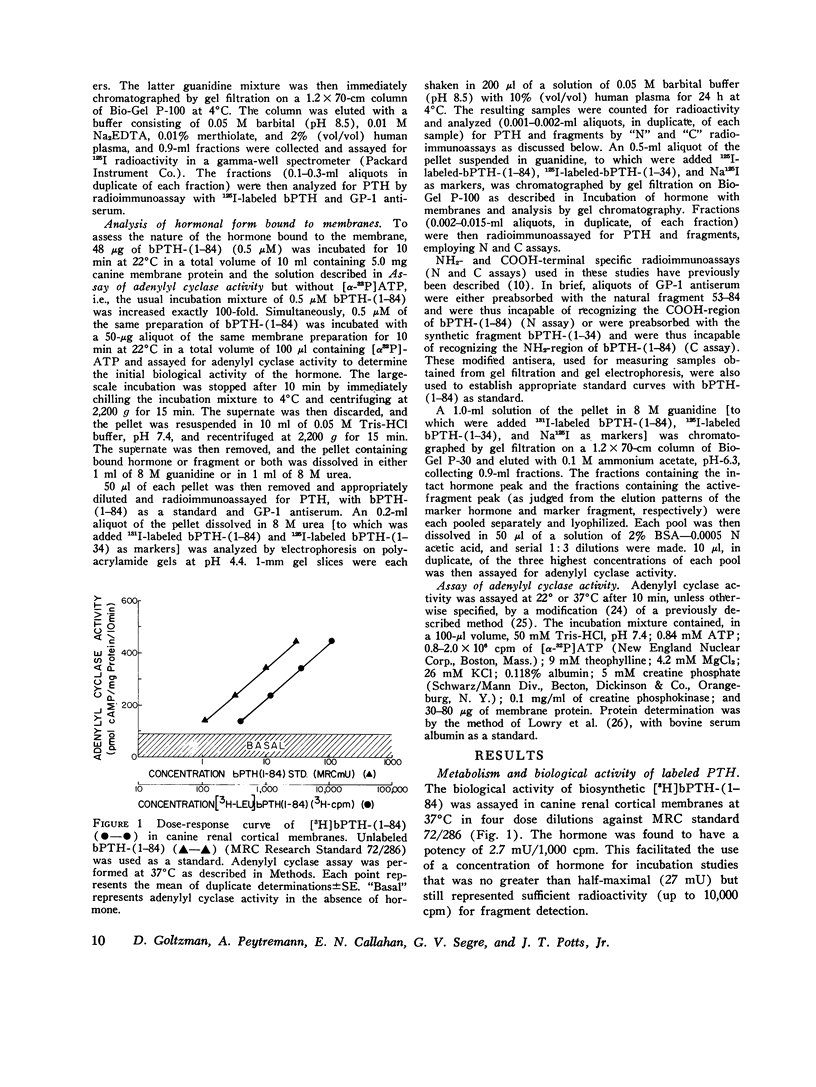
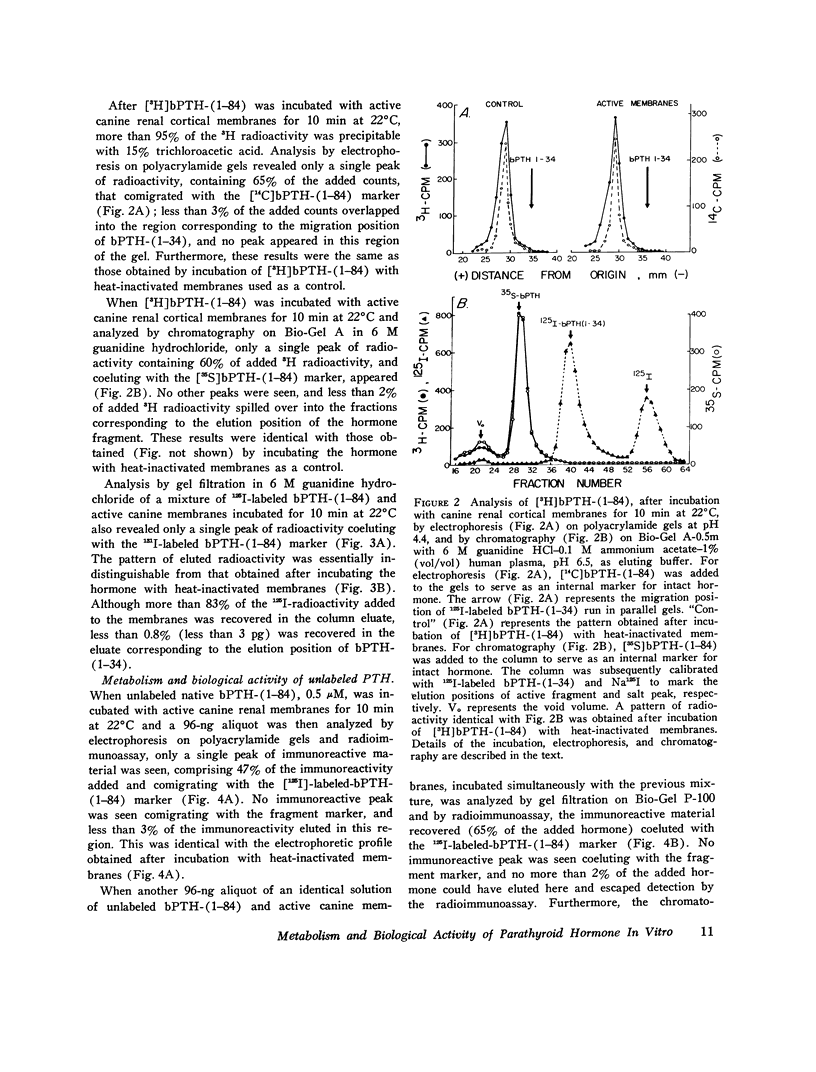
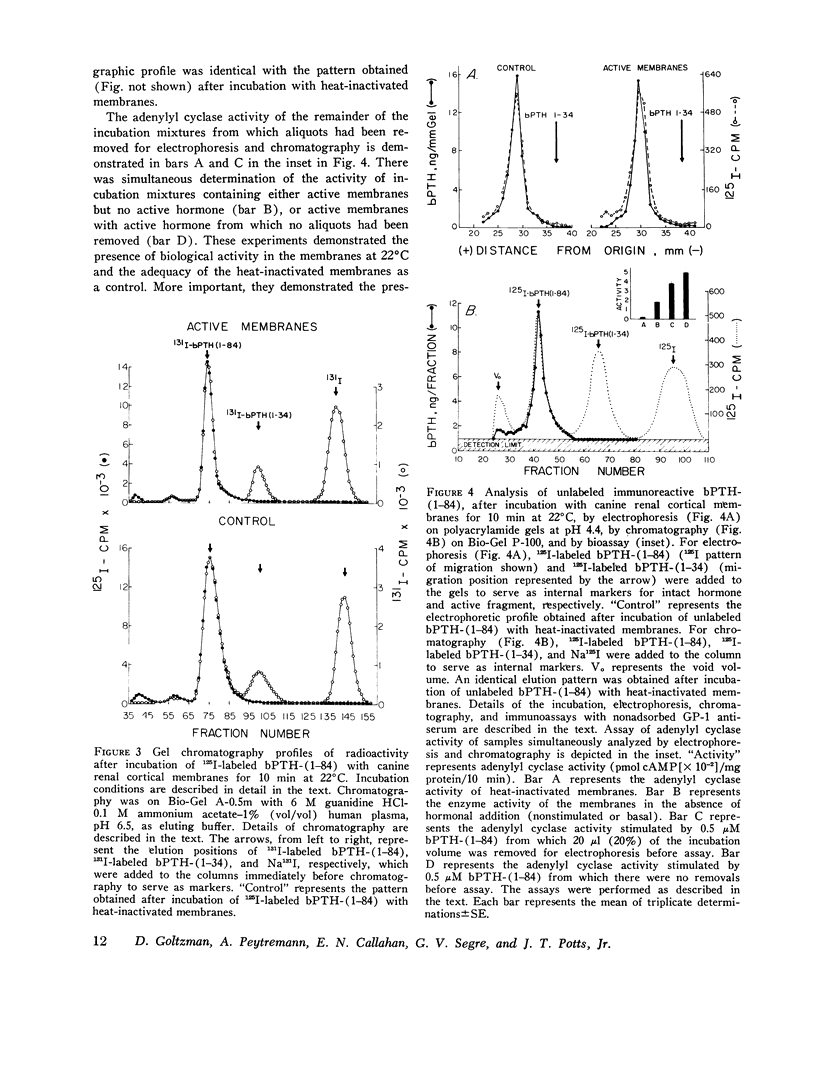
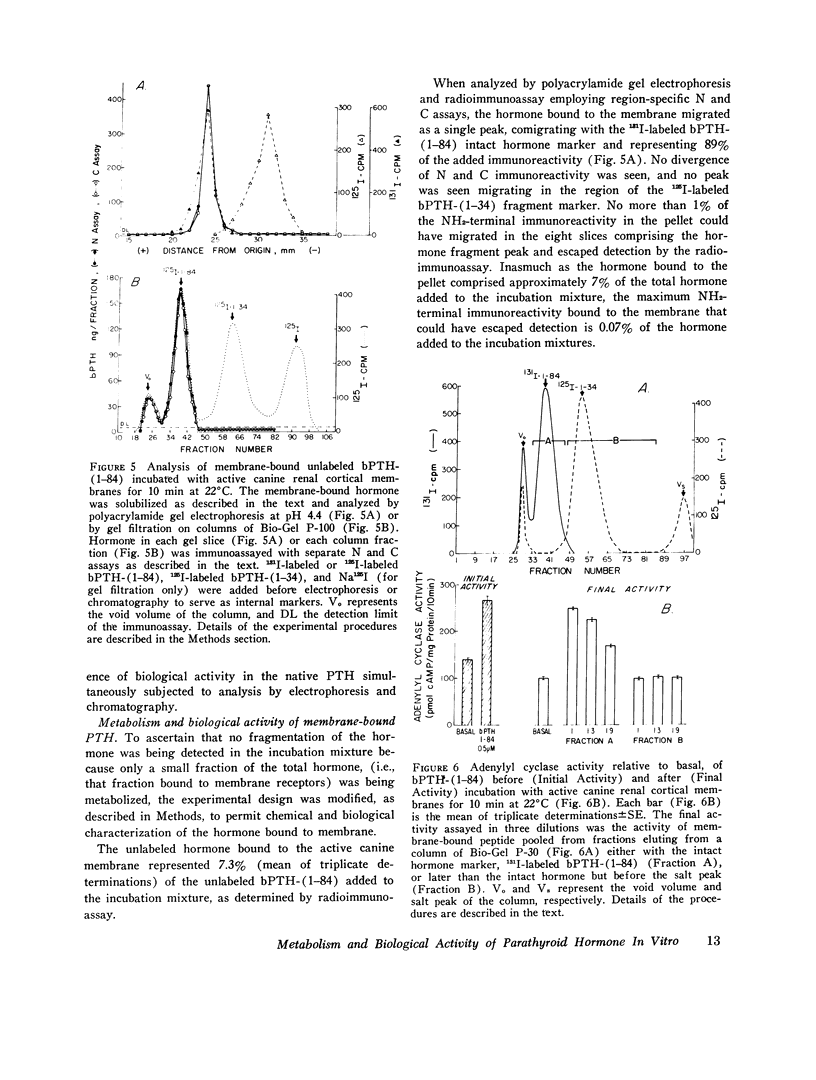
Abstract
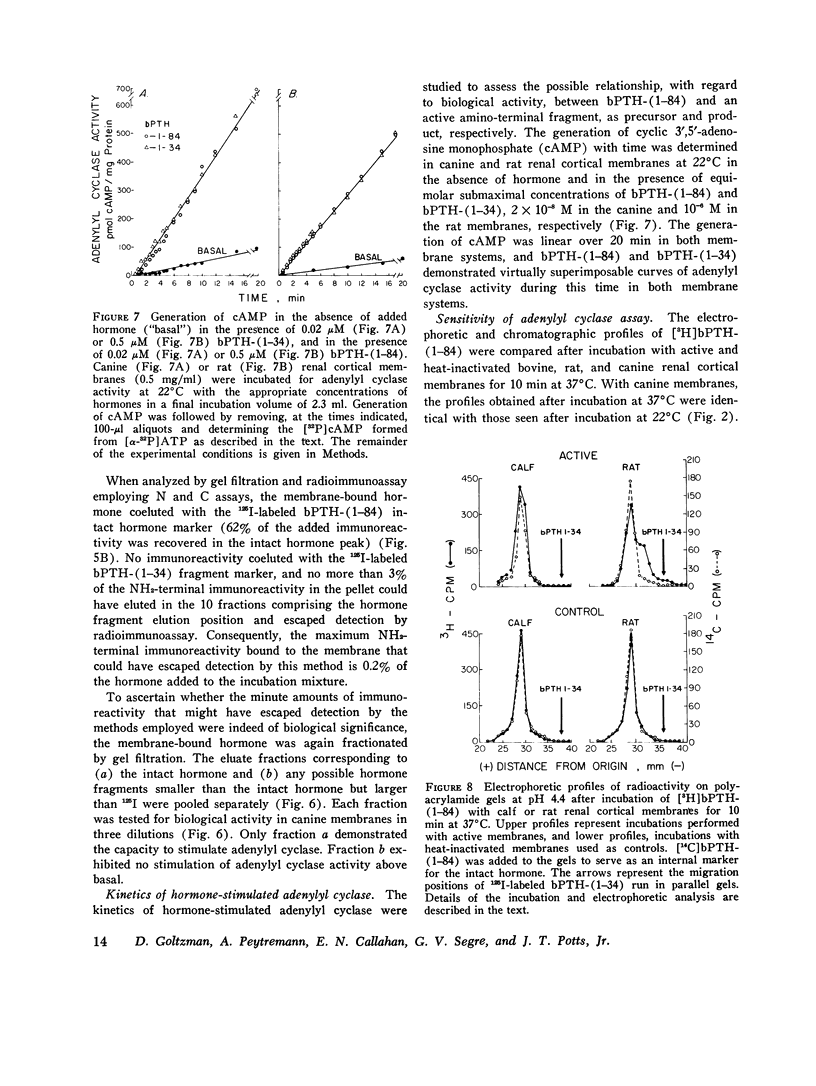
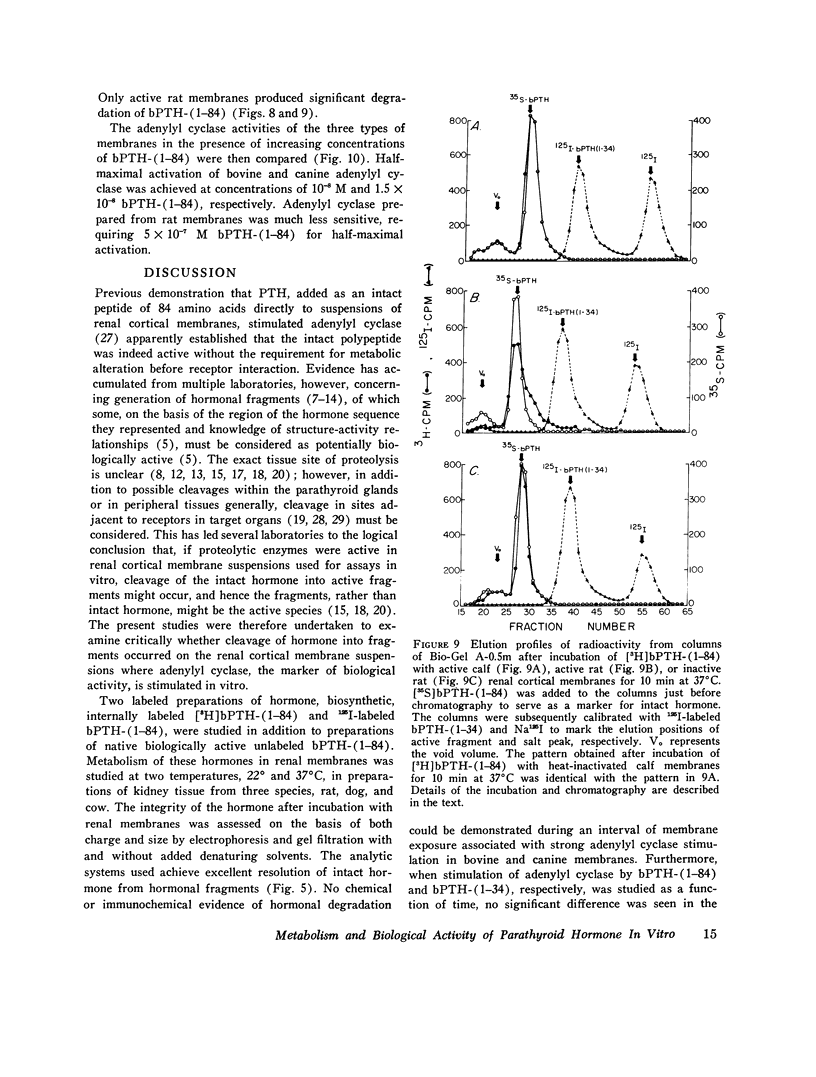
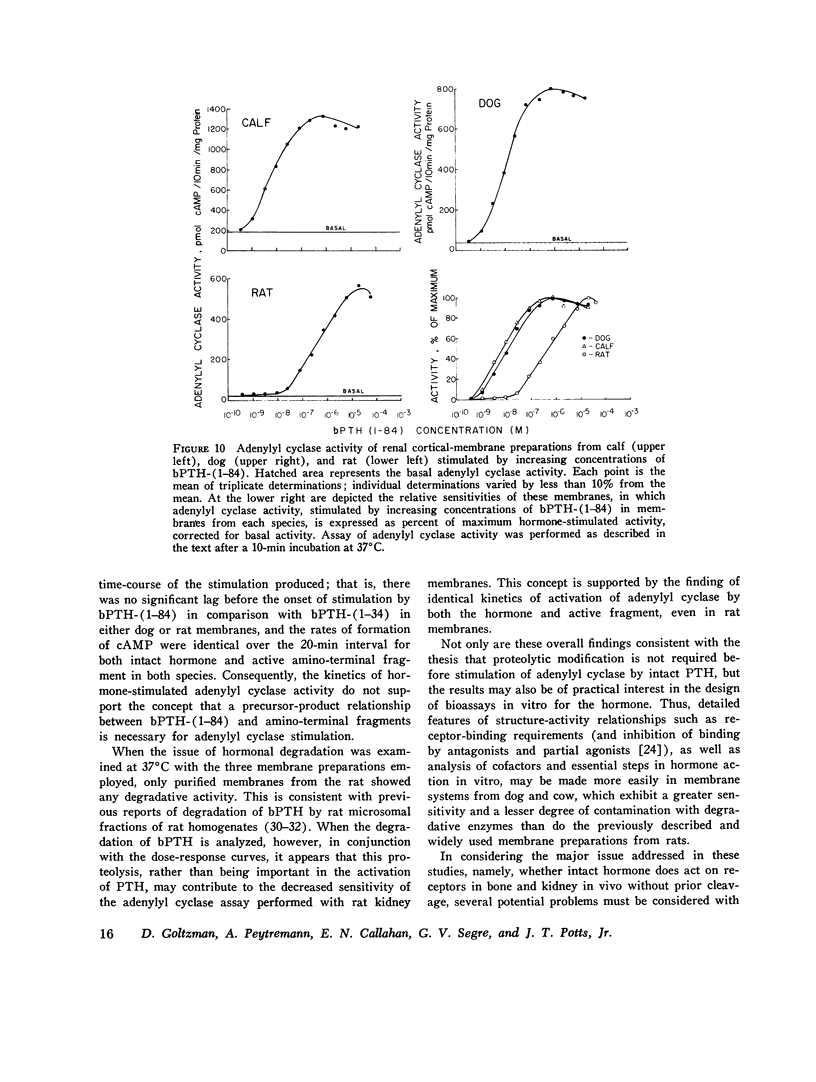
Recent studies from several laboratories have documented the presence of fragments of parathyroid hormone in blood or peripheral tissues or in both. Inasmuch as amino-terminal fragments are known to be biologically active, it has been suggested that fragments, rather than the intact polypeptide of 84 amino acids, might be the active molecular species in tissue fluids. Accordingly, the metabolism of native bovine parathyroid hormone, bPTH-(1-84), was studied in purified renal cortical membranes from several species and correlated with hormonal stimulation of adenylyl cyclase in these membranes in vitro. Analysis of whole incubation mixtures or membrane-bound hormone by gel electrophoresis and gel chromatography after incubation of [3H]bPTH-(1-84) or 125-I-labeled bPTH-(1-84) or unlabeled biologically active bPTH-(1-84) with purified canine renal cortical membranes revealed no evidence of proteolysis, and yet the uncleaved hormone readily stimulated adenylyl cyclase. Kinetic studies of hormone-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity revealed no difference in rate of onset of activity between bPTH-(1-84) And the active synthetic amino-terminal tetratriacontapeptide bPTH-(1-34), and hence there was no evidence of precursor-product relationship between the native hormone and an active amino-terminal fragment. The results suggest, insofar as the activity detected in these membranes reflects the biological response of the hormone in vivo, that the native hormone is indeed biologically active at the receptor level directly without the requirement for cleavage into active fragments.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud C. D., Goldsmith R. S., Bordier P. J., Sizemore G. W. Influence of immunoheterogeneity of circulating parathyroid hormone on results of radioimmunoassays of serum in man. Am J Med. 1974 Jun;56(6):785–793. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90806-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurbach G. D., Keutmann H. T., Niall H. D., Tregear G. W., O'Riordan J. L., Marcus R., Marx S. J., Potts J. T., Jr Structure, synthesis, and mechanism of action of parathyroid hormone. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1972;28:353–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson R. C., Jr, Riggs B. L., Pickard B. M., Arnaud C. D. Immunoreactive forms of circulating parathyroid hormone in primary and ectopic hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):175–181. doi: 10.1172/JCI107739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Immunochemical heterogeneity of parathyroid hormone in plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jul;28(7):1037–1047. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-7-1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canterbury J. M., Bricker L. A., Levey G. S., Kozlovskis P. L., Ruiz E., Zull J. E., Reiss E. Metabolism of bovine parathyroid hormone. Immunological and biological characteristics of fragments generated by liver perfusion. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1245–1253. doi: 10.1172/JCI108043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canterbury J. M., Levey G. S., Reiss E. Activation of renal cortical adenylate cyclase by circulating immunoreactive parathyroid hormone fragments. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):524–527. doi: 10.1172/JCI107211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canterbury J. M., Reiss E. Multiple immunoreactive molecular forms of parathyroid hormone in human serum. 1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1393–1398. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catherwood B., Singer F. R. Generation of a carboxyl-terminal fragment of bovine parathyroid hormone by canine renal plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):469–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90955-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Renal adenyl cyclase: anatomically separate sites for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin. Science. 1968 Feb 2;159(3814):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3814.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Bella F. P., Dousa T. P., Miller S. S., Arnaud C. D. Parathyroid hormone receptors of renal cortex: specific binding of biologically active, 125I-labeled hormone and relationship to adenylate cyclase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):723–726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Orimo H., Ohata M., Yoshikawa M. Enzymatic inactivation of parathyroid hormone by rat kidney homogenate. Endocrinology. 1970 Jan;86(1):42–49. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-1-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith R. S., Furszyfer J., Johnson W. J., Fournier A. E., Sizemore G. W., Arnaud C. D. Etiology of hyperparathyroidism and bone disease during chronic hemodialysis. 3. Evaluation of parathyroid suppressibility. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):173–180. doi: 10.1172/JCI107161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goltzman D., Goltzmann D., Peytremann A., Callahan E., Tregear G. W., Potts J. T., Jr Analysis of the requirements for parathyroid hormone action in renal membranes with the use of inhibiting analogues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3199–3203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Powell D., Murray T. M., Mayer G. P., Potts J. T., Jr Parathyroid hormone: secretion and metabolism in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2986–2991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Habener J. F., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Proparathyroid hormone: identification of a biosynthetic precursor to parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):643–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Aurbach G. D., Dawson B. F., Niall H. D., Deftos L. J., Potts J. T., Jr Isolation and characterization of the bovine parathyroid isohormones. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2779–2787. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Barling P. M., Hendy G. N., Segre G. V., Niall H. D., Aurbach G. D., Potts J. T., Jr, O'Riordan J. L. Isolation of human parathyroid hormone. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1646–1652. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R., Aurbach G. D. Bioassay of parathyroid hormone in vitro with a stable preparation of adenyl cyclase from rat kidney. Endocrinology. 1969 Nov;85(5):801–810. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-5-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. J., Melick R. A., de Luise M. Metabolism of parathyroid hormone. Degradation of 125I-labelled hormone by a kidney enzyme. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(4):509–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1110509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx S. J., Fedak S. A., Aurbach G. D. Preparation and characterization of a hormone-responsive renal plasma membrane fraction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6913–6918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. T., Jr, Tregear G. W., Keutmann H. T., Niall H. D., Sauer R., Deftos L. J., Dawson B. F., Hogan M. L., Aurbach G. D. Synthesis of a biologically active N-terminal tetratriacontapeptide of parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):63–67. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segre G. V., Habener J. F., Powell D., Tregear G. W., Potts J. T. Parathyroid Hormone in Human Plasma: IMMUNOCHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION AND BIOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3163–3172. doi: 10.1172/JCI107143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segre G. V., Niall H. D., Habener J. F., Potts J. T., Jr Metabolism of parathyroid hormone: physiologic and clinical significance. Am J Med. 1974 Jun;56(6):774–784. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90805-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman R., Yalow R. S. Heterogeneity of parathyroid hormone. Clinical and physiologic implications. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1958–1971. doi: 10.1172/JCI107380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe H. S., Martin T. J., Eisman J. A., Pilczyk R. Binding of parathyroid hormone to bovine kidney-cortex plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):913–921. doi: 10.1042/bj1340913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear G. W., Van Rietschoten J., Greene E., Keutmann H. T., Niall H. D., Reit B., Parsons J. A., Potts J. T., Jr Bovine parathyroid hormone: minimum chain length of synthetic peptide required for biological activity. Endocrinology. 1973 Dec;93(6):1349–1353. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-6-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear G. W., van Rietschoten J., Greene E., Niall H. D., Keutmann H. T., Parsons J. A., O'Riordan J. L., Potts J. T., Jr Solid-phase synthesis of the biologically active N-terminal 1 - 34 peptide of human parathyroid hormone. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Apr;355(4):415–421. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhead J. S., O'Riordan J. L., Keutmann H. T., Stoltz M. L., Dawson B. F., Niall H. D., Robinson C. J., Potts J. T., Jr Isolation and chemical properties of porcine parathyroid hormone. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2787–2792. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


