Abstract
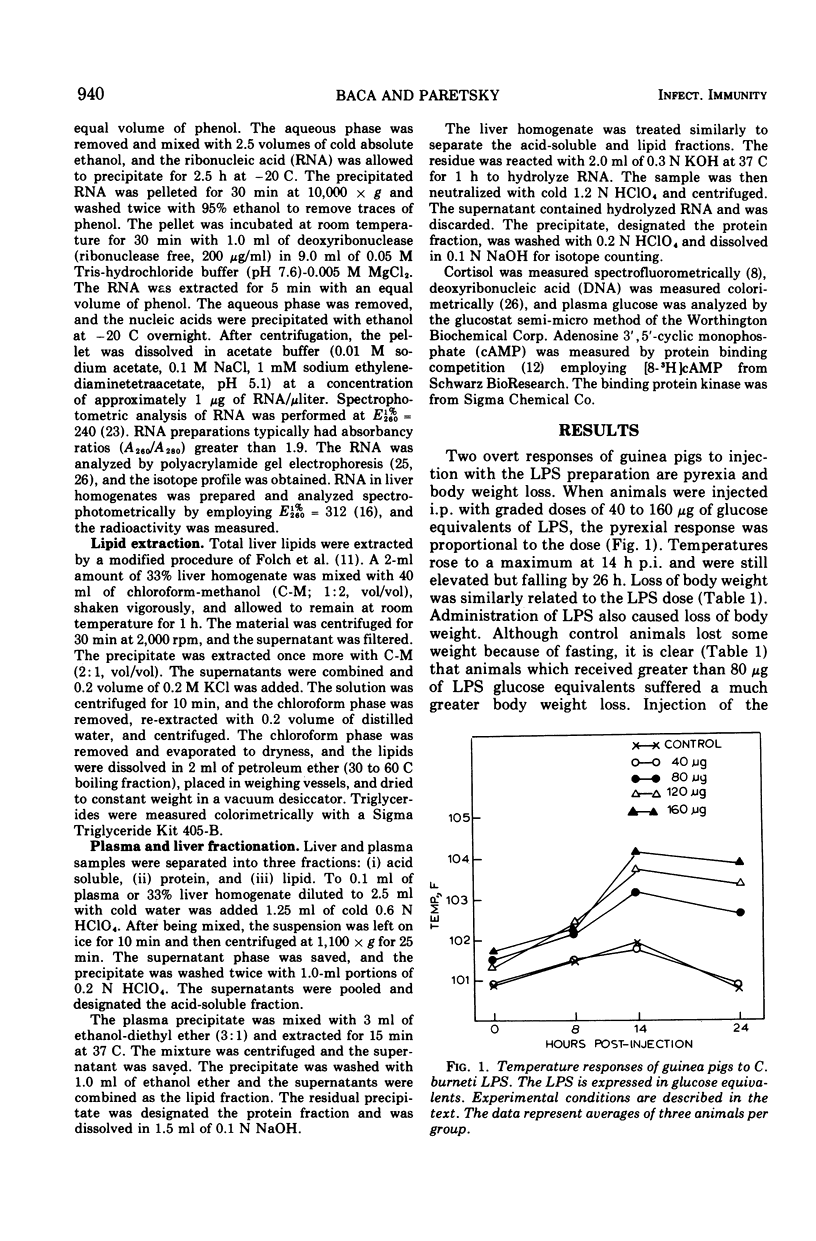
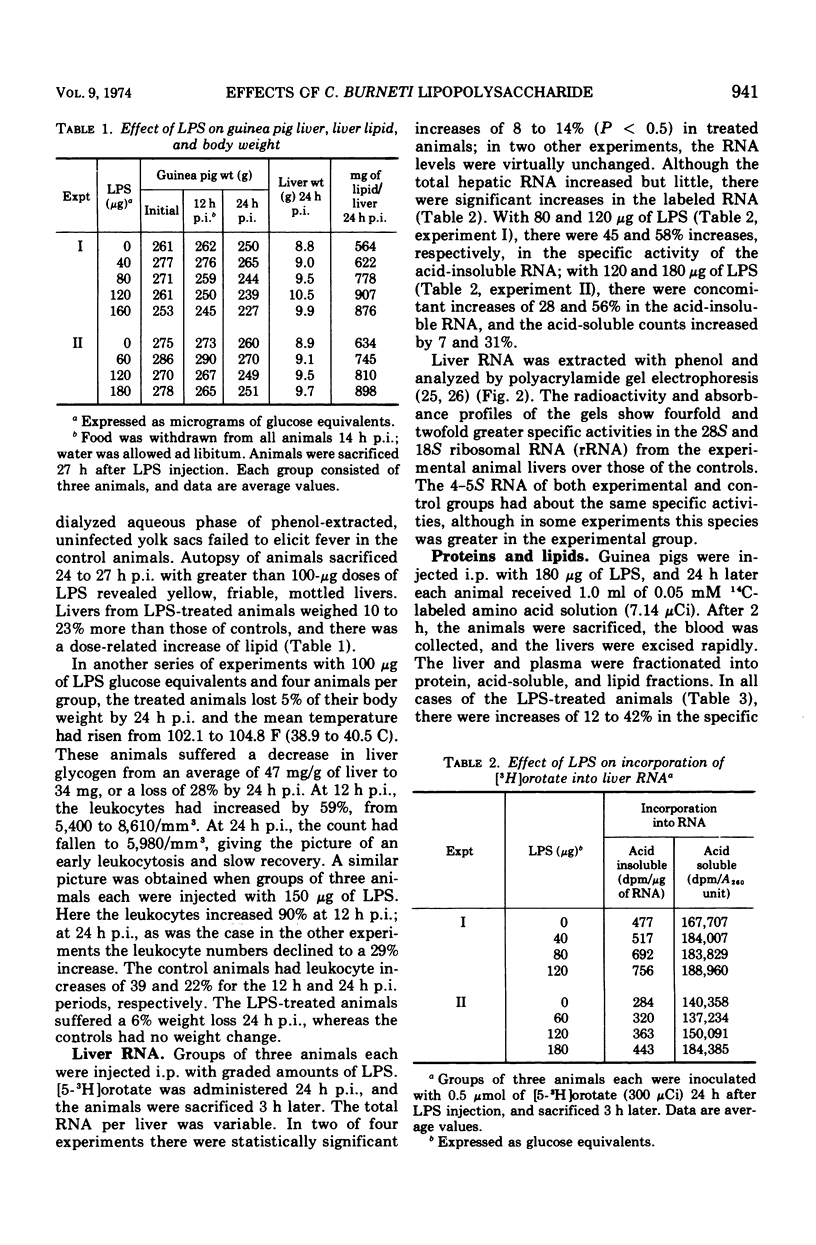
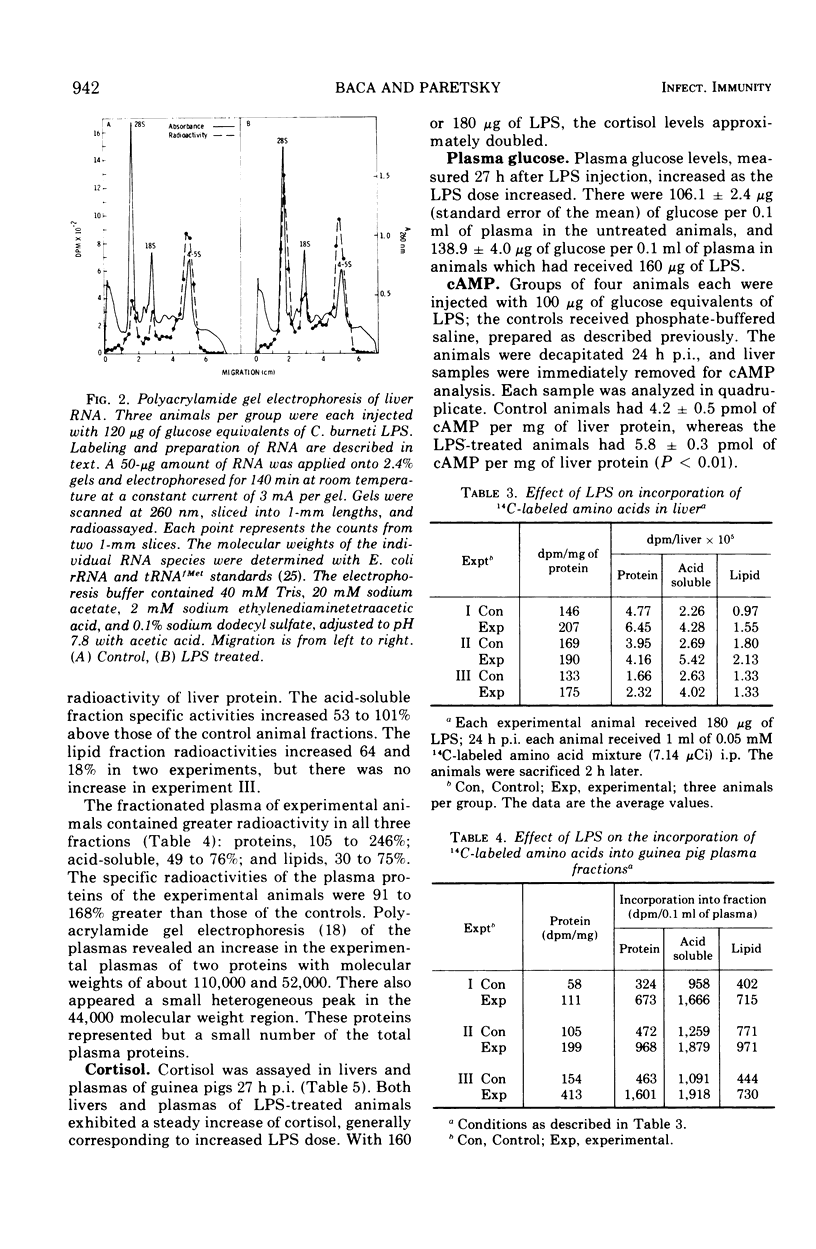
A lipopolysaccharide obtained in a dialyzed phenol extract from the rickettsia Coxiella burneti produced the following effects in guinea pigs after intraperitoneal injection: hyperthermia, loss of body weight, increased liver weight and concomitant lipid infiltration, elevated levels of hepatic and plasma cortisol, increased incorporation of [3H]orotic acid into hepatic 28S and 18S ribosomal ribonucleic acid, increased incorporation of 14C-labeled amino acids into liver and plasma protein, and leukocytosis. Most of these events also occur during infection of guinea pigs with C. burneti, and a causal relationship between the rickettsial lipopolysaccharide and the biochemical changes that occur during Q fever is suggested.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal M. K., Hanoune J., Yu F. L., Weinstein I. B., Feigelson P. Studies on the effect of cortisone on rat liver transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4806–4812. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman K., Southren A. L., Uretsky S. C., Zabos P., Acs G. Hydrocortisone induction of rat-liver leucyl-transfer RNA and its synthetases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3567–3569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREZINA R., SCHRAMEK S., URVOELGYI J. STUDY OF THE ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE OF COXIELLA BURNETI. 3. PYROGENIC EFFECT OF PHASE I ANTIGEN IN EXPERIMENTAL GUINEA PIGS. Acta Virol. 1965 Mar;9:180–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Partial chemical characterization of a toxic lipopolysaccharide from Coxiella burneti. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):959–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.959-961.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE P. M. Rickettsial and viral toxins. Am J Med Sci. 1961 Mar;241:383–405. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196103000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. R., Rubin R. T. New fluorometric method for the determination of cortisol in serum. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 11;29(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIGELSON M., GROSS P. R., FEIGELSON P. Early effects of cortisone on nucleic acid and protein metabolism of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 2;55:495–504. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90982-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH R. L., MCKAY D. G., TRAVERS R. I., SKRALY R. K. HYPERLIPIDEMIA, FATTY LIVER, AND BROMSULFOPHTHALEIN RETENTION IN RABBITS INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY WITH BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:563–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays A. P., Hill R. B., Jr Enzymes of lipid synthesis in the liver of the cortisone-treated rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 1;98(3):646–648. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Fleck A. Recent developments in the measurement of nucleic acids in biological materials. A supplementary review. Analyst. 1966 Feb;91(79):78–88. doi: 10.1039/an9669100078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARETSKY D., DOWNS C. M., SALMON C. W. SOME BIOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN THE GUINEA PIG DURING INFECTION WITH COXIELLA BURNETII. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:137–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.137-142.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueckemann J., Paretsky D. Changes in hepatic glycogen, protein, and ribonucleic acid synthesis, and some effects of cortisol, during Q fever. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):920–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.920-924.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. A., Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Presence of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in the rickettsia Coxiella burneti. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):365–366. doi: 10.1042/bj1250365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. A., Paretsky D. Ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in guinea pig liver during Q fever. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):718–724. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.718-724.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Powanda M. C., Pekarek R. S., Beisel W. R. Tissue amino acid flux after exposure of rats to Diplococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.556-562.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. M. Biological effects of bacterial endotoxins in man. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):259–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. Cortisone stimulation of nucleolar RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2177–2180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. Effects of cortisone on orotic acid transport and RNA synthesis in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Dec;141(2):662–667. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


