Abstract
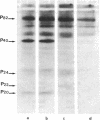
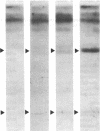
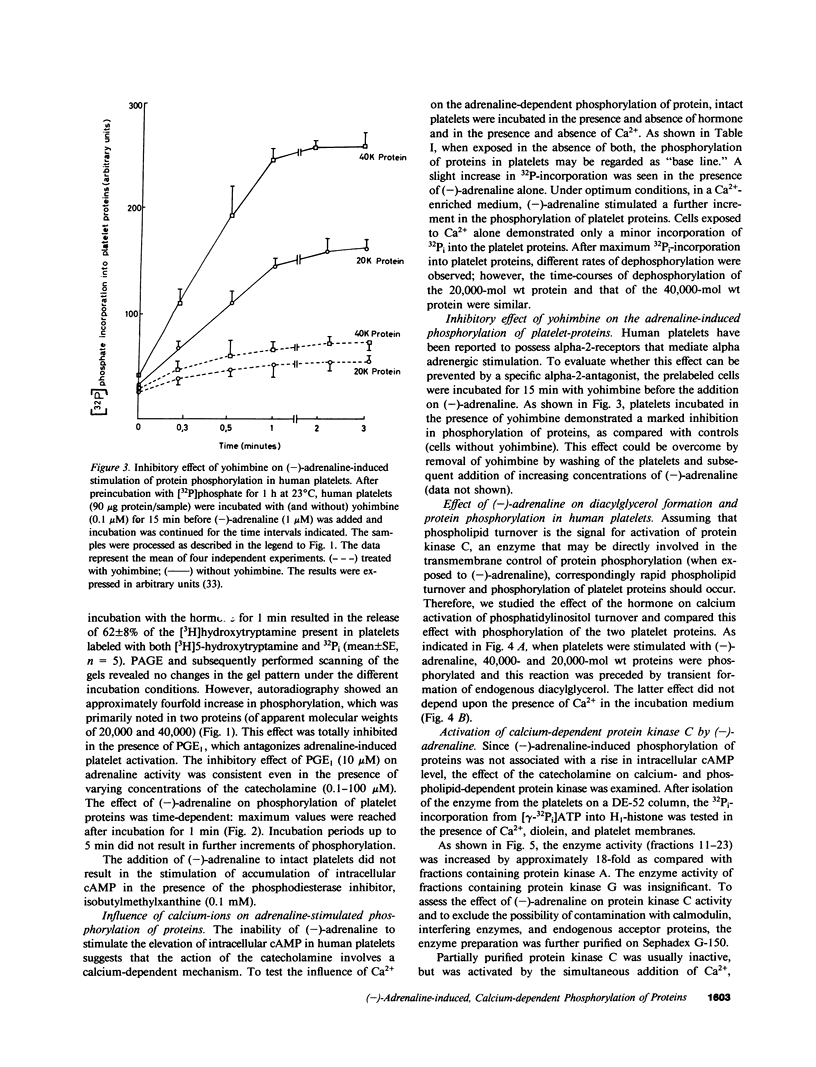
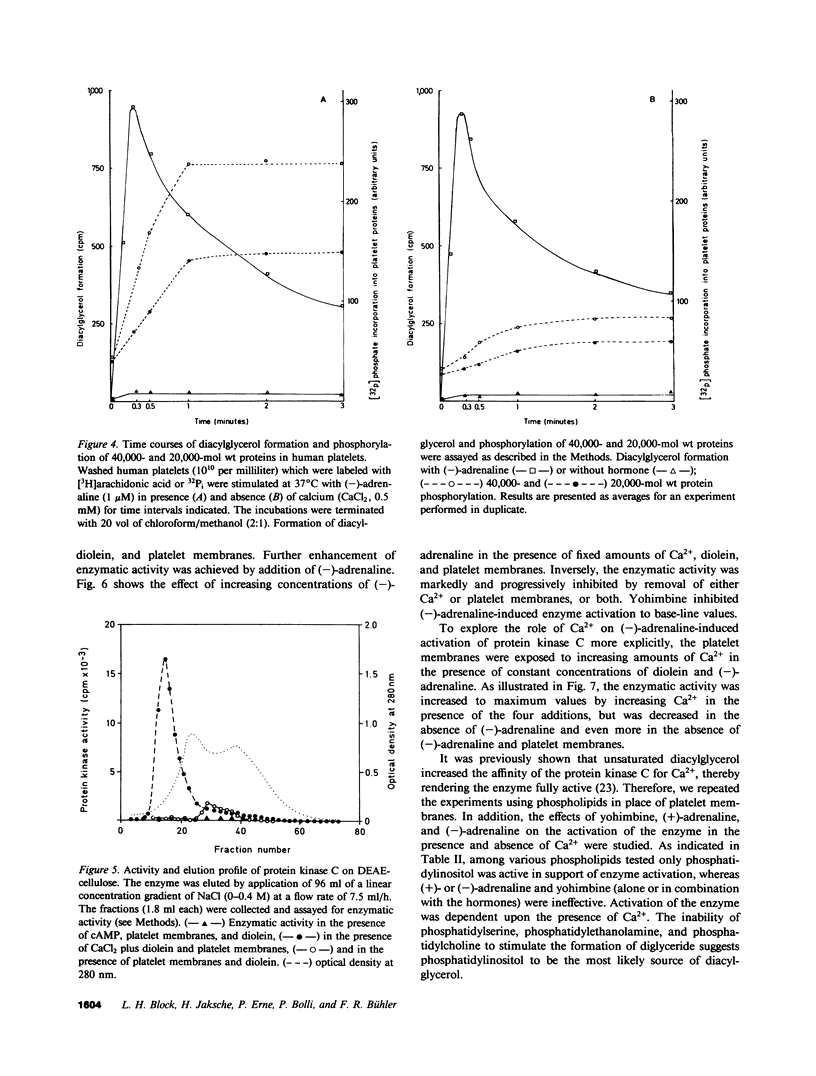
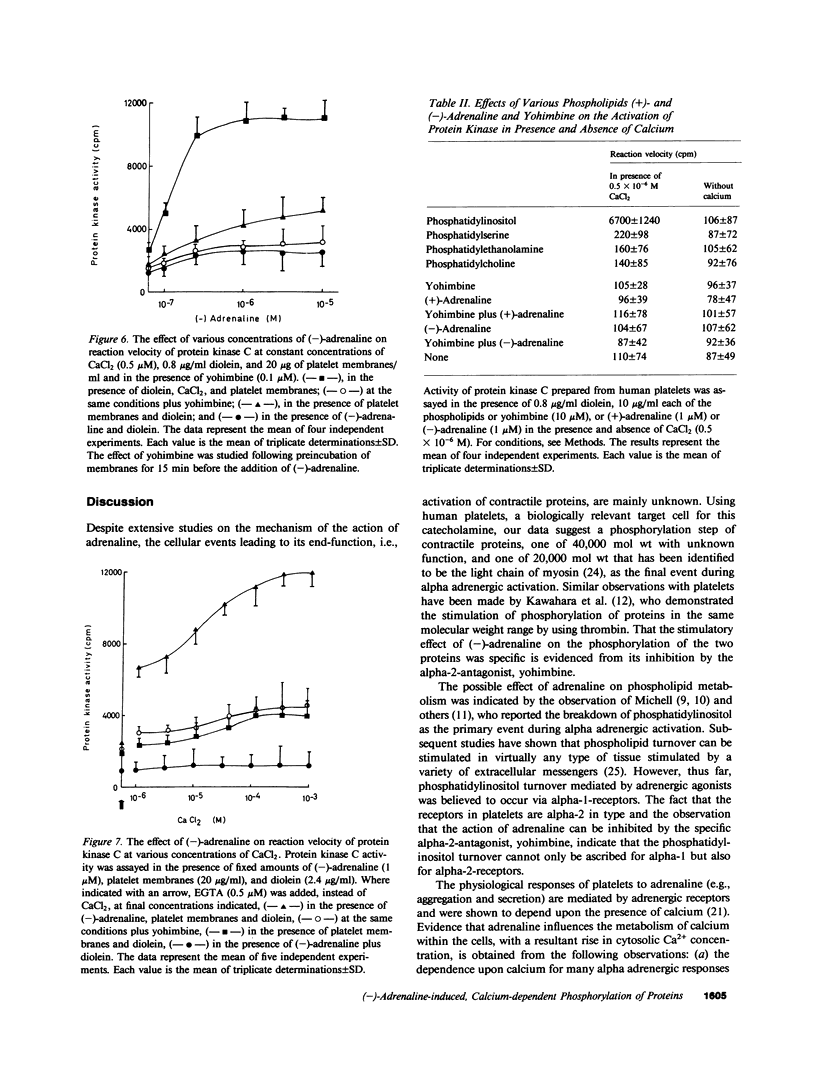
In human platelets, adrenaline stimulated, approximately four-fold, as compared with controls, the phosphorylation of primarily two proteins of apparent molecular weights of 20,000 and 40,000, respectively. Maximum phosphorylation occurred after incubation for 1 min and was inhibited by the addition of either yohimbine, prostaglandin E1, or EGTA. Phosphorylation of the two proteins was accompanied by diacylglycerol formation. The (-)-adrenaline-induced phosphorylation of proteins corresponds to the activation of a calcium-dependent protein kinase partially purified by DEAE-cellulose and Sephadex G150 column chromatography. The enzymatic activity was modulated by addition of (-)-adrenaline and CaCl2, by diolein, and in the presence of membranes or phosphatidylinositol but not phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. A phospholipid-dependent reaction appears to be involved in the molecular mechanism of action of adrenaline.
Full text
PDF
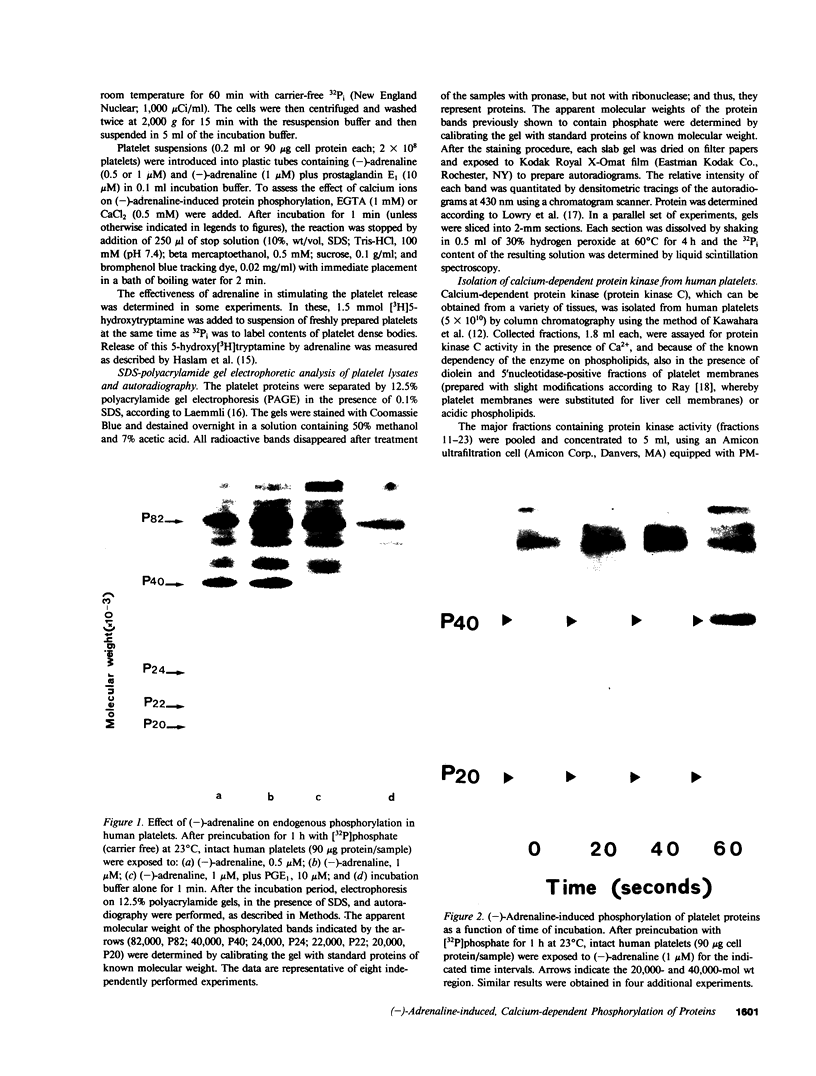
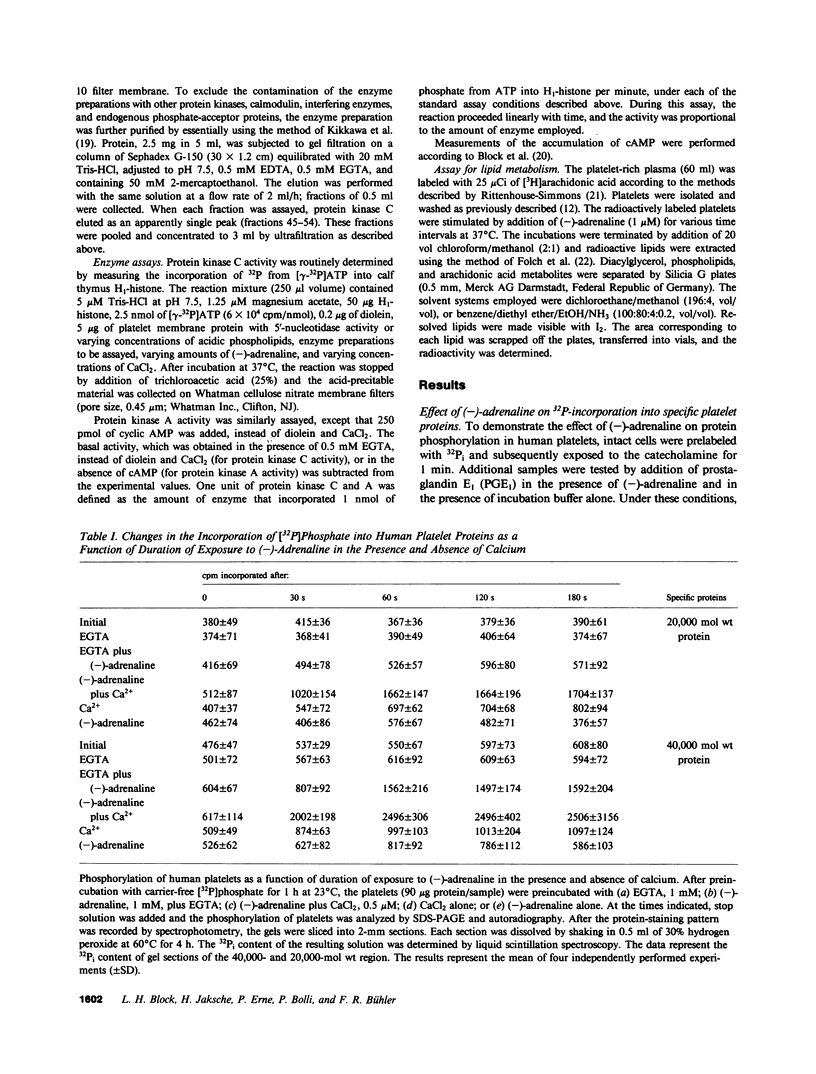


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Conti M. A. Phosphorylation of platelet myosin increases actin-activated myosin ATPase activity. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):597–598. doi: 10.1038/256597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F. D., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Studies on role of calcium in alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Majerus P. W. Isolation of human platelets and platelet surface membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:149–155. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. The interaction of cyclic nucleotides and calcium in the control of cellular activity. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:1–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Brumley F. T., Marks J. L., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Relationship between alpha-adrenergic stimulation of calcium efflux and activation of phosphorylase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4851–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block L. H., Locher R., Tenschert W., Siegenthaler W., Hofmann T., Mettler E., Vetter W. 125I-8-L-arginine vasopressin binding to human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):374–381. doi: 10.1172/JCI110265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Norepinephrine, vasopressin, glucagon, and A23187 induce efflux of calcium from an exchangeable pool in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erne P., Bühler F. R., Affolter H., Bürgisser E. Excitatory and inhibitory modulation of intracellular free calcium in human platelets by hormones and drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jul 22;91(2-3):331–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Lynham J. A., Fox J. E. Effects of collagen, ionophore A23187 and prostaglandin E1 on the phosphorylation of specific proteins in blood platelets. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):397–406. doi: 10.1042/bj1780397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Effects of calcium omission on acetylcholine-stimulated amylase secretion and phospholipid synthesis in pigeon pancreas slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 25;115(1):219–221. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. The relationship of calcium to receptor-controlled stimulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover. Effects of acetylcholine, adrenaline, calcium ions, cinchocaine and a bivalent cation ionophore on rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):479–485. doi: 10.1042/bj1480479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Cooperative roles of various membrane phospholipids in the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7146–7149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara Y., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Sano K., Nishizuka Y. Phospholipid turnover as a possible transmembrane signal for protein phosphorylation during human platelet activation by thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 17;97(1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandenheede J. R., De Wulf H. On the role of calcium as second messenger in liver for the hormonally induced activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 28;496(2):448–457. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90327-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie B. A., Putney J. W., Jr, Sherman J. M. alpha-Adrenergic, beta-adrenergic and cholinergic mechanisms for amylase secretion by rat parotid gland in vitro. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):351–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marier S. H., Putney J. W., Jr, Van de Walle C. M. Control of calcium channels by membrane receptors in the rat parotid gland. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:141–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Jones L. M. Enhanced phosphatidylinositol labelling in rat parotid fragments exposed to alpha-adrenergic stimulation. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;138(1):47–52. doi: 10.1042/bj1380047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. E., Nelson D. L. Calcium fluxes in isolated acinar cells from rat parotid. Effect of adrenergic and cholinergic stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3629–3636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Feinberg H., Le Breton G. C. Epinephrine induces Ca2+ uptake in human blood platelets. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):H483–H488. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.4.H483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parod R. J., Putney J. W., Jr An alpha-adrenergic receptor mechanism controlling potassium permeability in the rat lacrimal gland acinar cell. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:359–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K. A modified method for the isolation of the plasma membrane from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Kikkawa U., Sano K., Kaibuchi K., Yu B., Matsubara T., Nishizuka Y. Membrane phospholipid turnover, receptor function and protein phosphorylation. Prog Brain Res. 1982;56:287–301. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63780-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Maeno H., Greengard P. Regulation of endogenous phosphorylation of specific proteins in synaptic membrane fractions from rat brain by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8295–8305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]