Abstract
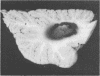
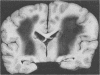
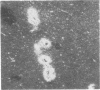
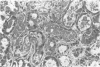
The neuropathological findings in six patients who developed neurological signs after the onset of "septic shock" caused by Gram-negative septicaemia are described. The changes in the brains were characteristic of acute haemorrhagic leucoencephalitis, and there was evidence, particularly in the kidneys, of disseminated intravascular coagulation with tubular necrosis and, in some, appearances indistinguishable from membrano-proliferative glomerulonephritis. It is agreed that acute haemorrhagic leucoencephalitis is another manifestation of a generalised Shwartzman reaction, and it is suggested that activation of complement is the final common pathway that produces tissue damage in the brain and kidney.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE H. E. Acute haemorrhagic leuco-encephalitis. Br Med J. 1956 Oct 6;2(4996):807–808. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4996.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAIN M. C., DACIE J. V., HOURIHANE D. O. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the possible role of vascular lesions in pathogenesis. Br J Haematol. 1962 Oct;8:358–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNSON J. G., DAVIS R. L. Systemic fibrinoid diseases, similarity to experimental lesions in rabbits. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Dec;60(6):593–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan P. O., Kies M. W., Lisak R. P., Sheremata W., Lamarche J. B. Immunologic mechanisms in experimental encephalomyelitis in nonhuman primates. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jul;29(1):4–9. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490250022002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. C., Vogel F. S. Hemorrhagic white matter infarction in three critically ill patients. Hum Pathol. 1977 Mar;8(2):121–132. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(77)80075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B. Encephalopathy following the administration of streptomycin and para-amino-salicylic acid. J Clin Pathol. 1953 May;6(2):128–131. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSERMELY H. Demyelinating encephalomyelitis following use of antitetanus serum. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1950 Nov;64(5):676–684. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1950.02310290072007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson A. R., MacDonald M. K., Fuster V., Cash J. D., Robson J. S. Glomerular coagulation in acute ischaemic renal failure. Q J Med. 1970 Oct;39(156):585–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The derivation of two distinct anaphylatoxin activities from the third and fifth components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):371–386. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDGE J. R. Diffuse encephalopathy after streptomycin treatment. Tubercle. 1951 Mar;32(3):58–60. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(51)80098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Ruddy S., Schur P. H., McCabe W. R. Activation of the properdin pathway of complement in patients with gram-negative of bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):937–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRABER C. D., TUMBUSCH W. T., RUDNICKI R. P., VOGEL E. H., Jr Generalized Shwartzman-like reaction following Serratia marcescens septicemia in a fatal burn. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1960 Apr;110:443–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENFIELD J. G. Encephalitis and encephalomyelitis in England and Wales during the last decade. Brain. 1950 Jun;73(2):141–166. doi: 10.1093/brain/73.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Shin H. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Interactions of the complement system with endotoxic lipopolysaccharide: consumption of each of the six terminal complement components. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):1049–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. D., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Richardson E. P., Jr Hypoxic-ischemic leukoencephalopathy in man. Arch Neurol. 1976 Jan;33(1):5–14. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500010007002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPROWSKI H., LeBELL I. The presence of complement-fixing antibodies against brain tissue in sera of persons who had received antirabies vaccine treatment. Am J Hyg. 1950 May;51(3):292–299. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P. Participation of intravascular coagulation in the pathogenesis of glomerular and vascular lesions. Kidney Int. 1975 Apr;7(4):242–253. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S., Kennedy L. Cerebral vascular permeability and cellular infiltration in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):859–869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Cochrane C. G., Carpenter C. B., Behan P. O. Allergic encephalomyelitis: effect of complement depletion with cobra venom. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):285–289. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH K. Streptomycin-P.A.S. hypersensitivity treated with ACTH. Lancet. 1952 Sep 27;2(6735):606–608. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)91597-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASLAND W. S., BARROWS L. J. A case of generalized Shwartzman phenomenon in the human. Arch Neurol. 1962 Jul;7:64–73. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210010070006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKAY D. G., WAHLE G. H., Jr Epidemic gastroenteritis due to Escherichia coli O111 B4. II. Pathologic anatomy, with special reference of the presence of the local and generalized Shwartzman phenomena. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Dec;60(6):679–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. K., Clarkson A. R., Davison A. M. The role of coagulation in renal disease. Perspect Nephrol Hypertens. 1973;1(Pt 2)(0):809–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Serum complement levels in bacteremia due to gram-negative organisms. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):21–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergenhagen S. E., Snyderman R., Gewurz H., Shin H. S. Significance of complement to the mechanism of action of endotoxin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;50:37–77. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46169-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard H. J., Nilsson U. R., Dalmasso A. P., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. A molecular concept of immune cytolysis. Arch Pathol. 1966 Sep;82(3):205–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immunohistochemical study of allergic encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):251–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H., Day N. K., Gewurz H., Good R. A. Prevention of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with cobra venom factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):555–560. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and autoimmune disease. Adv Immunol. 1966;5:131–208. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL D. S. The nosological unity of acute haemorrhagic leucoencephalitis and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Brain. 1955 Sep;78(3):369–376. doi: 10.1093/brain/78.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYMMERS W. S. Thrombotic microangiopathy (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura) associated with acute haemorrhagic leucoencephalitis and sensitivity to oxophenarsine. Brain. 1956 Sep;79(3):511–521. doi: 10.1093/brain/79.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N. Endotoxinaemia and the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Q J Med. 1975 Apr;44(174):389–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N. Intravascular coagulation in experimental acute renal failure. Assessment by radio-fibrinogen technique. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Jun 28;29(3):579–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]