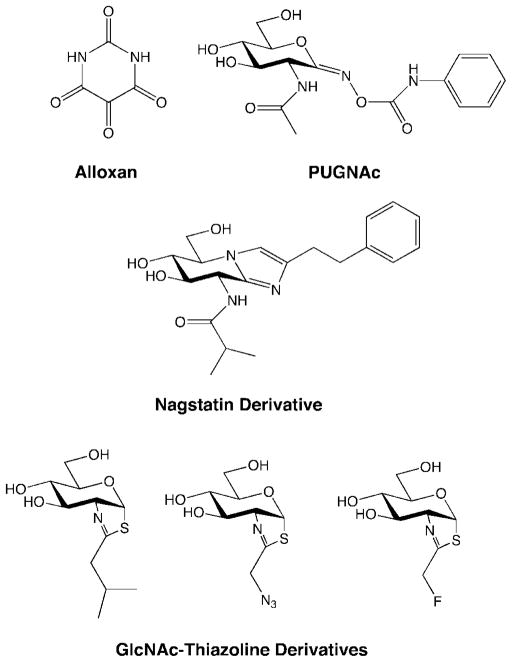
Well-known small-molecule inhibitors of OGT such as alloxan (Figure 14) show multiple nonspecific effects such as inhibition of OGA and glucokinase,265,266 as well as formation of superoxide radicals.267 To develop better pharmacological agents, Walker and co-workers screened a library using a high-throughput, fluorescence-based assay and identified several novel compounds that inhibited OGT activity in vitro.268 Notably, the compounds selectively inhibited OGT but not MurG, a related enzyme that also uses UDP-GlcNAc as a substrate.
As PUGNAc, the most commonly used OGA inhibitor, suffers from nonspecific activity toward β-hexosaminidase,269 several groups are working to develop more selective inhibitors. The Vocadlo and Hanover groups have extended the N-acyl substituent of PUGNAc to generate inhibitors with 10-fold selectivity for OGA over β-hexosaminidase.269,270 van Aalten and colleagues developed a nagstatin derivative based the crystal structure of a bacterial OGA (Figure 14).271 This molecule contains an isobutanamido group at the N8 position that improves selectivity by fitting into a pocket of the enzyme and a phenethyl group at the C2 position that interacts with a solvent-exposed tryptophan from bacterial OGA. More recently, the Hanover and Vocadlo groups independently developed novel OGA inhibitors based on the nonspecific hexosaminidase inhibitor GlcNAc-thiazaoline, by adding fluoro, azido, or alkyl substituents (Figure 14). The resultant inhibitors exhibited over 3000-fold selectivity for OGA over β-hexosaminidase.272,273
The development of such compounds may enable the selective inhibition of OGT and OGA in cultured neurons, as well as in vivo. The ability to perturb O-GlcNAc enzymes and glycosylation levels with small molecules should reveal new information about the functional roles of O-GlcNAc glycosylation in the nervous system, as well as facilitate the identification of signaling pathways that regulate OGT and OGA.
5. Glycosaminoglycans
5.1. Structure and Diversity
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are sulfated, linear polysaccharides that represent a central component of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and are involved in a myriad of biological functions, including blood coagulation,274,275 angiogene-sis,276–278 tumor growth and metastasis,279–281 neurite outgrowth,282–285 spinalcordinjury,286–288 anddevelopment.289–291 They are composed of repeating disaccharide units containing a hexuronic acid sugar linked to a hexosamine sugar.292,293 There are several classes of GAGs (Figure 15), each of which are distinguished by backbone composition, including heparin and heparan sulfate (HS), chondroitin sulfate (CS), dermatan sulfate (DS), keratan sulfate (KS), and hyaluronic acid (HA). Heparin and HS contain D-glucosamine (GlcN) and either D-glucuronic acid (GlcA) or L-iduronic acid (IdoA) connected by α(1–4) and β (1–4) linkages. In contrast, CS polymers contain N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) instead of GlcNAc in alternating β (1–3) and β (1–4) linkages to GlcA, whereas DS polymers have both GlcA and IdoA linked to GalNAc. Heparin/HS and CS/DS are attached to proteins through O-linkages to serine residues via a GlcAβ (1–3)Gal-β (1–3)Galβ (1–4)Xyl (Xyl = xylose) tetrasaccharide linker, forming glycoconjugates known as proteoglycans.294–296 KS is attached to proteoglycans through either N- or O-linkages. Hyaluronic acid is unique in that it is not protein-bound and is reportedly synthesized in the plasma membrane,296,297 whereas proteoglycans are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus.292,293
Figure 15.

Structures of GAG subclasses. Potential sulfation sites are indicated in red. R = SO3− or H; R1 = SO3−, H, or Ac; n = ~10–200.
In addition to having different backbone compositions, GAGs display remarkable structural variation through sulfation of various hydroxyl groups along the polysaccharide backbone (Figure 15). The sulfation patterns of GAGs are incredibly diverse, owing to the large number of potential sulfation sites and possible combinations of differentially sulfated disaccharides linked in tandem. For example, heparin and HS disaccharide units can be sulfated at the C-2 position of IdoA or the C-3 and C-6 positions of GlcN. The C-2 amine of GlcN can also be acetylated, sulfated, or unmodified. Similarly, CS can be sulfated at the C-4 and C-6 positions of GalNAc, as well as the C-2 and C-3 positions of GlcA. A simple HS disaccharide has 48 potential sulfated sequences, yielding tetrasaccharides with over 2300 possible sulfation sequences.
GAGs also vary in chain length from ~10 to 200 disaccharide units, with clusters of low and high sulfation along the polysaccharide backbone.298 Structural studies suggest that GAGs can adopt a variety of helical conformations, such as variance in helical pitch that may depend on the associated counterion.299,300 Further structural diversity is obtained from the conformational flexibility of the pyranose ring of IdoA, which exists in equilibrium between the chair and skew-boat conformations when sulfated at the C-2 position.298 Thus, the combination of different sequences, charge distributions, and conformations gives rise to tremendous chemical and structural diversity within glycosaminoglycan chains.
5.2. Neurobiological Functions
5.2.1. Neuronal Development
Evidence from genetic and biochemical approaches suggests that the sulfation patterns of GAGs are important for modulating their biological activity and can exert profound effects on organismal development. For instance, mutation of the N-deacetylase–N-sulfotransferase gene (Ndst-1) involved in HS biosynthesis inhibits growth factor signaling that disrupts normal embryonic development in Drosophila.290 HS and CS have been shown to interact with numerous growth factors and axon guidance proteins in a sulfation-specific manner.283,301–308 Moreover, the sulfation patterns of HS and CS change during the course of brain development,309,310 and specific CS sulfation patterns are differentially expressed in certain brain regions.311,312 The sulfation patterns of HS and CS are also organ- and age-specific, as is the expression of different sulfotransferases.309,310 Thus, HS and CS sulfation patterns in the brain are tightly regulated with the exquisite spatial and temporal control required for neuronal development.
5.2.2. Axon Guidance
In the developing nervous system, neurons are presented with a variety of molecular cues that guide axons to their proper targets. HS sulfation has been implicated in axon targeting through the interaction of the HS proteoglycan glypican-1 with Slit, a secreted protein important for axon guidance, axon branching, and neuronal cell migration.313,314 Slit repels axonal growth by binding to the Robo receptor.314,315 Removal of HS by heparinase treatment or addition of exogenous HS containing specific sulfation patterns inhibits Slit binding to Robo and abolishes the axonal repulsion mediated by Slit.304,315 These results suggest that HS and particular HS sulfation patterns play important roles in mediating the chemotropic actions of Slit. In other studies, HS sulfation was shown to be critical for neuronal outgrowth and axon guidance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Using genetic approaches, Hobert and colleagues demonstrated that certain neuronal subtypes require the HS-modifying enzymes C5-epimerase, 2-O-sulfotransferase, and 6-O-sulfotransferase for proper axon guidance.316 Interestingly, other subclasses of neurons require only the C5-epimerase or 2-O-sulfotrans-ferase, and some neuronal subtypes do not require any of the HS modifying enzymes. Cumulatively, these studies demonstrate that HS sulfation patterns play important roles in neuronal development and may encode axon guidance cues to direct neurons to their proper targets in vivo.
5.2.3. Spinal Cord Regeneration
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) are crucial components of perineuronal nets, structures of ECM molecules surrounding the soma and proximal dendrites of certain neurons in the brain and spinal cord.317,318 CSPGs and other ECM molecules are recruited to sites of CNS injury and form a portion of the glia scar, a structure that inhibits axonal regeneration and contributes to permanent paralysis in vivo. Several groups have demonstrated the importance of CSPGs and their associated sugar chains in mediating neuronal inhibition after spinal cord injury. For instance, CSPGs have been shown to inhibit the neurite outgrowth of DRG and CGN neurons in vitro.319,320 Moreover, degrading CS chains with chondroitinase ABC (ChABC), an enzyme that cleaves CS into disaccharide units, reverses the inhibitory effects of CSPGs on neurite outgrowth.321,322 Most notably, Fawcett, McMahon, and colleagues discovered that ChABC digestion of CSPGs promotes spinal cord regeneration in vivo, with concomitant partial recovery of proprioceptive behaviors and locomotor skills in mice.323,324 These and other studies indicate that CSPGs exert a crucial inhibitory role on neuronal regeneration and represent valid targets for therapeutic intervention. Such studies also underscore the importance of CS glycosaminoglycans in this process and the need to further understand the molecular mechanisms and sulfation patterns involved in directing their activity.
5.3. Challenges to the Study of GAGs
While GAGs play a fundamental role in many neurobiological processes, a molecular level understanding of the roles of specific sulfation sequences in mediating GAG functions is largely unknown. GAG biosynthesis is not template driven and lacks the proofreading capabilities of DNA biosynthesis, which results in greater chemical heterogeneity and structural diversity within GAG chains. Thus, GAGs purified from natural sources are often mixtures of compounds that contain different sulfation patterns and chain lengths. Characterization of these structures is challenging and is often described simply in terms of the percent composition of distinct sulfated disaccharide subunits. Little is known about the precise linear sequences of GAG polysaccharides, although methods to sequence short oligosaccharide sequences are becoming available.325–327 Given these challenges, the synthesis of homogeneous oligosaccharides containing defined sulfation sequences has the potential to significantly advance our understanding of the structure–activity relationships of glycosaminoglycans. Here, we will highlight chemical approaches that have helped to decipher the roles of GAGs in the nervous system and efforts to develop GAG-based therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases.
5.4. Synthetic Molecules for Probing Structure–Activity Relationships
As described above, the sulfation patterns of GAGs are important for directing their neurobiological functions. Although genetic approaches have revealed crucial roles for GAGs in neural development, such experiments lead to global changes in sulfation throughout the carbohydrate chain, precluding the identification of specific sulfation motifs responsible for biological activity. The use of chemically defined small-molecule GAGs has provided insight into their neurobiological roles and demonstrated the importance of specific sulfation sequences in mediating GAG functions.
5.4.1. Synthesis of Glycosaminoglycans
Early work on glycosaminoglycans focused primarily on the synthesis of heparin oligosaccharides.328–336 Heparin has been used since the 1940s as an antithrombic agent, and a unique heparin pentasaccharide sequence was discovered in the 1980s as a potent factor Xa inhibitor.298 The first syntheses of heparin pentasaccharides required over 60 steps, produced heparin in relatively low yield, and were impractical for the development of synthetic drugs. Since then, the efforts of multiple laboratories have contributed methods that allow for efficient syntheses of heparin, HS, and their analogues.337–344
GAGs are notoriously difficult to synthesize, requiring the formation of stereospecific glycosidic linkages, uronic acid donors and acceptors with low chemical reactivity, and sophisticated protecting group strategies to effect regioselective sulfation. Heparin, HS, and DS oligosaccharides also necessitate efficient syntheses of the challenging L-idopyranosyl sugar. The synthesis of GAGs has been summarized in several excellent reviews (see refs 337, 344–347) Recently, there has been great interest in generating libraries of sulfated compounds to probe the role of sulfation and identify biologically active sulfation motifs.2,285,339,340,342,348 In general, these approaches implement modular, convergent synthetic strategies that afford multiple sulfated structures from a common disaccharide synthon and thus minimize the number of steps.
Other strategies have employed chemoenzymatic routes to generate defined GAG oligosaccharides. Kobayashi and co-workers have capitalized on the promiscuity of hyaluronidase, an enzyme that normally catalyzes the hydrolysis of chondroitin in vivo, to effect glycosidic bond formation and generate GAG polymers.349–353 They were able to demonstrate the efficient polymerization of N-acetylhyalobiuronate [GlcAβ (1–3)GlcNAc] and N-acetylchondrosine [GlcAβ (1–3)GalNAc] derivatives to form HA and nonsulfated chondroitin, respectively, as well as unnatural chondroitin analogues.349 DeAngelis and colleagues have generated chimeric unsulfated GAG oligo- and polysaccharides through the use of hyaluronan and chondroitin synthases.354 Notably, Rosenberg and co-workers have developed a chemoenzymatic route toward the synthesis of a specific sulfated HS pentasaccharide that binds to antithrombin III.355 The authors used a nonsulfated polysaccharide obtained from E. coli as starting material and synthesized the final product using six recombinant sulfotransferases. This route achieved the synthesis of the sulfated structure in just six steps with at least a 2-fold greater yield relative to total chemical synthesis,356 although it was performed only on a milligram-scale. Thus, chemoenzymatic synthetic strategies can complement traditional synthetic approaches to provide facile, efficient methods to generate structurally defined natural and unnatural GAGs.
5.4.2. Effects of HS and DS Molecules on Neuronal Growth
Early studies of GAG function in the nervous system involved the use of GAGs purified from various biological sources, such as shark cartilage, bovine kidney, and the surface of tumor cells.357–360 For example, Prochiantz and Rousselet demonstrated that natural HS polysaccharides enhance axonal outgrowth, while inhibiting dendrite elongation. In contrast, DS polysaccharides favor the growth of both axons and dendrites.358 Small-molecule di- through hexasaccharides derived from HS and DS polysaccharides were found to have similar effects as the natural polysaccharides, providing the first evidence that the biological activity of GAGs can be recapitulated in short oligosaccharides.357,358
5.4.3. Neuroactive Small-Molecule Chondroitin Sulfates
Paradoxically, CS has been shown to both stimulate and inhibit neuronal growth, depending on the cellular context.361–363 However, the molecules used in those studies were ~200 saccharides in length, poorly defined, and heterogeneously sulfated. To address whether specific sulfation patterns were important for neuronal growth, Hsieh-Wilson and colleagues used a modular strategy to synthesize pure, chemically defined CS-E, CS-C, CS-A, and CS-R tetrasaccharides (Figure 16).283 Tetrasaccharides bearing the CS-E motif were found to stimulate the outgrowth of various neuron types, including hippocampal and dopaminergic neurons.283,285 A tetrasaccharide was found to be the minimal motif required for activity, as CS-E disaccharides had no effect on neurite outgrowth.285 Furthermore, tetrasaccharides bearing other prominent CS sulfation patterns found in the brain, such as CS-C and CS-A, had no significant growth-promoting activity, underscoring the importance of specific sulfation patterns in directing CS activity. Notably, the unnatural CS-R motif could not stimulate neurite outgrowth, despite having the same overall negative charge as CS-E.283 Thus, the precise arrangement of sulfate groups along the carbohydrate backbone is critical for the growth-promoting activity of CS, rather than nonspecific electrostatic interactions. Together, these results provide direct evidence for the existence of a “sulfation code” that dictates the neurobiological functions of CS.
Figure 16.

CS-E, -A, -C, and -R tetrasaccharides. Only the CS-E tetrasaccharide promotes neurite outgrowth.
5.5. Carbohydrate Microarrays for Studying GAG–Protein Interactions
Microarray technology has revolutionized the discovery of biological information obtained from both genomics and proteomics experiments. More recently, the advent of carbohydrate microarrays has made a similar impact on our understanding of protein–carbohydrate interactions.283,304,364–376 Carbohydrate microarrays provide a powerful tool for the rapid interrogation of these interactions in a high-throughput, chip-based format. They have also allowed for systematic investigations into the role of specific sulfation patterns in mediating the biological activities of GAGs.
5.5.1. Oligosaccharide Microarrays
As described above, studies using chemically defined oligosaccharides have implicated a tetrasaccharide bearing the CS-E sulfation motif as important for neurite outgrowth. To gain insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying its biological activity, the binding of various CS molecules to a panel of neuronal growth factors was examined using carbohydrate microarrays.283 CS oligosaccharides were synthesized with an allyl functionality at the reducing end of the sugar. Ozonolysis, followed by reaction with 1,2-(bisaminooxy)ethane converted the allyl group to an aminooxy functionality for rapid conjugation of the oligosaccharides to aldehyde-coated slides.283,374 Robotically printed glass slides were analyzed for the binding of CS-A, CS-C, CS-E, and CS-R tetrasaccharides to growth factors such as midkine, BDNF, and fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1). Midkine is a growth factor involved in neural tissue development and repair,377 whereas BDNF is a neurotrophin involved in nervous system development, synaptic plasticity, and neurodegenerative disease.378 Both midkine and BDNF were found to preferentially interact with the CS-E tetrasaccharide over other sulfation motifs. In contrast, FGF-1 did not interact with any CS molecules, consistent with earlier observations and further corroborating the method.309,379 Importantly, the novel interactions identified using these microarrays were validated in cellular assays and demonstrated to be important for CS-E-mediated neuronal growth. Blocking midkine, BDNF, or their cognate receptors using selective antibodies inhibited the neurite outgrowth induced by CS-E tetrasaccharides. These studies illustrate the power of carbohydrate microarrays to elucidate molecular interactions and mechanisms involving specific GAG sequences.
Seeberger and co-workers have used oligosaccharide microarrays to study the binding of heparin di-, tetra-, and hexasaccharides to FGF-1 and FGF-2.371,380 Both heparin tetra- and hexasaccharides were shown to interact with these growth factors, consistent with the minimum structural requirements known to bind FGF-1 and FGF-2. In the future, it will be interesting to examine the interactions of a panel of neuronal growth factors with different sulfated HS analogues and to compare their binding to both sulfated HS and CS molecules.
5.5.2. Polysaccharide Microarrays
In addition to oligosaccharide microarrays, polysaccharide microarrays have been developed and exploited for the study of GAG function. Although the structures of polysaccharides are less well-defined, polysaccharide microarrays can be readily assembled from commercially available compounds and can provide valuable information. For instance, such microarrays have revealed key structural determinants responsible for protein binding, such as the importance of sulfation at specific positions.283,304,374 They have also enabled rapid comparisons across different protein families or functional classes, as well as between different GAG subclasses (e.g., HA, HS, CS, DS, KS), providing a more comprehensive investigation into protein-binding specific-ity.304 Using polysaccharide microarrays, Shipp and Hsieh-Wilson found HS to interact in a sulfation-dependent manner with axon guidance proteins, such as Slit2, netrin1, ephrinA1, ephrinA5, and semaphorin5B.304 Slit2 interacted preferentially with 6-O-sulfated and N-sulfated HS sequences. Furthermore, the sulfation preferences of Slit2 and netrin1 were validated in cellular assays using differentially sulfated HS polysaccharides, which were shown to inhibit Slit- and netrin-mediated axonal guidance and neuronal migration.
Cumulatively, these studies demonstrate the ability of carbohydrate microarray technologies to distinguish the influence of fine structural details such as sulfation pattern on GAG–protein interactions. This methodology also provides a powerful platform to rapidly screen thousands of carbohydrate–protein interactions, which can help to identify the proteins mediating the biological functions of GAGs and uncover the diverse biological functions governed by these extraordinary molecules.
5.6. Glycosaminoglycan-Based Therapeutics
Historically, heparin oligo- and polysaccharides are known for their therapeutic value for the treatment of blood coagulation and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Studies on a synthetic sulfated pentasaccharide of heparin have helped to uncover the mechanism of heparin’s anticoagulant activity and led to development of the drug Arixtra for the treatment of pulmonary embolism and DVT.337 The development of additional GAG therapeutic molecules is underway to create potential treatments for cancer metastasis, Alzheimer’s disease, and axonal regeneration. Here, we review the current literature on GAGs as potential therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative disorders.
5.6.1. Prion Diseases
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies are prion diseases characterized by vacuolation, amyloid plaques containing amyloid fibrils, and neuronal degeneration. These diseases include scrapie, bovine spongiform encephalitis (also known as “mad cow disease”), Kuru (human form of transmissible spongiform encephalitis), Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), and Gerstmann–Straussler–Scheinker disease.381 The prion protein is the main component of amyloid fibrils, which are similar to the β-amyloid fibrils characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease.382 These proteins generally induce conformational changes of the protein from α-helix to β-sheet, which leads to aggregation and formation of plaques.383,384 Thus, molecules that inhibit prion protein aggregation and plaque formation have potential therapeutic value.
Avila and co-workers have investigated the effects of sulfated polysaccharides (heparin, KS, and CS), as well as the unsulfated polysaccharide HA, on prion polymerization in vitro.385 Sulfated GAGs led to significant inhibition of prion polymerization through the direct interaction of these molecules with prion amyloid fibrils. No polymerization inhibition or neuroprotection was observed with HA, suggesting that sulfation is critical for the observed activity.385 Interestingly, differentially sulfated GAGs led to different morphologies of the resulting fibrils. However, the polysaccharides used were from natural sources and thus contained some degree of heterogeneity. Systematic studies with GAGs of defined length and sulfation pattern have not yet been performed and may reveal new molecules with optimal activity as potential treatments for prion diseases.
5.6.2. Alzheimer’s Disease
Glycosaminoglycans have also been investigated as potential treatments for the pathogenesis and senile dementia associated with Alzheimer’s disease. HS proteoglycans are believed to promote aggregation of the β-amyloid peptide and hence contribute to the disease pathogenesis.386–391 In addition, HS has been shown to protect β-amyloid aggregates from proteolytic degradation392 and microglia phagocytosis in rodent brains,393,394 resulting in the persistence of amyloid deposits.395 Heparin also enhances the synthesis, secretion, and cleavage of the β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) in vitro, suggesting that heparin may contribute to amyloid fibril formation.396 Together, these studies suggest roles for GAGs in the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease and new potential avenues for therapeutic treatment.
Low molecular weight (LMW) heparin fragments and heparin disaccharides have been examined for their ability to affect amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. These heparin fragments, especially heparin disaccharides, inhibit binding of heparin to the β-amyloid peptide, as well as heparin-stimulated APP secretion in vitro. All LMW fragments used in these studies were found to cross the blood–brain barrier in an in vitro cell culture model, whereas passage of polysaccharides was significantly inhibited.397 Injection of LMW heparins into rat brains has also been shown to attenuate protein toxicity due to tau,398,399 a microtubule-associated protein whose aggregation is associated with the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.400 In addition, LMW heparins attenuate β-amyloid-mediated neurotoxicity and inflammation.401 Thus, LMW heparin molecules and their derivatives might be useful therapeutic agents to prevent or slow the progress of amyloidogenesis associated with Alzheimer’s disease.397,402
Two sulfated LMW glycosaminoglycans and their derivatives are currently in clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and senile dementia, and one drug, Ateroid marketed by Cornelli Consulting, is currently sold in Europe and Asia. Ateroid is mostly composed of LMW heparin and is used for the treatment of old-age dementia, ischemic vascular dementia, and multi-infarct dementia. Alzhemed (tramiprosate; 3-amino-1-propanesulfonic acid) is a small synthetic GAG-based mimetic currently in phase III clinical trials that inhibits the formation of β-amyloid fibrils.403 Results have been promising from phase II clinical trials in patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease, suggesting the potential of such approaches for the treatment of this disorder.
5.6.3. Future Challenges
Elucidating the molecular mechanisms governing the modes of glycosaminoglycan action, such as the presence of a “sulfation code”, will greatly facilitate the development of new therapeutics specifically targeted to treat disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, recently identified glycosaminoglycan mimetics such as Alzhemed can improve the pharmacokinetic properties of the molecules and create superior therapeutic agents. Given the scope of the current chemical methodology to study GAGs and their interactions, GAG-based therapeutic molecules are becoming highly attainable and may prove effective avenues for the treatment of diseases. As in the case of Arixtra, understanding the structure–activity relationships of GAGs and the “sulfation code” may yield molecules with fewer off-target side effects and enhanced therapeutic properties.
6. Summary and Future Directions
The development of new chemical approaches to investigate the biological functions of carbohydrates has accelerated our understanding of glycan structures and their contributions to neurobiology, cell signaling, and disease. These studies have revealed crucial roles for glycans in mediating neuronal growth, adhesion, migration, and regeneration. In addition, studies have implicated carbohydrates in modulating cell signaling, gene expression, and synaptic plasticity. As glycans are involved in a myriad of biological functions, understanding glycan function should continue to provide key insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying fundamental neurobiological processes. Moreover, our ability to understand and manipulate such processes using small molecules and glycan mimetics holds promise for many neurological disorders for which there are currently little or no therapeutic remedies.
The emergence of chemical technologies for labeling, detection, synthesis, and mimicry are slowly becoming standard in the field for investigating glycan function, and many of these tools are now commercially available. The ability to screen high-throughput carbohydrate microarrays should reveal hundreds of new molecular interactions with growth factors and other proteins. Such technologies allow the ability to profile oligosaccharide–protein binding interactions in ways that had only previously been available for protein and DNA interactions. In addition, these arrays may be useful for diagnostic testing, because many glycans are dysregulated in various disease states. The ability to chemically tag oligosaccharides has revolutionized glycoproteomics, and we are just on the cusp of uncovering a wealth of new information in the coming years in relation to signaling pathways and disease states. Furthermore, the synthesis of oligosaccharides and glycan mimetics has revealed detailed information regarding the structure–activity relationships of glycans and should impact investigations into new drugs or pathways for therapeutic intervention. Lastly, these versatile chemical tools enable analysis of glycans and perturbations in glycan function in vivo that until now have been unprecedented. As the repertoire of chemical tools for investigating glycan functions expands, an increasing number of oligosaccharide-mediated signaling pathways may be targeted for therapeutic intervention. The study of glycan structures should also reveal new biomarkers for early detection of certain diseases, for monitoring disease progression, or for measuring drug efficacy. We are only at the beginning of what promises to be an exciting new era for the field of glycomics, and there are many discoveries and applications still waiting to be explored.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the National Institutes of Health (Grant RO1 GM084724), National Science Foundation (Grant CHE-0239861), American Cancer Society (Grant RSG-05–106–01-CDD), Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program (Grant 14RT-0034), and Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Biographies

Heather E. Murrey received a B.A./M.S. degree in biochemistry from Brandeis University in 2000. She then conducted research at the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research in the laboratories of Peter S. Kim and Harvey F. Lodish. She is currently pursuing a Ph.D. at Caltech under the direction of Linda C. Hsieh-Wilson. Her graduate studies have focused on the role of fucosyl oligosaccharides in neuronal communication and development.

Linda C. Hsieh-Wilson received her B.S. degree in chemistry from Yale University in 1990. She then earned her Ph.D. degree in 1996 from the University of California at Berkeley, where she worked with Peter G. Schultz. After completing postdoctoral studies in neurobiology at The Rockefeller University with Nobel Laureate Paul Greengard in 2000, she joined the faculty at the California Institute of Technology, where she is currently Associate Professor of Chemistry. In 2005, she was appointed a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. Her research group works at the interface of organic chemistry and neurobiology to study the roles of carbohydrates and their associated proteins in transcription, neuronal signaling, and brain development.
References
- 1.Becker DJ, Lowe JB. Glycobiology. 2003;13:41–53. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwg054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gama CI, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9:609–619. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rampal R, Luther KB, Haltiwanger RS. Curr Mol Med. 2007;7:427–445. doi: 10.2174/156652407780831593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gabius HJ, Andre S, Kaltner H, Siebert HC. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1572:165–177. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nishihira J. Int J Mol Med. 1998;2:17–28. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Apweiler R, Hermjakob H, Sharon N. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:4–8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(99)00165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kleene R, Schachner M. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:195–208. doi: 10.1038/nrn1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rexach JE, Clark PM, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4:97–106. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wujek P, Kida E, Walus M, Wisniewski KE, Golabek AA. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:12827–12839. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313173200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rudd PM, Merry AH, Wormald MR, Dwek RA. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002;12:578–586. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yamaguchi H. Trends Glycosci Glycotechnol. 2002;14:139–151. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wells L, Vosseller K, Hart GW. Science. 2001;291:2376–2378. doi: 10.1126/science.1058714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Murrey HE, Gama CI, Kalovidouris SA, Luo WI, Driggers EM, Porton B, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:21–26. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503381102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kalovidouris SA, Gama CI, Lee LW, Hsieh-Wilson LC. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:1340–1341. doi: 10.1021/ja044631v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sandi C, Rose SPR, Mileusnic R, Lancashire C. Neuroscience. 1995;69:1087–1093. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Salinska E, Bourne RC, Rose SPR. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19:3042–3047. doi: 10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Welzl H, Stork O. News Physio Sci. 2003;18:147–150. doi: 10.1152/nips.01422.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Murphy KJ, Regan CM. Neuobiol Leran Mem. 1998;70:73–81. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1998.3839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jaeken J, Matthijs G. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2007;8:261–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.8.080706.092327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ohtsubo K, Marth JD. Cell. 2006;126:855–867. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Best T, Kemps E, Bryan J. Nutr Rev. 2005;63:409–418. doi: 10.1301/nr.2005.dec.409-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kudo T, Fujii T, Ikegami S, Inokuchi K, Takayama Y, Ikehara Y, Nishihara S, Togayachi A, Takahashi S, Tachibana K, Yuasa S, Narimatsu H. Glycobiology. 2007;17:1–9. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwl047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Muramatsu T. J Biochem. 2000;127:171–176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stickens D, Zak BM, Rougier N, Esko JD, Werb Z. Development. 2005;132:5055–5068. doi: 10.1242/dev.02088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Di Rocco M, Hennet T, Grubenmann CE, Pagliardini S, Allegri AEM, Frank CG, Aebi M, Vignola S, Jaeken J. J Inherited Metab Dis. 2005;28:1162–1164. doi: 10.1007/s10545-005-0137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Endo T, Toda T. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26:1641–1647. doi: 10.1248/bpb.26.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lowe JB, Marth JD. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:643–691. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Marquardt T, Denecke J. Eur J Pediatr. 2003;162:359–379. doi: 10.1007/s00431-002-1136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schachter H. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001;58:1085–1104. doi: 10.1007/PL00000923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Varki NM, Varki A. Lab Invest. 2007;87:851–857. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sato C. Trends Glycosci Glycotechnol. 2004;16:331–344. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Angata T, Varki A. Chem Rev. 2002;102:439–469. doi: 10.1021/cr000407m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Edelman GM. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rutishauser U, Landmesser L. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:422–427. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(96)10041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Malykh YN, Schauer R, Shaw L. Biochimie. 2001;83:623–634. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(01)01303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bast RC, Bates S, Bredt AB, Desch CE, Fritsche H, Fues L, Hayes DF, Kemeny NE, Kragen M, Jessup J, Locker GY, Macdonald JS, Mennel RG, Norton L, Ravdin P, Smith TJ, Taube S, Winn RJ. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:2843–2877. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ajioka Y, Allison LJ, Jass JR. J Clin Pathol. 1996;49:560–564. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.7.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kalela A, Ponnio M, Koivu TA, Hoyhtya M, Huhtala H, Sillanaukee P, Nikkari ST. Eur J Clin Invest. 2000;30:99–104. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2000.00607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Crocker PR, Hartnell A, Munday J, Nath D. Glycoconjugate J. 1997;14:601–609. doi: 10.1023/a:1018588526788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Corfield AP, Williams AJK, Clamp JR, Wagner SA, Mountford RA. Clin Sci. 1988;74:71–78. doi: 10.1042/cs0740071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gee GV, Dugan AS, Tsomaia N, Mierke DF, Atwood WJ. Glycoconjugate J. 2006;23:19–26. doi: 10.1007/s10719-006-5434-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Alexander DA, Dimock K. J Virol. 2002;76:11265–11272. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.22.11265-11272.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ciarlet M, Crawford SE, Estes MK. J Virol. 2001;75:11834–11850. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.23.11834-11850.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Huberman K, Peluso RW, Moscona A. Virology. 1995;214:294–300. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.9925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Crocker PR, Paulson JC, Varki A. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:255–266. doi: 10.1038/nri2056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Trapp BD. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1990;605:29–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kelm S, Pelz A, Schauer R, Filbin MT, Tang S, Debellard ME, Schnaar RL, Mahoney JA, Hartnell A, Bradfield P, Crocker PR. Curr Biol. 1994;4:965–972. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schachner M, Bartsch U. Glia. 2000;29:154–165. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-1136(20000115)29:2<154::aid-glia9>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.DeBellard ME, Tang S, Mukhopadhyay G, Shen YJ, Filbin MT. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7:89–101. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1996.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Filbin MT. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995;5:588–595. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mukhopadhyay G, Doherty P, Walsh FS, Crocker PR, Filbin MT. Neuron. 1994;13:757–767. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Montag D, Giese KP, Bartsch U, Martini R, Lang Y, Bluthmann H, Karthigasan J, Kirschner DA, Wintergerst ES, Nave KA, Zielasek J, Toyka KV, Lipp HP, Schachner M. Neuron. 1994;13:229–246. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90472-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Li CM, Tropak MB, Gerlai R, Clapoff S, Abramownewerly W, Trapp B, Peterson A, Roder J. Nature. 1994;369:747–750. doi: 10.1038/369747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Crocker PR, Kelm S, Hartnell A, Freeman S, Nath D, Vinson M, Mucklow S. Biochem Soc Trans. 1996;24:150–156. doi: 10.1042/bst0240150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Vyas AA, Patel HV, Fromholt SE, Heffer-Lauc M, Vyas KA, Dang JY, Schachner M, Schnaar RL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:8412–8417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.072211699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yang LJS, Zeller CB, Shaper NL, Kiso M, Hasegawa A, Shapiro RE, Schnaar RL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:814–818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.2.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Collins BE, Kiso M, Hasegawa A, Tropak MB, Roder JC, Crocker PR, Schnaar RL. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16889–16895. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.27.16889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sheikh KA, Sun J, Liu YJ, Kawai H, Crawford TO, Proia RL, Griffin JW, Schnaar RL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:7532–7537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chiavegatto S, Sun J, Nelson RJ, Schnaar RL. Exp Neurol. 2000;166:227–234. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2000.7504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Cremer H, Lange R, Christoph A, Plomann M, Vopper G, Roes J, Brown R, Baldwin S, Kraemer P, Scheff S, Barthels D, Rajewsky K, Wille W. Nature. 1994;367:455–459. doi: 10.1038/367455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tomasiewicz H, Ono K, Yee DL, Thompson C, Goridis C, Rutishauser U, Magnuson T. Neuron. 1993;11:1163–1174. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90228-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Acheson A, Sunshine JL, Rutishauser U. J Cell Biol. 1991;114:143–153. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bruses JL, Rutishauser U. Biochimie. 2001;83:635–643. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(01)01293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cremer H, Chazal G, Lledo PM, Rougon G, Montaron MF, Mayo W, Le Moal M, Abrous DN. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2000;18:213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(99)00090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cremer H, Chazal G, Carleton A, Goridis C, Vincent JD, Lledo PM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:13242–13247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Seki T, Rutishauser U. J Neurosci. 1998;18:3757–3766. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-10-03757.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cremer H, Chazal G, Goridis C, Represa A. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1997;8:323–335. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1996.0588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Muller D, Wang C, Skibo G, Toni N, Cremer H, Calaora V, Rougon G, Kiss JZ. Neuron. 1996;17:413–422. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Becker CG, Artola A, GerardySchahn R, Decker T, Welzl H, Schachner M. J Neurosci Res. 1996;45:143–152. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19960715)45:2<143::AID-JNR6>3.0.CO;2-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hu HY, Tomasiewicz H, Magnuson T, Rutishauser U. Neuron. 1996;16:735–743. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Uryu K, Butler AK, Chesselet MF. J Comp Neurol. 1999;405:216–232. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19990308)405:2<216::aid-cne6>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Butler AK, Uryu K, Chesselet MF. Dev Neurosci. 1998;20:253–262. doi: 10.1159/000017319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wood GK, Liang JJ, Flores G, Sultan A, Quirion R, Srivastava LK. Mol Brain Res. 1997;51:69–81. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(97)00209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Seki T, Arai Y. Neurosci Res. 1993;17:265–290. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(93)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kuhn HG, DickinsonAnson H, Gage FH. J Neurosci. 1996;16:2027–2033. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-06-02027.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Alonso G, Prieto M, Legrand A, Chauvet N. J Comp Neurol. 1997;384:181–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Theodosis DT, Rougon G, Poulain DA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:5494–5498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Yang PF, Yin XH, Rutishauser U. J Cell Biol. 1992;116:1487–1496. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Dityatev A, Dityateva G, Sytnyk V, Delling M, Toni N, Nikonenko I, Muller D, Schachner M. J Neurosci. 2004;24:9372–9382. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1702-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Vawter MP, Usen N, Thatcher L, Ladenheim B, Zhang PS, VanderPutten DM, Conant K, Herman MM, van Kammen DP, Sedvall G, Garver DL, Freed WJ. Exp Neurol. 2001;172:29–46. doi: 10.1006/exnr.2001.7790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Vawter MP. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;405:385–395. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00568-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Barbeau D, Liang JJ, Robitaille Y, Quirion R, Srivastava LK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Mikkonen M, Soininen H, Tapiola T, Alafuzoff I, Miettinen R. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:1754–1764. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Nakanishi S. Neuron. 1994;13:1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Hammond MSL, Sims C, Parameshwaran K, Suppiramaniam V, Schachner M, Dityatev A. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:34859–34869. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602568200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kelm S, Brossmer R, Isecke R, Gross HJ, Strenge K, Schauer R. Eur J Biochem. 1998;255:663–672. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2550663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Strenge K, Schauer R, Bovin N, Hasegawa A, Ishida H, Kiso M, Kelm S. Eur J Biochem. 1998;258:677–685. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2580677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.May AP, Robinson RC, Vinson M, Crocker PR, Jones EY. Mol Cell. 1998;1:719–728. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Blixt O, Collins BE, van den Nieuwenhof IM, Crocker PR, Paulson JC. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:31007–31019. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304331200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Vyas AA, Blixt O, Paulson JC, Schnaar RL. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:16305–16310. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500250200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Shelke SV, Gao GP, Mesch S, Gathje H, Kelm S, Schwardt O, Ernst B. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:4951–4965. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.04.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 1997;23:3–25. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(00)00129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Veber DF, Johnson SR, Cheng HY, Smith BR, Ward KW, Kopple KD. J Med Chem. 2002;45:2615–2623. doi: 10.1021/jm020017n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Zhang Y, Zhang XY, Wu DS, Verhaagen J, Richardson PM, Yeh J, Bo XN. Mol Ther. 2007;15:1796–1804. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Papastefanaki F, Chen P, Lavdas AA, Thornaidou D, Schachner M, Matsas R. Brain. 2007;130:2159–2174. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Brisson JR, Baumann H, Imberty A, Perez S, Jennings HJ. Biochemistry. 1992;31:4996–5004. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Toikka J, Aalto J, Hayrinen J, Pelliniemi LJ, Finne J. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28557–28559. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.44.28557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Torregrossa P, Buhl L, Bancila M, Durbec P, Schafer C, Schachner M, Rougon G. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:30707–30714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403935200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Wieser JR, Heisner A, Stehling P, Oesch F, Reutter W. FEBS Lett. 1996;395:170–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)01029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Kayser H, Ats C, Lehmann J, Reutter W. Experientia. 1993;49:885–887. doi: 10.1007/BF01952603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kayser H, Geilen CC, Paul C, Zeitler R, Reutter W. FEBS Lett. 1992;301:137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81233-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kayser H, Zeitler R, Hoppe B, Reutter W. J Labelled Compd Radiopharm. 1992;31:711–715. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Kayser H, Zeitler R, Kannicht C, Grunow D, Nuck R, Reutter W. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:16934–16938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Fitz W, Wong CH. J Org Chem. 1994;59:8279–8280. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kosa RE, Gross HJ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;190:914–920. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Sparks MA, Williams KW, Lukacs C, Schrell A, Priebe G, Spaltenstein A, Whitesides GM. Tetrahedron. 1993;49:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Schmidt C, Stehling P, Schnitzer J, Reutter W, Horstkorte R. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19146–19152. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.30.19146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Câmara J, ffrench-Constant C. J Neurol. 2007;254(Suppl 1):I15–I22. [Google Scholar]
- 109.Cudrici C, Niculescu T, Niculescu F, Shin ML, Rus H. J Rehab Res Dev. 2006;43:123–131. doi: 10.1682/jrrd.2004.08.0111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H. Brain. 1999;122:2279–2295. doi: 10.1093/brain/122.12.2279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Learish RD, Brustle O, Zhang SC, Duncan ID. Ann Neurol. 1999;46:716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.delosMonteros AE, Zhao P, Huang C, Pan T, Chang R, Nazarian R, Espejo D, deVellis J. J Neurosci Res. 1997;50:872–887. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19971201)50:5<872::AID-JNR23>3.0.CO;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Saito M, Kitamura H, Sugiyama K. J Neurochem. 2001;78:64–74. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Schmidt C, Ohlemeyer C, Kettenmann H, Reutter W, Horstkorte R. FEBS Lett. 2000;478:276–280. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01868-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Sweetnam P, Nestler E, Gallombardo P, Brown S, Duman R, Bracha HS, Tallman J. Mol Brain Res. 1987;2:223–233. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Sweetnam PM, Tallman JF. Mol Pharmacol. 1986;29:299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Buttner B, Kannicht C, Schmidt C, Loster K, Reutter W, Lee HY, Nohring S, Horstkorte R. J Neurosci. 2002;22:8869–8875. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-20-08869.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Charter NW, Mahal LK, Koshland DE, Bertozzi CR. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:9255–9261. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111619200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Couve A, Kittler JT, Uren JM, Calver AR, Pangalos MN, Walsh FS, Moss SJ. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001;17:317–328. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2000.0938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Gao LY, Gu XB, Yu DS, Yu RK, Zeng GC. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;224:103–107. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Mahal LK, Charter NW, Angata K, Fukuda M, Koshland DE, Bertozzi CR. Science. 2001;294:380–382. doi: 10.1126/science.1062192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Pon RA, Lussier M, Yang QL, Jennings HJ. J Exp Med. 1997;185:1929–1938. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.11.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Pon RA, Biggs NJ, Jennings HJ. Glycobiology. 2007;17:249–260. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwl075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Horstkorte R, Muhlenhoff M, Reutter W, Nohring S, Zimmer-mann-Kordmann M, Gerardy-Schahn R. Exp Cell Res. 2004;298:268–274. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Collins BE, Fralich TJ, Itonori S, Ichikawa Y, Schnaar RL. Glycobiology. 2000;10:11–20. doi: 10.1093/glycob/10.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Chou HH, Takematsu H, Diaz S, Iber J, Nickerson E, Wright KL, Muchmore EA, Nelson DL, Warren ST, Varki A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:11751–11756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.20.11751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Collins BE, Yang LJS, Mukhopadhyay G, Filbin MT, Kiso M, Hasegawa A, Schnaar RL. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:1248–1255. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.2.1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Mahal LK, Bertozzi CR. Chem Biol. 1997;4:415–422. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(97)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Mahal LK, Yarema KJ, Bertozzi CR. Science. 1997;276:1125–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5315.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Dube DH, Bertozzi CR. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003;7:616–625. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Jacobs CL, Yarema KJ, Mahal LK, Nauman DA, Charters NW, Bertozzi CR. Applications of Chimeric Genes and Hybrid Proteins Part B, Cell Biology and Physiology. In: Thorner J, Emr SD, Abelson JN, editors. Methods in Enzymology. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 2000. p. 327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Charter NW, Mahal LK, Koshland DE, Bertozzi CR. Glycobiology. 2000;10:1049–1056. doi: 10.1093/glycob/10.10.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Moloney DJ, Shair LH, Lu FM, Xia J, Locke R, Matta KL, Haltiwanger RS. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:9604–9611. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.13.9604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Kelly RJ, Rouquier S, Giorgi D, Lennon GG, Lowe JB. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:4640–4649. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Larsen RD, Ernst LK, Nair RP, Lowe JB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:6674–6678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Lowe JB. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1993;6:465–492. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(05)80155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Jork R, Smalla KH, Karsten U, Grecksch G, Ruthrich HL, Matthies H. Neurosci Res Commun. 1991;8:21–27. [Google Scholar]
- 138.Rose SPR, Jork R. Behav Neural Biol. 1987;48:246–258. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(87)90808-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Kaneko M, Kudo T, Iwasaki H, Ikehara Y, Nishihara S, Nakagawa S, Sasaki K, Shiina T, Inoko H, Saitou N, Narimatsu H. FEBS Lett. 1999;452:237–242. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00640-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Natsuka S, Lowe JB. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994;4:683–691. [Google Scholar]
- 141.Miyoshi E, Noda K, Yamaguchi Y, Inoue S, Ikeda Y, Wang WG, Ko JH, Uozumi N, Li W, Taniguchi N. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:9–20. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(99)00166-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Nishihara S, Iwasaki H, Kaneko M, Tawada A, Ito M, Narimatsu H. FEBS Lett. 1999;462:289–294. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01549-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Luo Y, Koles K, Vorndam W, Haltiwanger RS, Panin VM. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:9393–9399. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511975200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Wang Y, Shao L, Shi SL, Harris RJ, Spellman MW, Stanley P, Haltiwanger RS. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:40338–40345. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107849200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Springer TA. Cell. 1994;76:301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Lowe JB. Kidney Int. 1997;51:1418–1426. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Hooper LV, Gordon JI. Glycobiology. 2001;11:1R–10R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/11.2.1r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Guruge JL, Falk PG, Lorenz RG, Dans M, Wirth HP, Blaser MJ, Berg DE, Gordon JI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:3925–3930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Li YX, Li L, Irvine KD, Baker NE. Development. 2003;130:2829–2840. doi: 10.1242/dev.00498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Sasamura T, Sasaki N, Miyashita F, Nakao S, Ishikawa HO, Ito M, Kitagawa M, Harigaya K, Spana E, Bilder D, Perrimon N, Matsuno K. Development. 2003;130:4785–4795. doi: 10.1242/dev.00679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Block TM, Comunale MA, Lowman M, Steel LF, Romano PR, Fimmel C, Tennant BC, London WT, Evans AA, Blumberg BS, Dwek RA, Mattu TS, Mehta AS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:779–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408928102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Wang JW, Ambros RA, Weber PB, Rosano TG. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3654–3658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Yazawa S, Nakamura J, Asao T, Nagamachi Y, Sagi M, Matta KL, Tachikawa T, Akamatsu M. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1993;84:989–995. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1993.tb00190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Thompson S, Dargan E, Turner GA. Cancer Lett. 1992;66:43–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(92)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Lowe JB. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:531–538. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2003.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Vestweber D, Blanks JE. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:181–213. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1999.79.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Butcher EC, Picker LJ. Science. 1996;272:60–66. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5258.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Listinsky JJ, Siegal GP, Listinsky CM. Am J Clin Pathol. 1998;110:425–440. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/110.4.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Macartney JC. J Pathol. 1987;152:23–30. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Kim YJ, Borsig L, Varki NM, Varki A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:9325–9330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Orntoft TF, Vestergaard EM. Electrophoresis. 1999;20:362–371. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2683(19990201)20:2<362::AID-ELPS362>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Kim YJ, Varki A. Glycoconjugate J. 1997;14:569–576. doi: 10.1023/a:1018580324971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Miyake M, Taki T, Hitomi S, Hakomori S. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:14–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207023270103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Yakubenia S, Wild MK. FEBS J. 2006;273:4390–4398. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Science. 1999;284:770–776. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5415.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Rampal R, Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Nita-Lazar A, Kosik KS, Haltiwanger RS. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:32133–32140. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506104200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Lei L, Xu AG, Panin VM, Irvine KD. Development. 2003;130:6411–6421. doi: 10.1242/dev.00883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Haines N, Irvine KD. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:786–797. doi: 10.1038/nrm1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Okajima T, Irvine KD. Cell. 2002;111:893–904. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Louvi A, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:93–102. doi: 10.1038/nrn1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Lu LC, Stanley P. Functional Glycomics. In: Fukuda M, editor. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 417 Elsevier; Amsterdam: 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 172.Shi SL, Stanley P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:5234–5239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0831126100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Sukumar R, Rose SPR, Burgoyne RD. J Neurochem. 1980;34:1000–1006. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.McCabe NR, Rose SPR. Neurochem Res. 1985;10:1083–1095. doi: 10.1007/BF00965883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Pohle W, Acosta L, Ruthrich H, Krug M, Matthies H. Brain Res. 1987;410:245–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Bullock S, Rose SPR, Zamani R. J Neurochem. 1992;58:2145–2154. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Krug M, Wagner M, Staak S, Smalla KH. Brain Res. 1994;643:130–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Matthies H, Staak S, Krug M. Brain Res. 1996;725:276–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Zanetta JP, Reeber A, Vincendon G, Gombos G. Brain Res. 1977;138:317–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90749-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Krusius T, Finne J. Eur J Biochem. 1977;78:369–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Taniguchi T, Adler AJ, Mizuochi T, Kochibe N, Kobata A. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:1730–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Matsui Y, Lombard D, Massarelli R, Mandel P, Dreyfus H. J Neurochem. 1986;46:144–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Popov N, Schmidt S, Schulzeck S, Jork R, Lossner B, Matthies H. Pharmacol, Biochem Behav. 1983;19:43–47. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(83)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Gardiol A, Racca C, Triller A. J Neurosci. 1999;19:168–179. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-01-00168.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Torre ER, Sterward O. J Neurosci. 1996;16:5967–5978. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-19-05967.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Bullock S, Potter J, Rose SPR. J Neurochem. 1990;54:135–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Lorenzini CGA, Baldi E, Bucherelli C, Sacchetti B, Tassoni G. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1997;68:317–324. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1997.3798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Matthies H, Staak S, Krug M. Brain Res. 1996;725:276–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Krug M, Jork R, Reymann K, Wagner M, Matthies H. Brain Res. 1991;540:237–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90513-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Karsten U, Pilgrim G, Hanisch FG, Uhlenbruck G, Kasper M, Stosiek P, Papsdorf G, Pasternak G. Br J Cancer. 1988;58:176–181. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Hilfiker S, Pieribone VA, Czernik AJ, Kao HT, Augustine GJ, Greengard P. Philos Trans R Soc. 1999;354:269–279. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Ferreira A, Li L, Chin LS, Greengard P, Kosik KS. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;8:286–299. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1996.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Rabuka D, Hubbard SC, Laughlin ST, Argade SP, Bertozzi CR. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:12078–12079. doi: 10.1021/ja064619y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Sawa M, Hsu TL, Itoh T, Sugiyama M, Hanson SR, Vogt PK, Wong CH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:12371–12376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605418103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Hsu TL, Hanson SR, Kishikawa K, Wang SK, Sawa M, Wong CH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:2614–2619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611307104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Trachtenberg JT, Chen BE, Knott GW, Feng GP, Sanes JR, Welker E, Svoboda K. Nature. 2002;420:788–794. doi: 10.1038/nature01273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Luscher C, Nicoll RA, Malenka RC, Muller D. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:545–550. doi: 10.1038/75714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Hanover JA. FASEB J. 2001;15:1865–1876. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0094rev. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Slawson C, Hart GW. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13:631–636. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2003.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Hart GW, Housley MP, Slawson C. Nature. 2007;446:1017–1022. doi: 10.1038/nature05815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Slawson C, Housley MP, Hart GW. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:71–83. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Khidekel N, Ficarro SB, Peters EC, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:13132–13137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403471101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Comer FI, Hart GW. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:161–171. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(99)00176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Wells L, Hart GW. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:154–158. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Wells L, Whalen SA, Hart GW. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;302:435–441. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Zachara NE, O’Donnell N, Cheung WD, Mercer JJ, Marth JD, Hart GW. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:30133–30142. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403773200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Wells L, Vosseller K, Hart GW. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60:222–228. doi: 10.1007/s000180300017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Zachara NE, Hart GW. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1673:13–28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Fulop N, Marchase RB, Chatham JC. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;73:288–297. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.07.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Parker GJ, Lund KC, Taylor RP, McClain DA. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:10022–10027. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207787200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Dias WB, Hart GW. Mol BioSyst. 2007;3:766–772. doi: 10.1039/b704905f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Arnold CS, Hart GW. Trends Glycosci Glycotechnol. 1999;11:355–370. [Google Scholar]
- 213.Yao PJ, Coleman PD. Neurosci Lett. 1998;252:33–36. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00547-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Yao PJ, Coleman PD. J Neurosci. 1998;18:2399–2411. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-07-02399.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Griffith LS, Schmitz B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;213:424–431. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Ballatore C, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. doi: 10.1038/nrn2194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Liu F, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Hart GW, Gong CX. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:10804–10809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400348101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Robertson LA, Moya KL, Breen KC. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2004;6:489–495. doi: 10.3233/jad-2004-6505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Iyer SPN, Hart GW. Biochemistry. 2003;42:2493–2499. doi: 10.1021/bi020685a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Cole RN, Hart GW. J Neurochem. 2001;79:1080–1089. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Shafi R, Lyer SPN, Ellies LG, O’Donnell N, Marek KW, Chui D, Hart GW, Marth JD. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:5735–5739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.100471497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.O’Donnell N, Zachara NE, Hart GW, Marth JD. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:1680–1690. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.4.1680-1690.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Khidekel N, Ficarro SB, Clark PM, Bryan MC, Swaney DL, Rexach JE, Sun YE, Coon JJ, Peters EC, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:339–348. doi: 10.1038/nchembio881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Vosseller K, Trinidad JC, Chalkley RJ, Specht CG, Thalhammer A, Lynn AJ, Snedecor JO, Guan S, Medzihradszky KF, Maltby DA, Schoepfer R, Burlingame AL. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:923–34. doi: 10.1074/mcp.T500040-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Cole RN, Hart GW. J Neurochem. 1999;73:418–428. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0730418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Luthi T, Haltiwanger RS, Greengard P, Bahler M. J Neurochem. 1991;56:1493–1498. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Arnold CS, Johnson GVW, Cole RN, Dong DLY, Lee M, Hart GW. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28741–28744. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.46.28741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Roquemore EP, Chou TY, Hart GW. Methods Enzymol. 1994;230:443–460. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)30028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Comer FI, Vosseller K, Wells L, Accavitti MA, Hart GW. Anal Biochem. 2001;293:169–177. doi: 10.1006/abio.2001.5132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Snow CM, Senior A, Gerace L. J Cell Biol. 1987;104:1143–1156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Khidekel N, Arndt S, Lamarre-Vincent N, Lippert A, Poulin-Kerstien KG, Ramakrishnan B, Qasba PK, Hsieh-Wilson LC. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:16162–16163. doi: 10.1021/ja038545r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Ramakrishnan B, Qasba PK. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:20833–20839. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111183200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Tai HC, Khidekel N, Ficarro SB, Peters EC, Hsieh-Wilson LC. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:10500–10501. doi: 10.1021/ja047872b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Deller T, Korte M, Chabanis S, Drakew A, Schwegler H, Stefani GG, Zuniga A, Schwarz K, Bonhoeffer T, Zeller R, Frotscher M, Mundel P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:10494–10499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1832384100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Vazquez LE, Chen HJ, Sokolova I, Knuesel I, Kennedy MB. J Neurosci. 2004;24:8862–8872. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3213-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Sala C, Piech V, Wilson NR, Passafaro M, Liu GS, Sheng M. Neuron. 2001;31:115–130. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Israely I, Costa RM, Xie CW, Silva AJ, Kosik KS, Liu X. Curr Biol. 2004;14:1657–1663. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.08.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Zhang M, Wang W. Acc Chem Res. 2003;36:530–538. doi: 10.1021/ar020210b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Hsieh-Wilson LC, Khidekel N, Arndt SE, Tai H-C. U.S. Patent Application 20050130235. Method and compositions for the detection of protein glycosylation. 2005
- 240.Clark PM, Dweck JF, Mason DE, Hart C, Peters EC, Agnew BJ, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Unpublished results. [Google Scholar]
- 241.Vocadlo DJ, Hang HC, Kim EJ, Hanover JA, Bertozzi CR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:9116–9121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1632821100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Lubas WA, Smith M, Starr CM, Hanover JA. Biochemistry. 1995;34:1686–1694. doi: 10.1021/bi00005a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Nandi A, Sprung R, Barma DK, Zhao YX, Kim SC, Falck JR, Zhao YM. Anal Chem. 2006;78:452–458. doi: 10.1021/ac051207j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Sprung R, Nandi A, Chen Y, Kim SC, Barma D, Falck JR, Zhao YM. J Proteome Res. 2005;4:950–957. doi: 10.1021/pr050033j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Dube DH, Prescher JA, Quang CN, Bertozzi CR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:4819–4824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506855103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Wells L, Vosseller K, Cole RN, Cronshaw JM, Matunis MJ, Hart GW. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2002;1:791–804. doi: 10.1074/mcp.m200048-mcp200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Downs F, Herp A, Moschera J, Pigman W. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973;328:182–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90344-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Bertolini M, Pigman W. J Biol Chem. 1967;242:3776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Syka JEP, Coon JJ, Schroeder MJ, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:9528–9533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402700101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Golks A, Tran TTT, Goetschy JF, Guerini D. EMBO J. 2007;26:4368–4379. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Roquemore EP, Chevrier MR, Cotter RJ, Hart GW. Biochemistry. 1996;35:3578–3586. doi: 10.1021/bi951918j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Liu K, Paterson AJ, Chin E, Kudlow JE. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:2820–2825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.6.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Rex-Mathes M, Werner S, Strutas D, Griffith LS, Viebahn C, Thelen K, Schmitz B. Biochimie. 2001;83:583–590. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(01)01305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Marshall S, Bacote V, Traxinger RR. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:4706–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Griffith LS, Schmitz B. Eur J Biochem. 1999;262:824–831. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Buse MG. Am J Phys-Endocrinol Metab. 2006;290:E1–E8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00329.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.McClain DA, Lubas WA, Cooksey RC, Hazel M, Parker GJ, Love DC, Hanover JA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:10695–10699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152346899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Carrillo LD, Krishnamoorthy L, Mahal LK. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:14768–14769. doi: 10.1021/ja065835+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Thiel G, Cibelli G. J Cell Physiol. 2002;193:287–292. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Jones MW, Errington ML, French PJ, Fine A, Bliss TVP, Garel S, Charnay P, Bozon B, Laroche S, Davis S. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:289–296. doi: 10.1038/85138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Ong SE, Mittler G, Mann M. Nat Methods. 2004;1:119–126. doi: 10.1038/nmeth715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Wang Z, Pandey A, Hart GW. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6:1365–1379. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M600453-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Gould TD, Manji HK. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:1223–1237. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Doble BW, Woodgett JR. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:1175–1186. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Lee TN, Alborn WE, Knierman MD, Konrad RJ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;350:1038–1043. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.09.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Meglasson MD, Burch PT, Berner DK, Najafi H, Matschinsky FM. Diabetes. 1986;35:1163–1173. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.10.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Szkudelski T. Physiol Res. 2001;50:537–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Gross BJ, Kraybill BC, Walker S. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:14588–14589. doi: 10.1021/ja0555217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Kim EJ, Perreira M, Thomas CJ, Hanover JA. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:4234–4235. doi: 10.1021/ja0582915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Stubbs KA, Zhang N, Vocadlo DJ. Org Biomol Chem. 2006;4:839–845. doi: 10.1039/b516273d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Dorfmueller HC, Borodkin VS, Schimpl M, Shepherd SM, Shpiro NA, van Aalten DMF. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:16484–16485. doi: 10.1021/ja066743n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Knapp S, Abdo M, Ajayi K, Huhn RA, Emge TJ, Kim EJ, Hanover JA. Org Lett. 2007;9:2321–2324. doi: 10.1021/ol0706814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Macauley MS, Whitworth GE, Debowski AW, Chin D, Vocadlo DJ. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:25313–25322. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413819200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Barrow RT, Parker ET, Krishnaswamy S, Lollar P. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:26796–26800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Bourin MC, Lindahl U. Biochem J. 1993;289:313–330. doi: 10.1042/bj2890313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Iozzo RV. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:646–656. doi: 10.1038/nrm1702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Casu B, Guerrini M, Naggi A, Perez M, Torri G, Ribatti D, Carminati P, Giannini G, Penco S, Pisano C, Belleri M, Rusnati M, Presta M. Biochemistry. 2002;41:10519–10528. doi: 10.1021/bi020118n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Iozzo RV, San Antonio JD. J Clin Invest. 2001;108:349–355. doi: 10.1172/JCI13738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Liu DF, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, El Shabrawi Y, Sasisekharan R. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:568–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.012578299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Lokeshwar VB, Rubinowicz D, Schroeder GL, Forgacs E, Minna JD, Block NL, Nadji M, Lokeshwar BL. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:11922–11932. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008432200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Denholm EM, Lin YQ, Silver PJ. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;416:213–221. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)00884-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Bovolenta P, Fernaud-Espinosa I. Prog Neurobiol. 2000;61:113–132. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(99)00044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Gama CI, Tully SE, Sotogaku N, Clark PM, Rawat M, Vaidehi N, Goddard WA, Nishi A, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:467–473. doi: 10.1038/nchembio810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Schwartz NB, Domowicz M. Glycoconjugate J. 2004;21:329–341. doi: 10.1023/B:GLYC.0000046278.34016.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Tully SE, Mabon R, Gama CI, Tsai SM, Liu XW, Hsieh-Wilson LC. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:7736–7737. doi: 10.1021/ja0484045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 286.Barritt AW, Davies M, Marchand F, Hartley R, Grist J, Yip P, McMahon SB, Bradbury EJ. J Neurosci. 2006;26:10856–10867. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2980-06.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Yick LW, Wu WT, So KF, Yip HK, Shum DKY. Neuroreport. 2000;11:1063–1067. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200004070-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 288.Gorio A, Vergani L, Lesma E, Di Giulio AM. J Neurosci Res. 1998;51:559–562. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19980301)51:5<559::AID-JNR2>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Hacker U, Nybakken K, Perrimon N. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:530–541. doi: 10.1038/nrm1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 290.Lin XH. Development. 2004;131:6009–6021. doi: 10.1242/dev.01522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 291.Perrimon N, Bernfield M. Nature. 2000;404:725–728. doi: 10.1038/35008000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 292.Sugahara K, Kitagawa H. IUBMB Life. 2002;54:163–175. doi: 10.1080/15216540214928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 293.Silbert JE, Sugumaran G. IUBMB Life. 2002;54:177–186. doi: 10.1080/15216540214923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 294.Schwartz NB. Front Biosci. 2000;5:D649–D655. doi: 10.2741/a540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 295.Margolis RK, Margolis RU. Experientia. 1993;49:429–446. doi: 10.1007/BF01923587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 296.Sasisekharan R, Raman R, Prabhakar V. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2006;8:181–231. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 297.Itano N, Kimata K. IUBMB Life. 2002;54:195–199. doi: 10.1080/15216540214929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 298.Capila I, Linhardt RJ. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2002;41:391–412. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020201)41:3<390::aid-anie390>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 299.Schlessinger J, Plotnikov AN, Ibrahimi OA, Eliseenkova AV, Yeh BK, Yayon A, Linhardt RJ, Mohammadi M. Mol Cell. 2000;6:743–750. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 300.Millane RP, Mitra AK, Arnott S. J Mol Biol. 1983;169:903–920. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 301.Li FC, Shetty AK, Sugahara K. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:2956–2966. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609296200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 302.Noti C, de Paz JL, Polito L, Seeberger PH. Chem– Eur J. 2006;12:8664–8686. doi: 10.1002/chem.200601103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 303.Bao XF, Muramatsu T, Sugahara K. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:35318–35328. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507304200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 304.Shipp EL, Hsieh-Wilson LC. Chem Biol. 2007;14:195–208. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 305.Ashikari-Hada S, Habuchi H, Kariya Y, Itoh N, Reddi AH, Kimata K. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:12346–12354. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313523200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 306.Faham S, Linhardt RJ, Rees DC. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8:578–586. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 307.Ostrovsky O, Berman B, Gallagher J, Mulloy B, Fernig DG, Delehedde M, Ron D. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:2444–2453. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108540200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 308.Raman R, Venkataraman G, Ernst S, Sasisekharan V, Sasisekha-ran R. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:2357–2362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0437842100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 309.Brickman YG, Ford MD, Gallagher JT, Nurcombe V, Bartlett PF, Turnbull JE. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4350–4359. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.8.4350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 310.Kitagawa H, Tsutsumi K, Tone Y, Sugahara K. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31377–31381. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.50.31377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 311.Fernaud-Espinosa I, Nieto-Sampedro M, Bovolenta P. J Neuro-biol. 1996;30:410–424. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4695(199607)30:3<410::AID-NEU9>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 312.Properzi F, Carulli D, Asher RA, Muir E, Camargo LM, van Kuppevelt TH, ten Dam GB, Furukawa Y, Mikami T, Sugahara K, Toida T, Geller HM, Fawcett JW. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:378–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 313.Liang Y, Annan RS, Carr SK, Popp S, Mevissen M, Margolis RK, Margolis RU. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17885–17892. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.25.17885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 314.Ronca F, Andersen JS, Paech V, Margolis RU. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:29141–29147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100240200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 315.Hu HY. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:695–701. doi: 10.1038/89482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 316.Bulow HE, Hobert O. Neuron. 2004;41:723–736. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 317.Yamaguchi Y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000;57:276–289. doi: 10.1007/PL00000690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 318.Celio MR, Spreafico R, De Biasi S, Vitellaro-Zuccarello L. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:510–514. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(98)01298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 319.Snow DM, Mullins N, Hynds DL. Microsc Res Technol. 2001;54:273–286. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 320.Niederost BP, Zimmermann DR, Schwab ME, Bandtlow CE. J Neurosci. 1999;19:8979–8989. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-20-08979.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 321.Steinmetz MP, Horn KP, Tom VJ, Miller JH, Busch SA, Nair D, Silver DJ, Silver J. J Neurosci. 2005;25:8066–8076. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2111-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 322.Sango K, Oohira A, Ajiki K, Tokashiki A, Horie M, Kawano H. Exp Neurol. 2003;182:1–11. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(03)00090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 323.Bradbury EJ, Moon LDF, Popat RJ, King VR, Bennett GS, Patel PN, Fawcett JW, McMahon SB. Nature. 2002;416:636–640. doi: 10.1038/416636a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 324.Moon LDF, Asher RA, Rhodes KE, Fawcett JW. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:465–466. doi: 10.1038/87415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 325.Thanawiroon C, Rice KG, Toida T, Linhardt RJ. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:2608–2615. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304772200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 326.Saad OM, Leary JA. Anal Chem. 2003;75:2985–2995. doi: 10.1021/ac0340455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 327.Kinoshita A, Sugahara K. Anal Biochem. 1999;269:367–378. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 328.Petitou M, Duchaussoy P, Driguez PA, Jaurand G, Herault JP, Lormeau JC, van Boeckel CAA, Herbert JM. Angew Chem, Int Ed Engl. 1998;37:3009–3014. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19981116)37:21<3009::AID-ANIE3009>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 329.Helmboldt A, Petitou M, Mallet JM, Herault JP, Lormeau JC, Driguez PA, Herbert JM, Sinay P. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1997;7:1507–1510. [Google Scholar]
- 330.Chiba T, Jacquinet JC, Sinay P, Petitou M, Choay J. Carbohydr Res. 1988;174:253–264. [Google Scholar]
- 331.Petitou M, Duchaussoy P, Lederman I, Choay J, Jacquinet JC, Sinay P, Torri G. Carbohydr Res. 1987;167:67–75. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(87)80268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 332.Petitou M, Duchaussoy P, Lederman I, Choay J, Sinay P, Jacquinet JC, Torri G. Carbohydr Res. 1986;147:221–236. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 333.Jacquinet JC, Petitou M, Duchaussoy P, Lederman I, Choay J, Torri G, Sinay P. Carbohydr Res. 1984;130:221–241. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 334.Choay J, Petitou M, Lormeau JC, Sinay P, Casu B, Gatti G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983;116:492–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90550-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 335.Poletti L, Fleischer M, Vogel C, Guerrini M, Torri G, Lay L. Eur J Org Chem. 2001:2727–2734. [Google Scholar]
- 336.Van Boeckel CAA, Beetz T, Vos JN, Dejong AJM, Van Aelst SF, Van Den Bosch RH, Mertens JMR, Van Der Vlugt FA. J Carbohydr Chem. 1985;4:293–321. [Google Scholar]
- 337.Petitou M, van Boeckel CAA. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2004;43:3118–3133. doi: 10.1002/anie.200300640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 338.Haller M, Boons GJ. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1. 2001:814–822. [Google Scholar]
- 339.de Paz JL, Ojeda R, Reichardt N, Martin-Lomas M. Eur J Org Chem. 2003:3308–3324. [Google Scholar]
- 340.Orgueira HA, Bartolozzi A, Schell P, Litjens R, Palmacci ER, Seeberger PH. Chem– Eur J. 2003;9:140–169. doi: 10.1002/chem.200390009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 341.Lohman GJS, Seeberger PH. J Org Chem. 2004;69:4081–4093. doi: 10.1021/jo035732z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 342.Angulo J, Ojeda R, de Paz JL, Lucas R, Nieto PM, Lozano RM, Redondo-Horcajo M, Gimenez-Gallego G, Martin-Lomas M. ChemBioChem. 2004;5:55–61. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200300696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 343.Codee JDC, Stubba B, Schiattarella M, Overkleeft HS, van Boeckel CAA, van Boom JH, van der Marel GA. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:3767–3773. doi: 10.1021/ja045613g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 344.Seeberger PH, Werz DB. Nature. 2007;446:1046–1051. doi: 10.1038/nature05819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 345.Noti C, Seeberger PH. Chem Biol. 2005;12:731–756. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 346.Karst NA, Linhardt RJ. Curr Med Chem. 2003;10:1993–2031. doi: 10.2174/0929867033456891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 347.Poletti L, Lay L. Eur J Org Chem. 2003:2999–3024. [Google Scholar]
- 348.Gavard O, Hersant Y, Alais J, Duverger V, Dilhas A, Bascou A, Bonnaffe D. Eur J Org Chem. 2003:3603–3620. [Google Scholar]
- 349.Kobayashi S, Fujikawa S, Ohmae M. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:14357–14369. doi: 10.1021/ja036584x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 350.Kobayashi S, Itoh R, Morii H, Fujikawa SI, Kimura S, Ohmae M. J Polym Sci. 2003;41:3541–3548. [Google Scholar]
- 351.Kobayashi S, Morii H, Ito R, Ohmae M. Macromol Symp. 2002;183:127–132. [Google Scholar]
- 352.Kobayashi S, Uyama H, Kimura S. Chem Rev. 2001;101:3793–3818. doi: 10.1021/cr990121l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 353.Kobayashi S, Morii H, Itoh R, Kimura S, Ohmae M. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:11825–11826. doi: 10.1021/ja017104+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 354.Tracy BS, Avci FY, Linhardt RJ, DeAngelis PL. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:337–344. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607569200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 355.Kuberan B, Lech MZ, Beeler DL, Wu ZLL, Rosenberg RD. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:1343–1346. doi: 10.1038/nbt885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 356.Sinay P, Jacquinet JC, Petitou M, Duchaussoy P, Lederman I, Choay J, Torri G. Carbohydr Res. 1984;132:C5–C9. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 357.Lafont F, Prochiantz A, Valenza C, Petitou M, Pascal M, Rouget M, Rousselet A. Dev Biol. 1994;165:453–468. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 358.Lafont F, Rouget M, Triller A, Prochiantz A, Rousselet A. Development. 1992;114:17. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 359.Kitagawa H, Tanaka Y, Tsuchida K, Goto F, Ogawa T, Lidholt K, Lindahl U, Sugahara K. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:22190–22195. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.38.22190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 360.Sugahara K, Masuda M, Harada T, Yamashina I, Dewaard P, Vliegenthart JFG. Eur J Biochem. 1991;202:805–811. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 361.Nadanaka S, Clement A, Masayama K, Faissner A, Sugahara K. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:3296–3307. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.6.3296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 362.Dou CL, Levine JM. J Neurosci. 1995;15:8053–8066. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-12-08053.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 363.Brittis PA, Canning DR, Silver J. Science. 1992;255:733–736. doi: 10.1126/science.1738848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 364.Zhi ZL, Powell AK, Turnbull JE. Anal Chem. 2006;78:4786–4793. doi: 10.1021/ac060084f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 365.Carion O, Lefebvre J, Dubreucq G, Dahri-Correia L, Correia J, Melnyk O. ChemBioChem. 2006;7:817–826. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200500387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 366.Huang CY, Thayer DA, Chang AY, Best MD, Hoffmann J, Head S, Wong CH. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:15–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509693102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 367.Blixt O, Head S, Mondala T, Scanlan C, Huflejt ME, Alvarez R, Bryan MC, Fazio F, Calarese D, Stevens J, Razi N, Stevens DJ, Skehel JJ, van Die I, Burton DR, Wilson IA, Cummings R, Bovin N, Wong CH, Paulson JC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:17033–17038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407902101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 368.Adams EW, Ratner DM, Bokesch HR, McMahon JB, O’Keefe BR, Seeberger PH. Chem Biol. 2004;11:875–881. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 369.Fukui S, Feizi T, Galustian C, Lawson AM, Chai WG. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:1011–1017. doi: 10.1038/nbt735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 370.Houseman BT, Mrksich M. Chem Biol. 2002;9:443–454. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(02)00124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 371.de Paz JL, Noti C, Seeberger PH. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:2766–2767. doi: 10.1021/ja057584v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 372.Feizi T, Fazio F, Chai W, Wong CH. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13:637–645. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2003.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 373.Park S, Lee MR, Pyo SJ, Shin I. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:4812–4819. doi: 10.1021/ja0391661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 374.Tully SE, Rawat M, Hsieh-Wilson LC. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:7740–7741. doi: 10.1021/ja061906t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 375.Disney MD, Seeberger PH. Chem Biol. 2004;11:1701–1707. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 376.Wang DN, Liu SY, Trummer BJ, Deng C, Wang AL. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:275–281. doi: 10.1038/nbt0302-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 377.Muramatsu T. J Biochem. 2002;132:359–371. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 378.Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:677–736. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 379.Nandini CD, Mikami T, Ohta M, Itoh N, Akiyama-Nambu F, Sugahara K. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:50799–50809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404746200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 380.de Paz JL, Angulo J, Lassaletta JM, Nieto PM, Redondo-Horcajo M, Lozano RM, Gimenez-Gallego G, Martin-Lomas M. ChemBioChem. 2001;2:673–685. doi: 10.1002/1439-7633(20010903)2:9<673::AID-CBIC673>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 381.Prusiner SB. Science. 1991;252:1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 382.Selkoe DJ. Neuron. 1991;6:487–498. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 383.Pan KM, Baldwin M, Nguyen J, Gasset M, Serban A, Groth D, Mehlhorn I, Huang ZW, Fletterick RJ, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:10962–10966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 384.Safar J, Roller PP, Gajdusek DC, Gibbs CJ. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:20276–20284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 385.Perez M, Wandosell F, Colaco C, Avila J. Biochem J. 1998;335:369–374. doi: 10.1042/bj3350369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 386.Buee L, Ding WH, Anderson JP, Narindrasorasak S, Kisilevsky R, Boyle NJ, Robakis NK, Delacourte A, Greenberg B, Fillit HM. Brain Res. 1993;627:199–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90321-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 387.Buee L, Ding W, Delacourte A, Fillit H. Brain Res. 1993;601:154–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91706-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 388.Fraser PE, Nguyen JT, Chin DT, Kirschner DA. J Neurochem. 1992;59:1531–1540. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 389.Snow AD, Wight TN. Neurobiol Aging. 1989;10:510–512. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 390.Snow AD, Lara S, Nochlin D, Wight TN. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78:113–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00688198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 391.Snow AD, Kinsella MG, Prather PB, Nochlin D, Podlisny MB, Selkoe DJ, Kisilevsky R, Wight TN. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989;48:352–352. [Google Scholar]
- 392.Guptabansal R, Frederickson RCA, Brunden KR. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18666–18671. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.31.18666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 393.Shaffer LM, Dority MD, Guptabansal R, Frederickson RCA, Younkin SG, Brunden KR. Neurobiol Aging. 1995;16:737–745. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(95)00055-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 394.Shaffer LM, Dority MD, Younkin SG, Brunden KR. Neurobiol Aging. 1994;15:S152–S152. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(95)00055-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 395.Snow AD, Sekiguchi R, Nochlin D, Fraser P, Kimata K, Mizutani A, Arai M, Schreier WA, Morgan DG. Neuron. 1994;12:219–234. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 396.Leveugle B, Ding W, Durkin JT, Mistretta S, Eisle J, Matic M, Siman R, Greenberg BD, Fillit HM. Neurochem Int. 1997;30:543–548. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(96)00103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 397.Leveugle B, Ding WH, Laurence F, Dehouck MP, Scanameo A, Cecchelli R, Fillit H. J Neurochem. 1998;70:736–744. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70020736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 398.Walzer M, Lorens S, Hejna M, Fareed J, Hanin I, Cornelli U, Lee JM. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;445:211–220. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(02)01759-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 399.Dudas B, Cornelli U, Lee JM, Hejna MJ, Walzer M, Lorens SA, Mervis RF, Fareed J, Hanin I. Neurobiol Aging. 2002;23:97–104. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(01)00255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 400.Avila J. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:2922–2927. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.02.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 401.Bergamaschini L, Donarini C, Rossi E, De Luigi A, Vergani C, De Simoni MG. Neurobiol Aging. 2002;23:531–536. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 402.Leveugle B, Scanameo A, Ding W, Fillit H. Neuroreport. 1994;5:1389–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 403.Aisen PS, Saumier D, Briand R, Laurin J, Gervais F, Tremblay P, Garceau D. Neurology. 2006;67:1757–1763. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000244346.08950.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]