Abstract
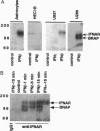
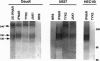
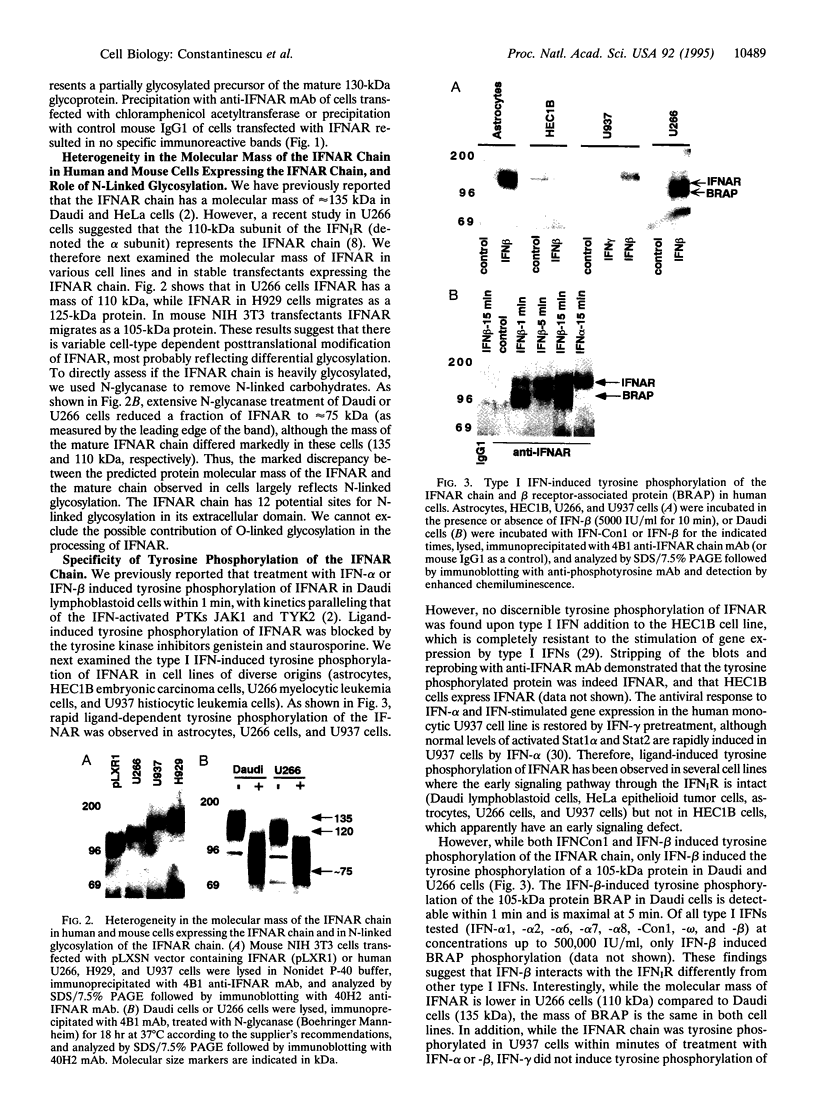
The IFNAR chain of the type I interferon (IFN) receptor (IFNIR) undergoes rapid ligand-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation and acts as a species-specific transducer for type I IFN action. Using the vaccinia/T7 expression system to amplify IFNAR expression, we found that human HeLa-S3 cells transiently express high levels of cell surface IFNAR chains (approximately 250,000 chains per cell). Metabolic labeling and immunoblot analysis of transfected HeLa cells show that the IFNAR chain is initially detected as 65-kDa and 98-kDa precursors, and then as the 130-kDa mature protein. Due to variation in N-glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of the mature IFNAR chain varies from 105 to 135 kDa in different cells. IFNIR structure was characterized in various human cell lines by analyzing 125I-labeled IFN cross-linked complexes recognized by various antibodies against IFNIR subunits and JAK protein-tyrosine kinases. Precipitation of cross-linked material from Daudi cells with anti-IFNAR antibodies showed that IFNAR was present in a 240-kDa complex. Precipitation of cross-linked material from U937 cells with anti-TYK2 sera revealed a 240-kDa complex, which apparently did not contain IFNAR and was not present in IFN-resistant HEC1B cells. The tyrosine phosphorylation and down-regulation of the IFNAR chain were induced by type I IFN in several human cell lines of diverse origins but not in HEC1B cells. However, of type I IFNs, IFN-beta uniquely induced the tyrosine phosphorylation of a 105-kDa protein associated with the IFNAR chain in two lymphoblastoid cell lines (Daudi and U266), demonstrating the specificity of transmembrane signaling for IFN-beta and IFN-alpha through the IFNAR chain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovich C., Shulman L. M., Ratovitski E., Harroch S., Tovey M., Eid P., Revel M. Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of the IFNAR chain of the type I interferon receptor and of an associated surface protein in response to IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):5871–5877. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M. High-affinity binding of 125I-labelled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):459–461. doi: 10.1038/284459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit P., Maguire D., Plavec I., Kocher H., Tovey M., Meyer F. A monoclonal antibody to recombinant human IFN-alpha receptor inhibits biologic activity of several species of human IFN-alpha, IFN-beta, and IFN-omega. Detection of heterogeneity of the cellular type I IFN receptor. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):707–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Faltynek C. R., D'Alessandro S. B., Baglioni C. Interaction of interferon with cellular receptors. Internalization and degradation of cell-bound interferon. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13291–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., D'Alessandro F., Diaz M. O., Gregory S. A., Neckers L. M., Nordan R. Characterization of three monoclonal antibodies that recognize the interferon alpha 2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7230–7234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Domanski P. Identification of a novel subunit of the type I interferon receptor localized to human chromosome 21. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10895–10899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Domanski P., Krolewski J. J., Fu X. Y., Reich N. C., Pfeffer L. M., Sweet M. E., Platanias L. C. Interferon alpha (IFN alpha) signaling in cells expressing the variant form of the type I IFN receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5660–5665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Pfeffer L. M., D'Alessandro F., Platanias L. C., Gregory S. A., Rosolen A., Nordan R., Cruciani R. A., Diaz M. O. Multichain structure of the IFN-alpha receptor on hematopoietic cells. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2126–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Porterfield B., Domanski P., Constantinescu S., Pfeffer L. M. Complementation of the interferon alpha response in resistant cells by expression of the cloned subunit of the interferon alpha receptor. A central role of this subunit in interferon alpha signaling. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9598–9602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O., Yan H., Domanski P., Handa R., Smalley D., Mullersman J., Witte M., Krishnan K., Krolewski J. Direct binding to and tyrosine phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the type I interferon receptor by p135tyk2 tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8133–8142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinescu S. N., Croze E., Wang C., Murti A., Basu L., Mullersman J. E., Pfeffer L. M. Role of interferon alpha/beta receptor chain 1 in the structure and transmembrane signaling of the interferon alpha/beta receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9602–9606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly C., Reich N. C. Double-stranded RNA activates novel factors that bind to the interferon-stimulated response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3756–3764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon alpha-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s). Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90106-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzog P. J., Hwang S. Y., Holland K. A., Tymms M. J., Iannello R., Kola I. A gene on human chromosome 21 located in the region 21q22.2 to 21q22.3 encodes a factor necessary for signal transduction and antiviral response to type I interferons. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14088–14093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Yamamoto K., Thierfelder W. E., Kreider B., Silvennoinen O. Signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily: JAKs and STATs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Improta T., Pine R., Pfeffer L. M. Interferon-gamma potentiates the antiviral activity and the expression of interferon-stimulated genes induced by interferon-alpha in U937 cells. J Interferon Res. 1992 Apr;12(2):87–94. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Miller D. G., Garcia J. V., Lynch C. M. Use of retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Methods Enzymol. 1993;217:581–599. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)17090-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura O., Ihle J. N. Subunit structure of the erythropoietin receptor analyzed by 125I-Epo cross-linking in cells expressing wild-type or mutant receptors. Blood. 1993 Apr 1;81(7):1739–1744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Cohen B., Rubinstein M. The human interferon alpha/beta receptor: characterization and molecular cloning. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Stebbing N., Donner D. B. Cytoskeletal association of human alpha-interferon-receptor complexes in interferon-sensitive and -resistant lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platanias L. C., Pfeffer L. M., Barton K. P., Vardiman J. W., Golomb H. M., Colamonici O. R. Expression of the IFN alpha receptor in hairy cell leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1992 Nov;82(3):541–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb06464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platanias L. C., Pfeffer L. M., Cruciani R., Colamonici O. R. Characterization of the alpha subunit of the IFN-alpha receptor. Evidence of N- and O-linked glycosylation and association with other surface proteins. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3382–3388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platanias L. C., Uddin S., Colamonici O. R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the alpha and beta subunits of the type I interferon receptor. Interferon-beta selectively induces tyrosine phosphorylation of an alpha subunit-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):17761–17764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin A., Sarkar F. H., Dutkowski R., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H., Gupta S. L. Receptors for human alpha and beta interferon but not for gamma interferon are specified by human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Bash D., Ruddle F. H. Antibodies to a cell-surface component coded by human chromosome 21 inhibit action of interferon. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):139–141. doi: 10.1038/260139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Orchansky P. The interferon receptors. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(3):249–275. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzé G., Lutfalla G., Gresser I. Genetic transfer of a functional human interferon alpha receptor into mouse cells: cloning and expression of its cDNA. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90738-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Broecke C., Pfeffer L. M. Characterization of interferon-alpha binding sites on human cell lines. J Interferon Res. 1988 Dec;8(6):803–811. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]