Abstract
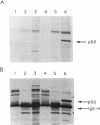
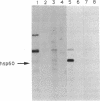
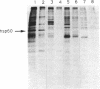
Ras proteins play a crucial role in the development of neoplasia and in signal transduction in normal cells. In a search for proteins interacting with p21ras, we previously identified a protein of 60 kDa (p60) through use of a chemical cross-linker. Using information from partial amino acid sequencing of the purified protein, we isolated full-length cDNA clones encoding this 60-kDa protein. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that p60 is the murine heat shock protein hsp60, a chaperonin. Association of hsp60 with p21ras appears physiological, as the amount of hsp60 complexed to p21ras was similar even in cells over-expressing p21ras, and reversing the order of cross-linking and lysis of the cells, which releases large amounts of hsp60 from mitochondria, did not alter the amount of hsp60 cross-linked to p21ras.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. Transduction of receptor signal into modulation of effector activity by G proteins: the first 20 years or so .... FASEB J. 1990 Nov;4(14):3178–3188. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.14.2172060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R. RAS genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: signal transduction in search of a pathway. Trends Genet. 1991 Jan;7(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90018-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Molecular chaperones. Unfolding protein folding. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):17–18. doi: 10.1038/352017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Cox A. D. Isoprenoid modification and plasma membrane association: critical factors for ras oncogenicity. Cancer Cells. 1991 Sep;3(9):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Riehl R., Wu L., Weinberg R. A. Identification of a nucleotide exchange-promoting activity for p21ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5998–6002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. The ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90300-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., de Gunzburg J., Riehl R., Weinberg R. A. p21ras-induced responsiveness of phosphatidylinositol turnover to bradykinin is a receptor number effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch P., Malkovsky M., Kovats S., Sturm E., Braakman E., Klein B. S., Voss S. D., Morrissey L. W., DeMars R., Welch W. J. Recognition by human V gamma 9/V delta 2 T cells of a GroEL homolog on Daudi Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1269–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.1978758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F. Processing and fatty acid acylation of RAS1 and RAS2 proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1266–1270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Vogel U. S. Modulation of guanine nucleotides bound to Ras in NIH3T3 cells by oncogenes, growth factors, and the GTPase activating protein (GAP). J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20437–20442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. ras and GAP--who's controlling whom? Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):921–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90054-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer P. J., Trimpe K. L., Pullano T., Ng S., LaVecchio J. A., Petit D. A., DeLellis R., Wolfe H., Carney W. P. Production and characterization of anti-RAS p21 monoclonal antibodies. Hybridoma. 1990 Dec;9(6):573–587. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1990.9.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. K., Kung H. F., Kamata T. Purification of a factor capable of stimulating the guanine nucleotide exchange reaction of ras proteins and its effect on ras-related small molecular mass G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8008–8012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi J., Sinha S., Aston R., Cussell D., Keen M., Sengupta U. Definition of species specific and cross-reactive antigenic determinants of Mycobacterium leprae using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jun;52(3):528–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarjour W., Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J., Denning S., Shaw M., Mimura T., Haynes B. F., Winfield J. B. Constitutive expression of a groEL-related protein on the surface of human gamma/delta cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1857–1860. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Dudani A. K., Singh B., Harley C. B., Gupta R. S. Primary structure of a human mitochondrial protein homologous to the bacterial and plant chaperonins and to the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Mizuno T., Fujioka H., Yamamoto T., Kishi K., Fukumoto Y., Hori Y., Takai Y. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21s (ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins) and characterization of stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2873–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Tumor suppressor genes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90641-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Langer T., Boteva R., Schramel A., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U. Chaperonin-mediated protein folding at the surface of groEL through a 'molten globule'-like intermediate. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):36–42. doi: 10.1038/352036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann J., Horwich A. L., Neupert W., Hartl F. U. Protein folding in mitochondria requires complex formation with hsp60 and ATP hydrolysis. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):125–130. doi: 10.1038/341125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roise D., Theiler F., Horvath S. J., Tomich J. M., Richards J. H., Allison D. S., Schatz G. Amphiphilicity is essential for mitochondrial presequence function. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):649–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Endo M., Nakafuku M., Akiyama T., Yamamoto T., Kaziro Y. Accumulation of p21ras.GTP in response to stimulation with epidermal growth factor and oncogene products with tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7926–7929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Miyajima A., Kaziro Y. Involvement of ras p21 protein in signal-transduction pathways from interleukin 2, interleukin 3, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, but not from interleukin 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3314–3318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldinger D., Eckerskorn C., Lottspeich F., Cleve H. Amino-acid sequence homology of a polymorphic cellular protein from human lymphocytes and the chaperonins from Escherichia coli (groEL) and chloroplasts (Rubisco-binding protein). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Oct;369(10):1185–1189. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.2.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M. H. Oncoproteins. GAPs in understanding Ras. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):696–697. doi: 10.1038/346696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. A cytosolic protein catalyzes the release of GDP from p21ras. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2181667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Okabe K., Polakis P., Halenbeck R., McCormick F., Brown A. M. ras p21 and GAP inhibit coupling of muscarinic receptors to atrial K+ channels. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90187-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Elliott T. J. Stress proteins, infection, and immune surveillance. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90861-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gunzburg J., Riehl R., Weinberg R. A. Identification of a protein associated with p21ras by chemical crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]