Abstract
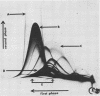
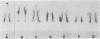
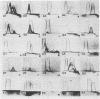
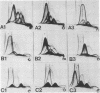
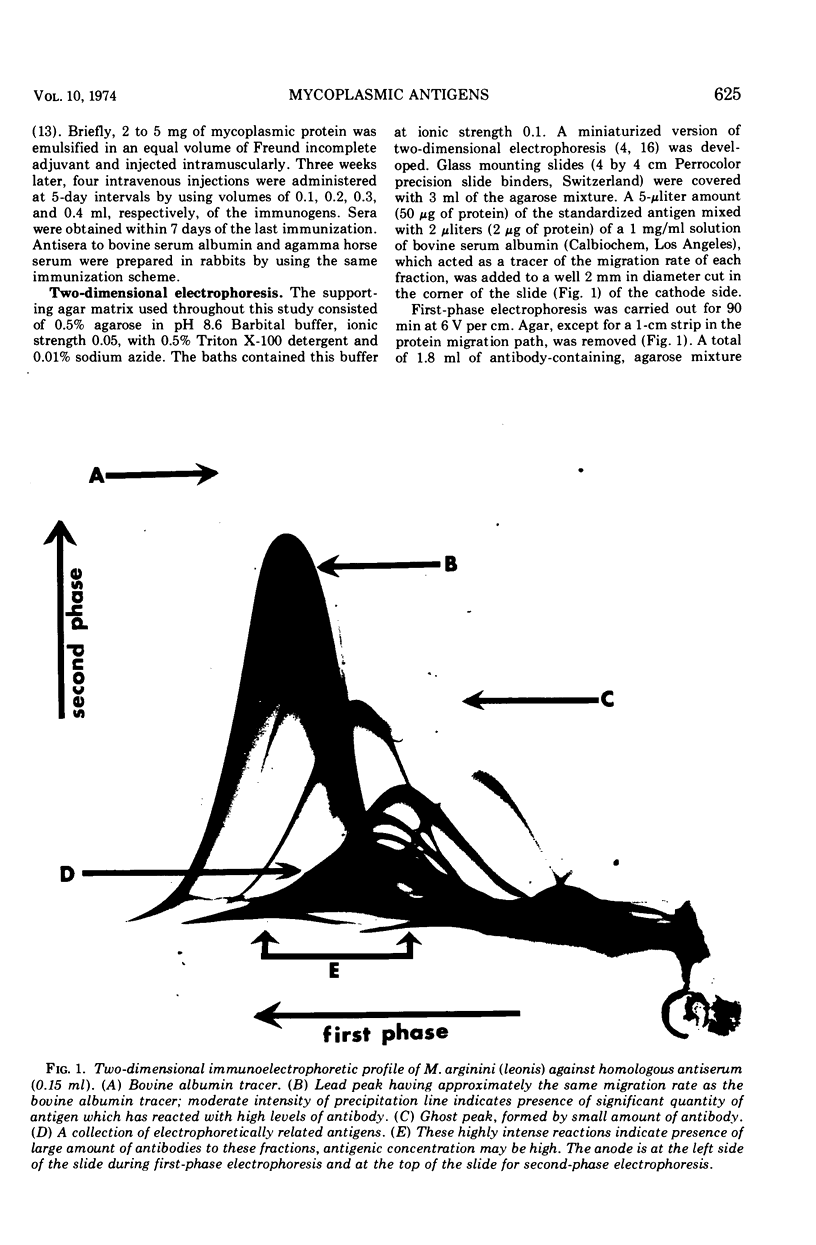
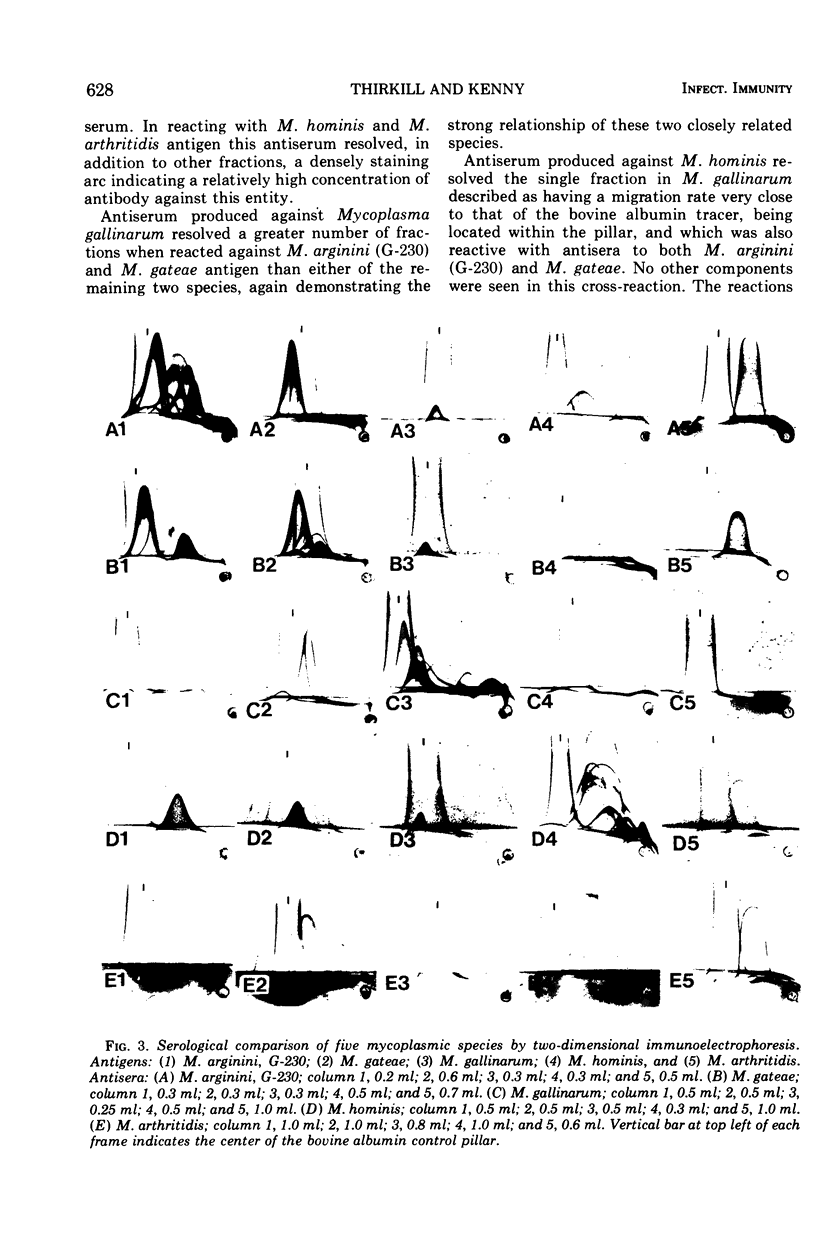
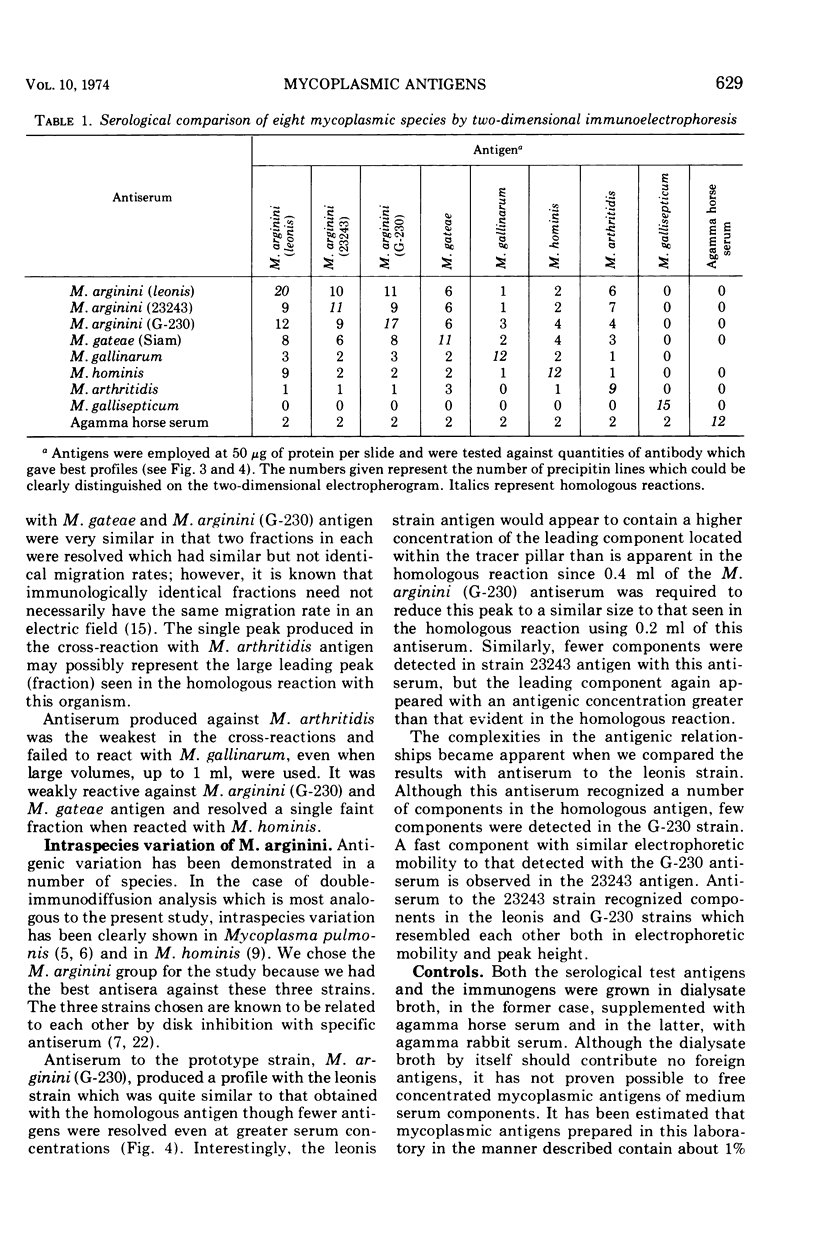
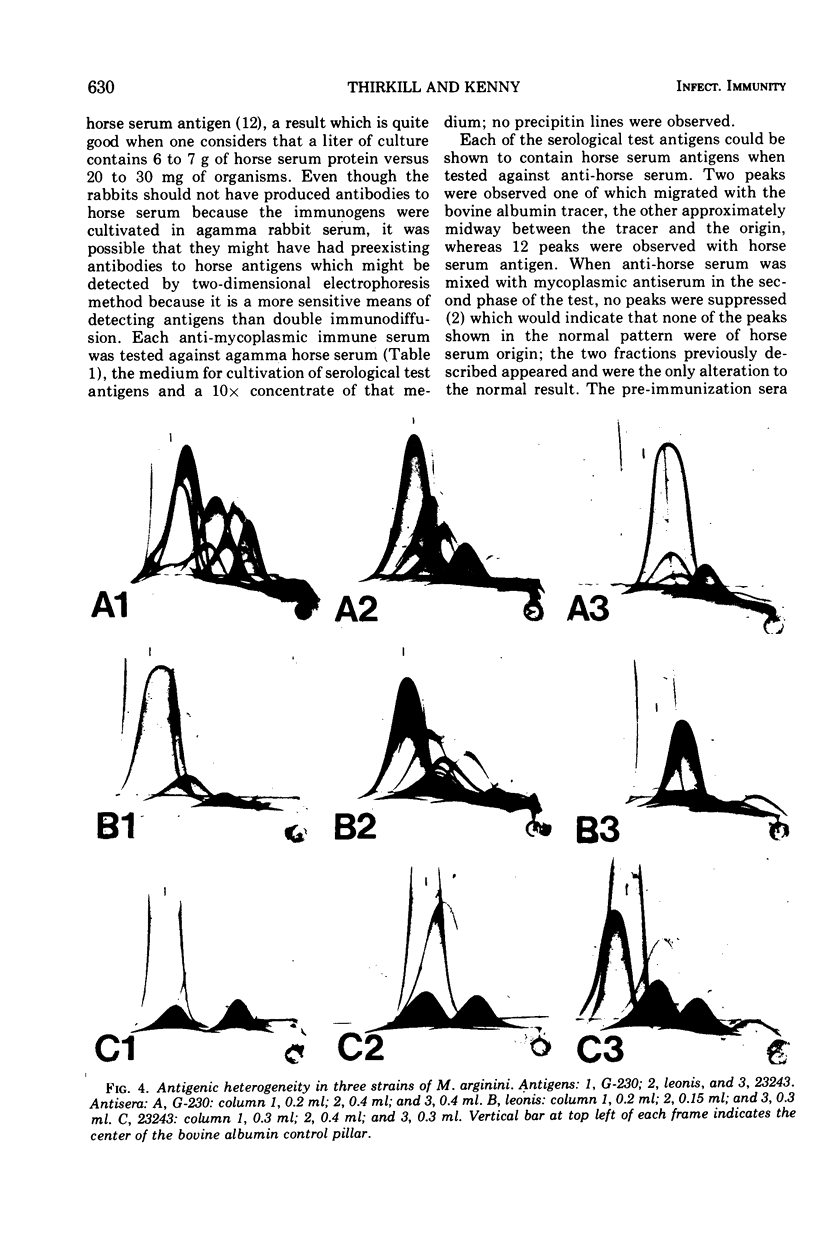
Five arginine-utilizing, nonglycolytic Mycoplasma species were compared serologically by two dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. The survey included: Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma arthritidis, Mycoplasma gateae, Mycoplasma gallinarum, and three strains of Mycoplasma arginini. Although the M. arginini strains showed strong cross-reactions, each strain produced a different antigenic profile which was distinct and which indicated significant antigenic differences between strains. The M. arginini strains showed strong relationships with M. gateae; lesser cross-reactions were observed with other strains. Common antigens were demonstrable in the entire group. When all these species were compared with a glycolytic species, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, no cross-reactions were observed. Two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis was a far more sensitive technique than double-immunodiffusion since as many as 20 components could be resolved.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsen N. H. Antigen-antibody crossed electrophoresis (Laurell) applied to the study of the antigenic structure of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):525–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.525-527.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H., Bock E. Identification and quantitation of antigens and antibodies by means of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. A survey of methods. J Immunol Methods. 1972 Jan;1(2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist L. M., Lau B. H., Winter C. E. Mycoplasma-associated immunosuppression: effect on hemagglutinin response to common antigens in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.410-415.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb B. J., Kenny G. E. Characterization of Mycoplasma pulmonis variants isolated from rabbits. I. Identification and properties of isolates. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1416–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1416-1424.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb B. J., Kenny G. E. Characterizion of Mycoplasma pulmonis variants isolated from rabbits. II. Basis for differentiation of antigenic subtypes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1425–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1425-1429.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn R. G., Kenny G. E. Differences in arginine requirement for growth among arginine-utilizing Mycoplasma species. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):611–618. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.611-618.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Axelsen N. H. Identification and quantitation of precipitins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis by means of crossed immunoelectrophoresis with intermediate gel. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. The antigens of Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Dec;67(4):585–602. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaklamanis E., Pavlatos M. The immunosuppressive effect of mycoplasma infection. I. Effect on the humoral and cellular response. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):695–702. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.510-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Serologic heterogeneity of the mycoplasmatales. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(Suppl):S2–S5. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.supplement_1.s2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Serological comparison of ten glycolytic Mycoplasma species. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1044–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1044-1055.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröll J. Immunochemical identification of specific precipitin lines in quantitative immunoelectrophoresis patterns. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Aug;24(1):55–60. doi: 10.3109/00365516909080132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. THE SEROLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION OF MYCOPLASMA STRAINS (PLEURO-PNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS) FROM VARIOUS SOURCES. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Jun;62:199–219. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock M. E., Bonner S. V. Comparison of undefined medium and its dialyzable fraction for growth of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):522–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.522-525.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet G. H., Wilson D. E., Gerber J. D. Application of electroimmunodiffusion and crossed electroimmunodiffusion to the comparative serology of a microorganism (Histoplasma capsulatum). J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):554–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., SOMERSON N. L., TURNER H. C., CHANOCK R. M. SEROLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS AMONG HUMAN MYCOPLASMAS AS SHOWN BY COMPLEMENT-FIXATION AND GEL DIFFUSION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1261–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1261-1273.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]