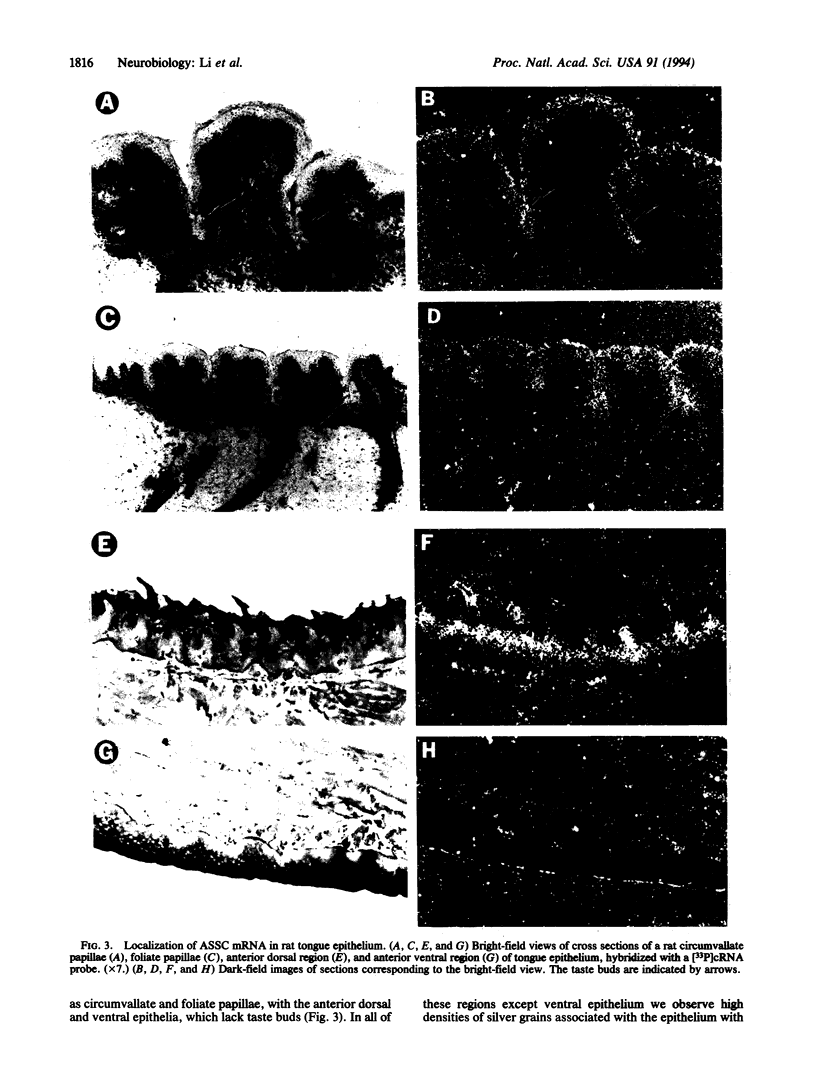
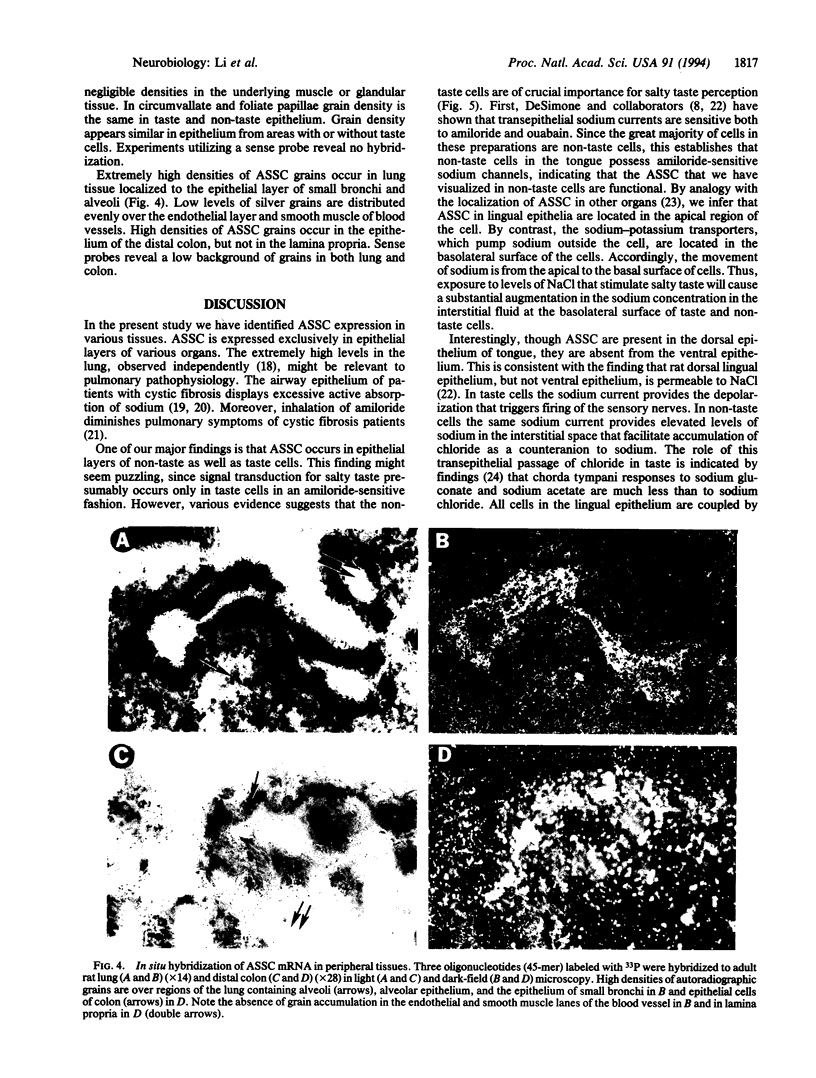
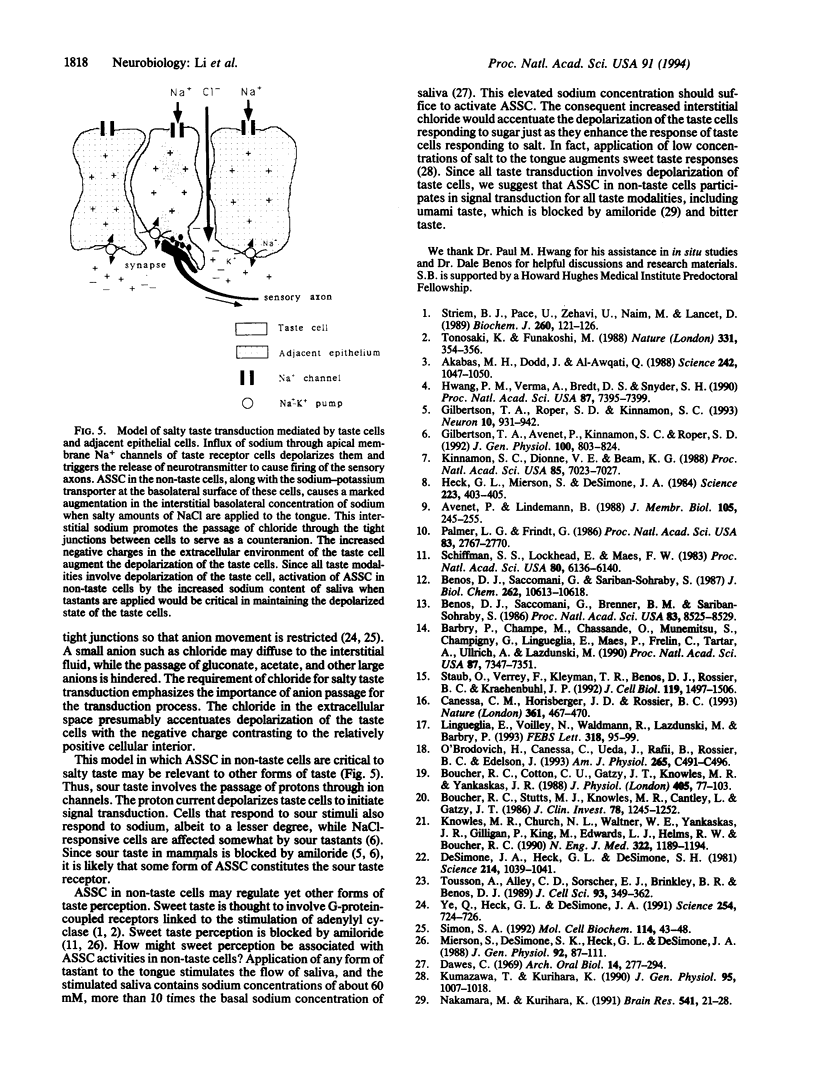
Abstract
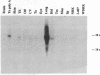
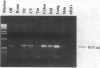
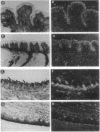
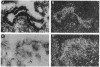
Salty taste is blocked by the diuretic amiloride, which inhibits specific sodium channels. We have isolated an amiloride-sensitive sodium channel (ASSC) from taste tissues by polymerase chain reaction and screening of a cDNA library prepared from rat circumvallate papillae. Northern analysis reveals ASSC in taste and non-taste tissues with the highest level of expression of ASSC in the lung. In situ hybridization establishes ASSC localizations in the epithelia of lung and colon as well as tongue epithelial layers containing and lacking taste buds. These results support a model in which ASSC in non-taste cells regulates responses of taste cells to salt as well as other tastants.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akabas M. H., Dodd J., Al-Awqati Q. A bitter substance induces a rise in intracellular calcium in a subpopulation of rat taste cells. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1047–1050. doi: 10.1126/science.3194756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avenet P., Lindemann B. Amiloride-blockable sodium currents in isolated taste receptor cells. J Membr Biol. 1988 Nov;105(3):245–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01871001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbry P., Champe M., Chassande O., Munemitsu S., Champigny G., Lingueglia E., Maes P., Frelin C., Tartar A., Ullrich A. Human kidney amiloride-binding protein: cDNA structure and functional expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Brenner B. M., Sariban-Sohraby S. Purification and characterization of the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel from A6 cultured cells and bovine renal papilla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Sariban-Sohraby S. The epithelial sodium channel. Subunit number and location of the amiloride binding site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10613–10618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cotton C. U., Gatzy J. T., Knowles M. R., Yankaskas J. R. Evidence for reduced Cl- and increased Na+ permeability in cystic fibrosis human primary cell cultures. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:77–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Cantley L., Gatzy J. T. Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelia. Abnormal basal rate and response to adenylate cyclase activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes C. The effects of flow rate and duration of stimulation on the condentrations of protein and the main electrolytes in human parotid saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Mar;14(3):277–294. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone J. A., Heck G. L., DeSimone S. K. Active ion transport in dog tongue: a possible role in taste. Science. 1981 Nov 27;214(4524):1039–1041. doi: 10.1126/science.7302576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbertson T. A., Avenet P., Kinnamon S. C., Roper S. D. Proton currents through amiloride-sensitive Na channels in hamster taste cells. Role in acid transduction. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Nov;100(5):803–824. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.5.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbertson T. A., Roper S. D., Kinnamon S. C. Proton currents through amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels in isolated hamster taste cells: enhancement by vasopressin and cAMP. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck G. L., Mierson S., DeSimone J. A. Salt taste transduction occurs through an amiloride-sensitive sodium transport pathway. Science. 1984 Jan 27;223(4634):403–405. doi: 10.1126/science.6691151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang P. M., Verma A., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Localization of phosphatidylinositol signaling components in rat taste cells: role in bitter taste transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7395–7399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnamon S. C., Dionne V. E., Beam K. G. Apical localization of K+ channels in taste cells provides the basis for sour taste transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7023–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Church N. L., Waltner W. E., Yankaskas J. R., Gilligan P., King M., Edwards L. J., Helms R. W., Boucher R. C. A pilot study of aerosolized amiloride for the treatment of lung disease in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 26;322(17):1189–1194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004263221704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa T., Kurihara K. Large enhancement of canine taste responses to sugars by salts. J Gen Physiol. 1990 May;95(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.5.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Expression cloning of an epithelial amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. A new channel type with homologies to Caenorhabditis elegans degenerins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierson S., DeSimone S. K., Heck G. L., DeSimone J. A. Sugar-activated ion transport in canine lingual epithelium. Implications for sugar taste transduction. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):87–111. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Kurihara K. Canine taste nerve responses to monosodium glutamate and disodium guanylate: differentiation between umami and salt components with amiloride. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91069-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H., Canessa C., Ueda J., Rafii B., Rossier B. C., Edelson J. Expression of the epithelial Na+ channel in the developing rat lung. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 1):C491–C496. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.2.C491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Amiloride-sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S. S., Lockhead E., Maes F. W. Amiloride reduces the taste intensity of Na+ and Li+ salts and sweeteners. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6136–6140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A. Influence of tight junctions on the interaction of salts with lingual epithelia: responses of chorda tympani and lingual nerves. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992 Sep 8;114(1-2):43–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00240296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub O., Verrey F., Kleyman T. R., Benos D. J., Rossier B. C., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Primary structure of an apical protein from Xenopus laevis that participates in amiloride-sensitive sodium channel activity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1497–1506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striem B. J., Pace U., Zehavi U., Naim M., Lancet D. Sweet tastants stimulate adenylate cyclase coupled to GTP-binding protein in rat tongue membranes. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):121–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2600121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonosaki K., Funakoshi M. Cyclic nucleotides may mediate taste transduction. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):354–356. doi: 10.1038/331354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tousson A., Alley C. D., Sorscher E. J., Brinkley B. R., Benos D. J. Immunochemical localization of amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in sodium-transporting epithelia. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jun;93(Pt 2):349–362. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Q., Heck G. L., DeSimone J. A. The anion paradox in sodium taste reception: resolution by voltage-clamp studies. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):724–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1948054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]