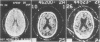
Abstract
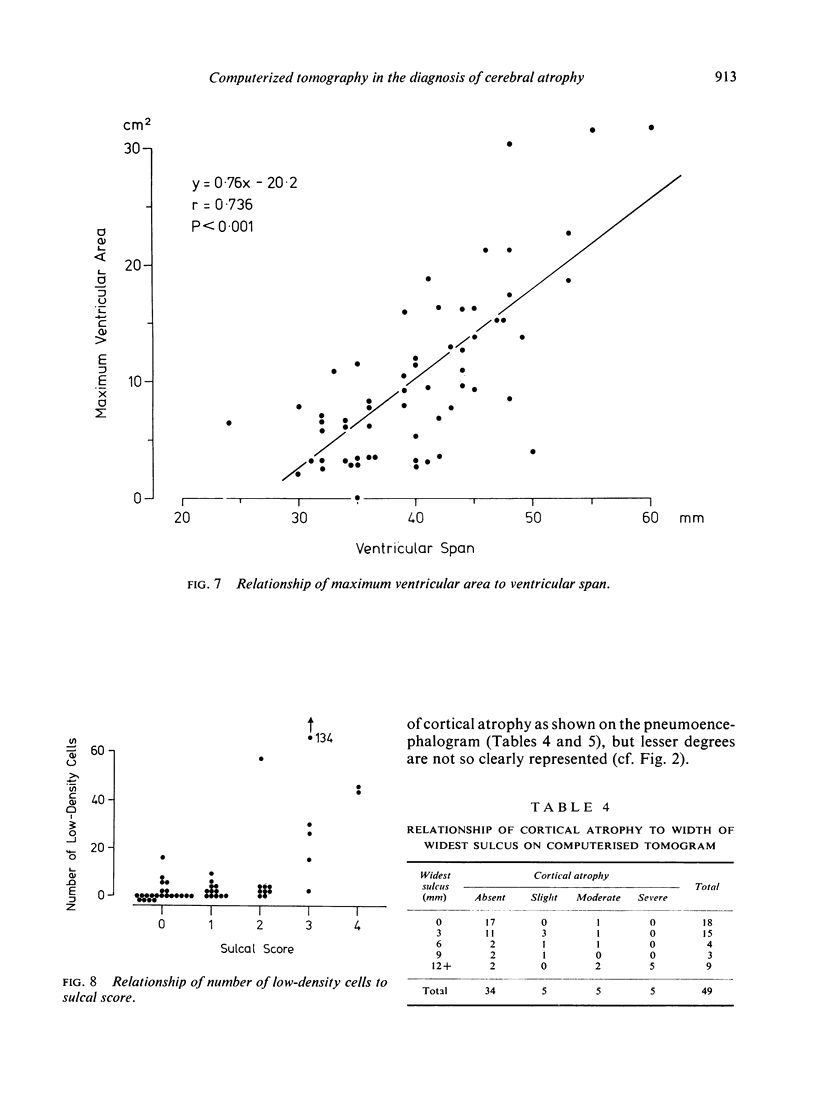
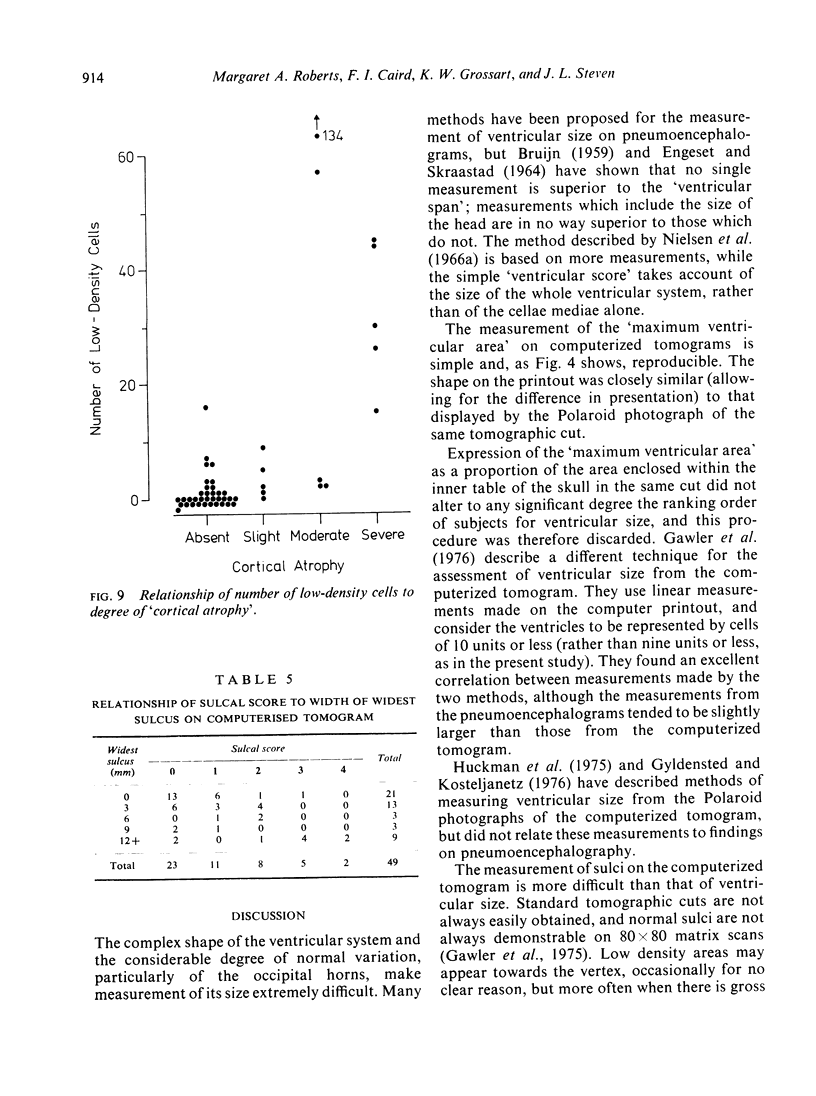
Computerized tomograms were studied of 67 adults whose lumbar pneumoencephalograms were normal or showed ventricular dilatation with or without widening of the sulci. The maximum ventricular area, measured from 80 x 80 matrix printouts, correlates well with measures of ventricular size on the pneumoencephalogram. An area of 10 cm2 is suggested as the upper limit of normal. The correlation between measures of sulcal width on computerized tomography and pneumoencephalography is less precise, but normal sulci and gross degrees of cortical atrophy can be identified.
Full text
PDF
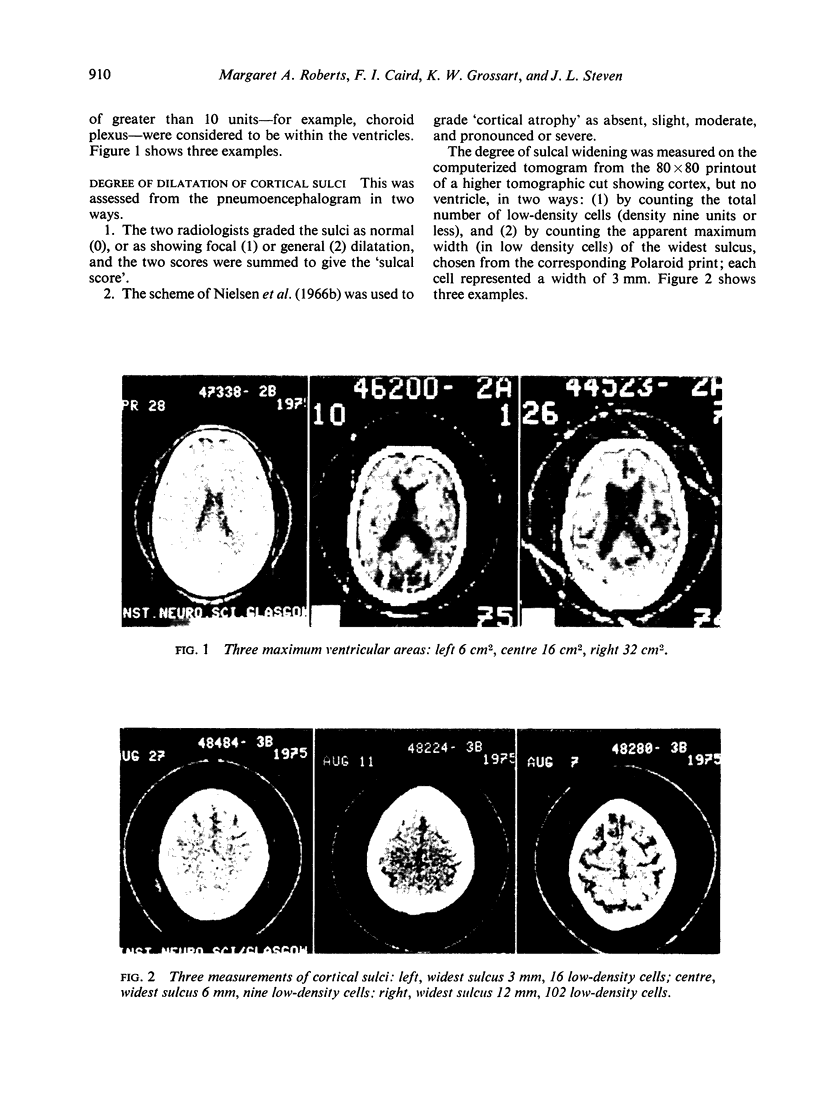
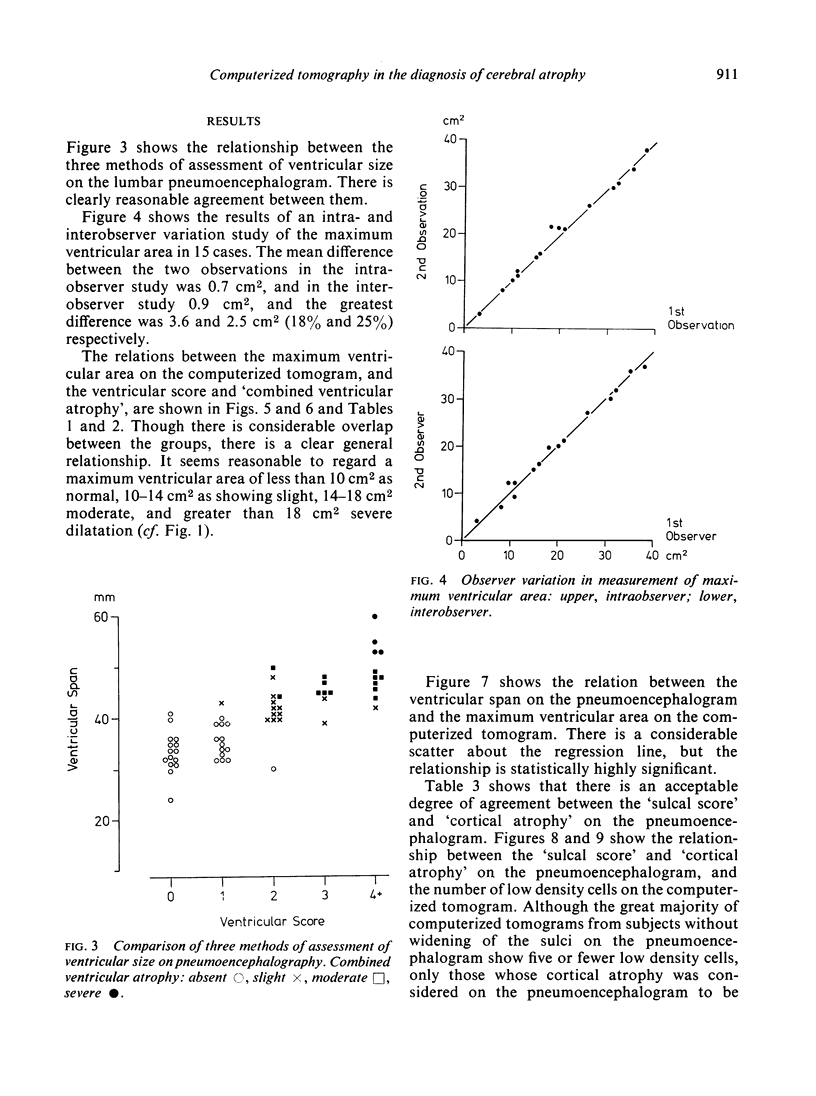
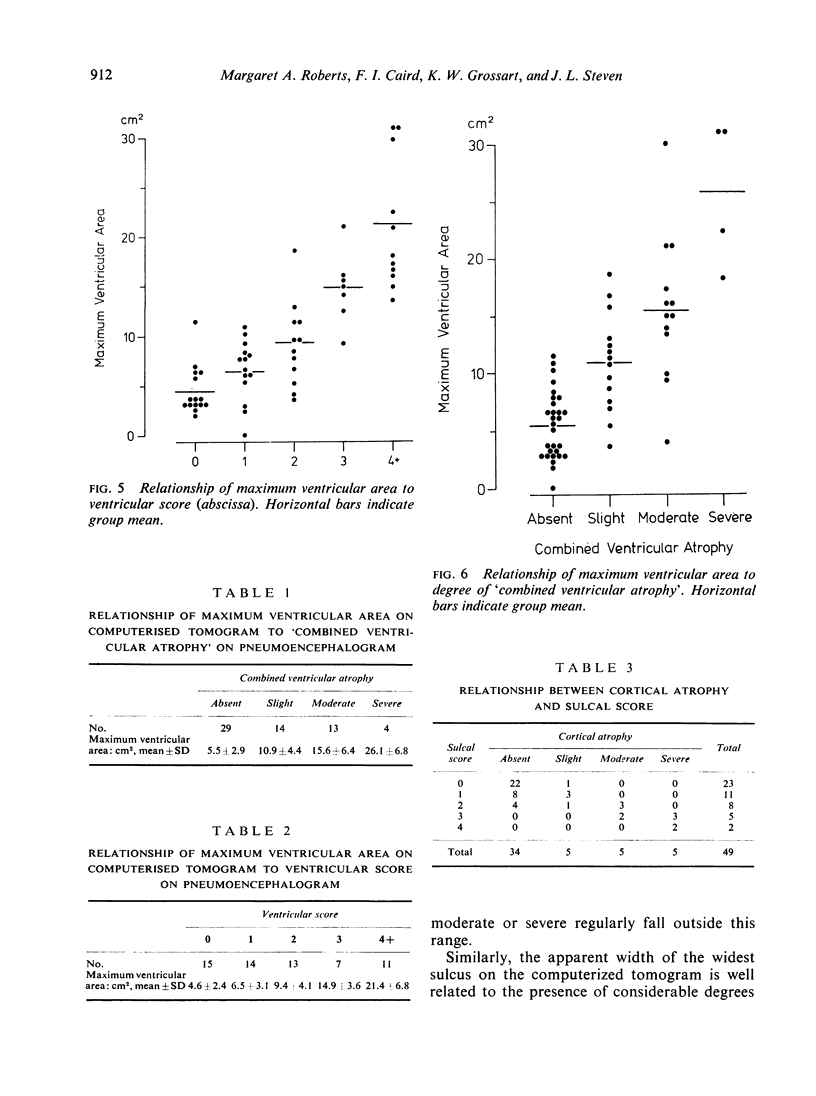

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrose J. Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography). 2. Clinical application. Br J Radiol. 1973 Dec;46(552):1023–1047. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-552-1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURHENNE H. J., DAVIES H. THE VENTRICULAR SPAN IN CEREBRAL PNEUMOGRAPHY. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1963 Dec;90:1176–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGESET A., SKRAASTAD E. METHODS OF MEASUREMENT IN ENCEPHALOGRAPHY. Neurology. 1964 May;14:381–385. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.5.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler J., Bull J. D., Du Boulay G. H., Marshall J. Computerized axial tomography: the normal EMI scan. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Oct;38(10):935–947. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.10.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler J., Du Boulay G. H., Bull J. W., Marshall J. Computerized tomography (the EMI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Mar;39(3):203–211. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.3.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyldensted C., Kosteljanetz M. Measurements of the normal hemispheric sulci with computer tomography: a preliminary study on 44 adults. Neuroradiology. 1975 Dec 19;10(3):147–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00341816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyldensted C., Kosteljanetz M. Measurements of the normal ventricular system with computer tomography of the brain. A preliminary study on 44 adults. Neuroradiology. 1976;10(4):205–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00329997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsfield G. N. Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography). 1. Description of system. Br J Radiol. 1973 Dec;46(552):1016–1022. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-552-1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckman M. S., Fox J., Topel J. The validity of criteria for the evaluation of cerebral atrophy by computed tomography. Radiology. 1975 Jul;116(1):85–92. doi: 10.1148/116.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Petersen O., Thygesen P., Willanger R. Encephalographic cortical atrophy. Relationships to ventricular atrophy and intellectual impairment. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1966 Jul;4(4):437–448. doi: 10.1177/028418516600400408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., Petersen O., Thygesen P., Willanger R. Encephalographic ventricular atrophy. Relationships between size of ventricular system and intellectual impairment. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1966 May;4(3):240–256. doi: 10.1177/028418516600400302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]