Abstract
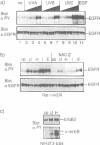
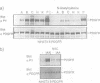
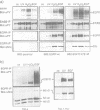
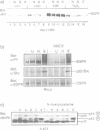
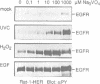
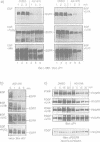
Several non-physiologic agents such as radiation, oxidants and alkylating agents induce ligand-independent activation of numerous receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and of protein tyrosine kinases at the inner side of the plasma membrane (e.g. Dévary et al., 1992; Sachsenmaier et al., 1994; Schieven et al., 1994; Coffer et al., 1995). Here we show additional evidence for the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and we show activation of v-ErbB, ErbB2 and platelet-derived growth factor receptor. As a common principle of action the inducing agents such as UVC, UVB, UVA, hydrogen peroxide and iodoacetamide inhibit receptor tyrosine dephosphorylation in a thiol-sensitive and, with the exception of the SH-alkylating agent, reversible manner. EGFR dephosphorylation can also be modulated by these non-physiologic agents in isolated plasma membranes in the presence of Triton X-100. Further, substrate (EGFR) and phosphatase have been separated: a membrane preparation of cells that have been treated with epidermal growth factor (EGF) and whose dephosphorylating enzymes have been permanently destroyed by iodoacetamide can be mixed with a membrane preparation from untreated cells which re-establishes EGFR dephosphorylation. This dephosphorylation can be modulated in vitro by UV and thiol agents. We conclude that RTKs exhibit significant spontaneous protein kinase activity; several adverse agents target (an) essential SH-group(s) carried by (a) membrane-bound protein tyrosine phosphatase(s).
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Baumann I., Stein B., Delius H., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate induction of the human collagenase gene is mediated by an inducible enhancer element located in the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2256–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Suhan J. P., McCormick F., Feramisco J. R. Localization of phospholipase A2 in normal and ras-transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1649–1658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauskin A. R., Alkalay I., Ben-Neriah Y. Redox regulation of a protein tyrosine kinase in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90114-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beerli R. R., Graus-Porta D., Woods-Cook K., Chen X., Yarden Y., Hynes N. E. Neu differentiation factor activation of ErbB-3 and ErbB-4 is cell specific and displays a differential requirement for ErbB-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6496–6505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. M., Hausdorff S. F., O'Reilly A. M., Freeman R. M., Neel B. G. Multiple requirements for SHPTP2 in epidermal growth factor-mediated cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;16(3):1189–1202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.3.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumell J. H., Burkhardt A. L., Bolen J. B., Grinstein S. Endogenous reactive oxygen intermediates activate tyrosine kinases in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 19;271(3):1455–1461. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.3.1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhmer F. D., Böhmer A., Obermeier A., Ullrich A. Use of selective tyrosine kinase blockers to monitor growth factor receptor dephosphorylation in intact cells. Anal Biochem. 1995 Jul 1;228(2):267–273. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor M. J., Wheeler L. A. Depletion of cutaneous glutathione by ultraviolet radiation. Photochem Photobiol. 1987 Aug;46(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1987.tb04762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. M., Wilkinson A. J., Baron M., Pastore A., Tappin M. J., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. The solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):339–341. doi: 10.1038/327339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daub H., Weiss F. U., Wallasch C., Ullrich A. Role of transactivation of the EGF receptor in signalling by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 1996 Feb 8;379(6565):557–560. doi: 10.1038/379557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Romero G., Zhang Z. Y., Dixon J. E., Larner A. C. In vitro activation of the transcription factor ISGF3 by interferon alpha involves a membrane-associated tyrosine phosphatase and tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6593–6599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D. M., Sap J., Silvennoinen O., Schlessinger J., Weiss A. The catalytic activity of the CD45 membrane-proximal phosphatase domain is required for TCR signaling and regulation. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):4002–4010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Smeal T., Karin M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Rosette C., DiDonato J. A., Karin M. NF-kappa B activation by ultraviolet light not dependent on a nuclear signal. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1442–1445. doi: 10.1126/science.8367725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr Mammalian genes induced by radiation; activation of genes associated with growth control. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:507–526. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs J., Huflejt M. E., Rothfuss L. M., Wilson D. S., Carcamo G., Packer L. Impairment of enzymic and nonenzymic antioxidants in skin by UVB irradiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Dec;93(6):769–773. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12284412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamett D. C., Greene T., Wagreich A. R., Kim H. H., Koland J. G., Cerione R. A. Heregulin-stimulated signaling in rat pheochromocytoma cells. Evidence for ErbB3 interactions with Neu/ErbB2 and p85. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):19022–19027. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.19022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamou S., Shimizu N. Hydrogen peroxide preferentially enhances the tyrosine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 3;357(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graus-Porta D., Beerli R. R., Hynes N. E. Single-chain antibody-mediated intracellular retention of ErbB-2 impairs Neu differentiation factor and epidermal growth factor signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1182–1191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Evidence for protein-tyrosine-phosphatase catalysis proceeding via a cysteine-phosphate intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17026–17030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Donoghue D. J. Structure and function of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and related proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Bushkin I., Dror R., Zick Y. The insulinomimetic agents H2O2 and vanadate stimulate protein tyrosine phosphorylation in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2896–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Rutter W. J., Zick Y. The insulinomimetic agents H2O2 and vanadate stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation of potential target proteins for the insulin receptor kinase in intact cells. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):631–635. doi: 10.1042/bj2880631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ernlund A., Rorsman C., Rönnstrand L. Dimerization of B-type platelet-derived growth factor receptors occurs after ligand binding and is closely associated with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8905–8912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Ponta H., Rahmsdorf H. J. DNA damage-induced gene expression: signal transduction and relation to growth factor signaling. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;119:187–223. doi: 10.1007/3540551921_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional responses to DNA-damaging agents. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. R., Hyman R., Sefton B. M. Differential effects of expression of the CD45 tyrosine protein phosphatase on the tyrosine phosphorylation of the lck, fyn, and c-src tyrosine protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1651–1656. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Larner A. C., Finbloom D. S. In vitro activation of a transcription factor by gamma interferon requires a membrane-associated tyrosine kinase and is mimicked by vanadate. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3984–3989. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Seeburg P. H., Gray A., Ullrich A., Scrace G. The c-sis gene encodes a precursor of the B chain of platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):921–928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Platelet-derived growth factor: identification of constituent polypeptide chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):66–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91941-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN U. V. Kinetics of uric acid transport in human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Nov 11;53:557–569. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90215-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Gazit A. Tyrosine kinase inhibition: an approach to drug development. Science. 1995 Mar 24;267(5205):1782–1788. doi: 10.1126/science.7892601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Nishimura R., Kashishian A., Batzer A. G., Kim W. J., Cooper J. A., Schlessinger J. A new function for a phosphotyrosine phosphatase: linking GRB2-Sos to a receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):509–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoglia S., Gray A., Dull T. J., Munemitsu S., Kun H. J., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Epidermal growth factor receptor cytoplasmic domain mutations trigger ligand-independent transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3048–3055. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Saltiel A. R. Expression of catalytically inactive Syp phosphatase in 3T3 cells blocks stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by insulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21239–21243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. C., Hale P., Pentland A. P. Ultraviolet B injury increases prostaglandin synthesis through a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. Evidence for UVB-induced epidermal growth factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3529–3533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Matozaki T., Horita K., Fujioka Y., Kasuga M. Role of SH-PTP2, a protein-tyrosine phosphatase with Src homology 2 domains, in insulin-stimulated Ras activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6674–6682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins L. A., Larsen I., Perrimon N. corkscrew encodes a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase that functions to transduce the terminal signal from the receptor tyrosine kinase torso. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90098-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N. The torso receptor protein-tyrosine kinase signaling pathway: an endless story. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90412-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quian X. L., Decker S. J., Greene M. I. p185c-neu and epidermal growth factor receptor associate into a structure composed of activated kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1330–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radler-Pohl A., Sachsenmaier C., Gebel S., Auer H. P., Bruder J. T., Rapp U., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced activation of AP-1 involves obligatory extranuclear steps including Raf-1 kinase. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1005–1012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppersberg J. P., Stocker M., Pongs O., Heinemann S. H., Frank R., Koenen M. Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):711–714. doi: 10.1038/352711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachsenmaier C., Radler-Pohl A., Zinck R., Nordheim A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J. Involvement of growth factor receptors in the mammalian UVC response. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk H., Klein M., Erdbrügger W., Dröge W., Schulze-Osthoff K. Distinct effects of thioredoxin and antioxidants on the activation of transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1672–1676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieven G. L., Mittler R. S., Nadler S. G., Kirihara J. M., Bolen J. B., Kanner S. B., Ledbetter J. A. ZAP-70 tyrosine kinase, CD45, and T cell receptor involvement in UV- and H2O2-induced T cell signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20718–20726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Herrlich P. UV-induced extracellular factor from human fibroblasts communicates the UV response to nonirradiated cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):861–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah G., Ghosh R., Amstad P. A., Cerutti P. A. Mechanism of induction of c-fos by ultraviolet B (290-320 nm) in mouse JB6 epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):38–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo Y., Witt E., Packer L. Antioxidant defense mechanisms in murine epidermis and dermis and their responses to ultraviolet light. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Mar;100(3):260–265. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak-Kroizman T., Lemmon M. A., Dikic I., Ladbury J. E., Pinchasi D., Huang J., Jaye M., Crumley G., Schlessinger J., Lax I. Heparin-induced oligomerization of FGF molecules is responsible for FGF receptor dimerization, activation, and cell proliferation. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1015–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Rahmsdorf H. J., Steffen A., Litfin M., Herrlich P. UV-induced DNA damage is an intermediate step in UV-induced expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, collagenase, c-fos, and metallothionein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5169–5181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kamps M. P. EGF-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of p185neu: a potential model for receptor interactions. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):995–1001. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. G., Chiu D. T., Errasfa M., Wang J. M., Qi J. S., Stern A. Effects of H2O2 on protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in HER14 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 1994 Mar;16(3):399–403. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vile G. F., Tanew-Ilitschew A., Tyrrell R. M. Activation of NF-kappa B in human skin fibroblasts by the oxidative stress generated by UVA radiation. Photochem Photobiol. 1995 Sep;62(3):463–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1995.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Qian X. L., Greene M. I. Intermolecular association of the p185neu protein and EGF receptor modulates EGF receptor function. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallasch C., Weiss F. U., Niederfellner G., Jallal B., Issing W., Ullrich A. Heregulin-dependent regulation of HER2/neu oncogenic signaling by heterodimerization with HER3. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 1;14(17):4267–4275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmuth I., Harth Y., Matsui M. S., Wang N., DeLeo V. A. Ultraviolet radiation induces phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 15;54(2):374–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasilenko W. J., Payne D. M., Fitzgerald D. L., Weber M. J. Phosphorylation and activation of epidermal growth factor receptors in cells transformed by the src oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):309–321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. D., Reuter C. W., Weber M. J. An incomplete program of cellular tyrosine phosphorylations induced by kinase-defective epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):12085–12093. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.12085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. M., Wang Y., Pallen C. J. Cell transformation and activation of pp60c-src by overexpression of a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):336–339. doi: 10.1038/359336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam H., Wilhelm D., Herr I., Steffen A., Herrlich P., Angel P. ATF-2 is preferentially activated by stress-activated protein kinases to mediate c-jun induction in response to genotoxic agents. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1798–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]