Abstract
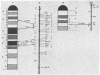
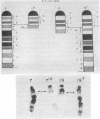
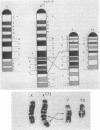
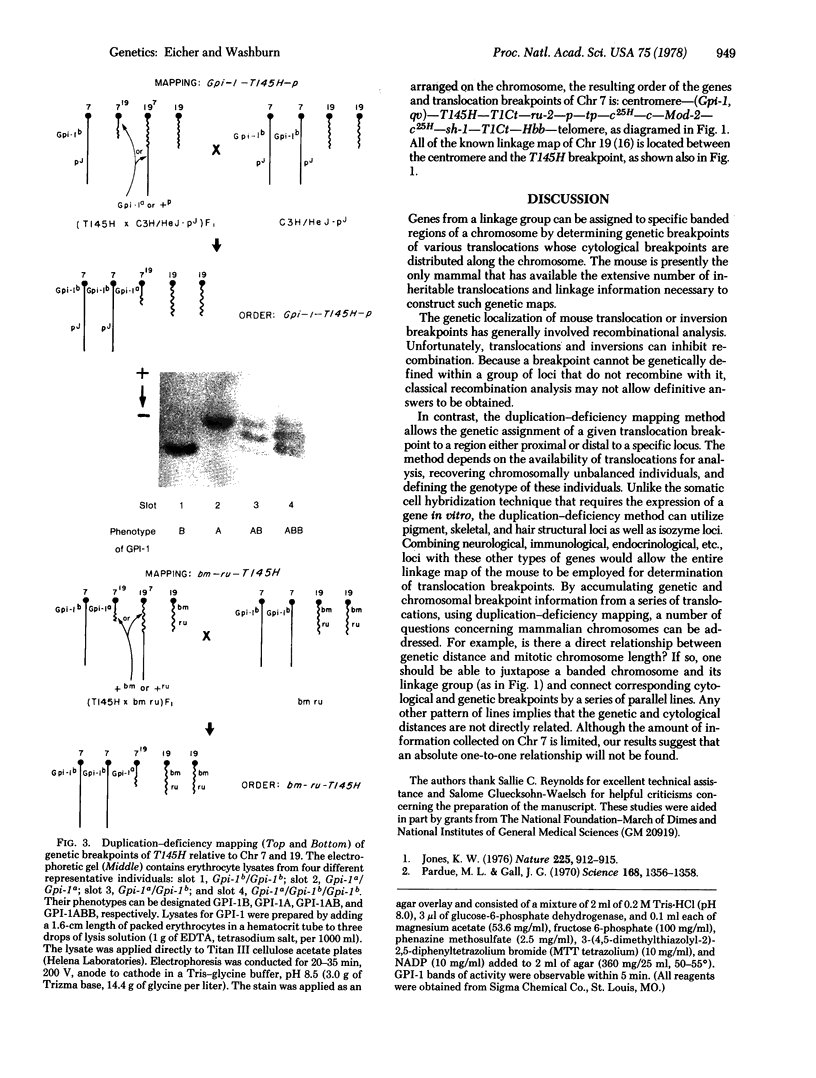
A genetic mapping procedure, called the duplication-deficiency method, is described. This method permits the genetic location of a translocation to be determined within a linkage group without the use of recombination. By utilizing the duplication-deficiency method to define the genetic breakpoints for a series of translocations involving a given chromosome and integrating this information with their cytological breakpoints, obtained by Giemsa banding, a genetic map of the chromosomes is constructed whereby groups of loci are assigned to banded regions. Duplication-deficiency mapping and Giemsa banding analysis of the T(X;7)1Ct and T(7;19)145H translocations together with information from the c25H deletion have permitted mouse chromosome 7 to be divided into six and chromosome 19 into two definable genetic regions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgerhout W. G., Jongsma A. P., de Wit J., van Someren H., Meera Khan P. Regional mapping of seven enzyme loci on human chromosome 1 by use of somatic cell hybridization. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(3):90–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATTANACH B. M. A chemically-induced variegated-type position effect in the mouse. Z Vererbungsl. 1961;92:165–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00890283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattanach B. M. The location of Cattanach's translocation in the X-chromosome linkage map of the mouse. Genet Res. 1966 Oct;8(2):253–256. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300010107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Green M. C. The T6 translocation in the mouse: its use in trisomy mapping, centromere localization, and cytological identification of linkage group 3. Genetics. 1972 Aug;71(4):621–632. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.4.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M. The Position of ru-2 and qv with Respect to the FLECKED Translocation in the Mouse. Genetics. 1970 Mar;64(3-4):495–510. doi: 10.1093/genetics/64.3-4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M. The genetic extent of the insertion involved in the flecked translocation in the mouse. Genetics. 1967 Feb;55(2):203–212. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M. The identification of the chromosome bearing linkage group XII in the mouse. Genetics. 1971 Oct;69(2):267–271. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M. Translocation trisomic mice: production by female but not male translocation carriers. Science. 1973 Apr 6;180(4081):81–81. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4081.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M. X-autosome translocations in the mouse: total inactivation versus partial inactivation of the X chromosome. Adv Genet. 1970;15:175–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P., Eicher E. M., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Demonstration in mouse of X-ray induced deletions for a know enzyme structural locus. Nature. 1974 Mar 29;248(447):416–418. doi: 10.1038/248416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Nesbitt M. Cattanach's translocation: cytological characterization by quinacrine mustard staining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2918–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Eicher E. M., Yu M. T., Atwood K. C. The chromosomal location of ribosomal DNA in the mouse. Chromosoma. 1974;49(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00348887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Warburton D., Atwood K. C. Location of ribosomal DNA in the human chromosome complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3394–3398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W. Chromosomal and nuclear location of mouse satellite DNA in individual cells. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):912–915. doi: 10.1038/225912a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W., Prosser J., Corneo G., Ginelli E. The chromosomal location of human satellite DNA 3. Chromosoma. 1973 Jul 18;42(4):445–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00399411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W., Purdom I. F., Prosser J., Corneo G. The chromosomal localisation of human satellite DNA I. Chromosoma. 1974;49(2):161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00348888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouri R. E., Miller D. A., Miller O. J., Dev V. G., Grewal M. S., Hutton J. J. Identification by quinacrine fluorescence of the chromosome carrying mouse linkage group I in the Cattanach translocation. Genetics. 1971 Sep;69(1):129–132. doi: 10.1093/genetics/69.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. W., Eicher E. M., Southard J. L. Chromosome 19 of the house mouse. J Hered. 1974 Sep-Oct;65(5):297–300. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Meredith R. Autosomal translocations causing male sterility and viable aneuploidy in the mouse. Cytogenetics. 1966;5(5):335–354. doi: 10.1159/000129909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Dev V. G., Tantravahi R., Miller O. J., Schiffman M. B., Yates R. A., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Cytological detection of the c-25H deletion involving the albino (c) locus on chromosome 7 in the mouse. Genetics. 1974 Nov;78(3):905–910. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.3.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Miller D. A., Kouri R. E., Dev V. G., Grewal M. S., Hutton J. J. Assignment of linkage groups 8 and X to chromosomes in Mus musculus and identification of the centromeric end of linkage group I. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(6):452–464. doi: 10.1159/000130165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt M. N., Francke U. A system of nomenclature for band patterns of mouse chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1973;41(2):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00319691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle A. G., Ford C. E., Beechey C. V. Meiotic disjunction in mouse translocations and the determination of centromere position. Genet Res. 1971 Oct;18(2):215–235. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300012611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triman K. L., Davisson M. T., Roderick T. H. A method for preparing chromosomes from peripheral blood in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;15(3):166–176. doi: 10.1159/000130515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe H. G. Mapping the hemoglobin locus in mice transmitting the flecked translocation. Genetics. 1967 Feb;55(2):213–218. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]