Abstract
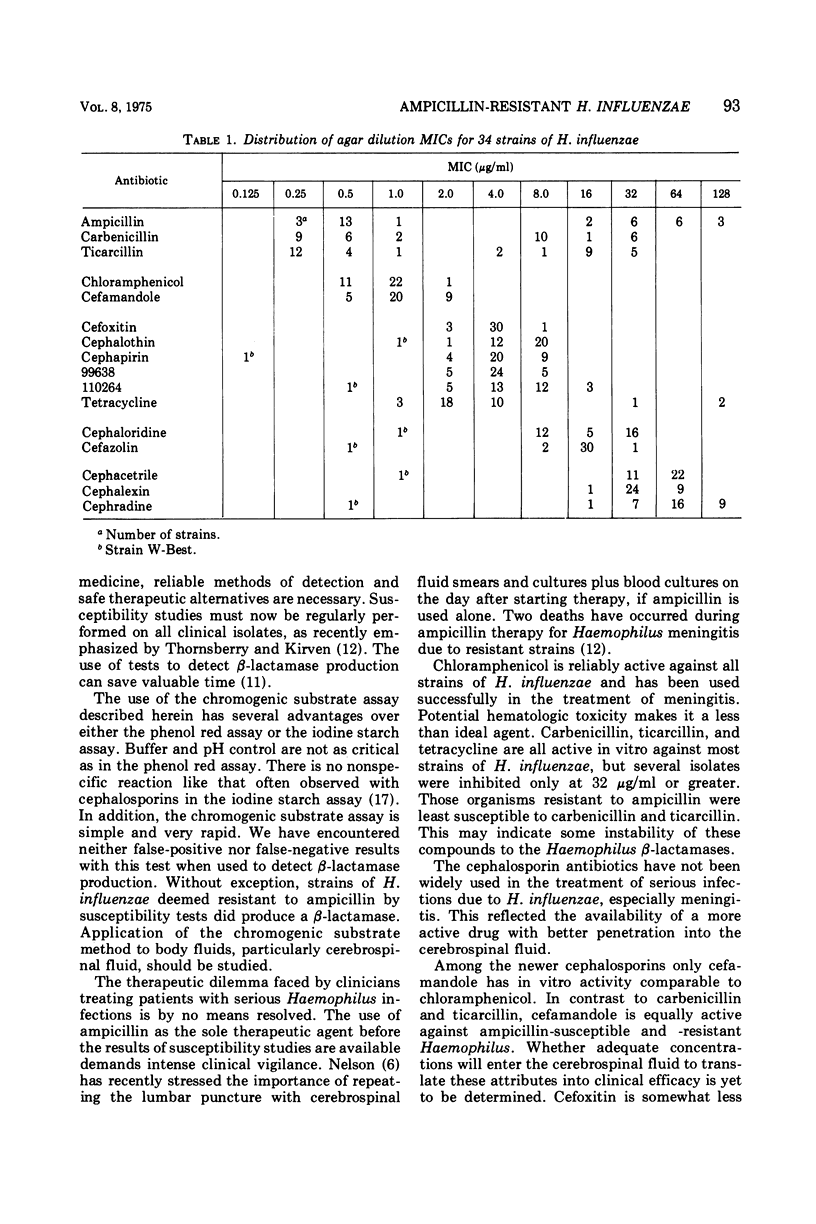
Ampicillin-resistant and -susceptible strains of Haemophilus influenzae were tested for susceptibility to 16 antibiotics. Chloramphenicol and a new cephalosporin, cefamandole, were most active with minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for all bacteria tested between 0.5 to 2.0 μg/ml. All but two organisms were susceptible to tetracycline. Ampicillin-resistant strains of H. influenzae were less susceptible (MIC, 4 to 32 μg/ml) to carbenicillin and ticarcillin than ampicillin-susceptible organisms (MIC, 0.25 to 1.0 μg/ml). A rapid assay for β-lactamase, utilizing a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate, detected enzyme production in all 17 ampicillin-resistant strains of H. influenzae.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farrar W. E., Jr, O'Dell N. M. Beta-lactamase activity in ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):625–629. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan W., Ross S., Rodriguez W., Controni G., Saz A. K. Haemophilus influenzae type B resistant to ampicillin. A report of two cases. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):298–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D. Editorial: Should ampicillin be abandoned for treatment of Haemophilus influenzae disease? JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):322–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M. Letter: Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae. Lancet. 1974 Jun 8;1(7867):1163–1164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90646-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. J., McReynolds J. W., Mock C. R., Bailey D. W. Letter: Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Lancet. 1974 Feb 23;1(7852):313–313. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92617-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae as determined by a rapid test for beta-lactamase production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):653–654. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):620–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomeh M. O., Starr S. E., McGowan J. E., Jr, Terry P. M., Nahmias A. J. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B infection. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):295–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]