Abstract
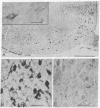
Well-characterized antisera to porcine beta-endorphin were used to localize immunoreactive sites in cryostat sections of formaldehyde-fixed rat brain by indirect immunohistochemistry. Specificity was established by absorption of immune sera with synthetic peptide fragments. Specific immunoreactivity was localized to neuronal perikarya in the basal tuberal hypothalamus, and to varicose nerve fibers which were distributed to midline nuclear areas throughout the diencephalon and anterior pons. These patterns of reactivity were unaffected by preabsorption of the immune sera with millimolar concentrations of Met5- or Leu5-enkephalin or alpha-endorphin. The beta-endorphin immunoreactive structures were morphologically separate from those cells and fibers reported to react with antisera to the enkephalins. One anti-beta-endorphin serum gave additional immunoreactivity with myelinated axons in limbic cortical zones; when absorbed with purified rat myelin basic protein, only the specific patterns of immunoreactivity remained. Thus, discrete beta-endorphin-containing neuronal circuits exist in rat brain and are anatomically distinguishable from enkephalin-containing nerve cell and fiber pathways.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Leppaluoto J., Vargo T. M., Guillemin R. Endorphins are located in the intermediate and anterior lobes of the pituitary gland, not in the neurohypophysis. Life Sci. 1977 Jan 1;20(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F., Segal D., Ling N., Guillemin R. Endorphins: profound behavioral effects in rats suggest new etiological factors in mental illness. Science. 1976 Nov 5;194(4265):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.185694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury A. F., Smyth D. G., Snell C. R. Biosynthetic origin and receptor conformation of methionine enkephalin. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):165–166. doi: 10.1038/260165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Goldstein A., Hi C. H. Opioid activity of a peptide, beta-lipotropin-(61-91), derived from beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1821–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. Opioid peptides endorphins in pituitary and brain. Science. 1976 Sep 17;193(4258):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.959823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R. Endorphins, brain peptides that act like opiates. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jan 27;296(4):226–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197701272960414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Ling N., Burgus R. Endorphines, peptides, d'origine hypothalamique et neurohypophysaire à activité morphinomimétique. Isolement et structure moléculaire de l'alpha-endorphine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Feb 23;282(8):783–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Ling N., Vargo T. Radioimmunoassays for alpha-endorphin and beta-endorphin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):361–366. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Vargo T., Rossier J., Minick S., Ling N., Rivier C., Vale W., Bloom F. beta-Endorphin and adrenocorticotropin are selected concomitantly by the pituitary gland. Science. 1977 Sep 30;197(4311):1367–1369. doi: 10.1126/science.197601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Yang H. Y., Fratta W., Costa E. Determination of methionine enkephalin in discrete regions of rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 7;134(2):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Terenius L., Elde R., Nilsson G. Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus L. H., Ling N., Guillemin R. beta-Lipotropin as a prohormone for the morphinomimetic peptides endorphins and enkephalins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2156–2159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Chung D. Isolation and structure of an untriakontapeptide with opiate activity from camel pituitary glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1145–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Tan L., Chung D. Isolation and primary structure of beta-endrophin and beta-lipotropin from bovine pituitary glands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1088–1093. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Tseng L. F., Wei E., Li C. H. beta-endorphin is a potent analgesic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2895–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A., Ling N. Common precursor to corticotropins and endorphins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K. Recent progress in the peroxidase-labeled antibody method. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Siggins G. R., Ling N., Bloom F. E., Guillemin R. Neuronal actions of endorphins and enkephalins among brain regions: a comparative microiontophoretic study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P. Influence of medial preoptic-anterior hypothalamic area stimulation of the excitability of mediobasal hypothalamic neurones in the rat. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(2):541–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P. Tuberoinfundibular neurons in the basomedial hypothalamus of the rat: electrophysiological evidence for axon collaterals to hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic areas. Brain Res. 1976 Mar 19;105(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Bayon A., Vargo T. M., Ling N., Guillemin R., Bloom F. Radioimmunoassay of brain peptides: evaluation of a methodology for the assay of beta-endorphin and enkephalin. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 15;21(6):847–852. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Vargo T. M., Minick S., Ling N., Bloom F. E., Guillemin R. Regional dissociation of beta-endorphin and enkephalin contents in rat brain and pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5162–5165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. S., Browne R. G., Bloom F., Ling N., Guillemin R. beta-Endorphin: endogenous opiate or neuroleptic? Science. 1977 Oct 28;198(4315):411–414. doi: 10.1126/science.910136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaab D. F., Pool C. W., Van Leeuwen F. W. Can specificity ever be proved in immunocytochemical staining. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 May;25(5):388–391. doi: 10.1177/25.5.325124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Neurotensin: immunohistochemical localization in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4059–4063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Akil H., Sullivan S., Barchas J. D. Immunocytochemical localization of methionine enkephalin: preliminary observations. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):733–738. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Barchas J. D., Li C. H. beta-Lipotropin: localization of cells and axons in rat brain by immunocytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5155–5158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Hong J. S., Costa E. Regional distribution of LEU and MET enkephalin in rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Apr;16(4):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]