Abstract
Toxocara canis, the common roundworm in the dog, can cause "visceral larva migrans" syndrome in humans, which may include generalised illness, eosinophilia, and symptoms arising from larval invasion of different organs. Of these, the clinically most important are liver, lungs, eyes and CNS. Involvement of the different parts of the CNS in human toxocaral disease has been described, but not the CT or MRI appearances of the cerebral lesions. In one case with a single focal epileptic fit, CT was described as normal. In the Toxocara canis case described, the cerebral lesions on MRI, before and after therapy, are shown.
Full text
PDF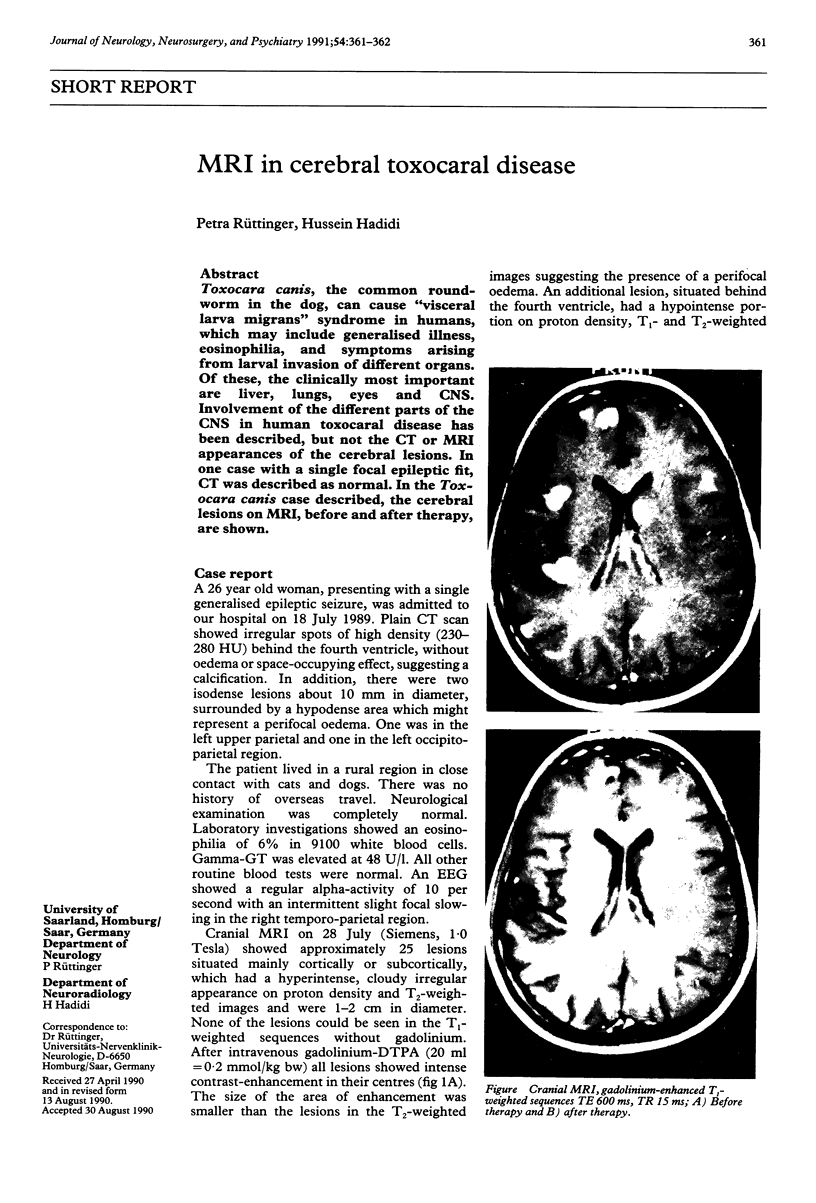

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAIN L., ALLAN B. ENCEPHALITIS DUE TO INFECTION WITH TOXOCARA CANIS. REPORT OF A SUSPECTED CASE. Lancet. 1964 Jun 20;1(7347):1355–1357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barriga O. O. A critical look at the importance, prevalence and control of toxocariasis and the possibilities of immunological control. Vet Parasitol. 1988 Sep;29(2-3):195–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(88)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H. Larva migrans visceralis (Toxocara canis) und Zentrales Nervensystem (ZNS). Nervenarzt. 1980;51(12):718–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Jensen A., Schall J., Weisner B., Lamina J. Eosinophile Meningo-enzephalo-myelitis und viszerales Syndrom durch Askaridenlarven beim Erwachsenen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1973 Jun 8;98(23):1175–1177. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1106989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. R., Keane C. T., O'Connor P., Mulvihill E., Holland C. The expanded spectrum of toxocaral disease. Lancet. 1988 Mar 26;1(8587):692–695. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91486-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]