Abstract
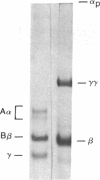
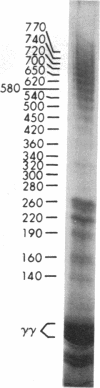
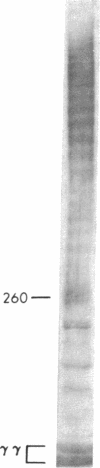
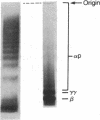
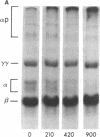
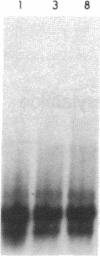
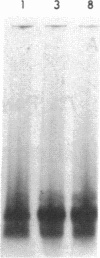
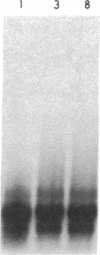
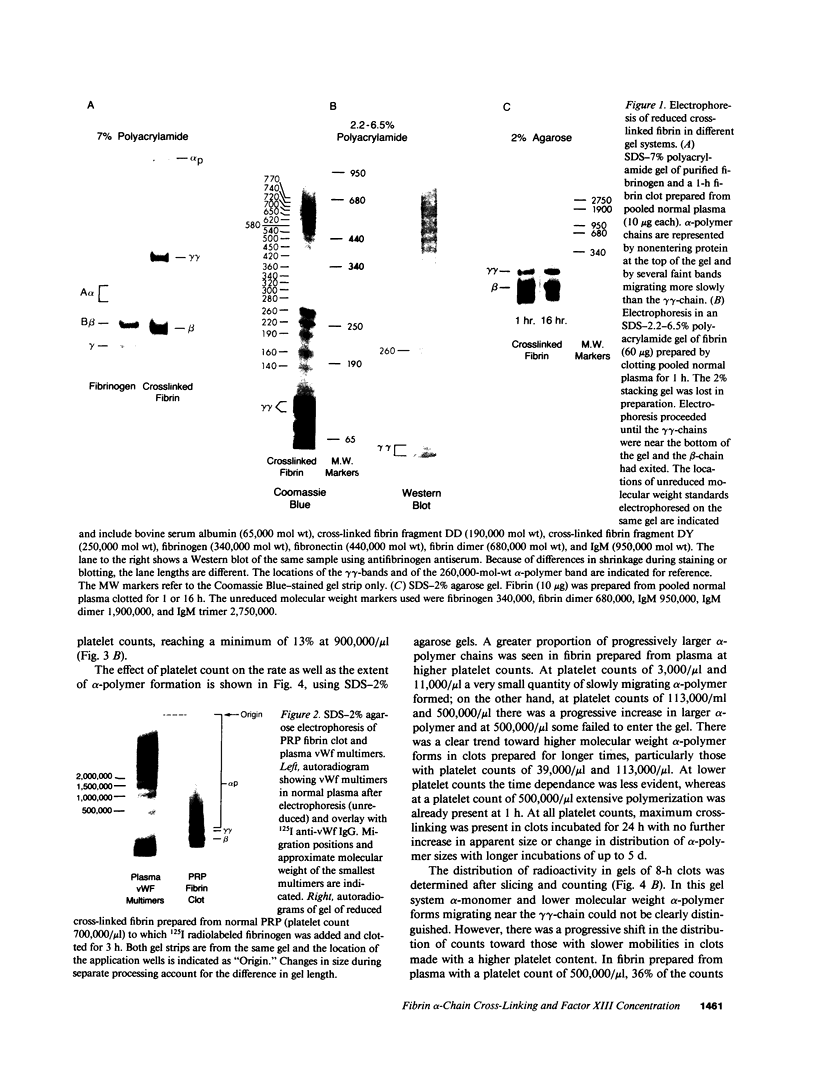
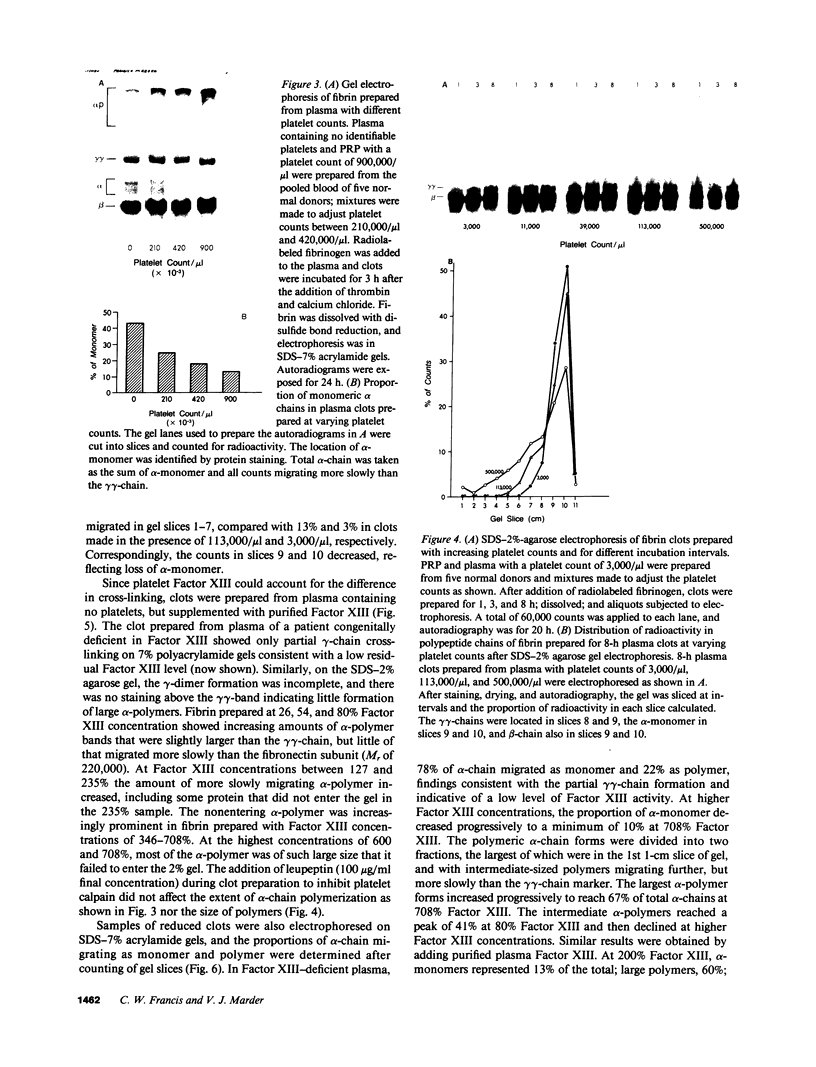
After fibrin polymerization, activated Factor XIII catalyzes the formation of intermolecular cross-links between gamma-chain pairs and also among two or more alpha-chains to form polymers. In this report we characterize the size and heterogeneity of alpha-chain polymers, establish the role of high concentrations of Factor XIII in determining the extent and rate of alpha-polymer formation, and also provide evidence that the Factor XIII required can be provided by platelets. Fibrin prepared from purified fibrinogen or platelet-deficient plasma contained a series of cross-linked alpha-chain polymers with Mr from 140,000 to 770,000 with a mean Mr difference of 32,000 consistent with a staggered, overlapping addition of monomers to the growing alpha-polymer chain. In plasma containing no platelets, alpha-polymer formation was incomplete with residual alpha-monomer remaining, but higher platelet counts facilitated more rapid cross-linking into larger polymers. Purified Factor XIII was equally effective as platelets in facilitating cross-linking. We conclude that cross-linked alpha-polymer chains are heterogeneous in size reaching a molecular weight of several million and that high concentrations of Factor XIII as provided by platelets are required for maximum cross-linking.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULUK K. Nieznane działanie krwinek płytkowych. Pol Tyg Lek (Wars) 1955 Feb 7;10(6):191–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball A. P., McKee P. A. Fibrin formation and dissolution in women receiving oral contraceptive drugs. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Apr;89(4):751–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn H. Comparative studies on the fibrin-stabilizing factors from human plasma, platelets and placentas. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:256–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. - cross-linking sites in human and bovine fibrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. I., Lewis M. S., Folk J. E. Relationships of the catalytic properties of human plasma and platelet transglutaminases (activated blood coagulation factor XIII) to their subunit structures. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):940–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connaghan D. G., Francis C. W., Lane D. A., Marder V. J. Specific identification of fibrin polymers, fibrinogen degradation products, and crosslinked fibrin degradation products in plasma and serum with a new sensitive technique. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):589–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Watt K. W., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence studies on the alpha chain of human fibrinogen. Exact location of cross-linking acceptor sites. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5405–5410. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Brown K. L., Credo R. B., Domanik R. A., Gray A., Stenberg P., Lorand L. Calcium-dependent unmasking of active center cysteine during activation of fibrin stabilizing factor. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3774–3780. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Cassman K. G., Cottrell B. A., Friezner S. J. Amino acid sequence studies on the alpha chain of human fibrinogen. Isolation and characterization of two linked alpha-chained cyanogen bromide fragments from fully cross-linked fibrin. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1715–1719. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:195–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Watt K. W., Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Riley M. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):464–468. doi: 10.1038/280464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jul 15;20(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Marder V. J., Martin S. E. Detection of circulating crosslinked fibrin derivatives by a heat extraction-SDS gradient gel electrophoretic technique. Blood. 1979 Dec;54(6):1282–1295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Marder V. J., Martin S. E. Plasmic degradation of crosslinked fibrin. I. Structural analysis of the particulate clot and identification of new macromolecular-soluble complexes. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):456–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Markham R. E., Jr, Marder V. J. Demonstration of in situ fibrin degradation in pathologic thrombi. Blood. 1984 May;63(5):1216–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretto L. J., Ferguson E. W., Steinman H. M., McKee P. A. Localization of the alpha-chain cross-link acceptor sites of human fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2184–2195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretto L. J., McKee P. A. Structure of alpha-polymer from in vitro and in vivo highly cross-linked human fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6614–6622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Whitaker A. N. Fibrin crosslinks and lysis rates. Thromb Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladner J. A., Nossal R. Effects of crosslinking on the rigidity and proteolytic susceptibility of human fibrin clots. Thromb Res. 1983 May 1;30(3):273–288. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hada M., Kaminski M., Bockenstedt P., McDonagh J. Covalent crosslinking of von Willebrand factor to fibrin. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Shainoff J. R. Factor VIII-related protein circulates in normal human plasma as high molecular weight multimers. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1056–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. The factor VIII complex: structure and function. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiesselbach T. H., Wagner R. H. Fibrin-stabilizing factor: a thrombin-labile platelet protein. Am J Physiol. 1966 Dec;211(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.6.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopaciuk S., Lovette K. M., McDonagh J., Chuang H. Y., McDonagh Subcellular distribution of fibrinogen and factor XIII in human blood platelets. Thromb Res. 1976 Apr;8(4):453–465. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90223-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Urayama T., De Kiewiet J. W., Nossel H. L. Diagnostic and genetic studies on fibrin-stabilizing factor with a new assay based on amine incorporation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1054–1064. doi: 10.1172/JCI106061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. I. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2111–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Soulen R. L., Atichartakarn V., Budzynski A. Z., Parulekar S., Kim J. R., Edward N., Zahavi J., Algazy K. M. Quantitative venographic assessment of deep vein thrombosis in the evaluation of streptokinase and heparin therapy. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 May;89(5):1018–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. E., Marder V. J., Francis C. W., Loftus L. S., Barlow G. H. Enzymatic degradation of the factor-VIII-von-Willebrand protein: a unique tryptic fragment with ristocetin cofactor activity. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh J., McDonagh R. P., Jr, Delâge J. M., Wagner R. H. Factor XIII in human plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):940–946. doi: 10.1172/JCI106053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh R. P., Jr, McDonagh J., Duckert F. The influence of fibrin crosslinking on the kinetics of urokinase-induced clot lysis. Br J Haematol. 1971 Sep;21(3):323–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Mattock P., Hill R. L. Subunit structure of human fibrinogen, soluble fibrin, and cross-linked insoluble fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):738–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Cross-linking of cold-insoluble globulin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6614–6621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Finlayson J. S., Peyton M. P., Nagai Y. Epsilon-(gamma glutamyl) lysine in fibrin: lack of crosslink formation in Factor 13 deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):770–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeghiero F., Barbui T., Dal Belin-Peruffo A., Dini E. Defective fibrin crosslinking in acute leukemia. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Dec 29;52(3):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Aoki N. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):290–297. doi: 10.1172/JCI109671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. Human Factor XIII from plasma and platelets. Molecular weights, subunit structures, proteolytic activation, and cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1395–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semeraro N., Collen D., Verstraete M. On the origin of the Aalpha chain heterogeneity of human fibrinogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):204–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Hermans J., McDonagh J., McDonagh R. P., Carr M. Effects of calcium ion and covalent crosslinking on formation and elasticity of fibrin cells. Thromb Res. 1975 Mar;6(3):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence studies on factor XIII and the peptide released during its activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):750–756. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]