Abstract
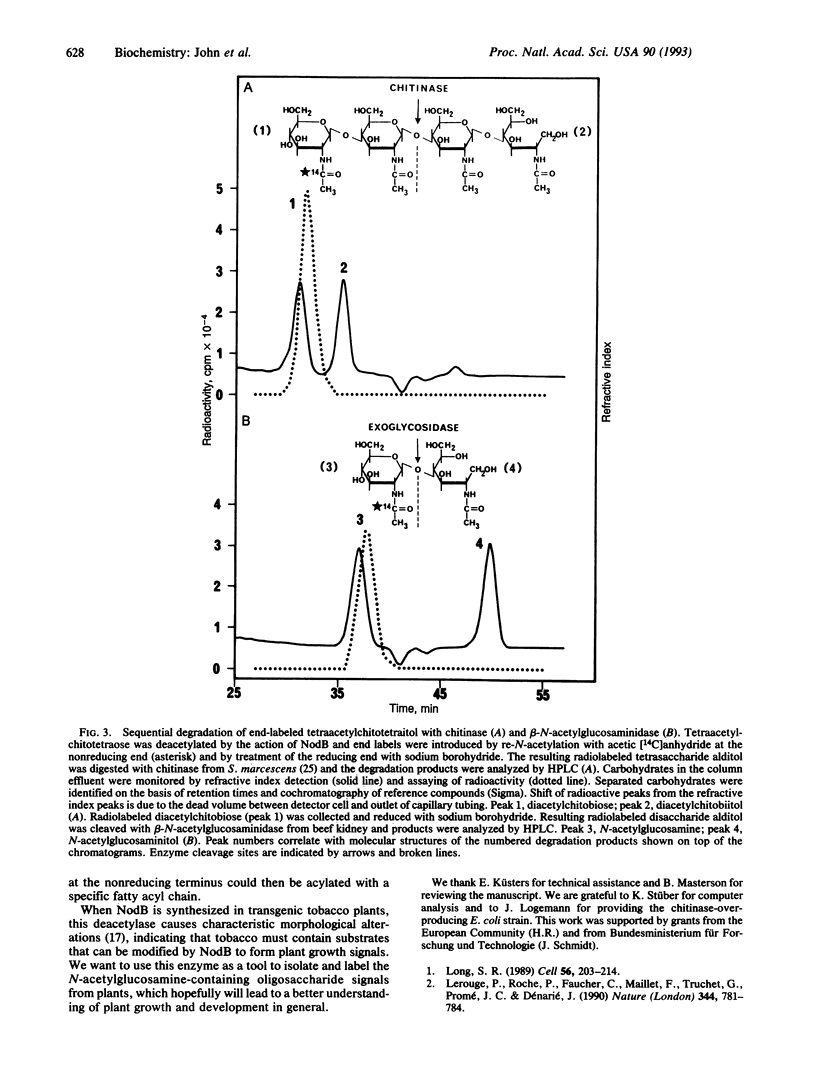
The common nodulation genes nodABC are conserved in all rhizobia and are involved in synthesis of a lipooligosaccharide signal molecule. This bacterial signal consists of a chitooligosaccharide backbone, which carries at the nonreducing end a fatty acyl chain. The modified chitooligosaccharide molecule triggers development of nodules on the roots of the leguminous host plant. To elucidate the specific role of the NodB protein in nodulation factor synthesis, we have purified recombinant NodB and determined its biochemical role by direct assays. Our data show that the NodB protein of Rhizobium meliloti deacetylates the nonreducing N-acetylglucosamine residue of chitooligosaccharides. The monosaccharide N-acetylglucosamine is not deacetylated by NodB. In the pathway of Nod factor synthesis, deacetylation at the nonreducing end of the oligosaccharide backbone may be a necessary requirement for attachment of the fatty acyl chain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Production of root hair deformation factors by Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes in Escherichia coli: HsnD (NodH) is involved in the plant host-specific modification of the NodABC factor. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00027330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E., Wasco W. Chitin and nodulation. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):710–710. doi: 10.1038/353710b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie A. A nod of recognition. Curr Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):382–384. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90200-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucher C., Maillet F., Vasse J., Rosenberg C., van Brussel A. A., Truchet G., Dénarié J. Rhizobium meliloti host range nodH gene determines production of an alfalfa-specific extracellular signal. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5489–5499. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5489-5499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Long S. R. Rhizobium--plant signal exchange. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):655–660. doi: 10.1038/357655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt J. High-resolution hydroxyapatite chromatography of proteins. Anal Biochem. 1984 Sep;141(2):466–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS D. M., KABAT E. A., SCHIFFMAN G. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON BLOOD GROUPS. XXXI. DESTRUCTION OF BLOOD GROUP A ACTIVITY BY AN ENZYME FROM CLOSTRIDIUM TERTIUM WHICH DEACETYLATES N-ACETYLGALACTOSAMINE IN INTACT BLOOD GROUP SUBSTANCES. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:437–443. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molano J., Durán A., Cabib E. A rapid and sensitive assay for chitinase using tritiated chitin. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. L., Cabib E. Serratia marcescens chitinase: one-step purification and use for the determination of chitin. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):402–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., John M., Kondorosi E., Kondorosi A., Wieneke U., Schröder G., Schröder J., Schell J. Mapping of the protein-coding regions of Rhizobium meliloti common nodulation genes. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1705–1711. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., John M., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Expression of the nodulation gene nodA in Rhizobium meliloti and localization of the gene product in the cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9581–9585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Wingender R., John M., Wieneke U., Schell J. Rhizobium meliloti nodA and nodB genes are involved in generating compounds that stimulate mitosis of plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8578–8582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze M., Quiclet-Sire B., Kondorosi E., Virelizer H., Glushka J. N., Endre G., Géro S. D., Kondorosi A. Rhizobium meliloti produces a family of sulfated lipooligosaccharides exhibiting different degrees of plant host specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):192–196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Sheeley D. M., van Brussel A. A., Glushka J., York W. S., Tak T., Geiger O., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N., Lugtenberg B. J. A novel highly unsaturated fatty acid moiety of lipo-oligosaccharide signals determines host specificity of Rhizobium. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):125–130. doi: 10.1038/354125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Brussel A. A., Zaat S. A., Cremers H. C., Wijffelman C. A., Pees E., Tak T., Lugtenberg B. J. Role of plant root exudate and Sym plasmid-localized nodulation genes in the synthesis by Rhizobium leguminosarum of Tsr factor, which causes thick and short roots on common vetch. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.517-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkley J. W., Tillman J. A simple thin-layer chromatographic technique for the separation of mono- and oligosaccharides. J Chromatogr. 1977 Feb 1;132(1):172–174. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93791-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells G. B., Lester R. L. Rapid separation of acetylated oligosaccharides by reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1979 Aug;97(1):184–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90344-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]