Abstract
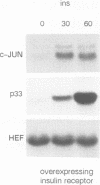
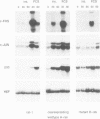
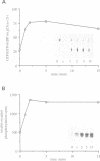
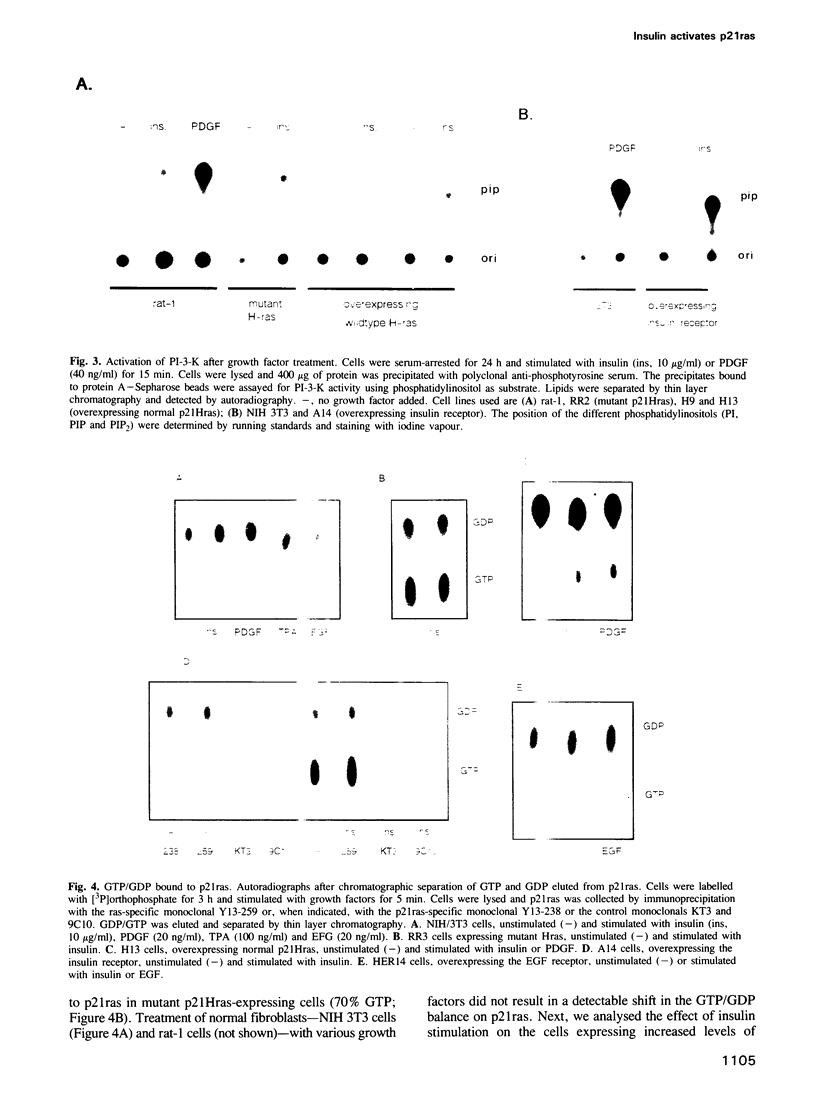
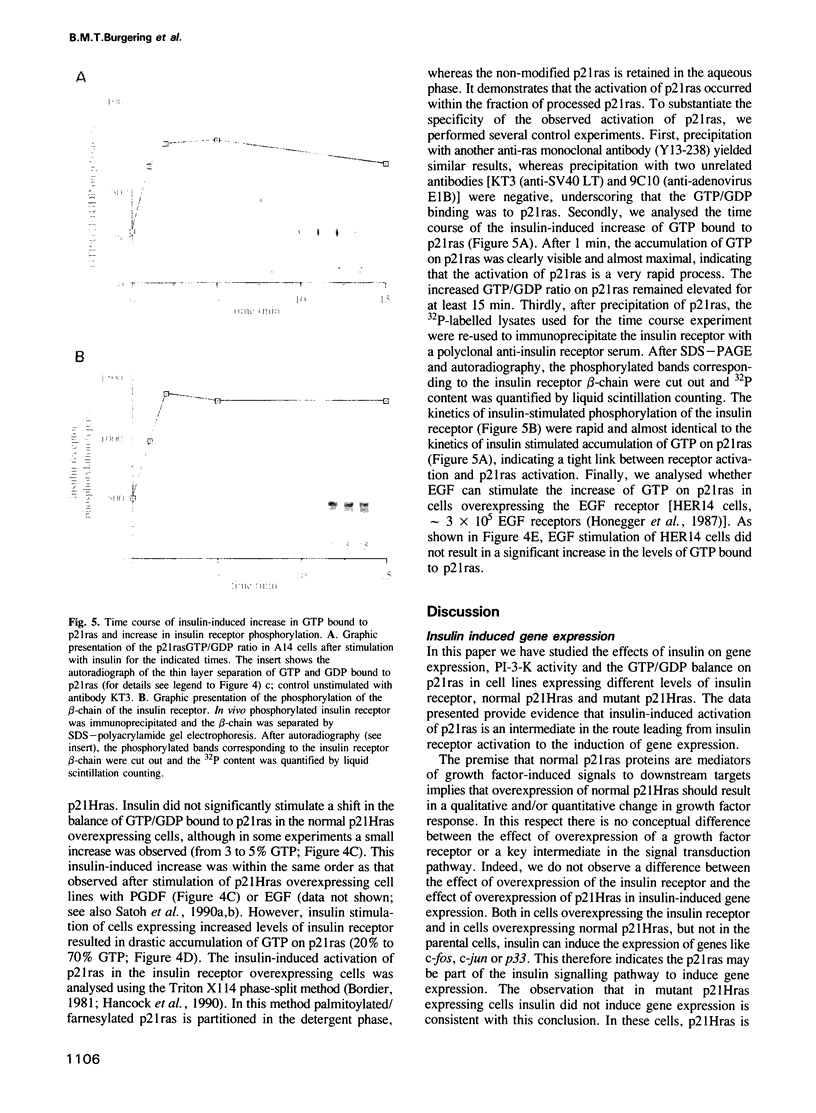
In fibroblasts, insulin is a weak mitogen and does not induce expression of c-fos, c-jun or p33. However, increasing the expression levels of either normal p21Hras or the insulin receptor, but not mutant p21Hras, enables insulin to induce the expression of these genes. In cells expressing elevated levels of insulin receptor, this process involves a rapid increase in p21rasGTP levels (from 20% to 70% GTP as a percentage of total guanine nucleotides). No increase in p21rasGTP levels was observed after PDGF and EGF stimulation of cells expressing high levels of the cognate receptor, stressing the specificity of the insulin-induced increase. We conclude that in fibroblasts, p21ras is an intermediate of the insulin signal transduction pathway involved in the regulation of gene expression and mitogenicity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballester R., Marchuk D., Boguski M., Saulino A., Letcher R., Wigler M., Collins F. The NF1 locus encodes a protein functionally related to mammalian GAP and yeast IRA proteins. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Snijders A. J., Maassen J. A., van der Eb A. J., Bos J. L. Possible involvement of normal p21 H-ras in the insulin/insulinlike growth factor 1 signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4312–4322. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai H., Szeberényi J., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on mitogenic signal transduction in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5314–5323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Riehl R., Wu L., Weinberg R. A. Identification of a nucleotide exchange-promoting activity for p21ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5998–6002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., de Gunzburg J., Riehl R., Weinberg R. A. p21ras-induced responsiveness of phosphatidylinositol turnover to bradykinin is a receptor number effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Schaber M. D., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Identification of guanine nucleotides bound to ras-encoded proteins in growing yeast cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10426–10429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagag N., Halegoua S., Viola M. Inhibition of growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells by microinjection of antibody to ras p21. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):680–682. doi: 10.1038/319680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino M., Kawakita M., Hattori S. Characterization of a factor that stimulates hydrolysis of GTP bound to ras gene product p21 (GTPase-activating protein) and correlation of its activity to cell density. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4169–4173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Krans H. M., Möller W. The effect of insulin, serum and dexamethasone on mRNA levels for the insulin receptor in the human lymphoblastoic cell line IM-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 19;930(1):72–78. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Viskochil D., Bollag G., McCabe P. C., Crosier W. J., Haubruck H., Conroy L., Clark R., O'Connell P., Cawthon R. M. The GAP-related domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product interacts with ras p21. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina J. L., Hamlin J., Larner J. Effects of insulin alone on the accumulation of a specific mRNA in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16418–16423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. D., Price B., Lloyd A. C., Self A. J., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Scrape-loading of Swiss 3T3 cells with ras protein rapidly activates protein kinase C in the absence of phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ko M., Ogura A., Liu D. G., Amano T., Takano T., Ikawa Y. Sarcoma viruses carrying ras oncogenes induce differentiation-associated properties in a neuronal cell line. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):73–75. doi: 10.1038/318073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A. Purification of the catalytically active phosphorylated form of insulin receptor kinase by affinity chromatography with O-phosphotyrosyl-binding antibodies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Oct;242(1):176–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Endo M., Nakafuku M., Akiyama T., Yamamoto T., Kaziro Y. Accumulation of p21ras.GTP in response to stimulation with epidermal growth factor and oncogene products with tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7926–7929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Endo M., Nakafuku M., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates formation of active p21ras.GTP complex in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5993–5997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Endo M., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Analysis of guanine nucleotide bound to ras protein in PC12 cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Watson T., Kung H. F., Curran T. Microinjection of transforming ras protein induces c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):523–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Blackshear P. J. Insulin and growth factor effects on c-fos expression in normal and protein kinase C-deficient 3T3-L1 fibroblasts and adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9453–9457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M., Kung H. F., Kamata T. A novel membrane factor stimulates guanine nucleotide exchange reaction of ras proteins. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80019-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D., Roberts T., Cantley L. Evidence for two distinct phosphatidylinositol kinases in fibroblasts. Implications for cellular regulation. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):165–174. doi: 10.1042/bj2470165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. A cytosolic protein catalyzes the release of GDP from p21ras. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2181667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., O'Connell P., Viskochil D., Cawthon R., Robertson M., Culver M., Dunn D., Stevens J., Gesteland R., White R. The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene encodes a protein related to GAP. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Tsai M. H., Stacey D. W. Cellular ras activity and phospholipid metabolism. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]