Abstract
Sexual differentiation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is induced by the consecutive action of two extrinsic cues--nitrogen deprivation and blue light. The definition of a blue light-dependent step in gamete formation provided a basis for the isolation of mutants altered in the signal transduction pathway by which light controls sexual differentiation. In one mutant (lrg1), gamete formation has become light independent. In the other mutant (lrg2), perception or transduction of the light signal appears to be partially impaired. In both mutants, the expression of genes activated by light in the late phase of gamete formation is affected. Genetic analyses showed that genes LRG1 and LRG2 are linked. The recessive nature of the lrg1-1 mutation implies that the gene encodes a negative factor or a protein that controls the activity of a negative factor. In the case of lrg2-1, neither wild-type nor mutant allele was dominant. Rather, two copies of the lrg2-1 gene simulate a wild-type phenotype. The identification of genetic loci in the pathway for blue light-mediated differentiation provides a basis for the isolation of signal transduction genes in Chlamydomonas.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. S., Monk B. C., Cohen R., Hwang C., Goodenough U. W. Sexual agglutinins from the Chlamydomonas flagellar membrane. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4593–4602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. F., Acker A. Gametic Differentiation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Control by Nitrogen and Light. Plant Physiol. 1992 Mar;98(3):822–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.98.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi P. M., Tchou-Wong K. M., Weinstein I. B. Overexpression of protein kinase C in HT29 colon cancer cells causes growth inhibition and tumor suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4650–4657. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Nagpal P., Peto C. A. Phenotypic and Genetic Analysis of det2, a New Mutant That Affects Light-Regulated Seedling Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):445–459. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Peto C. A. Mutations in the DET1 gene affect cell-type-specific expression of light-regulated genes and chloroplast development in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8776–8780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Peto C., Feinbaum R., Pratt L., Ausubel F. Arabidopsis thaliana mutant that develops as a light-grown plant in the absence of light. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):991–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90950-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrochano L. M., Cerdá-Olmedo E. Sex, light and carotenes: the development of Phycomyces. Trends Genet. 1992 Aug;8(8):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90252-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degli-Innocenti F., Russo V. E. Isolation of new white collar mutants of Neurospora crassa and studies on their behavior in the blue light-induced formation of protoperithecia. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):757–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.757-761.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Caspar T., Quail P. H. cop1: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1172–1182. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Matsui M., Wei N., Wagner D., Chu A. M., Feldmann K. A., Quail P. H. COP1, an Arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a protein with both a zinc-binding motif and a G beta homologous domain. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90555-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. S., Levine R. P. Cytochrome f and plastocyanin: their sequence in the photosynthetic electron transport chain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1665–1669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. A., Gressel J., Malkin S., Epel B. L. Modified cryptochrome in vivo absorption in dim photosporulation mutants of Trichoderma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2736–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khurana J. P., Poff K. L. Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana with altered phototropism. Planta. 1989;178:400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Fukuzawa H., Shimada T., Saito T., Matsuda Y. Primary structure and expression of a gamete lytic enzyme in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: similarity of functional domains to matrix metalloproteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4693–4697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscum E., Hangarter R. P. Arabidopsis Mutants Lacking Blue Light-Dependent Inhibition of Hypocotyl Elongation. Plant Cell. 1991 Jul;3(7):685–694. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.7.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson C. E., Singleton C. K. V4, a gene required for the transition from growth to development in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1992 Apr;150(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90238-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooney J. L., Yager L. N. Light is required for conidiation in Aspergillus nidulans. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1473–1482. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond P., Short T. W., Briggs W. R., Poff K. L. Light-induced phosphorylation of a membrane protein plays an early role in signal transduction for phototropism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May;89(10):4718–4721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock R. A., Quail P. H. Novel phytochrome sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana: structure, evolution, and differential expression of a plant regulatory photoreceptor family. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1745–1757. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short T. W., Briggs W. R. Characterization of a Rapid, Blue Light-Mediated Change in Detectable Phosphorylation of a Plasma Membrane Protein from Etiolated Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):179–185. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewavas A., Gilroy S. Signal transduction in plant cells. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90255-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warpeha K. M., Hamm H. E., Rasenick M. M., Kaufman L. S. A blue-light-activated GTP-binding protein in the plasma membranes of etiolated peas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8925–8929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener D., Beck C. F. Identification of novel genes specifically expressed in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii zygotes. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jun;16(6):937–946. doi: 10.1007/BF00016066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissig H., Beck C. F. Action Spectrum for the Light-Dependent Step in Gametic Differentiation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1991 Sep;97(1):118–121. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman B. K., Briggs W. R. Phototropic Dosage-Response Curves for Oat Coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1963 May;38(3):248–253. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
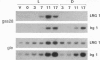
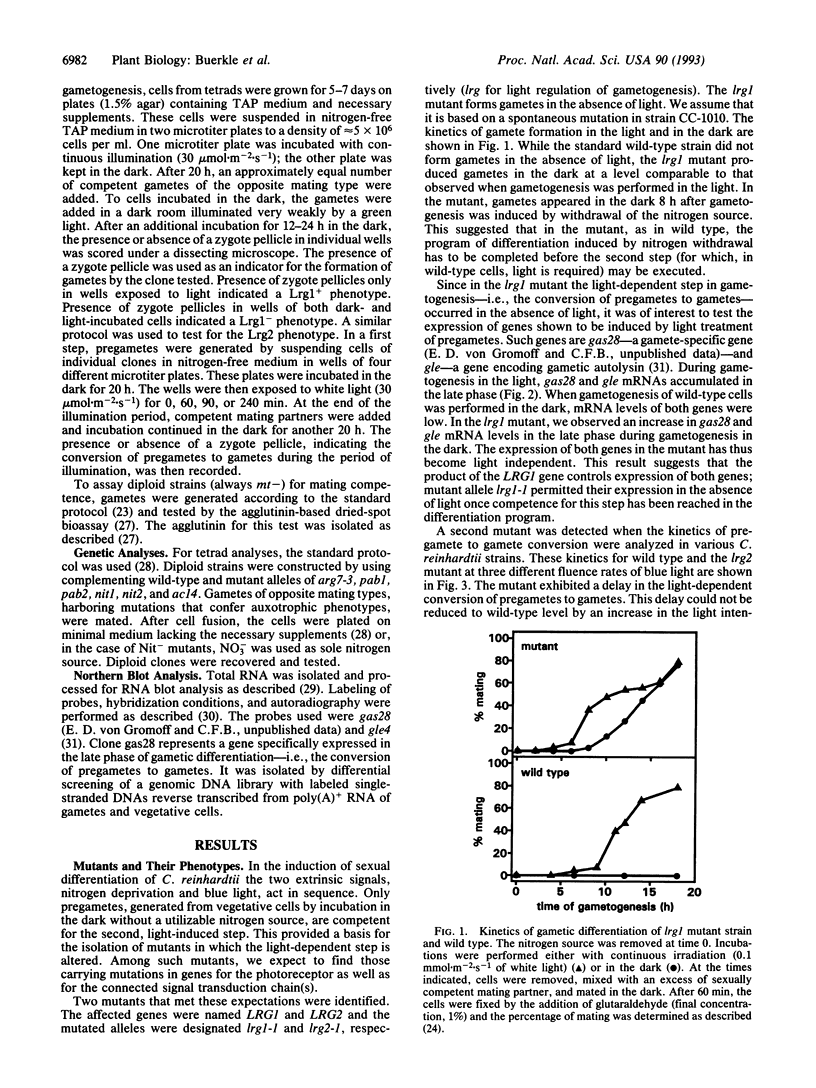
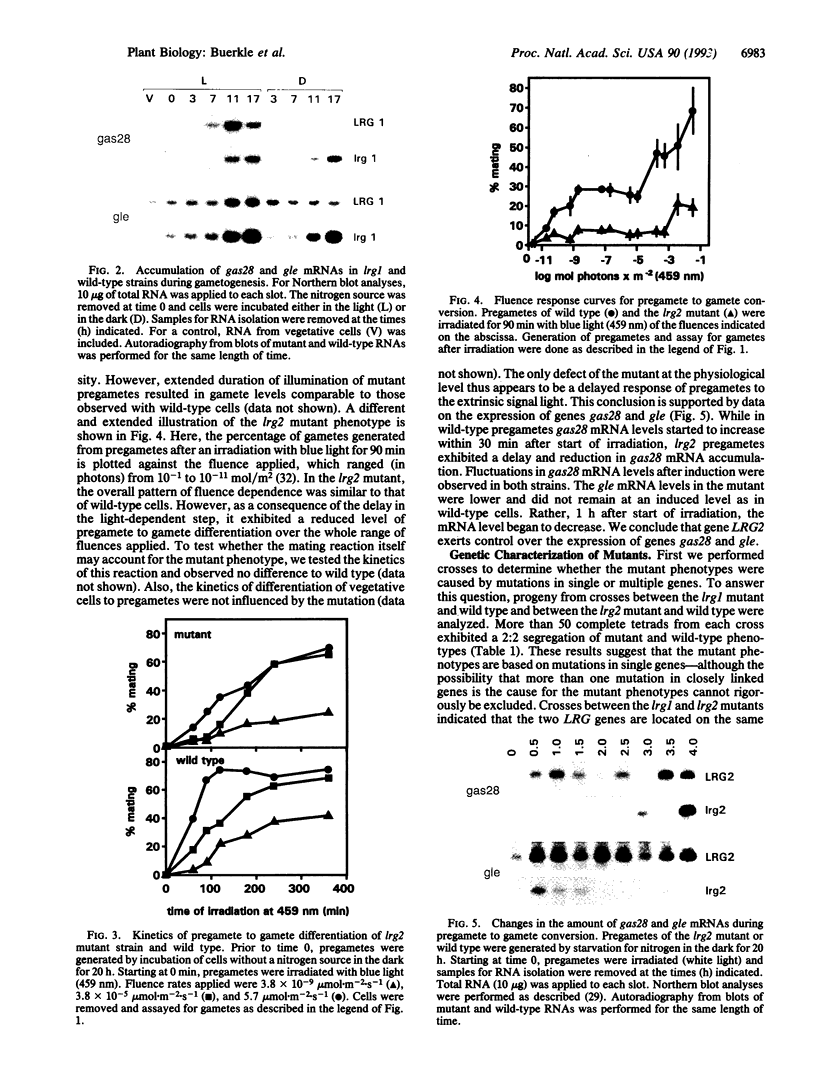
- von Gromoff E. D., Treier U., Beck C. F. Three light-inducible heat shock genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3911–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]