Abstract
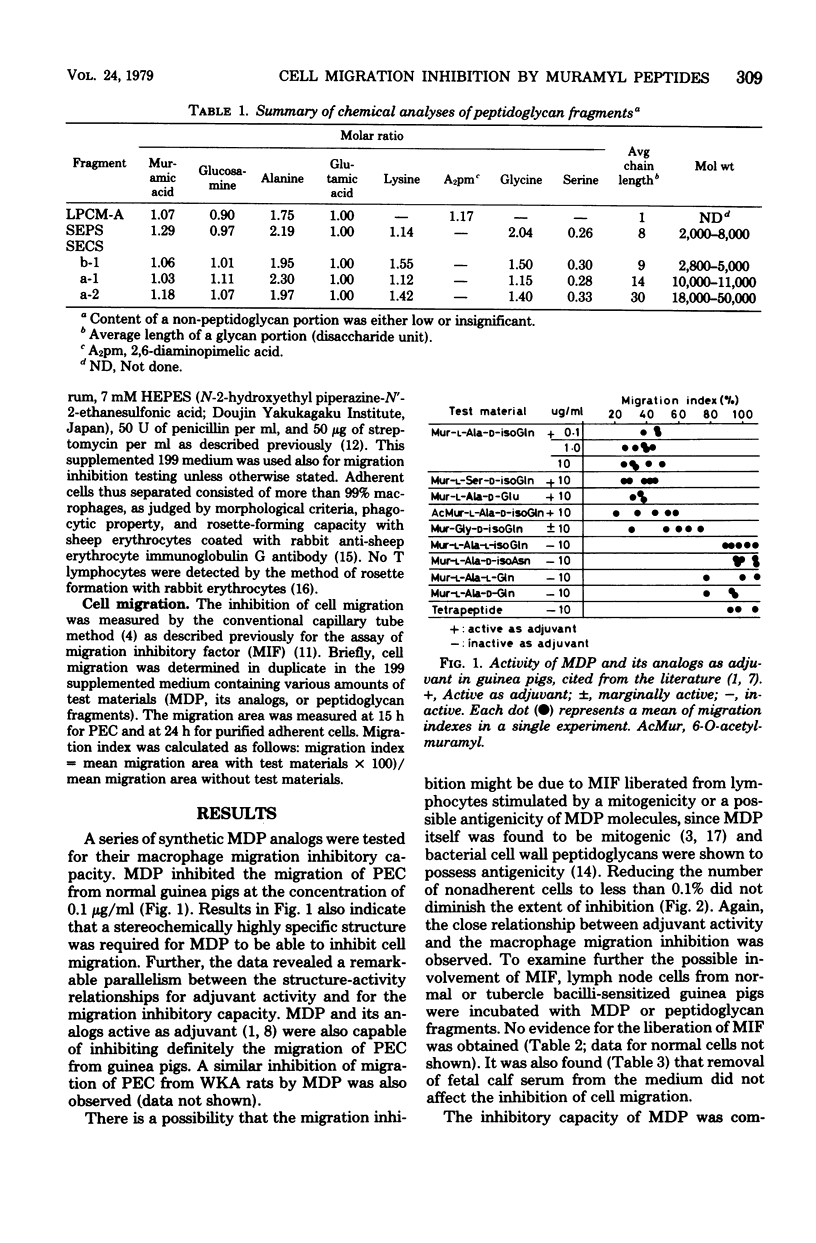
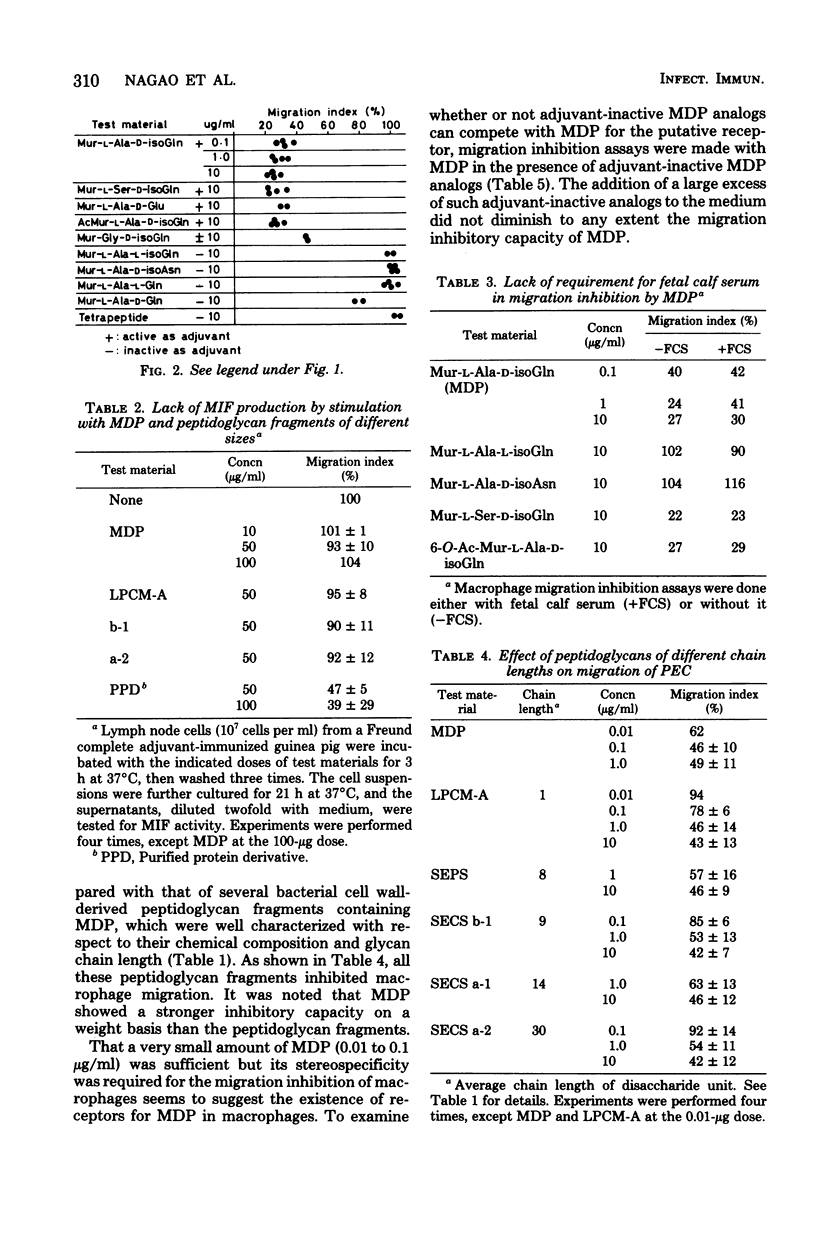
In the capillary tube migration system a synthetic muramyl dipeptide (MDP; N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine), a part of bacterial cell wall peptidoglycans, inhibited the migration of peritoneal exudate macrophages from normal guinea pigs or rats. The migration inhibition was also caused by some MDP-containing peptidoglycan fragments from cell walls of Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus epidermidis. The migration inhibition could not be explained on the basis of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. A stereochemically highly specific structure of MDP required for its adjuvant activity was also required for the macrophage migration inhibition. These findings suggest that MDP and MDP-containing cell wall fragments may activate macrophages and that this activation may be important in the exertion of their adjuvant activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam A., Devys M., Souvannavong V., Lefrancier P., Choay J., Lederer E. Correlation of structure and adjuvant activity of N-acetyl muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine (MDP), its derivatives and analogues. Anti-adjuvant and competition properties of stereoisomers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90999-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Lefrancher P., Choay J., Lederer E. Enhancement of nonspecific immunity to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine) and several analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2089–2093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damais C., Parant M., Chedid L. Nonspecific activation of murine spleen cells in vitro by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetyl-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine). Cell Immunol. 1977 Nov;34(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro: its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell-antigen interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):72–77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori K., Tanaka A. Granuloma formation by synthetic bacterial cell wall fragment: muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.613-620.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman D. H. Regulation of endotoxin-induced inhibition of macrophage migration by fresh serum. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.371-377.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Strominger J. L. Structure of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureaus. IX. Mechanism of hydrolysis by the L11 enzyme. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2745–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Watanabe Y., Kinoshita F., Shimono T., Morisaki I. Immunoadjuvant activities of synthetic N-acetyl-muramyl-peptides or -amino acids. Biken J. 1975 Jun;18(2):105–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Watanabe Y., Shimono T., Kinoshita F., Narita T. Immunoadjuvant activities of peptidoglycan subunits from the cell walls of Staphyloccus aureus and Lactobacillus plantarum. Biken J. 1975 Jun;18(2):93–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi M., Onoue K. Functional activation of immune lymphocytes by antigenic stimulation in cell mediated immunity. I. Requirement for macrophages in antigen-induced MIF production by guinea pig immune lymphocytes in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jul;18(1):220–232. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi M., Onoue K. Functional activation of immune lymphocytes by antigenic stimulation in cell-mediated immunity. II. Analysis of the macrophage-replacing activity of the LPS-stimulated macrophage culture supernatant in the antigenic activation of purified immune lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai A., Watt W. B. The determination of the molecular size of peptides and proteins by chromatography on bio gel P-100 columns in phenol-acetic acid-water (1:1:1,W-V-V) solvent mixture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 29;214(3):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90305-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Herberman R., Frank M. M., Green I. Receptors for complement and immunoglobulin on human leukemic cells and human lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1933–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI106999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadecker M. J., Bishop G., Wortis H. H. Rosette formation by guinea pig thymocytes and thymus derived lymphocytes with rabbit red blood cells. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1834–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Tarumi Y., Ikenaka K. Mitogenic activity of adjuvant-active N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine and its analogues. Biken J. 1977 Jun;20(2):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Nagao S., Nagao R., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Stimulation of the reticuloendothelial system of mice by muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.302-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Nagao S., Saito R., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Correlation of stereochemically specific structure in muramyl dipeptide between macrophage activation and adjuvant activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Nagao S., Tanaka A., Koga T., Onoue K. Inhibition of macrophage migration by synthetic muramyl dipeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):923–928. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


