Abstract
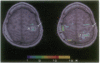
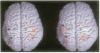
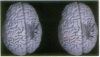
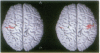
Functional magnetic resonance imaging was used to map the hand sensorimotor area of hemiparetic adolescents and young adults who had suffered unilateral brain damage in the perinatal period. Unlike normal subjects, who exhibit cortical activation primarily contralateral to voluntary finger movements, the hemiparetic patients' intact hemispheres were equally activated by contralateral and ipsilateral finger movements. Our findings are consistent with previous clinical observations and animal experiments which suggest that the immature brain is able to reorganize in response to focal injury.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaf A. A. The sensitive period: transfer of fixation after occlusion for strabismic amblyopia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1982 Jan;66(1):64–70. doi: 10.1136/bjo.66.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandettini P. A., Jesmanowicz A., Wong E. C., Hyde J. S. Processing strategies for time-course data sets in functional MRI of the human brain. Magn Reson Med. 1993 Aug;30(2):161–173. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910300204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandettini P. A., Wong E. C., Hinks R. S., Tikofsky R. S., Hyde J. S. Time course EPI of human brain function during task activation. Magn Reson Med. 1992 Jun;25(2):390–397. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910250220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belliveau J. W., Kennedy D. N., Jr, McKinstry R. C., Buchbinder B. R., Weisskoff R. M., Cohen M. S., Vevea J. M., Brady T. J., Rosen B. R. Functional mapping of the human visual cortex by magnetic resonance imaging. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):716–719. doi: 10.1126/science.1948051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y., Towle V. L., Levin D. N., Balter J. M. Functional mapping of human motor cortical activation with conventional MR imaging at 1.5 T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1993 Nov-Dec;3(6):869–875. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880030613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet F., DiPiero V., Wise R. J., Brooks D. J., Dolan R. J., Frackowiak R. S. The functional anatomy of motor recovery after stroke in humans: a study with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jan;29(1):63–71. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebatch J. G., Deiber M. P., Passingham R. E., Friston K. J., Frackowiak R. S. Regional cerebral blood flow during voluntary arm and hand movements in human subjects. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jun;65(6):1392–1401. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.65.6.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Burton H., Raichle M. E. Mapping human somatosensory cortex with positron emission tomography. J Neurosurg. 1987 Jul;67(1):34–43. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.1.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frahm J., Bruhn H., Merboldt K. D., Hänicke W. Dynamic MR imaging of human brain oxygenation during rest and photic stimulation. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1992 Sep-Oct;2(5):501–505. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880020505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafton S. T., Woods R. P., Mazziotta J. C., Phelps M. E. Somatotopic mapping of the primary motor cortex in humans: activation studies with cerebral blood flow and positron emission tomography. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Sep;66(3):735–743. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.3.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. RECEPTIVE FIELDS OF CELLS IN STRIATE CORTEX OF VERY YOUNG, VISUALLY INEXPERIENCED KITTENS. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Nov;26:994–1002. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.6.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks S. P., D'Amato C. J. Motor-sensory and visual behavior after hemispherectomy in newborn and mature rats. Exp Neurol. 1970 Dec;29(3):416–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttenlocher P. R., Bonnier C. Effects of changes in the periphery on development of the corticospinal motor system in the rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991 Jun 21;60(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(91)90054-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttenlocher P. R., Raichelson R. M. Effects of neonatal hemispherectomy on location and number of corticospinal neurons in the rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1989 May 1;47(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(89)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. G., Ashe J., Hendrich K., Ellermann J. M., Merkle H., Uğurbil K., Georgopoulos A. P. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of motor cortex: hemispheric asymmetry and handedness. Science. 1993 Jul 30;261(5121):615–617. doi: 10.1126/science.8342027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong K. K., Belliveau J. W., Chesler D. A., Goldberg I. E., Weisskoff R. M., Poncelet B. P., Kennedy D. N., Hoppel B. E., Cohen M. S., Turner R. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity during primary sensory stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5675–5679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. N., Hu X. P., Tan K. K., Galhotra S., Pelizzari C. A., Chen G. T., Beck R. N., Chen C. T., Cooper M. D., Mullan J. F. The brain: integrated three-dimensional display of MR and PET images. Radiology. 1989 Sep;172(3):783–789. doi: 10.1148/radiology.172.3.2788893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. C., Huttenlocher P., Banich M. T., Duda E. Factors affecting cognitive functioning of hemiplegic children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1987 Feb;29(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1987.tb02104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewine J. D., Astur R. S., Davis L. E., Knight J. E., Maclin E. L., Orrison W. W., Jr Cortical organization in adulthood is modified by neonatal infarct: a case study. Radiology. 1994 Jan;190(1):93–96. doi: 10.1148/radiology.190.1.8259435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Kaas J. H., Wall J. T., Sur M., Nelson R. J., Felleman D. J. Progression of change following median nerve section in the cortical representation of the hand in areas 3b and 1 in adult owl and squirrel monkeys. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):639–665. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Lee T. M., Nayak A. S., Glynn P. Oxygenation-sensitive contrast in magnetic resonance image of rodent brain at high magnetic fields. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Apr;14(1):68–78. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Tank D. W., Menon R., Ellermann J. M., Kim S. G., Merkle H., Ugurbil K. Intrinsic signal changes accompanying sensory stimulation: functional brain mapping with magnetic resonance imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5951–5955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLSTEIN M. A., HOOD P. N. Infantile spastic hemiplegia. I. Incidence. Pediatrics. 1954 Nov;14(5):436–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons T. P., Garraghty P. E., Ommaya A. K., Kaas J. H., Taub E., Mishkin M. Massive cortical reorganization after sensory deafferentation in adult macaques. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1857–1860. doi: 10.1126/science.1843843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran V. S. Behavioral and magnetoencephalographic correlates of plasticity in the adult human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10413–10420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Larsen B., Lassen N. A., Skinhøj E. Supplementary motor area and other cortical areas in organization of voluntary movements in man. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Jan;43(1):118–136. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Meyer E., Shibasaki T., Yamamoto Y. L., Thompson C. J. Regional cerebral blood flow changes in cortex and basal ganglia during voluntary movements in normal human volunteers. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Aug;48(2):467–480. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.2.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Le Bihan D., Moonen C. T., Despres D., Frank J. Echo-planar time course MRI of cat brain oxygenation changes. Magn Reson Med. 1991 Nov;22(1):159–166. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910220117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiller C., Chollet F., Friston K. J., Wise R. J., Frackowiak R. S. Functional reorganization of the brain in recovery from striatocapsular infarction in man. Ann Neurol. 1992 May;31(5):463–472. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. J. Cerebral hemispherectomy for infantile hemiplegia. A report of 50 cases. Brain. 1970;93(1):147–180. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods B. T., Teuber H. L. Changing patterns of childhood aphasia. Ann Neurol. 1978 Mar;3(3):273–280. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods B. T., Teuber H. L. Mirror movements after childhood hemiparesis. Neurology. 1978 Nov;28(11):1152–1157. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.11.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolsey C. N., Erickson T. C., Gilson W. E. Localization in somatic sensory and motor areas of human cerebral cortex as determined by direct recording of evoked potentials and electrical stimulation. J Neurosurg. 1979 Oct;51(4):476–506. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.4.0476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]