Abstract
Background
The power of the genome wide association studies starts to go down when the minor allele frequency (MAF) is below 0.05. Here, we proposed the use of Cohen’s h in detecting disease associated rare variants. The variance stabilizing effect based on the arcsine square root transformation of MAFs to generate Cohen’s h contributed to the statistical power for rare variants analysis. We re-analyzed published datasets, one microarray and one sequencing based, and used simulation to compare the performance of Cohen’s h with the risk difference (RD) and odds ratio (OR).
Results
The analysis showed that the type 1 error rate of Cohen’s h was as expected and Cohen’s h and RD were both less biased and had higher power than OR. The advantage of Cohen’s h was more obvious when MAF was less than 0.01.
Conclusions
Cohen’s h can increase the power to find genetic association of rare variants and diseases, especially when MAF is less than 0.01.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-875) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Effect size, Cohen’s h, Odds ratio, Power, Rare variant
Background
The prevailing hypothesis in genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of genetic diseases is “common disease, common variant” [1, 2]. The development of microarray based genotyping greatly accelerated GWASs [3–5] and lead to the identification of hundreds of genetic variants causing susceptibility to complex diseases. Most identified common variants confer relatively small risk (odds ratio (OR) at 1.1-1.5) and explain only a modest proportion concerning the heritability of these diseases [6, 7]. In contrast, most of the identified rare variants have ORs above 2 [8, 9]. This leads to the question of how the missing heritability can be explained and the search for the possible contribution by rare variants [1, 10–12]. One technical obstacle to GWAS on rare variants is the calling algorithm of microarray based genotyping. The reliability of genotyping calls drops when the minor allele frequency (MAF) falls below 5%. Recent improvement in genotype calling algorithms of microarrays and growing availability of next generation sequencing technology make rare variant searching feasible [13].
Many strategies have been developed to analyze disease-associated rare variants, e.g. the collapsing method [14, 15], the weighted approach [16–18], and regression-based analysis [19, 20]. Generally, these strategies emphasize the significance of rare variants by either analyzing a cluster on aggregate or setting larger weights on them. These studies focus on hypothesis testing with the aim of increasing the power of detecting associated rare variants. The variability of odds ratio increases at the lower end of MAF, e.g. MAF =0.001 [21–23]. Recent studies raised issues of the OR based analysis of GWAS [12, 21, 24, 25]. They predicted additional loci to be uncovered by more powerful GWAS for these studied traits and combined with published loci could explain around 15-20% of heritability of these traits.
The aim of this study was to examine the distributions and properties of Cohen’s h [26], and compared its performance in analyzing GWAS data with OR and RD using publicly available GWAS datasets as well as simulated datasets. We used the coronary artery disease (CAD) GWAS dataset from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (WTCCC) [4], as well as a sequencing-based T1D dataset. We determined the Cohen’s h equivalents to the OR for declaring a mild, moderate and large effect. To take advantage of the fact that the power of Cohen’s h does not depend on MAFs, we describe how to use Cohen’s h to evaluate the power and sample sizes required in rare variant studies. Other possible applications of Cohen’s h for such studies of rare variants are also discussed.
Methods
Theoretical properties of effect size measures: risk difference, Cohen’s h and odds ratio
For biallelic SNPs with minor allele A, and major allele a, the case (group D) and control (group 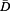 ) populations had n1 and n2 allele counts, respectively. Let p1 = P(A|D) be the MAF of the case group and
) populations had n1 and n2 allele counts, respectively. Let p1 = P(A|D) be the MAF of the case group and 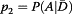 be the MAF of the control group. These three ES measures are functions of MAFs from case and control groups. RD is defined as d = p1 - p2, and the estimator is
be the MAF of the control group. These three ES measures are functions of MAFs from case and control groups. RD is defined as d = p1 - p2, and the estimator is 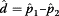 , where
, where 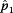 and
and 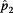 are the maximum likelihood estimators of p1 and p2, respectively. The definition for Cohen’s h is
are the maximum likelihood estimators of p1 and p2, respectively. The definition for Cohen’s h is 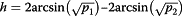 , and the estimator is
, and the estimator is 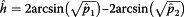 . The allelic OR can be defined as
. The allelic OR can be defined as 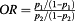 , and the corresponding estimator is
, and the corresponding estimator is 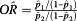 .
.
The derivations of the asymptotic distributions of estimators and their applications to the calculation of the p-values were described in Additional file 1. When the normality approximation fails due to extremely low MAF, the p-values were validated by the Fisher’s exact test. The performance of these ES measures were evaluated by accuracy, precision (i.e., bias and mean square error (MSE)), and type I error rate. Furthermore, statistical power was computed by assuming a balanced case–control design with independent cases and controls. The power formula for testing H0 : p1 - p2 = 0 vs. H1 : p1 - p2 ≠ 0 with a total of n independent cases and controls (i.e. n1 = n2 = n) 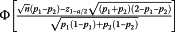 , where Φ denotes the cumulative normal distribution and z1 - α/2 was the 100(1-α/2)-th percentile. The power for H0 : OR = 1 vs. H1 : OR = c could be determined provided that the MAF in the control group, p2, and c were known according to the above formula where the MAF in the case group could be calculated as p1 = (OR * p2)/(OR * p2 - p2 + 1). In the case of Cohen’s h, the association test can be set as H0 : h = 0 vs. H1 : h = δ, and the power formula is
, where Φ denotes the cumulative normal distribution and z1 - α/2 was the 100(1-α/2)-th percentile. The power for H0 : OR = 1 vs. H1 : OR = c could be determined provided that the MAF in the control group, p2, and c were known according to the above formula where the MAF in the case group could be calculated as p1 = (OR * p2)/(OR * p2 - p2 + 1). In the case of Cohen’s h, the association test can be set as H0 : h = 0 vs. H1 : h = δ, and the power formula is 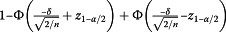 . The sample size n was varied from 1,000 to 10,000 and the MAF in the control group was varied from 0.001 to 0.05. The c values for OR of 1.8, 2, and 3, and δ values of 0.08, 0.1, and 0.13 for Cohen’s h were considered for p2 < 0.05. We used a nominal significance level of 5 × 10-8 to calculate the statistical power of a GWAS.
. The sample size n was varied from 1,000 to 10,000 and the MAF in the control group was varied from 0.001 to 0.05. The c values for OR of 1.8, 2, and 3, and δ values of 0.08, 0.1, and 0.13 for Cohen’s h were considered for p2 < 0.05. We used a nominal significance level of 5 × 10-8 to calculate the statistical power of a GWAS.
Simulations and data analysis
GWAS data from the WTCCC, quality control and filtering
We obtained genotyping data of 1,988 CAD patients and 3,004 shared controls (1,504 from 1,958 Birth Cohort Controls (58C) and 1,500 from UK Blood Services sample (NBS)) from the WTCCC archive. The majority of subjects were of European descent. All individuals were genotyped using Affymetrix GeneChip 500 K arrays. Details of the study samples were described in the original report [4]. We calculated RD, Cohen’s h and log(OR) using this dataset. The individuals dropped in the WTCCC study because of evidence of non-European descent or genotyping problems were excluded in the current analysis. A total of 1,926 subjects with CAD and 2,938 common controls were included for further analysis. We further dropped the SNPs with bad genotype calling, as suggested in the original report. The exclusion criteria for SNPs were (1) MAF in shared controls is less than 0.002, at which there were less than 3 individuals for any genotype, (2) call rate <95%, and (3) Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium exact test P value <5.7*10-7 in shared controls and (4) allele frequency difference test based on two samples proportion test P value <5.7 × 10-7 between 58C and NBS. A total of 413,059 SNPs consisting of 52,220 (12.64%) rare SNPs (MAF < 0.05) and 360,839 (87.36%) common SNPs (MAF≧0.05) passed this filter.
Using simulation to estimate type I error rate and power
To assess statistical properties of ES measures in terms of bias, MSE, and type I error rate, we performed simulations of a pseudo case–control study using the two shared controls. We randomly selected 1,480 subjects from pooled shared controls as pseudo-cases and kept the remaining 1,458 samples as pseudo-controls. For every replication, we calculated the ES estimate by each measure and tested the association for each SNP. The bias was calculated as the mean deviation of estimates from 0 per replication, and the MSE was the mean of the square of the bias. The fraction of times that the p-values of the association tests were less than 0.05 was the empirical type I error rate. These three indices for rare and common variants on each autosome were shown in Additional file 2 (bias, MSE) and Additional file 3 (type I error rate).
To better compare the performance of Cohen’s h with other methods including Combined Multivariate and Collapsing Method (CMC) [15], Weighted Sum Statistic (WSS) [16] and Variable Threshold (VT) [17], we used simulated rare variants datasets generated by the SimRare program ([27], http://code.google.com/p/simrare/). SimRare uses the forward-time simulation program to generate sequence data. Evolution parameters used were: (1) an additive multi-locus model with selection coefficient distribution by Kryukov [28], (2) the mutation rate was 1.8×10-8, and (3) the effective population sizes were 8,100, 8,100, 7,900, 900,000 with 500, 10, 370 generations, respectively. Fifty replications of fixed gene lengths including 250, 500, 1,000, 2,000, and 5,000 base pairs were simulated. The longer gene length produced a larger number of rare variants. The corresponding mean numbers of rare variants were 46.2, 96, 187.5, 377.7 and 944.3. For the setting of risk simulations, we assume a model with a disease prevalence rate of 1% and 2,000 cases and 2,000 controls. The power was assessed at OR = 0.5 for protective mutations and OR = 3 for detrimental mutations with an additive mode of inheritance over 1,000 replications. For CMC, WSS and VT, p-values were obtained empirically through 1,000 permutations for each replication (i.e., gene-specific). For single-marker testing methods such as RD, Cohen’s h and OR, the smallest p-value for testing the rare variant was recorded for each replication. We defined the unadjusted power for single marker testing methods as the proportion of replicates with minimum p-values < =0.05. Furthermore, we used Bonferroni correction and the Benjamin-Hochberg procedure [29] to adjust for multiple testing.
Applying Cohen’s h to microarray and sequencing-based datasets
We compared the three measures described above on one microarray typed (CAD) [4] and one sequence based (T1D) [30] dataset. For the CAD dataset, the association tests were used separately for the analysis of rare variants (0.05 > MAF ≧0.002) and common variants. For each SNP, the magnitude of ES was estimated by RD, OR, and Cohen’s h. Moreover, we adjusted the significance level by Bonferroni correction at a p-value threshold of 1.2 × 10-7(0.05/41,3059). The sequence based T1D dataset was retrieved from http://www.sciencemag.org/content/early/2009/03/05/science.1167728/rel-suppl/62c4d688b3668c3c/suppl/DC1. A total of 179 rare variants (defined as MAF < 3%) in 10 candidate genes were used in the current study [30].
Results
Performance of ES measures: bias, MSE, type I error and power
Table 1 summarizes the accuracy (bias), precision (MSE) and type 1 error rate of RD, Cohen’s h, and OR for common and rare variants. Box-plots of the distributions of estimates of RD, Cohen’s h, and log(OR) for rare and common SNPs on each autosome are presented in Additional file 4 and Additional file 5. Among the 22 autosomes, mean biases and MSEs based on log(OR) of rare SNPs were larger than those of common SNPs, while RD and Cohen’s h obtained more similar estimates regardless of the MAFs. Thus, the OR would be more sensitive to changes in MAFs. Figure 1 presents the estimated type I error rates for RD, Cohen’s h, and log(OR) for common SNPs and rare SNPs. The performance of each measure of ES was very close for common SNPs in each autosome. The range of type I error rate for every ES measure was approximately (0.041, 0.056), and the average type I error rates for 22 autosomes were the same (0.05). As for rare SNPs, ranges of type I error rates of RD, Cohen’s h, and OR were (0.037, 0.065), (0.042, 0.068), and (0.036, 0.061), respectively. The value of the type I error rate for each ES measure was slightly larger than 0.05 at a few autosomes. The results indicated that every ES measure would probably produce slightly inflated type 1 error rates concerning the effect of rare variants in genetic association studies. Results from these simulations indicated that the estimate of OR for rare variant disease association might have greater bias and variability compared with RD and Cohen’s h. Equally important is the conclusion that the true significance may be missed by relatively large variation of OR estimates, followed by a loss of power to detect rare variants. This suggests potential utility of Cohen’s h for detecting rare variants associated with complex diseases.
Table 1.
Biases, MSEs and type I error rates for RD, Cohen’s h and OR
| ES | Type of SNP | No. SNPs | Bias | MSE | Min | Max | Type I error rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD | Common | 360839 | 0.00004 | 0.00012 | -0.046 | 0.044 | 0.050 |
| Rare | 52220 | 0.00002 | 0.00001 | -0.015 | 0.015 | 0.051 | |
| Cohen’s h | Common | 360839 | 0.00008 | 0.00068 | -0.103 | 0.097 | 0.050 |
| Rare | 52220 | 0.00018 | 0.00072 | -0.091 | 0.092 | 0.056 | |
| log(OR) | Common | 360839 | 0.00021 | 0.00477 | -0.346 | 0.346 | 0.050 |
| Rare | 52220 | 0.00178 | 0.11395 | -2.707 | 2.739 | 0.048 |
Figure 1.
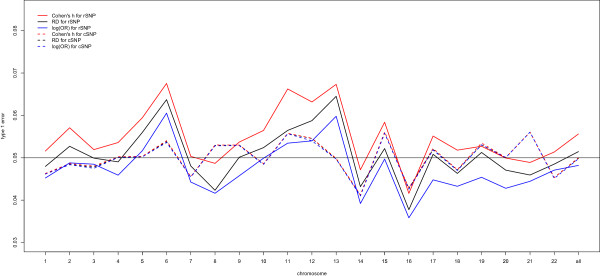
Mean of empirical type I error rates for risk difference (RD), Cohen’s h and log(OR) in each autosome.
Table 2 showed the power of analyzing one marker at a time in comparison with methods (joint analysis methods) of jointly analyzing a group of mutations including CMC, WSS and VT in detecting disease associated genes. The power was lowest for single-marker tests and increased with the number of rare variants. When there were 96 variants within the gene on average, the unadjusted power was 0.465, 0.393, 0.521 and >0.878 for RD, OR, Cohen’s h and joint analysis methods, respectively. As the mean number of variants was increased from 96 to 377.7, the unadjusted power for the single-marker test increased to 0.88, 0.814, 0.918 and 1 for RD, OR, Cohen’s h and joint analysis methods, respectively. For these situations, the greatest power was observed in joint analysis methods, followed by Cohen’s h, which was always the largest of the three single-marker tests taking into account the adjustment for multiple testing. The results highlighted that for rare variants, Cohen’s h was a better association measure than RD and OR.
Table 2.
Empirical power for tests at nominal level 0.05 based on 1000 replicates
| Fixed gene length (bp) | Mean no of rare SNPs | RD | OR | Cohen’s h | CMC | WSS | VT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 46.2 | 0.491 | 0.644 | 0.501 | ||||
| Unadj. | 0.142 | 0.107 | 0.178 | |||||
| BH | 0.042 | 0.037 | 0.051 | |||||
| Bonf. | 0.037 | 0.030 | 0.043 | |||||
| 500 | 96 | 0.878 | 0.931 | 0.882 | ||||
| Unadj. | 0.465 | 0.393 | 0.521 | |||||
| BH | 0.106 | 0.080 | 0.135 | |||||
| Bonf. | 0.087 | 0.064 | 0.113 | |||||
| 1000 | 187.5 | 0.992 | 0.998 | 0.992 | ||||
| Unadj. | 0.584 | 0.509 | 0.652 | |||||
| BH | 0.136 | 0.109 | 0.162 | |||||
| Bonf. | 0.121 | 0.083 | 0.141 | |||||
| 2000 | 377.7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Unadj. | 0.880 | 0.814 | 0.918 | |||||
| BH | 0.254 | 0.194 | 0.306 | |||||
| Bonf. | 0.211 | 0.143 | 0.256 | |||||
| 5000 | 944.3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Unadj. | 0.973 | 0.94 | 0.987 | |||||
| BH | 0.370 | 0.265 | 0.451 | |||||
| Bonf. | 0.305 | 0.191 | 0.388 |
Unadj.: Without adjustment for multiple testing. BH: Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. Bonf.: Bonferroni correction.
Statistical power required to detect disease association of rare SNPs based on Cohen’s h
Generally, the statistical power is related to the magnitude of the ES, the sample size, and the variance of the estimator of ES. The variance of each of the ES measures except Cohen’s h is related to the MAF in cases and controls (shown in Additional file 1). Accordingly, a MAF threshold was adopted to avoid limited power for SNPs with low MAF, and the threshold chosen also depended on the sample size of the study and the expected ES values. Figure 2A illustrated the relationship between the statistical power and the MAFs in the control group given similar magnitudes of ES for OR and Cohen’s h (n =5,000). Cohen’s h was more powerful than OR (Figure 2B). Even at a stringent significance level of α =10-8, the power of Cohen’s h remained higher than that of OR at α =5 × 10-8 for SNPs with MAF < 0.001 (data not shown).
Figure 2.
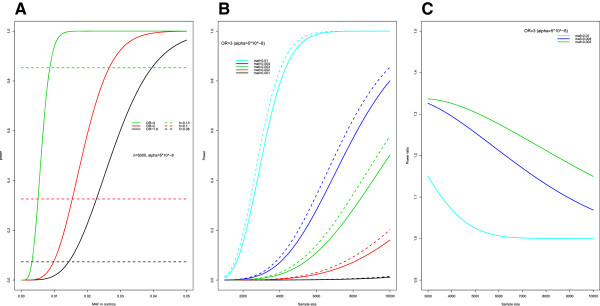
Relationship between power and needed sample size based on OR and Cohen’s h for rare SNPs. (A) Line plot shows the power estimated by OR (bold line) and Cohen’s h (dotted line) at the same threshold. (B) power curves given fixed OR =3 with corresponding Cohen’s h at varying MAF in controls. (C) Power ratio at varying MAF in controls and varying sample size.
For p2 ≤ 0.01, when the sample sizes increased from 1,000 to 10,000 and, we found that for all scenarios, the power of Cohen’s h remained higher than that of OR for the same ES measures (Figure 2B). For a SNP with OR =3 and p2 = 0.01, a total sample size of 4,060 (2,030 cases and 2,030 controls) was needed to achieve 80% statistical power to detect the effect at a genome-wide significance level of 5 × 10-8. However, the statistical power of Cohen’s h was approximately 85% with the same sample size. Additionally, the power ratio of the power based on Cohen’s h versus that of OR was consistently larger than 1 (Figure 2C). Hence, Cohen’s h was more powerful at identifying rare SNPs. The notable power gain of Cohen’s h at lower MAFs might contribute to the findings for rare SNPs.
Analyses of rare SNPs in CAD data
We performed single marker association tests using all three ES measures on the WTCCC CAD GWAS data. A total of 2,938 common controls and 1,926 cases with CAD were included in this study. We applied one single marker test at each of the 52,220 rare SNPs and 360,839 common SNPs separately. In addition, when the MAF in CAD patients was extremely low i.e. <0.002, the asymptotic assumption might not hold. In this case, the statistical significance of the p-values was validated by Fisher’s exact test. Bonferroni correction adjusted p-value of 0.05/413,059 was the criteria to declare genome-wide significance for any SNP (Figure 3). Table 3 summarized the number of significant SNPs, and genes that had been identified or validated for CAD based on OR, RD, and Cohen’s h, respectively. We found that among the 26 SNPs associated with CAD, 17 were on chromosome 9p21.3. The association of these regions with CAD was reported [4, 23]. All 3 ES measures identified the same 5 genes associated with CAD. The relevance of 4 of these genes, PLCL2, SAMD12-AS1, GAN, and MEF2NB-MEN2B, to intermediated cardiac phenotypes was reported [31–33].
Figure 3.
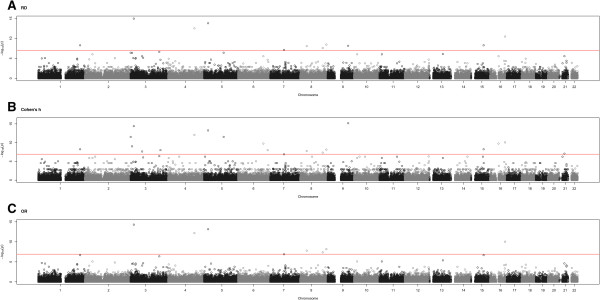
Manhattan plot showing the significance of association between all rare SNPs and CAD. For all panels, the genome-wide significance threshold of 0.05/403,089 is shown. Distributions of -log10 p-values for (A) risk difference, (B) Cohen’s h and (C) log(OR).
Table 3.
Significant SNPs for CAD under different ES measures at genome-wide significance levels
| Type of SNPs | Significant SNPs | OR | RD | Cohen’s h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common | Number | 26 | 26 | 26 |
| Median | 1.327 | 0.065 | 0.134 | |
| Range | (0.757, 6.104) | (-0.063, 0.354) | (-0.129, 0.795) | |
| Rare | Number | 9 | 13 | 18 |
| Median | 2.144 | 0.021 | 0.119 | |
| Range | (1.88, 2.41) | (-0.009, 0.038) | (-0.167, 0.179) |
Interestingly, when analyzing rare SNPs, the numbers of significant SNPs were different for each ES measure. Cohen’s h identified most SNPs, followed by RD, then OR. Compared to the OR results, there were 4 and 9 more SNPs detected by RD and Cohen’s h, respectively (Table 3). The substantial power gain of Cohen’s h leads to the identification of more significant rare SNPs. Some SNPs which were reported to be associated with CAD, such as rs17146094 (within EIF4H gene), and rs6674781 (near rs6671793), were identified by RD and Cohen’s h but not OR [5, 34].
Surprisingly, 6 further SNPs detected only by Cohen’s h, consistent with the findings based on Fisher’s exact test, were located in regions that are known to be associated with CAD, cholesterol, and arteries (Table 4). This finding again shows the ability of Cohen’s h to identify potential rare SNPs associated with disease and other intermediate disease phenotypes. Although SNPs implicated by our analysis are tightly correlated with other validated relevant SNPs in the region and are likely to be in linkage disequilibrium with the causal variant, most of the significant rare SNPs remain directly correlated to CAD. Caution should be taken on interpreting these results from the rare-variant analysis of the three WTCCC datasets as the reliability of current microarray based genotyping still needs improvement for MAF <5%.
Table 4.
Replication of rare SNPs showing statistically significant effect at genome-wide significance levels (1.2 × 10 -7 ) for CAD
| Chr | ES | SNP | Nearest gene or SNP | Location | MAF in controls | MAF in cases | OR | P-value | RD | P-value | Cohen’s h | P-value | Exact test P-value b | Association of SNP or proxy with other cardiovascular phenotypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genes | within | associated | interval | |||||||||||
| 3 | All | rs17042882 | PLCL2 | 3p24.3 | 0.028 | 0.061 | 2.255 | 4.88 × 10-15 | 0.033 | 1.11 × 10-15 | 0.163 | 4.00 × 10-15 | --- | Heart failure, Arthritis |
| 3 | h | rs16827563 | VEPH1 | 3q24-q25 | 0.005 | 0 | NA | NA | -0.005 | 2.18 × 10-5 | -0.119 | 1.02 × 10-8 | 7.3 × 10-7 | Carotid artery disease, Diabetes Mellitus |
| 7 | RD | rs17146094 | EIF4H | 7q11.23 | 0.017 | 0.034 | 2.036 | 1.27 × 10-7 | 0.017 | 7.15 × 10-8 | 0.109 | 1.32 × 10-7 | --- | CAD |
| 8 | All | rs16891338 | SAMD12-AS1 | 8q24.12 | 0.023 | 0.043 | 1.908 | 4.11 × 10-8 | 0.02 | 2.50 × 10-8 | 0.113 | 4.66 × 10-8 | --- | Blood Pressure |
| 8 | All | rs16908145 | FLJ45872 | 8q24.23 | 0.022 | 0.043 | 1.998 | 6.54 × 10-9 | 0.021 | 3.46 × 10-9 | 0.12 | 7.08 × 10-9 | --- | |
| 15 | RD, h | rs7163007 | MAP2K5 | 15q23 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 5.551 | 2.13 × 10-7 | 0.009 | 5.33 × 10-9 | 0.121 | 5.85 × 10-9 | --- | BMI, Diabetes Mellitus |
| 16 | All | rs16955238 | GAN | 16q24.1 | 0.022 | 0.046 | 2.143 | 8.91 × 10-11 | 0.024 | 3.41 × 10-11 | 0.135 | 8.53 × 10-11 | --- | Cholesterol |
| 16 | h | rs7197337 | ANKRD26P1 | 16q11.2 | 0.006 | 0 | NA | NA | -0.006 | 2.88 × 10-6 | -0.132 | 1.76 × 10-10 | 2.3 × 10-8 | |
| 19 | All | rs11671119 | MEF2B MEF2NB | 19p13.11 | 0.033 | 0.071 | 2.239 | 0 | 0.038 | 0 | 0.174 | 0 | --- | Diabetes Mellitus |
| SNPs near associated SNPs within 500 kb | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | RD, h | rs6674781 | rs6671793 | 2a | 0.002 | 0.011 | 5.55 | 2.13 × 10-7 | 0.009 | 5.33 × 10-9 | 0.121 | 5.85 × 10-9 | --- | Coronary disease |
| 3 | h | rs17064749 | rs7615788 | 10a | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.124 | 8.36 × 10-5 | -0.007 | 2.84 × 10-6 | -0.116 | 2.28 × 10-8 | 4.2 × 10-7 | Cholesterol |
| 3 | h | rs10510375 | rs1450097 | 400a | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.11 | 2.97 × 10-5 | -0.008 | 4.03 × 10-7 | -0.127 | 9.67 × 10-10 | 2.2 × 10-8 | Cholesterol, HDL |
| 3 | h | rs6805861 | rs10510197 | 250a | 0.007 | 0 | NA | NA | -0.007 | 3.84 × 10-7 | -0.145 | 2.92 × 10-12 | 1.2 × 10-9 | Cholesterol, HDL |
| 4 | All | rs890447 | rs97669522 | 25a | 0.043 | 0.078 | 1.883 | 6.49 × 10-13 | 0.035 | 3.09 × 10-13 | 0.148 | 8.35 × 10-13 | --- | CAD |
| 5 | All | rs159171 | rs10520872 | 500a | 0.025 | 0.055 | 2.27 | 6.88 × 10-14 | 0.03 | 1.62 × 10-14 | 0.156 | 5.51 × 10-14 | --- | Cholesterol, LDL |
| 5 | h | rs41349146 | rs2431337 | 500a | 0.007 | 0 | NA | NA | -0.007 | 3.84 × 10-7 | -0.145 | 2.92 × 10-12 | 1.2 × 10-9 | Arteries |
| 6 | h | rs41518850 | rs12190287 | 300a | 0.006 | 0 | NA | NA | -0.006 | 2.88 × 10-6 | -0.132 | 1.76 × 10-10 | 2.3 × 10-8 | CAD |
| 6 | h | rs4398751 | rs9397922 | 150a | 0.005 | 0 | NA | NA | -0.005 | 2.18 × 10-5 | -0.119 | 1.02 × 10-8 | 7.3 × 10-7 | Lipoprotein |
| 8 | All | rs16883114 | rs10503973 | 200a | 0.021 | 0.041 | 1.993 | 1.57 × 10-8 | 0.02 | 8.57 × 10-9 | 0.117 | 1.69 × 10-8 | --- | Cholesterol, LDL |
| 9 | RD, h | rs12343115 | rs2149998 | 300a | 0.009 | 0 | NA | NA | -0.009 | 6.97 × 10-9 | -0.167 | 6.66 × 10-16 | 3.6 × 10-12 | Myocardial Infarction |
| 18 | All | rs41477147 | rs10502528 | 150a | 0.028 | 0.065 | 2.413 | 0 | 0.037 | 0 | 0.179 | 0 | --- | Arteries |
| (rs1595963) | ||||||||||||||
| 21 | h | rs7276641 | rs2829644 | 300a | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.198 | 2.50 × 10-5 | -0.008 | 2.81 × 10-6 | -0.111 | 8.91 × 10-8 | --- | Coronary disease |
adenotes the physical distance (in kb) to the nearest validated SNP. bFisher’s exact test is only required when the asymptotic assumption does not hold. NA: not available; Chr., chromosome; MAF, minor allele frequency; location according to NCBI Build 37.5; Association of SNP or proxy with other cardiovascular phenotypes was based on the HuGE Navigator database (http://hugenavigator.net/HuGENavigator/startPagePubLit.do), dbSNP (NCBI website: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP/) and MalaCards (http://www.malacards.org/pages/whatsmalacards).
Application to sequencing based T1D data
We also tested Cohen’s h on sequencing data. There were 179 rare variants in 10 candidate genes previously studied in connection with T1D. Four SNPs (rs35667974, rs35337543, ss107794687, and ss107794688) which were shown to be associated with T1D in the previous study were also identified by RD, Cohen’s h and OR. Another SNP, ss107794716 residing within the AIRE gene, was identified by both of RD and Cohen’s h but not OR (RD = 0.006, p = 0.034; Cohen’s h = 0.106, p = 0.019; OR = 7.04, p = 0.068). The association of this region and the AIRE gene with T1D was documented [35–37]. In addition, the magnitudes of p-values of significant rare variants obtained from Cohen’s h are the smallest. The results indicates that Cohen’s h are more likely to identify associated rare variants compared to OR.
Distribution of ES values for rare variants based on CAD data
The distributions of ES values for rare variants reflected the magnitude of rare variant-disease associations. We further explored the ES distributions of Cohen’s h and OR with regard to robustness and interpretation using the GWAS data. The two panels in Figure 4 showed the scatter plot of OR and Cohen’s h for the rare and common SNPs, respectively, in the CAD dataset. The ranges of ORs among rare SNPs were obviously broader than those of common SNPs. For Cohen’s h, the ranges were comparable for rare and common SNPs. This indicated that Cohen’s h is more robust at lower MAF compared to OR.
Figure 4.
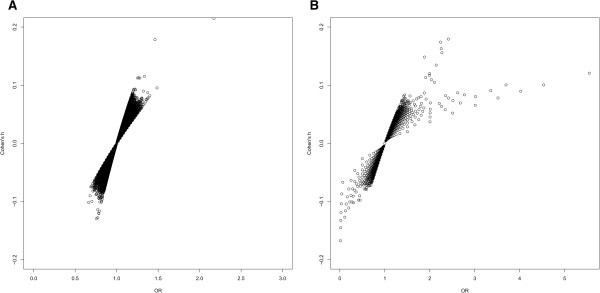
Scatter plot of OR and Cohen’s h for rare and common SNPs in CAD. (A) common SNPs and (B) rare SNPs. Despite the seemingly more outliers using the OR criteria, more outliers using Cohen’s h criteria were statistically significant.
Thresholds of Cohen’s h for the evaluation of small, medium, and large differences between proportions were previously recommended as 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8, respectively [26]. However, the proportion of values of Cohen’s h larger than 0.2 was extremely low from our analysis of GWAS data (Figure 4). Therefore, we determined the empirical thresholds of Cohen’s h comparable to commonly used cut points for OR in terms of mild, moderate and large effects. The relationship between OR and Cohen’s h can be derived as 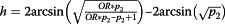 given the MAF of the control group, p2, and the OR. We found that the relationship between the MAF and Cohen’s h for rare SNPs was similar to that for common SNPs. As MAF increases, the magnitudes of Cohen’s h turned out to be greater at fixed OR. As such, we determined thresholds for Cohen’s h according to the average value of varying MAFs. For common SNPs, the values at 1.2 and 1.5 for OR are comparable to thresholds at 0.075 and 0.15 for Cohen’s h, respectively. As for rare SNPs, Cohen’s h had thresholds 0.05 and 0.1 corresponding to mild and moderate effects of OR at 1.5 and 2. One can choose dynamic thresholds for Cohen’s h with varying MAFs; however, this approach is not practical in comparison to using the p value of the calculated h. Using the above criteria, we further subdivided all common SNPs into the mild, moderate, and larger effect categories (Table 5). The proportions of each category estimated from the OR and Cohen’s h values for common SNPs resulted in good agreement (see Additional file 6). For common SNPs, the proportion of large ES (i.e., |log(OR)| > log(1.5)) falls in the range of (0.001%, 0.033%) for CAD, CD (data not shown), and RA (data not shown). This finding is consistent with that obtained from Cohen’s h (i.e., |h| >0.15). Notably, there was a trend that SNPs with lower MAF were more likely to have moderate to large ESs by either measure. However, for rare SNPs, the proportions of the three categories did not align (see Additional file 7). The proportion of large effects based on OR (i.e. |log(OR)| > log(2)) rose to 6.296% in CAD, revealing that approximately 3,288 rare SNPs have large ESs. In contrast, the estimates from Cohen’s h with comparably large ESs to OR, lead to markedly fewer, 42 in total, rare SNPs.
given the MAF of the control group, p2, and the OR. We found that the relationship between the MAF and Cohen’s h for rare SNPs was similar to that for common SNPs. As MAF increases, the magnitudes of Cohen’s h turned out to be greater at fixed OR. As such, we determined thresholds for Cohen’s h according to the average value of varying MAFs. For common SNPs, the values at 1.2 and 1.5 for OR are comparable to thresholds at 0.075 and 0.15 for Cohen’s h, respectively. As for rare SNPs, Cohen’s h had thresholds 0.05 and 0.1 corresponding to mild and moderate effects of OR at 1.5 and 2. One can choose dynamic thresholds for Cohen’s h with varying MAFs; however, this approach is not practical in comparison to using the p value of the calculated h. Using the above criteria, we further subdivided all common SNPs into the mild, moderate, and larger effect categories (Table 5). The proportions of each category estimated from the OR and Cohen’s h values for common SNPs resulted in good agreement (see Additional file 6). For common SNPs, the proportion of large ES (i.e., |log(OR)| > log(1.5)) falls in the range of (0.001%, 0.033%) for CAD, CD (data not shown), and RA (data not shown). This finding is consistent with that obtained from Cohen’s h (i.e., |h| >0.15). Notably, there was a trend that SNPs with lower MAF were more likely to have moderate to large ESs by either measure. However, for rare SNPs, the proportions of the three categories did not align (see Additional file 7). The proportion of large effects based on OR (i.e. |log(OR)| > log(2)) rose to 6.296% in CAD, revealing that approximately 3,288 rare SNPs have large ESs. In contrast, the estimates from Cohen’s h with comparably large ESs to OR, lead to markedly fewer, 42 in total, rare SNPs.
Table 5.
Proportions of SNPs with mild, moderate, and large effect for CAD GWAS data
| Type of | No. of | Mild effect (%) | Moderate effect (%) | Large effect (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNPs | SNPs | OR | Cohen’s h | OR | Cohen’s h | OR | Cohen’s h |
| Common | 360839 | 99.453 | 99.936 | 0.546 | 0.063 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Rare | 52220 | 69.772 | 73.416 | 23.932 | 26.505 | 6.296 | 0.079 |
The respective thresholds of ORs for mild, moderate and large effect at common SNPs were |log(OR)|≦log(1.2), log(1.2) < |log(OR)|≦log(1.5), and |log(OR)| > log(1.5), whereas Cohen’s h had respective thresholds of |h|≦0.075, 0.075 < |h|≦0.15, and |h| > 0.15. The respective thresholds of ORs for mild, moderate and large effect at rare SNPs were |log(OR)|≦log(1.5), log(1.5) < |log(OR)|≦log(2), and |log(OR)| > log(2), whereas Cohen’s h had respective thresholds of |h|≦0.05, 0.05 < |h|≦0.1, and |h| > 0.1.
Discussion
Despite the hundreds of common genetic variants associated with complex diseases identified by GWAS, only a small fraction of heritability of most common complex genetic diseases are explained by these genes. Currently, an increasing number of studies are focusing on rare disease-associated variants that might shed light on the issue of missing heritability. The power of GWAS falls steeply with MAFs for values <0.01. We compared Cohen’s h with OR on simulated and real data. Our results supported the following conclusions. First, estimates of the ES measures were biased at low MAF regardless of the method used. The estimates of log(OR) were more biased and exhibited greater MSE for rare variants than RD and Cohen’s h, as was reported [21, 24]. In contrast to previous simulation studies [21, 22, 24], we found slightly increased false positive associations for rare variants (Figure 1) exceeding the nominal level (5%). Possible strategies to address this problem included the adoption of a more stringent significance level to prevent inflated false positive results and to aggregate multiple rare SNPs to avoid the burden of multiple testing [38]. We noticed that single marker testing was not as efficient as methods that jointly analyze a group of mutations such as CMC, WSS and VT. Some studies had demonstrated that CMC, WSS and VT would encounter the loss of power when the direction of effects in the combined variants is not consistent, or when a small fraction of variants are associated with disease, as compared to single marker testing [39, 40]. Hence, we recommend using Cohen’s h for screening purpose to uncover SNPs that might be overlooked by the OR or RD based statistic commonly used in GWAS. Once the candidate genes were flagged, more sophisticated statistical methods and re-sequencing of these potential target regions and more would be needed for validation.
Second, we compared the empirical distributions of ORs and Cohen’s h for common and rare variants corresponding to the null hypothesis of WTCCC GWAS with ~2000 cases and 3000 controls. To the best of our knowledge, most studies used significant or susceptible SNPs from GWAS findings to examine the distributions of ORs for common and rare variants [8, 12, 25]. However, very weak genetic effects would likely be missed by studies using only significant SNPs. In our study, the empirical distributions of ORs could be useful for setting realistic conditions related to the OR for rare variants in future simulation studies because the vast majority of studies typically utilize the OR as the ES measure. A quick search in PubMed using “Cohen’s h” did not find any genetic association studies. To our knowledge, the first paper that mentioned the application of Cohen’s h for rare variant was Evangelou & Ioannidis [41]. Our study provided supporting evidence that the application of Cohen’s h for rare variant analysis was appealing. Additionally, we made an evaluative judgment on whether the estimated value of Cohen’s h should be considered mild, moderate, or large to improve its interpretation. As was widely known, low frequency SNPs had moderate-to-large effects (compared to common SNPs,) based on the OR and Cohen’s h. However, for SNPs with MAFs between 0.002 and 0.05, the percentages of large effects based on OR (6.296%) were much greater than those obtained using Cohen’s h (0.079%). We argued that the relative greater bias of OR based estimates might be responsible for this large difference. The most common argument against the use of data transformation is the problem of interpretability in effect size estimation. The impression of imperfect correlation between Cohen’s h and effect size needs further study.
Third, our finding also showed that Cohen’s h could uncover rare disease-associated variants missed by OR based analysis. The arcsine square root transformation stabilized Cohen’s h so its asymptotic variance did not depend on the allele frequency. Accordingly, its power to detect a genetic association was relatively robust at low MAF. The data presented here suggest that test based on Cohen’s h is an appropriate substitute for OR (Table 4). The vast majority of the rare disease-associated variants identified by OR was detrimental. On the contrary, one was more likely to discover both risk and protective variants using Cohen’s h. Caution should be taken on interpreting these results from the rare-variant analysis of the three WTCCC datasets as the reliability of current microarray based genotyping still needed improvement for MAF <5%. Next-generation sequencing technologies, such as the 1000 Genome project, will identify many more variants with very low MAFs; thus, the application of Cohen’s h is appropriate. Additionally, estimating and presenting Cohen’s h facilitates future meta-analysis of GWAS data [41]. However, further studies are needed to address the slight bias and to control the false positive rates associated with the analysis of rare variants. In this situation, all other methods suffer from inflated type I error rates. Thus, alternative methods will need to be developed based on Cohen’s h to account for the increased numbers of false positives. There are likely several factors that contribute to the inflated type I error rates, such as population stratification and linkage disequilibrium among rare variants. One possible direction is to use methods to jointly analyze a group of mutations within a gene, or functional unit, as performed in previous studies [14–20]. Additional studies are required to delineate the optimal application and interpretation of results based on Cohen’s h.
Conclusions
Using simulated and publically available data, our results suggested that Cohen’s h, a difference-type measure based on the arcsine square root transformation of minor allele frequencies, was less biased and substantially more powerful than OR in detecting the association of rare variants and complex genetic diseases. Our method offers a useful option for researchers who wish to quantify rare variants associated with diseases.
Electronic supplementary material
Additional file 1: Additional information of sampling distributions of RD, Cohen’s h and OR. (PDF 246 KB)
Additional file 2: Biases and MSEs for RD, Cohen’s h and log(OR) for 22 chromosomes. (PDF 116 KB)
Additional file 3: Type I error rates for RD, Cohen’s h and log(OR) for 22 chromosomes. (PDF 91 KB)
Additional file 4: Box-plot of effect sizes for rare SNPs based on two shared controls in WTCCC data. Panel A: RD; Panel B: Cohen’s h; Panel C: log(OR). (PDF 262 KB)
Additional file 5: Box-plot of effect sizes for common SNPs based on two shared controls in WTCCC data. Panel A: RD; Panel B: Cohen’s h; Panel C: log(OR). (PDF 353 KB)
Additional file 6: Proportions of mild, moderate, and large effect for common SNPs in CAD. Grey bar represents OR and Black bar denotes Cohen’s h. (PDF 254 KB)
Additional file 7: Proportions of mild, moderate, and large effect for rare SNPs in CAD. Grey bar represents OR and Black bar denotes Cohen’s h. (PDF 250 KB)
Acknowledgements
This study makes use of data generated by the Wellcome Trust Case–Control Consortium. A full list of the investigators who contributed to the generation of the data is available from http://www.wtccc.org.uk. Funding for the project was provided by the Wellcome Trust under award 076113. We are grateful to WTCCC for granting the access of GWAS data.
Funding
This work was supported by the Taiwan National Science Council [NSC 101-2118-M-320-001 and NSC 102-2118-M-320-001]. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- MAF
Minor allele frequency
- SNP
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- RD
Risk difference
- OR
Odds ratio
- GWAS
Genome-wide association study
- ES
Effect size
- CAD
Coronary artery disease
- WTCCC
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium
- 58C
1958 Birth Cohort Controls
- NBS
UK Blood Services sample
- MSE
Mean square error
- CMC
Combined Multivariate and Collapsing Method
- WSS
Weighted sum statistic
- VT
Variable threshold.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Authors’ contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: JY and SW. Performed the experiments: SW. Analyzed the data: SW. Wrote the paper: JY and SW. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Shu-Hui Wen, Email: shwen@mail.tcu.edu.tw.
Jih-I Yeh, Email: jihiyeh@gms.tcu.edu.tw.
References
- 1.Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, Goldstein DB, Hindorff LA, Hunter DJ, McCarthy MI, Ramos EM, Cardon LR, Chakravarti A, Cho JH, Guttmacher AE, Kong A, Kruglyak L, Mardis E, Rotimi CN, Slatkin M, Valle D, Whittemore AS, Boehnke M, Clark AG, Eichler EE, Gibson G, Haines JL, Mackay TFC, McCarroll SA, Visscher PM. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature. 2009;461:747–753. doi: 10.1038/nature08494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Asimit J, Zeggini E. Rare variant association analysis methods for complex traits. Annu Rev Genet. 2010;44:293–308. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Klein RJ, Zeiss C, Chew EY, Tsai JY, Sackler RS, Haynes C, Henning AK, SanGiovanni JP, Mane SM, Mayne ST, Bracken MB, Ferris FL, Ott J, Barnstable C, Hoh J. Complement factor H polymorphism in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Science. 2005;308:385–389. doi: 10.1126/science.1109557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature. 2007;447(7145):661–678. doi: 10.1038/nature05911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Feng T, Zhu X. Genome-wide searching of rare genetic variants in WTCCC data. Hum Genet. 2010;128(3):269–280. doi: 10.1007/s00439-010-0849-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schork NJ, Murray SS, Frazer KA, Topol EJ. Common vs rare allele hypotheses for complex diseases. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009;19(3):212–219. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA, Ramosa EM, Mehtac JP, Collins FS, Manolio TA. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;2009(106):9362–9367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903103106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bodmer W, Bonilla C. Common and rare variants in multifactorial susceptibility to common diseases. Nat Genet. 2008;40(6):695–701. doi: 10.1038/ng.f.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Neale BM, Rivas MA, Voight BF, Altshuler D, Devlin B, Orho-Melander M, Kathiresan S, Purcell SM, Roeder K, Daly MJ. Testing for an unusual distribution of rare variants. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(3):e1001322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cirulli ET, Goldstein DB. Uncovering the roles of rare variants in common disease through whole-genome sequencing. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:415–425. doi: 10.1038/nrg2779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dickson SP, Wang K, Krantz I, Hakonarson K, Goldstein DB. Rare variants create synthetic genome-wide associations. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(1):e1000294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Park JH, Wacholder S, Gail MH, Peters U, Jacobs KB, Chanock SJ, Chatterjee N. Estimation of ES distribution from genome-wide association studies and implications for future discoveries. Nat Genet. 2010;42(7):570–575. doi: 10.1038/ng.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 2012;491:56–65. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Morgenthaler S, Thilly WG. A strategy to discover genes that carry multi-allelic or mono-allelic risk for common diseases: A cohort allelic sums test (CAST) Mutat Res. 2007;615:28–56. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li B, Leal SM. Methods for detecting associations with rare variants for common diseases: application to analysis of sequence data. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;83:311–321. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.06.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Madsen BE, Browning SR. A groupwise association test for rare mutations using a weighted sum statistic. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(2):e1000384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Price AL, Kryukov GV, de Bakker PI, Purcell SM, Staples J, Wei LJ, Sunyaev SR. Pooled association tests for rare variants in exon-resequencing studies. Am J Hum Genet. 2010;86:832–838. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Feng T, Elston RC, Zhu X. Detecting rare and common variants for complex traits: sibpair and odds ratio weighted sum statistics (SPWSS, ORWSS) Genet Epidemiol. 2011;35:398–409. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Han F, Pan W. A data-adaptive sum test for disease association with multiple common or rare variants. Hum Hered. 2010;70:42–54. doi: 10.1159/000288704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hoffman TJ, Marini NJ, Witte JS. Comprehensive approach to analyzing rare genetic variants. PLoS ONE. 2011;5(11):e13584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Garner C. Upward bias in odds ratio estimates from Genome-wide association studies. Genet Epidemiol. 2007;31:288–295. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rücker G, Schwarzer G, Carpenter J, Olkin I. Why add anything to nothing? The arcsine difference as a measure of treatment effect in meta-analysis with zero cells. Stat Med. 2009;28:721–738. doi: 10.1002/sim.3511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wei YC, Wen SH, Chen PC, Wang CH, Hsiao CK. A simple Bayesian mixture model with a hybrid procedure for genome-wide association studies. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010;18(8):942–947. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Spencer C, Hechter E, Vukcevic D, Donnelly P. Quantifying the underestimation of relative risks from Genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(3):e1001337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Park JH, Gail MH, Weinberg CR, Carroll RJ, Chung CC, Wang Z, Chanock SJ, Fraumeni JF, Chatterjee N. Distribution of allele frequencies and ESs and their interrelationships for common genetic susceptibility variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(44):18026–18031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114759108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2. Hinsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988. pp. 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Li B, Wang G, Leal SM. SimRare: a program to generate and analyze sequence-based data for association studies of quantitative and qualitative traits. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(20):2703–2704. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kryukov GV, Shpunt A, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Sunyaev SR. Power of deep, all-exon resequencing for discovery of human trait genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:3871–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812824106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 1995;57:289–300. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nejentsev S, Walker N, Riches D, Egholm M, Todd JA. Rare variants of IFIH1, a gene implicated in antiviral responses, protect against type 1 diabetes. Science. 2009;324:387–389. doi: 10.1126/science.1167728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cunnington MS, Mayosi BM, Hall DH, Avery PJ, Farrall M, Vickers MA, Watkins H, Keavney B. Novel genetic variants linked to coronary artery disease by genome-wide association are not associated with carotid artery intima-media thickness or intermediate risk phenotypes. Atherosclerosis. 2009;203(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kathiresan S, Srivastava D. Genetics of human cardiovascular disease. Cell. 2012;148:1242–1257. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Torkamani A, Topol EJ, Schork NJ. Pathway analysis of seven common diseases assessed by genome-wide association. Genomics. 2008;92(5):265–272. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kaess BM, Tomaszewski M, Braund PS, Stark K, Rafelt S, Fischer M, Hardwick R, Nelson CP, Debiec R, Huber F, Kremer W, Kalbitzer HR, Rose LM, Chasman DI, Hopewell J, Clarke R, Burton PR, Tobin MD, Hengstenberg C, Samani NJ. Large-scale candidate gene analysis of HDL particle features. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(1):e14529. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang J, Liu H, Liu Z, Liao Y, Guo L, Wang H, He L, Zhang X, Xing Q. A functional alternative splicing mutation in AIRE gene causes autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(1):e53981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Herold KC, Vignali DAA, Cooke A, Bluestone JA. Type 1 diabetes: translating mechanistic observations into effective clinical outcomes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:243–256. doi: 10.1038/nri3422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Luce S, Briet C, Bécourt C, Lemonnier F, Boitard C. The targeting of β-cells by T lymphocytes in human type 1 diabetes: clinical perspectives. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(Suppl. 3):89–97. doi: 10.1111/dom.12159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Stringer S, Wray NR, Kahn RS, Derks EM. Underestimated ESs in GWAS: fundamental limitations of single SNP analysis for dichotomous phenotypes. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(11):e27964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lee S, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M, Lin X. Rare-variant association analysis: study designs and statistical tests. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;95(1):5–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.06.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu DJ, Peloso GM, Zhan X, Holmen O, Zawitowski M, Feng S, Nikpay M, Auer PL, Goel A, Zhang H, Peters U, Farrall M, Orho-Melander M, Kooperberg C, McPherson R, Watkins H, Willer CJ, Hveem K, Melander O, Kathiresan S, Abecasis GR. Meta-analysis of gene-level tests for rare variant association. Nat Genet. 2014;46:200–204. doi: 10.1038/ng.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Evangelou E, Ioannidis JPA. Meta-analysis methods for genome-wide association studies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:379–389. doi: 10.1038/nrg3472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Additional information of sampling distributions of RD, Cohen’s h and OR. (PDF 246 KB)
Additional file 2: Biases and MSEs for RD, Cohen’s h and log(OR) for 22 chromosomes. (PDF 116 KB)
Additional file 3: Type I error rates for RD, Cohen’s h and log(OR) for 22 chromosomes. (PDF 91 KB)
Additional file 4: Box-plot of effect sizes for rare SNPs based on two shared controls in WTCCC data. Panel A: RD; Panel B: Cohen’s h; Panel C: log(OR). (PDF 262 KB)
Additional file 5: Box-plot of effect sizes for common SNPs based on two shared controls in WTCCC data. Panel A: RD; Panel B: Cohen’s h; Panel C: log(OR). (PDF 353 KB)
Additional file 6: Proportions of mild, moderate, and large effect for common SNPs in CAD. Grey bar represents OR and Black bar denotes Cohen’s h. (PDF 254 KB)
Additional file 7: Proportions of mild, moderate, and large effect for rare SNPs in CAD. Grey bar represents OR and Black bar denotes Cohen’s h. (PDF 250 KB)


