Abstract
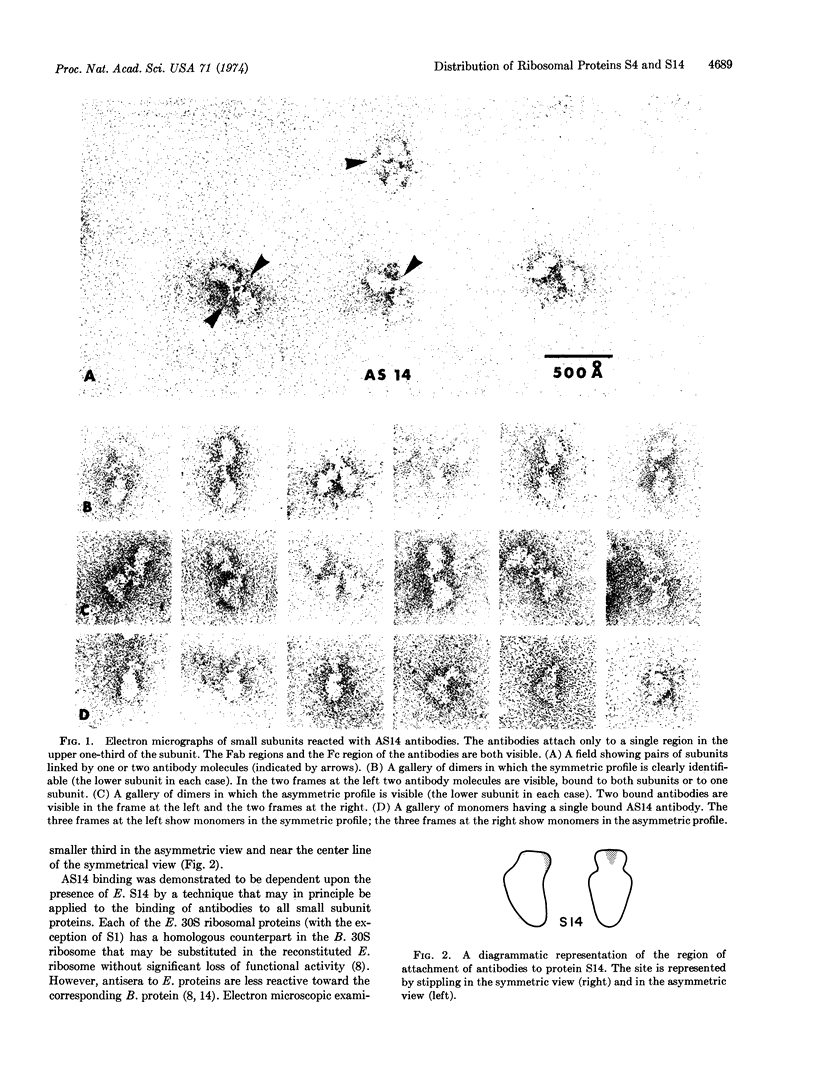
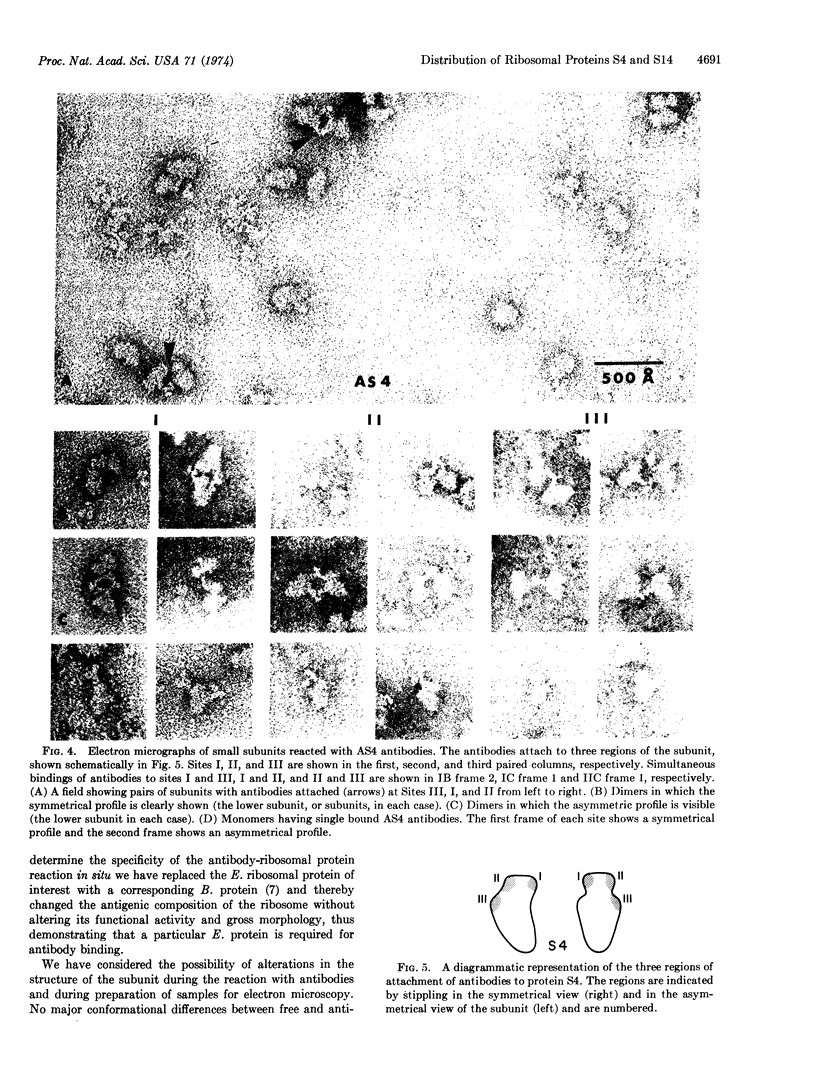
Binding sites for antibodies specific for proteins S4 and S14 of the small subunit of E. coli ribosomes have been mapped on the surface of the subunit by electron microscopy. Antibody binding to reconstituted subunits was shown to depend specifically on the presence of E. coli S4 and S14. Anti-S14 IgG was found to bind to a limited region of the ribosome surface. In contrast anti-S4 IgG was found to bind to three separated regions of the ribosome surface, suggesting S4 has an elongated conformation in situ.
Keywords: Bacillus stearothermophilus, IgG antibody, ribosome topography, reconstitution
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DEDMON R. E., HOLMES A. W., DEINHARDT F. PREPARATION OF FLUORESCEIN ISOTHIOCYANATE-LABELED GAMMA-GLOBULIN BY DIALYSIS, GEL FILTRATION, AND IONEXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY IN COMBINATION. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:734–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.734-739.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Reconstitution of Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunits from purified molecular components. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5720–5730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higo K. I., Loertscher K. Amino-terminal sequences of some Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal proteins and functionally corresponding Bacillus stearothermophilus ribosomal proteins. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):180–186. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.180-186.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higo K., Held W., Kahan L., Nomura M. Functional correspondence between 30S ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):944–948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Thompson J. D., Anderegg J. W. X-ray scattering study of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono K., Isono S., Stöffler G., Visentin L. P., Yaguchi M., Matheson A. T. Correlation between 30S ribosomal proteins of Bacillus stearothermophilus and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 20;127(2):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00333666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki K., Sabol S., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message. VII. Role of initiation factors in formation of the chain initiation complex with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelong J. C., Gros D., Gros F., Bollen A., Maschler R., Stöffler G. Function of individual 30S subunit proteins of Escherichia coli. Effect of specific immunoglobulin fragments (Fab) on activities of ribosomal decoding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):248–252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard K. R., Kleinschmidt A. K., Lake J. A. Caulobacter crescentus bacteriophage phiCbK: structure and in vitro self-assembly of the tail. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 15;81(3):349–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARRACK J. R., HOCH H., JOHNS R. G. S. The valency of antibodies. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Jun;32(3):212–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonomura Y., Blobel G., Sabatini D. Structure of liver ribosomes studied by negative staining. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):303–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinbolt J., Schiltz E. The primary structure of ribosomal protein S4 from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 1;36(3):250–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Hasenbank R., Lütgehaus M., Maschler R., Morrison C. A., Zeichhardt H., Garrett R. A. The accessibility of proteins of the Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit to antibody binding. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 20;127(2):89–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00333659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Sequence differences of Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal proteins as determined by immunochemical methods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2143–2152. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wabl M. R. Electron microscopic localization of two proteins on the surface of the 50 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli using specific antibody markers. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 5;84(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90582-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B. Studies on the primary structure of 20 proteins from Escherichia coli ribosomes by means of an improved protein sequenator. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 1;36(3):247–249. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80382-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaguchi M., Roy C., Matheson A. T., Visentin L. P. The amino acid sequence of the N-terminal region of some 30S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus: homologies in ribosomal proteins. Can J Biochem. 1973 Aug;51(8):1215–1217. doi: 10.1139/o73-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]