Abstract
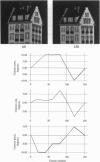
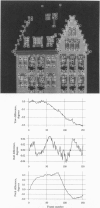
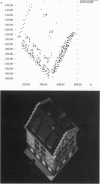
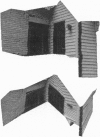
Inferring scene geometry and camera motion from a stream of images is possible in principle, but it is an ill-conditioned problem when the objects are distant with respect to their size. We have developed a factorization method that can overcome this difficulty by recovering shape and motion without computing depth as an intermediate step. An image stream can be represented by the 2F x P measurement matrix of the image coordinates of P points tracked through F frames. Under orthographic projection this matrix is of rank 3. Using this observation, the factorization method uses the singular value decomposition technique to factor the measurement matrix into two matrices, which represent object shape and camera motion, respectively. The method can also handle and obtain a full solution from a partially filled-in measurement matrix, which occurs when features appear and disappear in the image sequence due to occlusions or tracking failures. The method gives accurate results and does not introduce smoothing in either shape or motion. We demonstrate this with a series of experiments on laboratory and outdoor image streams, with and without occlusions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Prazdny K. Egomotion and relative depth map from optical flow. Biol Cybern. 1980;36(2):87–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00361077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]