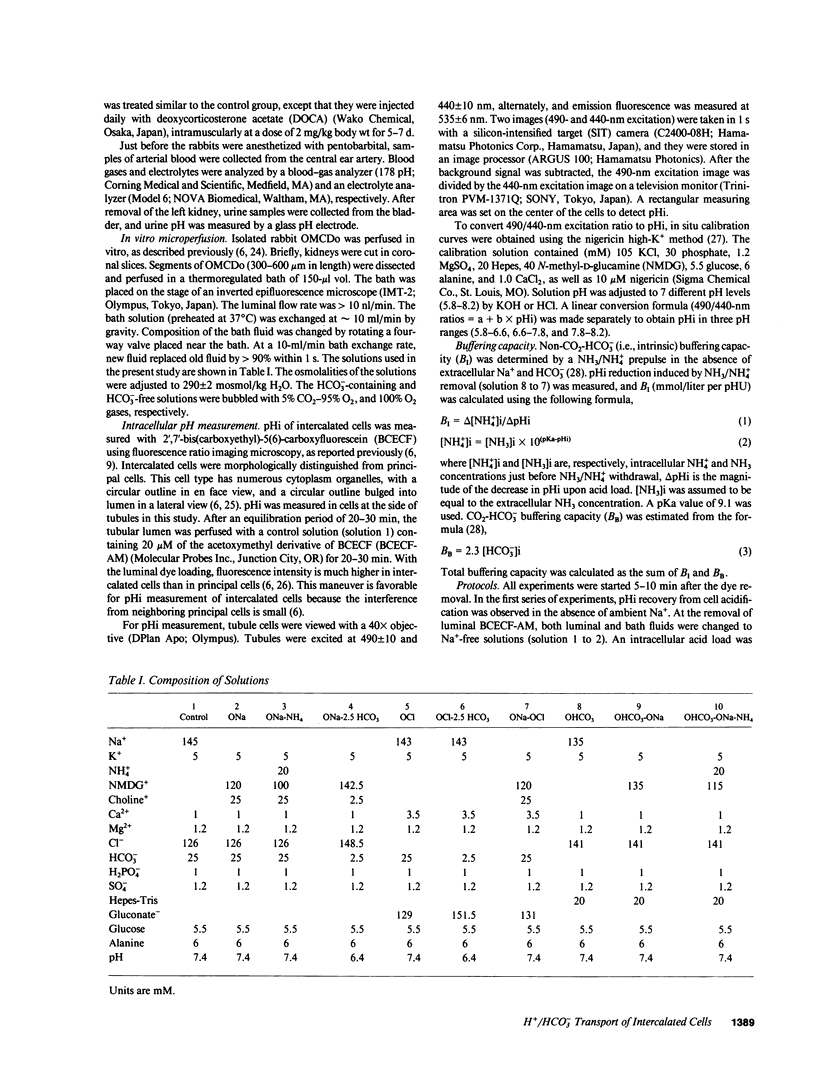
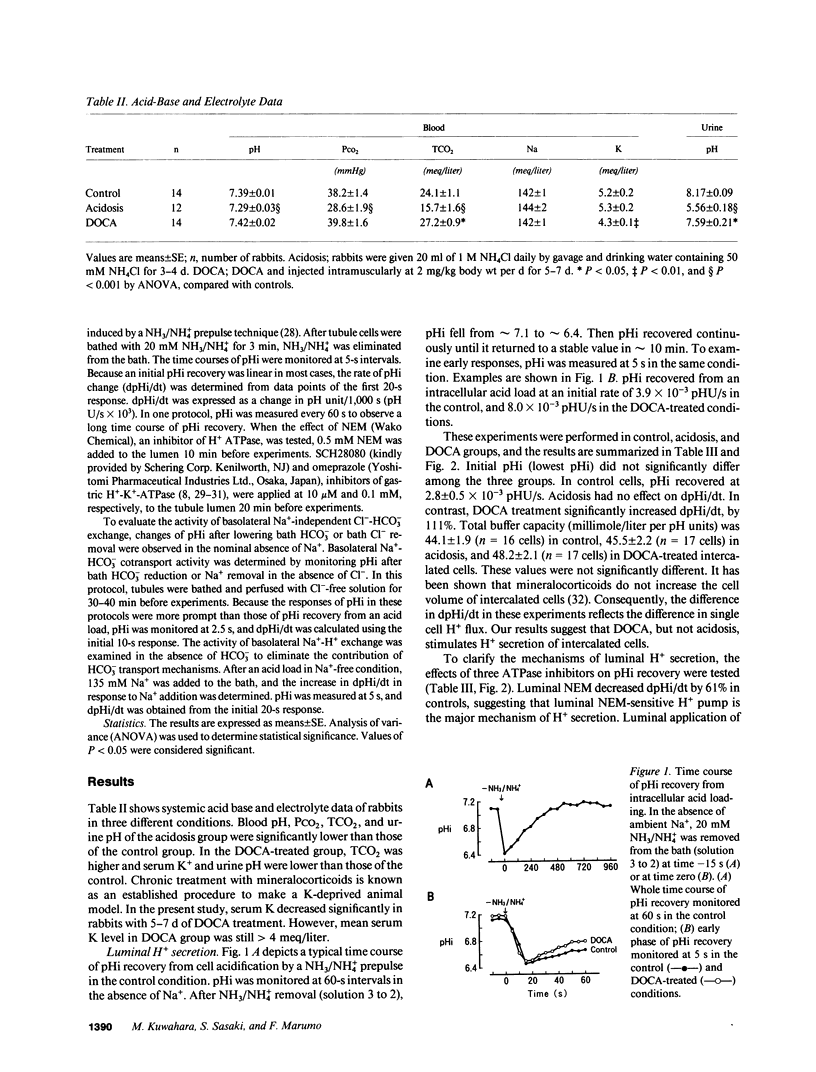
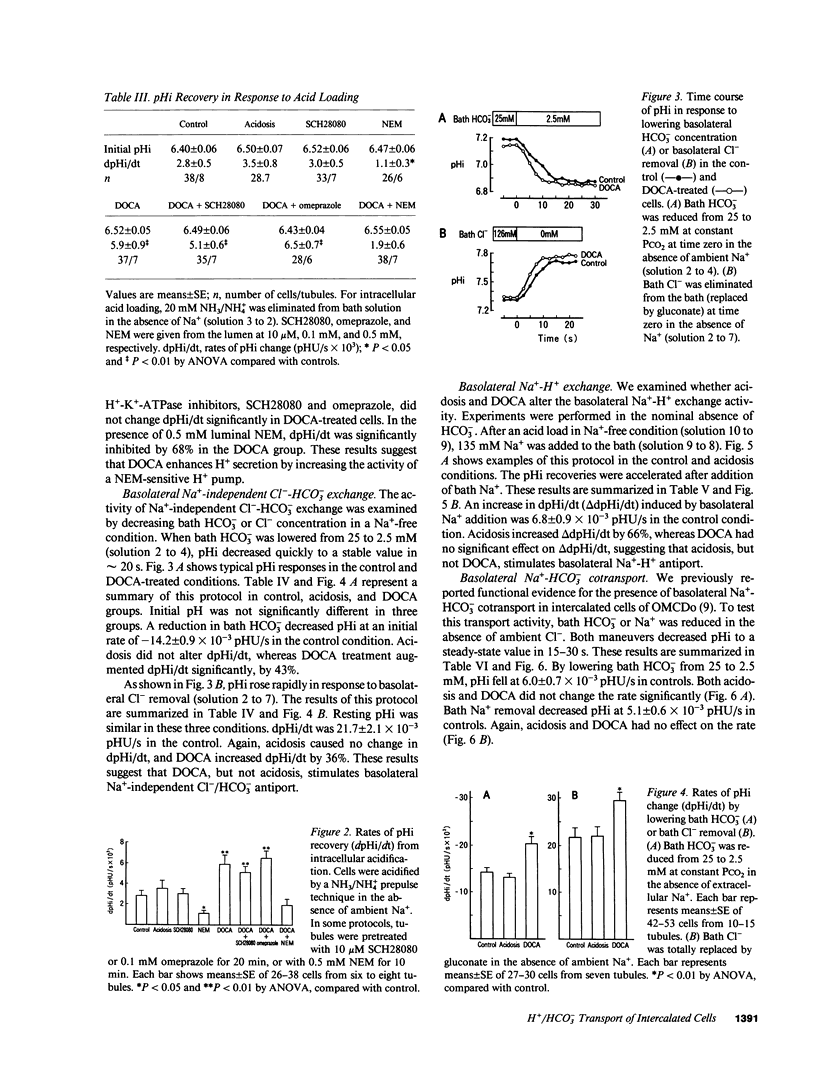
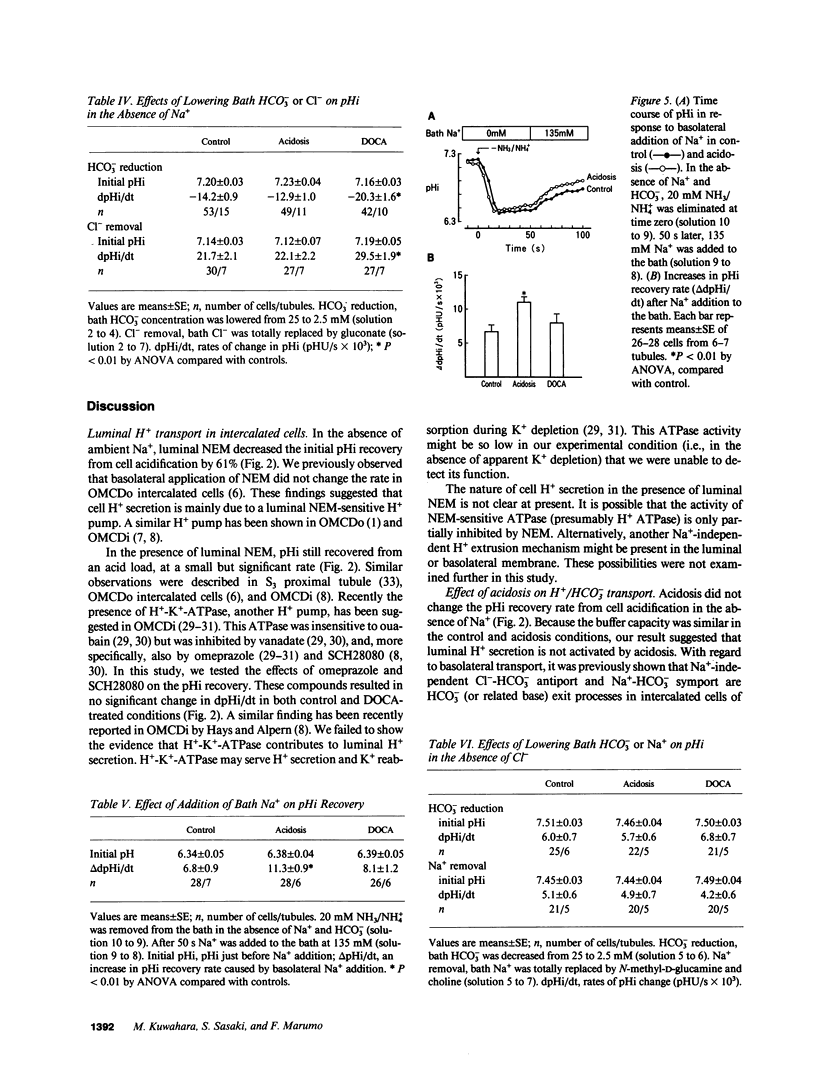
Abstract
The effects of acidosis and mineralocorticoids on cellular H+/HCO3- transport mechanisms were examined in intercalated cells of the outer stripe of outer medullary collecting duct (OMCDo) from rabbit. Intracellular pH (pHi) of intercalated cells was monitored by fluorescence ratio imaging using 2',7'-bis(carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein (BCECF). pHi recovered from an acid load at 2.8 +/- 0.5 x 10(-3) pHU/s in the absence of ambient Na+. This pHi recovery rate was similar in chronic acidosis induced by NH4Cl loading, but it was enhanced (+111%) by treatment with deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA). In a DOCA-treated group, luminal 10 microM SCH28080 and 0.1 mM omeprazole, H(+)-K(+)-ATPase inhibitors, did not change the pHi recovery rate, while luminal 0.5 mM N-ethylmaleimide blocked the rate by 68%. DOCA, but not acidosis, increased (approximately 40%) initial pHi response to bath HCO3- or Cl- reduction in Na(+)-free condition. After an acid load in the absence of Na+ and HCO3-, pHi response to basolateral Na+ addition was stimulated (+66%) by acidosis, but not by DOCA. Our results suggest that (a) mineralocorticoids stimulate H+/HCO3- transport mechanisms involved in transepithelial H+ secretion, i.e., a luminal NEM-sensitive H+ pump and basolateral Na(+)-independent Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange; and (b) acidosis enhances the activity of basolateral Na(+)-H+ exchange that may be responsible for pHi regulation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Na-H exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):29–52. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breyer M. D., Jacobson H. R. Regulation of rabbit medullary collecting duct cell pH by basolateral Na+/H+ and Cl-/base exchange. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1172/JCI114264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Hirsch S., Gluck S. Localization of a proton-pumping ATPase in rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2114–2126. doi: 10.1172/JCI113833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet J. R., Lopes A. G., Boron W. F. Basolateral Na-H exchange in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Dec;86(6):795–812. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.6.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. E., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Metabolic acidosis and parathyroidectomy increase Na+-H+ exchange in brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):F217–F222. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet A., Marsy S. Characterization of K-ATPase activity in distal nephron: stimulation by potassium depletion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F418–F423. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Narang N. Effects of aldosterone on NEM-sensitive ATPase in rabbit nephron segments. Kidney Int. 1988 Jul;34(1):13–17. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Narang N. Ouabain-insensitive K-adenosine triphosphatase in distal nephron segments of the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1172/JCI113436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Narang N. Stimulation of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive ATPase in the collecting duct segments of the rat nephron by metabolic acidosis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;63(10):1291–1296. doi: 10.1139/y85-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geibel J., Giebisch G., Boron W. F. Basolateral sodium-coupled acid-base transport mechanisms of the rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F790–F797. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. R., Alpern R. J. Apical and basolateral membrane H+ extrusion mechanisms in inner stripe of rabbit outer medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):F628–F635. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.4.F628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. R., Alpern R. J. Basolateral membrane Na(+)-independent Cl-/HCO3- exchange in the inner stripe of the rabbit outer medullary collecting tubule. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Feb;95(2):347–367. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Moe O., Tejedor A., Alpern R. J. Preincubation in acid medium increases Na/H antiporter activity in cultured renal proximal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4742–4745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khadouri C., Marsy S., Barlet-Bas C., Doucet A. Short-term effect of aldosterone on NEM-sensitive ATPase in rat collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 2):F177–F181. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.2.F177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Properties of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):F461–F469. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.6.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J., Cujdik T., Sacktor B. Na+-H+ exchange in isolated renal brush-border membrane vesicles in response to metabolic acidosis. Kinetic effects. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13224–13227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Pearce D., Lynch C., Xi X. P., Reudelhuber T. L., Pouysségur J., Rector F. C., Jr Expression of rat renal Na/H antiporter mRNA levels in response to respiratory and metabolic acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):747–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI115057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I. Apical Na+/H+ antiporter and glycolysis-dependent H+-ATPase regulate intracellular pH in the rabbit S3 proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):928–935. doi: 10.1172/JCI113184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz I. Basolateral membrane Na+/H+ antiport, Na+/base cotransport, and Na+-independent Cl-/base exchange in the rabbit S3 proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):616–622. doi: 10.1172/JCI113925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara M., Sasaki S., Marumo F. Cell pH regulation in rabbit outer medullary collecting duct cells: mechanisms of HCO3(-)-independent processes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F902–F909. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara M., Sasaki S., Marumo F. Cl-HCO3 exchange and Na-HCO3 symport in rabbit outer medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 2):F635–F642. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.5.F635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski M. E., Kurtzman N. A. Characterization of acidification in the cortical and medullary collecting tubule of the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2050–2059. doi: 10.1172/JCI111170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombard W. E., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Bicarbonate transport in cortical and outer medullary collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):F289–F296. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.3.F289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen K. M., Tisher C. C. Cellular response to acute respiratory acidosis in rat medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):F670–F679. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.6.F670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen K. M., Tisher C. C. Response of intercalated cells of rat outer medullary collecting duct to chronic metabolic acidosis. Lab Invest. 1984 Sep;51(3):268–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahnensmith R. L., Aronson P. S. The plasma membrane sodium-hydrogen exchanger and its role in physiological and pathophysiological processes. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):773–788. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Davidson K. K. Bicarbonate transport in collecting tubules from outer stripe of outer medulla of rabbit kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F816–F822. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mujais S. K. Effects of aldosterone on rat collecting tubule N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive adenosine triphosphatase. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Jan;109(1):34–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murer H., Hopfer U., Kinne R. Sodium/proton antiport in brush-border-membrane vesicles isolated from rat small intestine and kidney. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):597–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini S., Laski M. E., Kurtzman N. A. NEM-sensitive ATPase activity in rat nephron: effect of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F297–F304. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Al-Awqati Q. Carbon dioxide causes exocytosis of vesicles containing H+ pumps in isolated perfused proximal and collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1638–1644. doi: 10.1172/JCI111871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. K., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Mineralocorticoid modulation of rabbit medullary collecting duct acidification. A sodium-independent effect. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):77–83. doi: 10.1172/JCI110986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange K., Spring K. R. Cell membrane water permeability of rabbit cortical collecting duct. J Membr Biol. 1987;96(1):27–43. doi: 10.1007/BF01869332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. J., Ives H. E., Alpern R. J., Yee V. J., Warnock D. G., Rector F. C., Jr Increased Vmax for Na+/H+ antiporter activity in proximal tubule brush border vesicles from rabbits with metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F339–F343. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., O'Neil R. G., Pryor J. L., Boulpaep E. L. Modulation of cell membrane area in renal collecting tubules by corticosteroid hormones. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):439–445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Kurtz I. H+/base transport in principal cells characterized by confocal fluorescence imaging. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):C365–C373. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner I. D., Hamm L. L. Regulation of intracellular pH in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):274–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI114423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner I. D., Hamm L. L. Use of fluorescent dye BCECF to measure intracellular pH in cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F957–F964. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S. Active proton secretion and potassium absorption in the rabbit outer medullary collecting duct. Functional evidence for proton-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):361–365. doi: 10.1172/JCI114165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Silva P., Seifter J. L. Intracellular pH regulation and proton transport by rabbit renal medullary collecting duct cells. Role of plasma membrane proton adenosine triphosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):113–120. doi: 10.1172/JCI112264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


